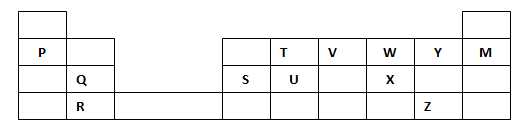
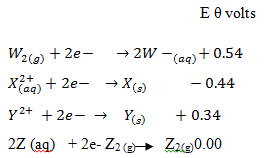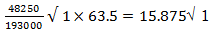- The grid below forms part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
- Write the general name given to the elements to which Y and Z belong. (1mk)
- An element N has an atomic number of 15. Write down its electronic arrangement and hence fix it in its right position on the grid above. (2mks)
Electronic arrangement - Compare the size of the atom of R and that of its ion. Explain your answer. (2mks)
- Give the formula of the compound formed between
- P and W ½ mk
- T and Y ½ mk
- Compare the melting points of element Q and S. Explain (2mks)
- State the least reactive element in the grid. Give a reason for your answer (2mks)
Element
Reason - Give two advantages that element S has over element Q in making electric cables (2mks)
- Draw (a) dot (.) and cross (x) diagram to represent the bonding in compound formed between T and Y (2mks)
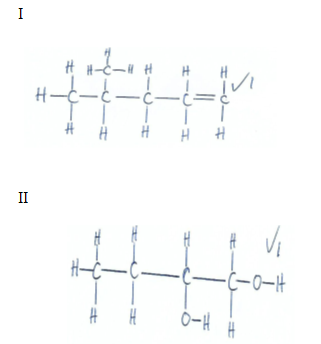
- Study the condensed formulae below and answer the questions that follow
-
- CH3CH (CH3) CH2CHCH2
- CH3CH2CH (OH) CH2OH
- Draw the structural formula of each of the compounds I and II (2mks)
- Give the systematic name of each of the compounds represented by the formulae above (2mks)
- To which homologous series does the compound represented by I belong (1mk)
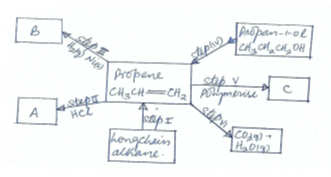
- The flow chart below shows some reactions starting with a long chain alkane. Study it and answer the questions that follows.
- Name substance (3mks)
A
B
C - What is the name given to the process represented by
Step I ½ mk
Step III½ mk
Step IV ½ mk
Step VI ½ mk - Write down the chemical equation represented by the reaction in step VI (1mk)
- Name substance (3mks)
-
-
- The following table shows the standard reduction potentials for four half cells. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements
- Explain why the Z half- cell has 0.00 voltage (1mk)
- Identify the strongest reducing agent (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction which takes place when solid X is added to the solution containing Y2+ ions (1mk)
- Which two half-cells above would provide the highest voltage if connected? (1mk)
- Calculate the voltage generated by the half-cell you have mentioned in (IV) above (2mks)
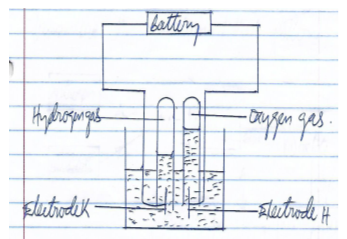
- The following diagram shows the electrolysis of water that is slightly acidic study it and answer the questions that follows.
- Identify (1mk)
Electrode K - Why was it necessary to acidify the water? (1mk)
- Explain why the water could not be acidified using hydrochloric acid if the desired products were oxygen and hydrogen (1mk)
- During the electrolysis of aqueous copper (II) sulphate 48,250 coulombs of electricity were used. Calculate the mass of copper that was deposited at the cathode (2mks
(IF=96500columbs Cu=63.5)
- Identify (1mk)
- The following table shows the standard reduction potentials for four half cells. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements
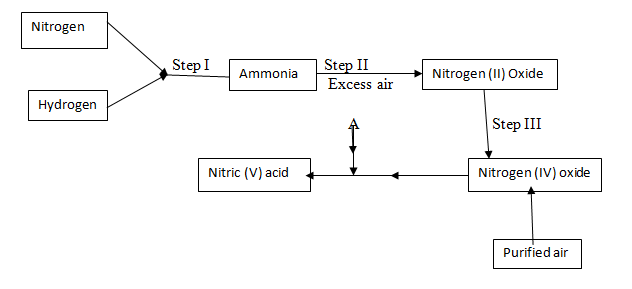
- The diagram below represent two industrial processes; one leading to the manufacture of ammonia and the second leading to the manufacture of Nitric acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Describe one large scale source of
- Nitrogen (1mk)
- Hydrogen (1mk)
- Name the catalyst required in
Step II______________________________ - Write the chemical equation for the reaction that takes place between ammonia and oxygen in the presence of the catalyst you have named in b (i) above (1mk)
- Ammonia reacts with nitric acid to form substance P.
- write the chemical equation for the formation of substance P (1mk)
- Give one possible use of substance P (1mk)
- Give the general name given to the process represented by Step I (1mk)
- Nitrogen and hydrogen reacts according to the following equation at 450°c and 200 atmospheres
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)→ 2NH3 (g)- State and explain how the yield of ammonia would be affected if the pressure is reduced (2mks)
- Name one use of nitric acid apart from making substance P named in (c) above (1mk)
- Name substance A and write an equation to show how it reacts with nitrogen (IV) oxide to form nitric (V) acid
Substance A
Equation
- Describe one large scale source of
-
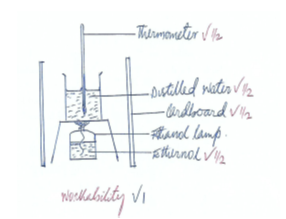
- Draw a diagram in the space provided below to show how the heat of combustion of ethanol can be measured experimentally (3mks)
- In an experiment to measure the heat of combustion of ethanol the following data was collected.
Volume of water 450cm³
Initial temperature of water 25°c
Final temperature of water 46.5°c
Mass of ethanol + lamp before heating 125.5g
Mass of ethanol + lamp after heating 124.0g
calculate:- Heat evolved during the experiment (Density of water =1g/cm³. Specific heat capacity of water =4.2KJ Kg-1K-1) (2mks)
- Molar heat of combustion of ethanol (C=12, O=16, H=1) (2mks)
- The molar heat of combustion obtained from an experiment like the one above is usually lower than the theoretical value. Explain (2mks)
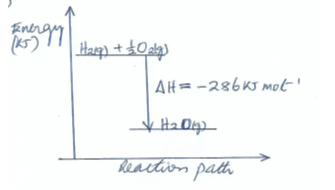
- The molar heat of combustion of hydrogen is given as -286KJmol-1
- Write the thermochemical equation for the reaction above (1 ½ mk)
- Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction in c(i) above (2mks)
-
- What is a fuel? (1mk)
- Name one environmental effect of using carbon and some of its compounds as fuels( ½mk)
-
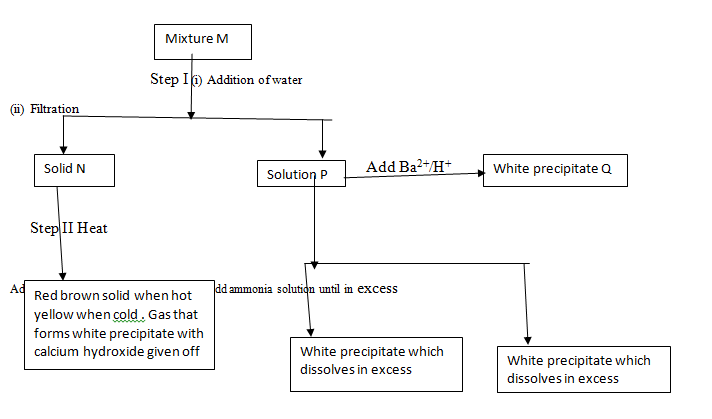
- The diagram above shows some reactions starting with mixture M. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the possible identity of
Solid N (1mk)
Solid P(1mk) - Write the formula of the identity of white precipitate Q
- Describe the test that can be carried out to test for the presence of the cation in solid N and give the possible observations if the test is positive. Fill this information in the table below.
Test
Observation
1.
2.
- Name the possible identity of
- Starting with Copper (II) Oxide, explain a step by step method that can be used to prepare crystals of copper (II) sulphate (3mks)
- The diagram above shows some reactions starting with mixture M. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
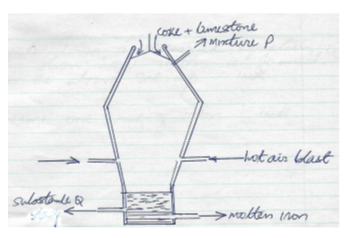
- The diagram below shows a blast furnace that is used in the extraction of iron
- State the composition of mixture P (2mk)
- Write down the use of the following in the process above.
- Limestone
- Coke
- Name substance Q and write chemical equations to show how it is formed
Name (1mk)
Chemical equations (2mks) - Write down a chemical equation to show how iron is formed in the above set-up. (1mk)
- Name one use of iron (1mk)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- halogens √ 1
- Electron arrangement 2.8.5 √1
position: group V period 3√1 - The atom of R is larger √ ½ // has a larger atomic radius than the ion √ ½ This is because the ion of R is formed when the atom loses the electrons in the outermost energy level √ ½ therefore, the ion has one less energy level than the atom.√ ½
-
- P2W// WP2 √ ½
- TY4//Y4T √ ½
- S has a higher √ ½ melting point than Q √ ½
This is because e S has more valence electrons in its metallic structure hence a stronger metallic bond √ ½ than Q √ ½ - M √1
It has a completely filled outermost energy level √ ½ and therefore, does not need to react with other elements to gain stability √ ½ - S has a higher electrical conductivity than Q.
S does not corrode easily like Q. -
-
-
-
- I 4-methylpent-i-ene √1
II but-1,2-diol √1 - Alkenes √1
-
-
- A 1-chloropropane // 2-chloropropane √1
B Propane √1
C polypropene - Step I thermo//catalytic cracking of alkanes √ ½
Step III Hydrogenation √ ½
Step IV dehydration √ ½
Step VI Combustion // burning in air √ ½ - 2CH3CH=CH2 (g) + 9O2(g) →6CO2(g) + 6H2O(g) √ ½ balanced √ ½ state symbols
- A 1-chloropropane // 2-chloropropane √1
-
-
-
- It is the reference // standard half- cell √ 1
- X√ 1 Do not accept X2+
- X(s) + Y2+(aq)→ Y(s) + X2+(aq) √ 1
- W2 (g) + 2e- → 2W-(aq) √ ½ and X2+ + 2e- X(s)
Accept W2 (g)/2W-(aq) // X(s) /X2+(aq) - E θcell =Ered –Eox Ecell = 0.54-(-0.44)√ 1
=0.98V√ 1
-
- Cathode √ 1
- To improve the conductivity of the water √ 1
- Acidifying with hydrochloric acid could lead to chlorine being discharged at theanode √ 1
- Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu(s)
1 mole of copper requires
63.5g→ 193000c
48,250c
-
-
-
- Fractional distillation of liquefied air √ 1 (reject from air)
- Electrolysis of water//dilute sodium chloride//any dilute √ 1(reject from water etc) Accept cracking of long chain alkane
-
- Platinum-rhodium//platinum√ 1
- 4NH3(g)+5O2(g → 4NO(g) + 6H2 O(g)√ 1
-
- NH3(g) + HNO3(g)→NH4NO3 (aq)
- As a fertilizer
- The haber process
-
- it lowers the yield. This is because lowering pressure favours the backward reaction // equilibrium shift to the left √ 1 and therefore lowering the ammonia yield √ ½
- manufacture of explosives
Manufacture of dyes and drugs
Purifications of metals
Etching designs on some metals √ any1
- 4NO2(g) + 2H2 O (l) + O2(g)→4HNO3(aq) √ 1 accept
2NO2(g) + H2O→HNO3(aq) + HNO2(aq)
2HNO2(aq) + O2(g)→2HNO3(aq)
-
-
-
-
-
- the calculation of the theoretical value assumes an ideal situation 1
However in an experiment, some heat is always lost to the to the surrounding 1
-
-
- H2(g) + ½ O2(g) →H2O(g) mol-1 ½
-
-
- A fuel is a substance that produces useful energy when it undergoes a chemical or nuclear reaction 1
- causing global warming//green house effect ½
-
-
-
- N: lead (II) carbonate //PbCO3
P: zinc sulphate/ZnSO4 - BaSO4
-
Test
Observation
1.To a sample of solid N in a test tube add dilute nitric acid. ½ filter the mixture and retain the filtrate for test 2 below ½
Effervescence occurs ½ //bubbles produced
A colourless solution is formed ½
2.To a little of the filtrate in a test tube add 2-3 drops of sodium chloride solution //HCL ½ warm the mixture ½
A white precipitate is formed ½ Which dissolves on warming ½
- N: lead (II) carbonate //PbCO3
- - To about 50cm3 of 2M sulphiric (VI) acid add copper (II) oxide a little at a time stirring until there is no further change. ½
- filter the mixture and retain the filtrate ½
- Put the filtrate in an evaporating dish and heat it over a water bath until it is ready to crystalize ½
- Stop heating the filtrate and let it cool slowly ½
- After crystals have formed filter the mixture and retain the residue ½
-Dry the crystals between filter papers ½ to obtain dry crystals of copper (II) sulphate
-
-
- Carbon (IV) oxide 1 + Carbon (II) oxide 1// CO2,CO
-
- when heated it produces carbon (iv) oxide which is necessary in the process 1
- Reduces carbon (IV) oxide to Carbon (II) oxide ½ which in turn reduces iron one to iron
- Slag 1
CaO (s) + SiO (s)→ CaSiO3 (l) 1
CaO(s) + Al2O3(s)→CaAL2O4 1 - 2Fe2O3(s) +3C(s)→Heat 4Fe(l) +3CO2(g) //
1any one (1)
Fe2CO3(s) +3CO(g)→2Fe(l) + 3CO2(g) - –Construction of buildings
-Making of vehicle parts and other machines
-Making of stainless steel
-Making of iron sheets 1any
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 - KCSE 2019 BAHATI MOCK EXAMINATION (WITH MARKING SCHEME).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students