- State the functions of each of the following organelles: (2mks)
- Plasma membrane
- Ribosom
-
- State two ways by which leaves of plants are adapted to gaseous exchange. (2mks)
- Name the structure from which the above process occurs. (1mk)
- How do identical and fraternal twins arise?
- Identical (2mks)
- Fraternal (1mk)
- State three reasons why it is important for plants to lose water to the atmosphere. (3mks)
- What is meant by destarching a leaf? (1mk)
- State two ways in which sunlight increases the rate of transpiration. (2mks)
- List two features of flowers that attract insect pollinators. (2mks)
- State three activities in human digestive system that depend on respiration. (3 mks)
- In the table below, indicate the deficiency diseases caused by lack of given nutrients in man. (2mks)
Nutrient
Deficiency disease
Iron
Vitamin A
-
- Give two ways in which red blood cells are adapted to carry out their functions. (2mks)
- Name chemical forms in which carbon IV oxide is transported in the human body. (2mks)
- Name any two divisions of the kingdom plantae. (2mks)
-
- Name the hormone produced in human body when one takes in a large amount of water. (1mk)
- What disease results from the inadequate production of the hormone in 12(a) above? (1mk)
-
- A cow in a paddock was found to be infected with ticks. State the trophic level occupied by the (2mks)
- Cow
- Tick
- Give one disadvantage of using pesticide to eliminate the ticks. (1mk)
- Write a food chain arising from the above feeding relationship (1 mk)
- A cow in a paddock was found to be infected with ticks. State the trophic level occupied by the (2mks)
- State two roles of water in germinating seeds? (2mks)
-
- State two limitations of fossil records as an evidence for organic evolution theory. (2mks)
- State an idea that led to the formulation of Lamarck’s theory of evolution. (1mk)
- Explain what happens to red blood cells placed in distilled water for 20 minutes. (3 mks)
-
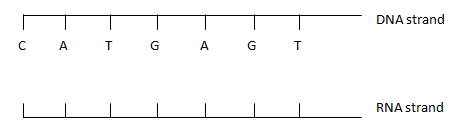
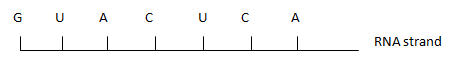
- Write the base sequence of M RNA that would be coded from the DNA strand shown below.
- How many nitrogenous bases code for a single amino acid? (1mk)
- Write the base sequence of M RNA that would be coded from the DNA strand shown below.
- Why are animal cells put in isotonic solution when performing an experiment? (2mks)
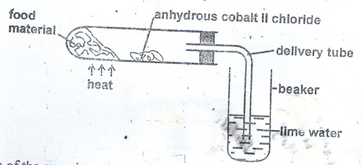
- Study the diagram below
- Suggest the aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- Account for the results observed at the end of the experiment. (2mks)
- Explain why a camel has a longer nephron than a whale. (3 mks)
- State role of the following bacteria in the nitrogen cycle. (3mks)
- Nitrosomonas
- Nitrobacter
- Azotobacter
- Explain the importance of each of the following during digestion in man.
- teeth (1mk)
- Saliva .(1mk)
-
- Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (2mks)
- Name one kingdom with:
- Prokaryotic cells (1mk)
- Eukaryotic cells(1mk)
- What would blood gain on passing through each of the following organs:
- The lungs(1mk)
- Active muscles(1mk)
- How do sunken stomata lower the rate of transpiration? (2 mks)
- State two adaptations of fruits dispersed by wind. (2mks)
-
- Describe two ways how white blood cells fight against infection. (2mks)
- State the function of blood platelets (1mk)
- Calculate the diameter of the cells in micro-metre( µm) given that the diameter of the field of view is 3mm and that they are 10 cells across the field of view, the total magnification was x100. (3mks)
-
- Apart from AIDs, name one diseases of the reproductive system in man that is caused by viruses. (1mk)
- State one way by which HIV/AIDs is transmitted from mother to child. (1mk)
-
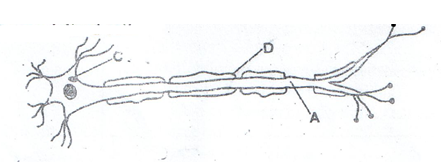
- Below is a diagram of a specialized cell:
- Name parts (2mks)
A
D - What is the role of part D? (1mk)
- Name parts (2mks)
- State two roles of progesterone. (3mks)
- Below is a diagram of a specialized cell:

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Control movement of materials in and out of the cell;
Enclose the cell contents - Site of protein synthesis;
- Control movement of materials in and out of the cell;
-
-
- Presence of stomata to allow passage of gases;
- Presence of intercellular spaces/air passages to allow free circulation of air;
- Thin to allow easy diffusion of gases;
- Flattened shape to offer large surface area of air to reach cells;
- Moist inner surface of cells to allow easy diffusion of gases;
- Exposure to air to allow easy diffusion of gases;
Mark only first two.
- Stomata
-
-
- Identical – a fertilized ovum divided into two; and develops into two separate embryos;
- Fraternal – two different ova are fertilized;(by different sperms)
- -Cools the plant cells
- Provide mechanism through which mineral salts and water are transported in plants cell
- Removal of excess water from the plants.
- Maintain turgor of cells
- Process by which the leaf is made devoid of starch; (by keeping it in dark (about 48 hours); so that all starch present is used up.)
- -By increasing internal leaf temperature thus high rate of evaporation of water from the leaf;
-By increasing the size of stomata opening aperture hence large surface area for water loss;
- -brightly colored petals;
-Sweet scented
- nectar from nectaries (nectaries glands);
They Mark only first two
- - Absorption of digested food materials
- Secretion of digested enzymes/hormones/mucus
- Contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles of alimentary canal to bring about peristalsis
- Chewing/mastication(movement of jaw muscles)
- iron-anaemia, Vit A-Night blindness/poor night vision
-
- -lack of nucleus increasing the surface area of haemoglobin package;
-Small in size to squeeze in the small capillaries;
-Numerous/many to increase surface for efficient transport of oxygen;
-Biconcave to increase the surface area for oxygen to diffuse in;
Mark only first two. - – Weak carbonic acid;
- Hydrogen carbonate;
- Carbaminohaemoglobin
- -lack of nucleus increasing the surface area of haemoglobin package;
- – Bryophyta;
-Spermatophyta/spermaphyta
-Pteridophyta; -
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)/ Vasopresin;
- Diabetes insipidus; rej. Water diabetes
-
-
- Primary consumer;
- Secondary consumer;
- -Pollutes environment;
- kill non-targeted organisms
Mark first one - grass/plants → cow → tick
-
-
- Hydrolysis of stored food;
- Acts as a solvent for hydrolysed foods;
- Medium of transport;
- Activation of enzymes for hydrolysed foods;
- Medium for enzymatic reactions;
- Soften seed coat to allow plumule and radical to come out;
Marked only first two
-
- Desctruction of fossils by geological activities;
Distortion of information due to sedimentation;
Missing record/linkss;
only first two - – the theory of need;
- the theory of use and disuse;
- acquired traits can be inherited;
- Desctruction of fossils by geological activities;
- Red blood cells draw in water by osmosis. They swell/enlarge and the cell membrane Bursts ( by a process called haemolysis)
-
-
- Three;
-
- To maintain osmotic pressure of the cells in the tissue; to as to obtain accurate results.
To avoid the cell gaining or loosing water;which can inaccurate resu;lts -
- - To investigate products of (aerobic) respiration
-To investigate the gas produced during respiration
Reject anaerobic respiration - – Lime water form white precipitate; to show that carbon IV oxide is produced;
- blue cobalt II chloride turns pink; due to the presence of water produced when food burns
Mark the two points independently
- - To investigate products of (aerobic) respiration
- A camel is a desert animal, a larger nephron increases the surface area; for reabsorption of water; to conserve it; while a whale is an aquatic animals (hence does not need to conserve water)
-
- Converts Ammonia to nitrites;
- Converts nitrites to nitrates;
- Fix nitrogen into ammonia which is then converted to nitrates;
-
- Cut /chew/crush/grind food to increase surface area for digestion;/easy swallowing.
- -Contain water which is a medium for chemical reactions; / acts as a solvent.
-Contain salivary amylase/ptyalin which digests starch to maltose.
-contain mucus/mucin to lubricate food material
Any first one.
-
- Prokaryotic – nuclear materials not membrane bound (naked;)
Eukaryotic – nuclear bound by membrane; NB-Use sentence connector i.e. use of while for student to score) -
- Monera;
- Protoctista/plantae/animalia/fungi;
- Prokaryotic – nuclear materials not membrane bound (naked;)
-
- The lungs – oxygen;
- Active muscles carbon IV oxide;/ lactic acid.
- Water vapour accumulates in the pits/depression; lowering the water vapour concentration gradient thus lowering the rate of water loss from the leaves.
- -Are small and light to be carried easily by wind;
-Develop wing-like extensions to increase surface area for increased buoyancy in the air;
-Have hair like structures or floss to increase buoyancy in the air; (only first two). -
- -By engulfing and digesting pathogens;
-By secretion of antibodies; which destroy pathogens and their products. - blood clotting to stop further bleeding
- -By engulfing and digesting pathogens;
-
-
- Hepatitis B;
Herpes; - – Breast feeding;
-Through placenta;
- Hepatitis B;
-
-
- A – Axon;
D – myelin sheath; - insulate the axon;
- A – Axon;
- -growth of mammary glands
-Inhibit FSH;
-Inhibit prolactin release
Inhibits contraction of myometrium;
Only first two
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download BIOLOGY PAPER 1 - KCSE 2019 BAHATI MOCK EXAMINATION (WITH MARKING SCHEME).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students