SECTION A (30MKS)
Answer all questions in this section on spaces provided.
- Name two field management that are carried out to obtain optimum plant population in a crop field (1mk)
- Give two factors which characterize small scale farming (1mk)
- Give one examples of each of the following categories of water pipes
- Metal pipes (½mk)
- Horse pipes (½mk)
- Name three forms of horticulture practiced in Kenya (1½mk)
- State four disadvantages of growing one type of crop on piece of land continuously(2mks)
- Outline four qualities of a mother plant from which vegetative propagation material should be obtained (2mks)
- State two ways in which crop rotation controls weeds (1mk)
- Give two reasons for imposing quarantine on imported planting materials (1mk)
- State two mechanical methods of separating soil particles according to sizes during soil analysis (1mk)
- Name four settlement schemes that the Kenyan government started as a result of the success of the million Acre scheme (2mks)
- State three practices which encourage soil erosion (1½mks)
- State four characteristics of a good vegetable seedling (2mks)
- List four pose-harvest practices that are carried out in maize production (2mks)
- List four environmental factors that affect crop production in Kenya (2mks)
- Give four reasons for seed selection in crop production (2mks)
- Give two benefits of top-dressing in management of grass pasture (1mk)
- State four disadvantages of communal land tenure system (2mks
- State any two benefits a farmer would get by having correct plant population in the production of annual crops (1mk)
- Define the term opportunity cost as used in economic (1mk)
- State four pieces of information contained on a land title deed. (2mks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
Answer all questions in this section
- The table below shows PH value of different soil samples. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Soil sample PH value
S1 3
S2 4
S3 5
S4 6
S5 7
S6 8
S7 9
S8 10- Which soil sample has the highest acidity (1mk)
- Which soil sample has the lowest alkalinity (1mk)
- State two ways in which the PHvalue of sample 3 can be raised (2mks)
- Which of the above soil sample is suitable for growing maize (1mk)
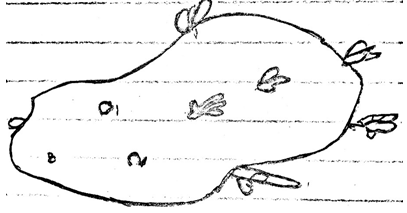
- The diagram below illustrates a seed potato prepared for planting. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the practice used in preparing the seed potato above for planting (1mk)
- Describe the procedure followed in preparing seed potatoes for planting. (8mks)
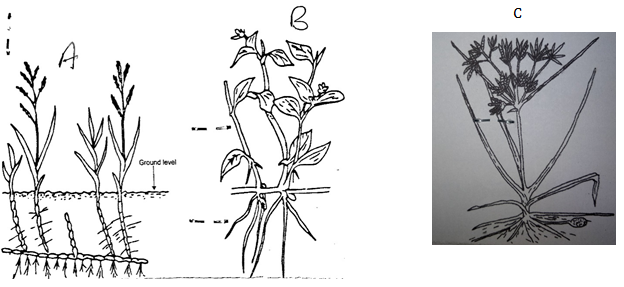
- Below are diagrams of common weeds found in a crop field, study them carefully and answer questions that follow.
- Identify the weeds (3mks)
Weed A
Weed B
Weed C - State one reason why weed A is difficult to control (1mk)
- State one economic use of weed B (1mk)
- Identify the weeds (3mks)
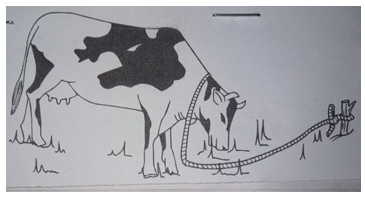
- Below is a method used in pasture management. Study it carefully and answer questions that follow.
- Identify the type of grazing shown above (1mk)
- State two limiting of the practice above (2mks)
- Below is a diagram of common pest found in the field. Study it carefully and answer questions that follows
- Identify the pest (1mk)
- State the stage at which the pest attack maize (1mk)
- State one effect of the pest on crop production (1mk)
SECTION C (40MKS)
Answer any two questions only from this section
-
- Explain five ways in which biotic factors influence crop production in Agriculture (10mks)
- Explain four ways in which Government policy improves agricultural production (4mks)
- Describes the properties of Nitrogenous fertilizer (6mks)
-
- Describe the effects of pests on Beans in the field (4mks)
- Describe the production of cabbage under the following seed headings.
- Seed bed preparation (3mks)
- Transplanting of seedlings (4mks)
- Describe various nursery management practices carried out on cabbage seeding in the nursery (5mks)
- Describe how water is treated to remove solid impurities (4mks)
-
- Describe five ways in which a grass cover help to conserve soil (5mks
- Describe maize production under following sub-headings.
- Land preparation (3mks)
- Planting (6mks)
- Field management practices (6mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Field management for optimum plant population
- Gapping
- Thinning ( 2 x½=1mk)
- Factors that characterize small scale farming
- Requires small piece of land
- Low capital investment
- Low yields
- Simple farm tools /equipment’s ( 2 x ½=1mk)
-
-
- Metal pipes
- Galvanized iron pipes
- Alluminum pipes ( 1 x ½mk)
-
- Hose pipes
- Rubber hose pipe
- Plastic hose pipe ( 1 x ½mk)
-
- Forms Horticulture practices
- Pomology /pomo-culture
- Olericulture
- Floriculture ( 3 x½=1½mks)
- Disadvantages of growing one crop on a piece of continuously
- Build up pest and disease
- Build up weeds
- depletion of minerals specific to the crop
- Destroys soil structure ( 4 x ½=2mks)
- Qualities of a good mother plant for vegetative propagation
- Healthy /free diseases/pests
- Tolerance to salinity
- Compatible to variety of scion
- numerous root system
- High yielding
- Production of quality products
- vigorous /fast growing (4 x ½=2mks)
-
- alternating different families of crops, makes it easy to control /remove the weeds
- Weeds specific to certain crops are easily controlled by alternating the crops of different type eg. strigaspecific to grass.
- Alternating difficult to weed crops with easy to weeds-maker it easily to control weeds (2 x ½==1mk)
- Reasons for imposing quarantine on planting materials
- Prevent introduction weeds
- Prevent introduction of pests and diseases from other countries ( 2 x½=1mk)
- Mechanical method of separating soil particles
Sieving using sieves of different sizes
Dissolving soil in jar of water, shaking and allowing it to settle down ( 2 x ½=1mk)
- Settlement schemes in Kenya as result of success of million acre
- Jet schemes
- Harakaschemes
- Shirikaschemes
- Larisettlement schemes
- Squatters’ settlement schemes
- Z -plots
- Harambee schemes
- Olkalou salient scheme (4 x ½=2mks)
- Practices which encourages soil erosion
- Overstocking
- Burning vegetation cover
- deforestation
- Planting annual crops on steep slopes
- Ploughing up and down the slope
- Clean weeding leaving the land unprotected. ( 3 x ½=1½mk)
- Characteristics of good vegetable seedling
- Free from pests and disease
- Vigorous growth
- Free from physical deformities
- Correct stage of growth/height 10-15cm, 4-6 true leaves ( 4 x ½=2mk)
- Posts –Harvest practices
- Drying
- Dusting /seed dressing
- Sorting and grading
- Processing
- Packing ( 4 x ½=2mk)
- Environmental factors affecting crop production
- Rainfall
- Temperatures
- Wind
- Soil type ( 4 x ½=2mk)
- Reasons for seed selection
- High quality
- High yield
- High germination rate
- To reduce chances of disease/pest attackCrops / avoid spread of weeds
- Seeds that can grow in specific area ( 4 x ½=2mk)
- Benefits of top dressing grass pasture
- Replenish the soil nutrients
- High herbage yields
- High herbage nutritive value
- Improve chemical and physical condition of the soil
- Enable microbial to break organic matter ( 2 x ½=1mk)
- Disadvantages of communal land tenure system
- Difficult to control pest/parasites/disease
- No incentive to conserve land
- Difficult to make sound farm plan
- Difficult to control breeding in livestock
- Land disputes are common
- An individual cannot use land to get loan ( 4 x ½mk)
- Benefits of correct plant population
- Obtain high quality crop
- Obtain high yields
- Help the farmer to control soil erosion/ soil and water conservation ( 2 x ½=1mk)
-
- Opportunity cost is the value of foregone best alternative/revenue as result of choosing the best alternative. ( 1 x 1=1mk)
- Details of tittle deed
- Name of owner
- Size of land
- Land parcel number/location
- Type of ownerships
- Kind of right of owning land
- Seal of issuing officer
- Date of registration
- Signature of issuing officer/name of officer ( 4 x ½=2mk)
SECTION B (20MKS)
-
- Sample S1 (1 x 1=1mk)
- Sample S8 (1 x 1=1mk)
- Application of lime
Application of basic fertilizer (2 x 1=2mks) - Sample S3 ( 1 x 1=1mk)
-
- Chitting/sprouting ( 1 x 1=1mk)
-
- Arrange seed potato in layers of 2/3 deep in partially dark room
- Arrange the seeds with rose and facing upwards and heel end downwards
- Allow diffused light through. ( 3 x 1=3mks)
-
- Weed A – Couch grass /Digitariascalarum
Weed B – Wondering jew/Commelinaspp
Weed C – Nut grass / Cyperusrotundus ( 3 x 1=3mks) - Underground rhizomes/structure
Ability to propagate vegetatively ( 1 x 1=1mk) - Livestock feed
Vegetable for human beings ( 1 x 1=1mk)
- Weed A – Couch grass /Digitariascalarum
-
- Tethering (1mk)
- Few animals can be reared by this method
Animal can strangle itself to death (2 x 1=2mks
-
- Squirrel ( 1 x 1=1mk)
- Planting time (1 x 1=1mk)
- Unearth seeds/eat reducing the plant population (1 x 1=1mk)
SECTION C (40MKS)
-
- Influence of Biotic factor on crop production
- Pest – They feed on part /whole plant reducing the yields Transmit diseases to crops
- Parasites – Transmit diseases to livestock / suck blood leading to anaemia
- Decomposers – Break down organ matter releasing nutrients to plant
- Pathogens – Transmit diseases to crops and livestock
- Predators – They kill other animals/some eat pest reducing population.
- Pollinators – transfer pollen grains from plant to plant causing pollination and fertilization.
- Nitrogen fixing bacteria – convert atmospheric nitrogen to nitrate –making it available to plant
Stating 5 x =5mks
Explaining 5x1=5mks
- How Government policy improves Agricultural production
- Land reform policy to enable improve land ownership
- Provision of extension services/education
- Help control parasites/diseases and weeds effectively
- Provision of storage facilities for bulky commodities
- Establish openers to supply inputs and market Agricultural goods.
- Provide subsidies on Agricultural inputs
- Impose high taxation on imports to protect local Agricultural products
- Improve laws toregulate quality of Agriculture
- Facilitate conservation of naturalresources
- Establish national food security ( 4 x 1=4mks)
- Properties of nitrogenous fertilizers
- They are highly soluble in soil water
- They are easily leached to lower horizons
- They have short residual effect hence need frequent application
- They are highly volatile, they should be applied on moist soil
- They have burning effect, they burn the vegetation part, they should not come into contact with green part.
- They are hygroscopic they absorb atmosphericvapour and cake
- They are highly corrosive, they burn the epithelial cells of palm
(6 clearly explain/deserved one mark) (6 x 1=6mks)
Note: The underlined is a must to score.
- Importance of irrigation
- Improves crops yields
- Ensure steady supply of food throughout the year
- Maximum utilization of resources where the soil is fertile
- Reclamation of arid/semi-arid areas/land
- Provide regular and adequate supply of water
- Source of employment in areas where it is used extensively
- Promote crop production for export
- Allow growing of paddy rice
- Allow growing of crops in green houses (5 x 1=5mks)
- Influence of Biotic factor on crop production
-
- Effects of pests on beans
- Some pests transmit disease e.gaphids
- Some pest eat growing points causing stunted growth
- Some pests eats pods/fruit lowering the quality/quantity of crop
- Some pest eats roots, damage/causing wilting
- Some pests injure the plant causing wound which allow germs to enter the plant
- Some pests eat the seeds in the soil reducing plant population.
- Some insect toxic substances into the plant resulting ……growth (4 x 1=4mks)
-
- Production of cabbage
Seedbed preparation- Prepare the land during dry period
- Clear the vegetation
- Remove the stumps
- dig deeply to remove perennial weeds
- harrow the land to medium tilth ( 3 x 1=3mks)
- Transplanting
- Transplant at the onset of rain
- Transplant seedlings are 1 month old 10-15cm /Have 4-6 true leaves
- Select healthy seedlings
- Select vigorous growing seedlings
- Dig transplanting holes 60cm by 60cm
- Use phosphate fertilizer
- Water the nursery before uprooting the seedlings
- Use garden trowel/ uproot seedlings with ball of soil round the root zone to avoid damage
- Place the seedlings in the hole and fill with soil up the level of soil in the nursery
- Firm the soil around the base of seeding
- Put shade if necessary ( 4 x 1=4mks)
- Production of cabbage
- Nursery management cabbage seedling in the nursery
- Water nursery frequently, with enough water morning an evening
- Uproot the weeds to avoid nutrients competition
- Control pest by use of appropriate pesticide
- Erect a shade to prevent sunlight from scorching the seedlings
- Control diseases by use of appropriate fungicides
- Carrying out thinning to avoid competition for nutrients
- Remove the much as seeds start germinating ( 5 x 1=5mks)
Clearly explained to score
- Treating water to remove solid impurities
- Filtration at the intake, water passes through series of sieves to remove solid particles.
- coagulation and sedimentation
- Allum is added to coagulate solid particles to settle down
- Filtrating tank-water passes through tank lined with different types of sand to remove the remaining solid particles ( 4 x 1=4mks)
- Effects of pests on beans
-
-
- Grass cover reduces the speed of run off which lowers the erosive power of run-off
- Grass cover reduces/intercepts the impact of raindrops which reduces splash erosion
- Grass cover protects soil surface hence reducing wind erosions
- Grass roots hold soil particles together from being carried always by erosion agents.
- Grass cover reduces speed of run-off there by increases infiltration of water
- Organic matter from grass improves soil structure which improves infiltration rate of water, hence reducing erosive power of run-off ( 5 x 1=5mks)
NB/must be explanations not stating
-
-
- Clear land and remove stumps
- Remove all the perennial weeds/plough/dig in dry seasons
- Carry out secondary cultivation
- Harrow to medium tilth ( 3 x 1=3mks)
-
- Select suitable maize variety to the environment.
- Dig holes 2.5cm -10cm deep depending on soil moisture
- Digat spacing 23-50cm x 75-90cm apart
- Apply phosphate fertilizer
- Apply phosphate fertilizer at 120kg/hectare
- Place 2 seeds per hole
- Plant certified /healthy seeds ( 6 x 1=6mks)
-
- Gapping
- Thinning
- Control weeds by use of appropriate method
- Top dress using nitrogenous fertilizer
- Apply nitrogenous fertilizer at height of 40-60cm /knee high
- Apply 200kg of nitrogen per hectare
- Control stalk borer by use of appropriate pesticides
- Control disease by use of appropriate fungicides ( 6 x 1=6mks)
-
-
Download AGRICULTURE PAPER 1 - KCSE 2019 ALLIANCE GIRLS MOCK EXAMINATION (WITH MARKING SCHEME).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students