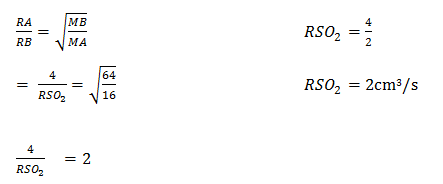- The table below shows pH values of solutions ABC and D
Give solution that is;Solution
A
B
C
D
pH value
1
7
10
13
- Acidic (1mk)
- Weak base (1mk)
- Neutral (1mk)
- Give the product formed when solution A react with a carbonate salt (1mk)
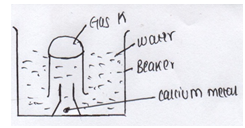
- The set up below was used to collect gas K produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal
- Name gas K (1mk)
- An organic compound P contains 64.9% carbon, 13.5 Hydrogen and the rest of the % is oxygen.
- Determine empirical formula of the compound (3mks)
- Determine the molecular formula given that the relative formula mass of P is 74 (1mk)
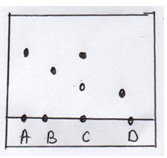
- The diagram below shows spots of pure substances A, B and D on a chromatography paper. Spot C is that of the mixture.
- On the diagram show the following
- Baseline (½mk)
- Solvent front (½mk)
- Which substances are present in C (2mks)
- On the diagram show the following
- In a reaction 20cm3 of 0.1m sodium carbonate completely reacted with 13cm3 of dilute sulphuric (V) acid. Find h concentration of suphuric acid in moles per litres (3mks)
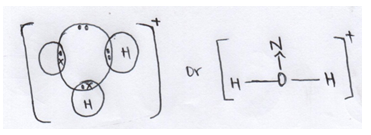
- Using dots (·) and crosses (X) draw the structure of hydroxonium ion (H3O+) (2mks)
- Study the information below and answer the questions that follows. Letters do not represent the actual symbol of element.
Element
Atomic No
Ionization energy kJmol
P
4
1800
Q
12
1450
R
20
1150
- What is the general name given to the group in which element P, Q and R belong? (1mk)
- Explain why P has highest ionization energy (2mks)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between element Q and water (1mk)
- The diagram below shows catalytic oxidation of ammonia gas. Use it to answer the questions that follows.
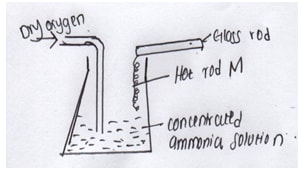
- Name metal M (1mk)
- State and explain two observations made inside the flask (2mks)
- In an experiment a gas jar containing some damp iron fillings was inverted in a trough containing some water and the set up was left for 3 days.
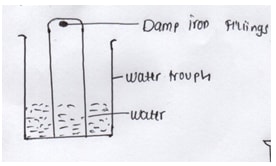
- Why was iron fillings moistened (1mk)
- State and explain observation made after 3 days (2mks)
-
- Distinguish between hygroscopy and efflorescence (2mks)
- Starting with lead (II) oxide, describe how you would prepare lead (II) sulphute (3mks)
-
- Define the term isotope (1mk)
- Chlorine gas has a mass of 35.5. It is made up of two isotope and . Determine the relative abundance of each isotope in the chlorine gas. (2mks)
- Explain the reason why Aluminium is used for making utensils like sufuria (1mk)
- Describe a chemical test to differentiate between carbon (IV) oxide and carbon (II) oxide gas (2mks)
-
- State Graham’s law of diffusion (1mk)
- 120cm3 of methane gas takes 30 seconds to diffuse through a certain membrane. Determine the rate of diffusion of surphure (IV) oxide gas through the same membrane (C=12, H=1, S=32, O=16) (3mks)
- Study the set up below and answer the questions that follow
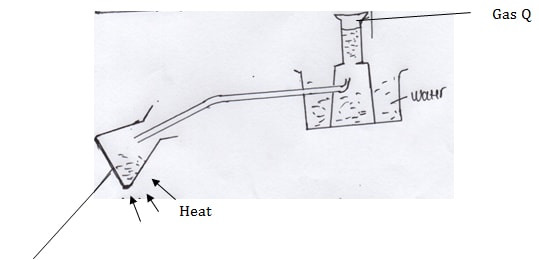
- Name gas Q (1mk)
- Identify solid K (1mk)
- What is the purpose of calcium oxide in the experiment (1mk)
- Both ions and have an electron configuration of 2.8.8
- Write the electron arrangement for:
Y (½mk)
Z (½mk) - What is the mass number of atom Z given that it has 20 neutrons (1mk)
- Write the electron arrangement for:
- Magnesium ribbon was burnt in air;
- State the observation made (1mk)
- Write the equations for the reaction (2mks)
-
- Distinguish between a weak acid and a dilute acid (2mks
- Giving a reason, identify an acid in the reverse reaction below (2mks)
H3O+ (aq) + NH3(g) →NH4+ + H2O (l)
Acid (½mk)
Reason (½mk)
- What causes water hardness (1mk)
-
- Using ionic equation, explain how sodium carbonate removes permanent hardness (1mk)
- State one disadvantage of using hardness in the boilers (1mk)
- Study the equation below
CH3CHClCHClCH3- Give the structural formula of Q (1mk)
- Name the type of reaction in the equation above (1mk)
- To which family of hydrocarbons does Q belong? (1mk)
- Consider the scheme below for allotropes of sulphur
Allotrope J
Allotrope K
- What is the significance of temperature 960C (1mk)
- Name allotrope J and K (2mks)
- In term of structure and bonding explain why Diamond is used in drilling and graphite used as a lubricant (2mks)
- The table below gives the bond energies of some compounds.
Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction H2(g) + Cl2(g) →2HCl(g) (3mks)Bond
Bond energy kJ/mole
H-H
435
Cl-Cl
244
H-Cl
431
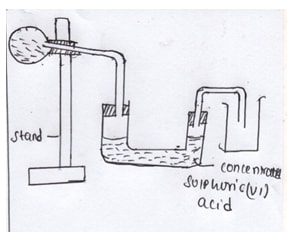
- The diagram above shows the effect of electric current on lead (II) bromide. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
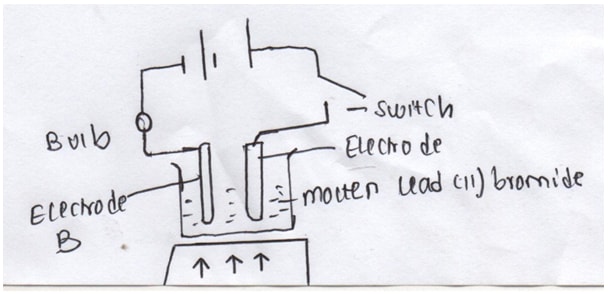
- On the diagram, Name electrodes A and B (2mks)
- State the observations made at electrode A (1mk)
- Write the equation that takes place at electrode B (1mk)
- The diagram below represents the apparatus used to prepare and collect dry ammonia gas.
- State two mistakes in the set up of apparatus (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction apparatus (2mks)
- The table below gives the solubilities of potassium bromide and potassium sulphate at 00C and 400
Identify the crystals (1mk)When an aqueous mixture containing 60g of potassium bromide and 7g of potassium sulphate in 100g of water at 800C was cooled to 00C, some crystals were formed.Substance
Solubility g/100 water at
00C
400C
Potassium bromide
55
75
Potassium sulphate
10
12
- Determine the mass of crystals formed (1mk)
- Name the method used to obtain the crystals (1mk)
- Study the diagram below
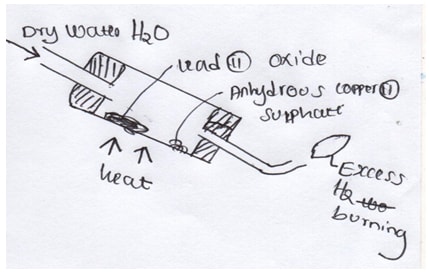
- What is the observation made on anhydrous copper (II) sulphate (1mk)
- Write an aqueous for the reaction ,between hydrogen gas and lead (II) oxide (1mk)
- What is the property of hydrogen gas being investigated above (1mk)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- A √1
- C√1
- B√1
- Salt, carbon (IV) oxide, water√1 (4mks)
- Hydrogen gas√1 (1mk)
Elements C H O
-
- % Mass 64.9 √1 5 21.6
Molar mass 12 1 16
Moles 5.41 13.5√1 1.35
Ratio 4 10 1
Empirical formula C4 H10O (3mks) - Molar mass (C4H10O)n =74
74 n =74 n=1√ ½
74 74
=C4H10O√ ½ (1mk)
- % Mass 64.9 √1 5 21.6
- Solvent front
- Base line shown on the diagram (1mk)
- A√(1)& 1 √(1) (2mks)
- Na2 CO3+ H2SO4→Na2SO4 + CO2 ( g) + HO2 (l)
Moles of Na2CO3 =20x0.1 √(1) = 0.002 moles
1000
Mole ratio 1:1√1 Moles of acid = 0.002√1
Molarity = 0.002 x 1000 =0.15 MH2 SO4
-
- Alkaline earth metal √1 (01)
- P has smallest√1 atomic radius some electrons of P are closer√1 to nucleus
hence strongly held by the nucleus (02) - Q(s) + 2 H2O →26 H2)√ + H2(g)(01)
-
- platinum √1(01)
- Brown fumes, hot rod continues to glow (02)
-
- ensure iron fillings √1 stick at the top of gas jar (01)
- Ironfillings change √ to brown as it combines with water and oxygen to form
Rust .Water rises in gas jar to occupy the space that was left when oxygen was used up.
- Hygroscopy is the process by which salts
- Absorb water when exposed to atmosphere and become damp: while efflorescence is the process by which salts lose their water of crystallization to the at atmosphere. (02)
- To a given volume of nitric (v) acid add excess of lead (II) oxide √1 until some residue are left in the beaker.
- Filter to √1 to obtain Lead (II) Nitrate solution and lead (II) oxide residue.
- To the filtrate √1add excess solution of sodium sulphate to ensure complete precipitation.
- Filter to obtain√ lead (II) sulphate as residue and sodium nitrate solution as filtrate.
Rinse the residue and dry√1 between filter papers.
-
- Are atoms of the same element with same atomic number but different mass number. (2mks)
35.5=35xy+ (100-y) 37
100
35.5 =35y + 37000- 37
cl = 100 - 75
3550 = 35x – 37 +3700 = 25 %
3550 – 3700 = -2y
-150 = -2
= 75% (2mks)
- Are atoms of the same element with same atomic number but different mass number. (2mks)
- Aluminum reacts with oxygen forming insoluble aluminum oxide which prevent further corrosion. (1mks)
- Pass the two gases separately through Ca(OH)2 Solution. White ppt is observed with carbon (IV) Oxide while no white ppt formed with carbon(II) Oxide (2 mks)
-
- The rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density provided physical conditions remain constant. ( 1mk)
-
-
- Methane (1mk)
- Sodium hydroxide (1mk)
- Absorb moisture from the air so as to ensure sodium hydroxide remaining solid state (1mk)
-
- Y-2.8.6 ( ½ mk)
Z- 2.8.8.2 ( ½ mk - 40 (1mk)
- Y-2.8.6 ( ½ mk)
-
- white solid (1mk)
- 2Mg(s) + O2(g)→2MgO(S)
- 6 Mg (S) +2N2(g) →2Mg3N2 (S) Mg 3 N2 white solid (1mk)
-
- Weak acid has less hydrogen ion concentration per given volume while dilute acid has higher solvent molecule concentration per given volume (2mks)
- Acid – NH4+√(½) reason donate the proton√(½) (H+) ( 1mk)
- ca2+ or Mg2+ (1mk)
-
- Mg2+ + CO32- →Mgco3 (s) (1 mk)
- Deposition of fir which is an insulator (1mk)
-
- Addition reaction (1mk)
- Alkenes (1mk)
-
- Transition temperature (1mk)
- J- Rhombic sulphur (α sulphur) ( 1mk)
K-Monoclinic sulphur (β Sulphur) ( 1mk)
- carbon atoms in diamond are bonded to each other by strong covalent bonds while in graphite it has weak intermolecular forces between the hexagonal layers hence slide over each other (2mks)
- Bond breaking Bond formation
1x435 = 435 √(1)
2x431 =862√(1)
1x244 = 244 + 679
Total energy Bond breaking + bond formation
679 +(-862) (1)
= - 183 kJ/Mol (3mks)
-
- A- Anode (1mk)
B- Cathode (1mk) - Brown fumes are seen (1mk)
pb 2+ +2e →pb (s) (1mk)
- A- Anode (1mk)
- – Wrong drying agent
-
- Wrong method of gas collection (2mks)
- NH4CL(s) + KOH(aq) →Kcl(S) +NH3 (g)+HO2 (l) (1mk)
- potassium Bromide (1mk)
- 60 -55 = 5g (1mk)
- Fractional crystallization (1mk)
-
- it changes from white to blue (1mk)
- Pbo(s)+H2(g) →Pb (s) +H 2O (l) (1mk)
- Reduction (1mk)
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 - KCSE 2019 ALLIANCE GIRLS MOCK EXAMINATION (WITH MARKING SCHEME).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students