SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer ALL Questions in the Spaces Provided
- Differentiate between olericulture and pomoculture. (2mks)
- Give four reasons why a well drained soil is suitable for crop production. (2mks)
- State four reasons for deep ploughing during land preparation. (2mks)
- Name four types of water pumps which can be used on the farm. (2mks)
- State four characteristics that make a crop suitable for green manuring. (2mks)
- List any four pieces of information which should be shown on Health record. (2mks)
- Give four reasons for seed selection in crop production. (2mks)
- List five management practices carried out on a kale nursery two weeks after its establishment. (2½mks)
- Differentiate between rogueing and thinning. (2mks)
- Name three diseases that attack cabbage. (1½mks)
- State four ecological requirements of tomatoes. (2mks)
- List four factors that will lower demand of a commodity. (2mks)
- State four routine practices of care and management of trees. (2mks)
- State four ways by which a farmer can make efficient use of a pasture crop. (2mks)
- List four pieces of information found on a title deed. (2mks)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions in the spaces provided in this section
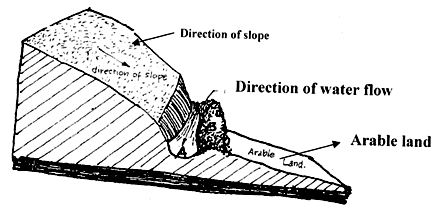
- The illustration below shows a newly constructed cut-off drain. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- How can part of the structure labeled B be stabilized after it has been constructed? (1mk)
- Identify the part of the cut-off drain labeled A. (1mk)
- Describe the procedure of constructing a cut-off drain. (2mks)
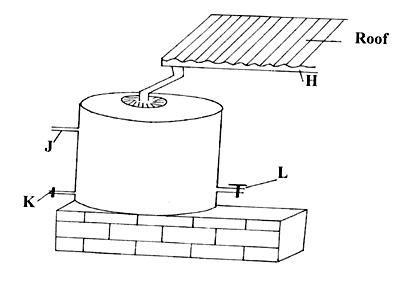
- The diagram below shows a house water storage tank. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the parts of the tank labeled:
H:……………………………………………………………………………… (1mk)
K:……………………………………………………………………………… (1mk) - Give the function of the part labeled J. (1mk)
- Identify the parts of the tank labeled:
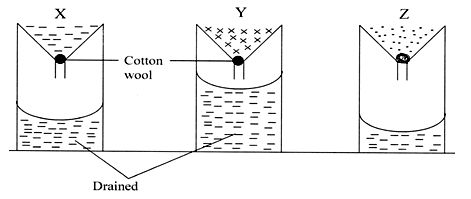
- The experiment below was set to compare the porosity and water holding capacity of three different types of soils.
- Identify the soils in each of the following funnels labeled. (1½mks)
X:
Y:
Z: - Which of the types of soil can be said to have the highest porosity rate? (½mk)
- Give reasons for your answers in (ii) above. (2mks)
- Which type of soil would be suitable for planting paddy rice? (1mk)
- Explain your answer in (iv) above. (1mk)
- Identify the soils in each of the following funnels labeled. (1½mks)
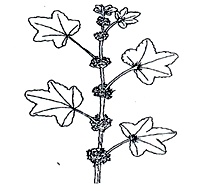
- Below is a diagram of a Common East African Weed.
- Identify the weed illustrated above. (1mk)
- Give one harmful effect of the weed illustrated above to livestock. (1mk)
- State two methods of controlling the weed illustrated above. (1mk)
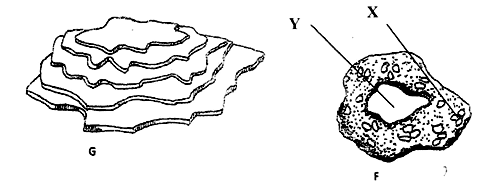
- The diagrams below illustrate some soil structures. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the soil structures F and G. (1mk)
F:………………………………………………………………………………………………..
G:……………………………………………………………………………………………….. - Name the part labeled X and Y in diagram F. (1mk)
X:………………………………………………………………………………………………
Y:………………………………………………………………………………………………. - State two ways through which structure G influence crop production. (2mks)
- Identify the soil structures F and G. (1mk)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided
-
- Describe the field production of irrigated rice under the following sub-headings:
- Field preparation. (6mks)
- Water control (3mks)
- Field management (5mks)
- Describe the precautions taken while harvesting:
- Pyrethrum (3mks)
- Tea (3mks)
- Describe the field production of irrigated rice under the following sub-headings:
-
- Name two types of inventory records in the farm. (1mk)
- Explain six importance of farm budgeting. (6mks)
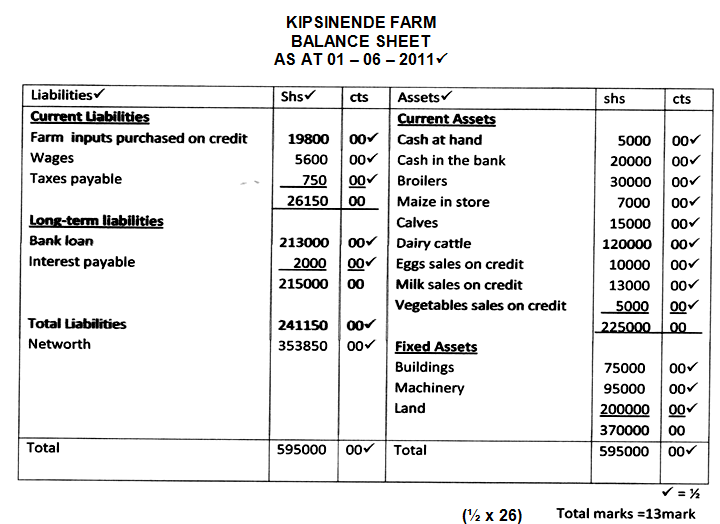
- The inventory for Kipsinende farm as at 01.06.2011
Kshs.
Cash at hand 5,000
Broilers 30,000
Maize in store 7,000
Calves 15,000
Dairy cattle 120,000
Buildings 75,000
Machinery 95,000
Land 200,000
On the same day, the following information was obtained from the farmers records
Kshs.
Interest payable 2,000
Cash in the bank 20,000
Taxes payable 750
Wages payable 5,600
Bank loan 213,000
Egg sales on credit 10,000
Milk sales on credit 13,000
Farm inputs purchased on credit 19,800
Vegetable sales on credit 5,000
Required: Prepare a balance sheet for the farm. (13mks)
-
- Outline the process of treating water for domestic use using chemical treatment system. (12mks)
- Explain five physical factors that increases the rate of soil erosion in a farm. (5mks)
- Explain how monoculture leads to loss of soil nutrients. (3mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Olericulture is the growing of vegetables while Pomoculture is the growing of fruits.(Mark as a whole) (1 x 2 = 2mks)
-
- Has improved soil structure.
- Has reduced leaching.
- Has improved water holding capacity.
- Has increased cation exchange capacity.
- Has high micro organisms which increases decomposition of organic mater which decompose to release nutrients. (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- Facilitates aeration.
- Facilitates drainage.
- Breaks hard pans / facilitate water infiltration.
- Brings up leached nutrients.
- Facilitates development of deep rooted crops.
- Exposes lower soil layers to weathering.
- Exposes soil borne pests and pathogens.
- Removes deep rooted weeds. (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- Centrifugal / Rotar dynamic pump
- Reciprocating / piston pump.
- Hydram pump
- Rotary pump (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- Rapid growth rate.
- Production of abundant foliage.
- Rich in plant nutrients / leguminous / rich in nitrogen.
- Ability to decay quickly.
- Adaptable to wide range of conditions / hardy. (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- Date of treatment.
- Symptoms of disease.
- Animals affected.
- Drugs which were used.
- Cost of treatment. (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- To obtain seed suitable to ecological conditions.
- To obtain pure planting material.
- To increase germination percentage.
- To remove pests and disease infested planting material. (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- Watering
- Weed control.
- Pricking out
- Pest control
- Disease control
- Hardening off (5 x ½ = 1½mks)
- Rogueing is the uprooting and destruction of crops that are infested with pests and diseases. Thinning is the uprooting / removal of excess seedlings to allow space for the remaining seedlings. (Mark as a whole) (1 x 2 = 2mks)
-
- Damping off
- Black rot
- Downy mildew (3 x ½ = 1½mks)
-
- Altitude should be 0 – 2100m above sea level.
- Rainfall should range between 760 – 1300mm per year.
- Temperature should range between 18 – 290C
- The soil pH should be between 5.5 – 6.5 (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- High price of commodity.
- Expected decrease in price of the commodity.
- Advertisement reduction.
- Decrease in population size.
- Reduced income of consumers / inflation.
- Lower tastes and preferences by consumer / reduced fashion of commodity.
- When price of substitute decreases. (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- Protection of trees.
- Grafting old trees. (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- Rotational grazing / controlled grazing.
- Proper stocking rate.
- Conserve excess pasture.
- Timely defoliation.
- Practice zero grazing.
- Graze different classes / species of animals. (4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- The name and signature of owner of the land / identification number of owner.
- The size of land.
- The land parcel number.
- Type of owner, if any.
- Seal of issuing officer and signature of issuing officer.
- The date of registration. (4 x ½ = 2mks)
SECTION B
-
-
- By planting grass / suitable vegetation.
- Channel / trench.
- - MeasureP and markP the layout of drain.
- Dig and removeP soil from the channel and heap it on the lowerPr side of the drain.(4x ½ = 2mks)
-
-
- H – Gutter (1 x 1 = 1mk)
K – Drainage pipe (1 x 1 = 1mk) - Let out excess water (1 x 1 = 1mk)
- H – Gutter (1 x 1 = 1mk)
-
- X – Loam
Y – Sand
Z – Clay (3 x ½ = 1½mks) - Soil Y (sandy) ( ½ mk)
- It has drained the highest amount of water as opposed to others. (1mk)
- Soil Z / Clay soil (1mk)
- It is not easily drained / does not loose water easily when flooded for rice production.
- X – Loam
-
- - Mallow weed / Malva verticillata. (1 x 1 = 1mk)
- - Poisonous / Toxic to livestock. (1 x 1 = 1mk)
- - Mechanical (Acc. any specific method)
-Biological
-Cultural (Acc. any specific method)
-Chemical (Acc. any correct chemical)
Rej. Legislative. (any 2 x ½ = 1mk) - Presence of underground storage structures / rhizomes which are difficult to control. (1mk)
-
- F – Granular structure (½mk)
G – Platy structure (½mk) - X – Humus with clay (½mk)
Y – Air space (½mk) - - Impedes drainage / water infiltration.
-Prevent root penetration.
-Influence soil aeration. (any 2x1 = 2mks)
- F – Granular structure (½mk)
SECTION C
-
- Field preparation
- The field should be cultivated to a fine tilth.
- Construct / repair bund around the field.
- Flood the field 4 days after transplanting.
- Flood the field up to 10cm above the surface.
- Puddle the soil to the required tilth / rotavate the soil.
- Level the field by dragging a board to obtain level seedbed.
- Construct inlet and outlet. (5 x 1 = 5mks)
- Water control
- Increase water level from 5cm to 15cm.
- Water is increased gradually.
- Allow water to flow slowly through the fields / allow fresh water at 2 – 3 weeks interval.
(3 x 1 = 3mks)
- Field management
- Control weeds by uprooting / use of appropriate herbicide
- Control birds by scaring or by destroying breeding colonies.
- Water should be changed every 2 – 3 weeks / let water flow slowly through the field.
- Drain water 3 weeks before harvesting / when heads turn down.
- Maintain level of water at 1/3 height of plants until 3 weeks before harvesting.
- Top dress with sulphate of ammonia at 250kg/ha in two portions.
- Top dress just before transplanting and after 40 days.
- Control diseases i.e. Anthracnose by growing resistant varieties, use clean seeds. Or bacteria blight uprooting and destroying infected plants or spray with colliar oxychloride. (5x1 = 5mks)
- Pyrethrum
- Picked flowers are put into open woven baskets to allow proper ventilation.
- Only dry flowers are picked to avoid fermentation and heating up.
- Flowers are not compacted in the basket to avoid heating up and fermentation.
(3x1 = 3mks)
- Tea
- Tea leaves are not compressed in a basket.
- Harvested tea leaves are kept cool under a shade as harvesting continues.
- Tea leaves are delivered to the factory on the same day after harvesting. (1x3 = 3mks)
- Field preparation
-
- Consumable goods inventory records.
- Permanent goods inventory records. (2 x ½ = 1mk)
- Helps in decision making
- Enables the farmers to predict future returns.
- Helps farmer to avoid incurring losses by investing in less profitable enterprises.
- It ensures a periodic analysis of the farm business.
- It acts as a record which can be used for future reference.
- It pin points efficiency or weakness in farm operations.
- Enables farmers to secure loans from financial institutions. (6 x 1 = 6mks)
-
- Consumable goods inventory records.
-
- Stage I – Filtration at the water intake.
Water is made to pass through series of sieves so that large particles are trapped.
Stage II – Softening of water
Water is mixed with soda ash (NAHCO2) in small tank to soften it.
Stage III – Coagulation and sedimentation
Allum is added to water to facilitate coagulation and sedimentation.
Water stays in the tank for 36 hours to kill bilharzias.
Tanks open to remove bad small / odour and for aeration.
Stage IV – Filtration
Water passes through filtration tank where all remains solid particles removed.
Stage V – Chlorination
Water enters chlorination tank where chlorine is added to kill germs.
Stage VI – Storage
Treated water is stored in large tanks before distribution.
(stage mentioned – 1mk, explanation – 1mk) (6 x 2 = 12mks) -
- Nature of soil e.g. sandy soils are easily eroded whereas clay is resistant to erosion.
- Shape of the land – the steeper the shape of the land the higher the erosivity.
- Rainfall intensity – the higher the intensity of rain the higher the erosion.
- Rainfall amount – the higher the amount of rainfall the higher the erosion.
- Strength of wind – the stronger the wind the higher the erosive power.
- Bareness of the land – bare land are prone to erosion.
(5 explained points) (5 x 1 = 5mks) NB: No mark for just stating.
-
- One type of nutrient is used leading to its exhaustion.
- Nutrient is used from a certain zone where roots can reach.
- Leads to build up of certain pests and diseases. (3 x 1 = 3mks)
- Stage I – Filtration at the water intake.
Download AGRICULTURE PAPER 1 - 2019 KCSE TAP TRIAL MOCK EXAMS (QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students