INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- This paper consists of THREE sections A, B and C.
- Answer ALL questions in Section A and B.
- Answer any TWO questions in section C.
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and no questions are missing.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
SECTION A (30 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section
- State four effects of fleas in poultry.(2 marks
- Name two breeds of dairy cattle with the highest
- butter fat content (1 mark)
- milk yield (1 mark)
- State four ways in which vaccines are administered to livestock. (2 marks)
- State four characteristics of animals which require a high maintenance ration. (2 marks)
- State four microbial activities that occur in the rumen. (2 marks)
- Name four pests that attack bees. (2 marks)
- Name four mineral deficiency livestock disorders. (2 marks)
- State four control measures for fowl typhoid. (2 marks)
- State the function of each of the following:
- mallet (½ mark)
- trocar and canula (½ mark)
- garden line (½ mark)
- stock and die (½ mark)
- State four maintenance practices carried out on a wheelbarrow. (2 marks)
- State four limitations of biogas as a source of power on the farm. (2 marks)
- State four functional differences between disc and mouldboard ploughs. (2 marks
- State four advantages of the Kenya Top Bar Hive (K.T.B.H.) over the log hive. (2 marks)
- Distinguish between the following practices as used in livestock production:
- tupping and serving (1 mark)
- ringing and raddling (1 mark)
-
- Name the causal organism for East Coast Fever. (½ mark)
- State three ways in which infectious diseases spread from one animal to another. (1½ marks)
SECTION B (20 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- The diagram below illustrates a practice in poultry rearing.
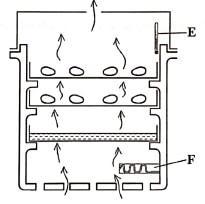
- Identify the practice. (1 mark)
- Name the part labelled
E...................(1 mark)
F....................(1 mark) - Explain two activities not shown in the illustration but very important for the practice to succeed. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows the reproductive system of a hen.
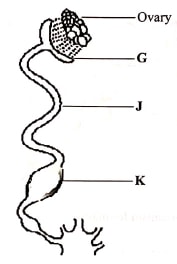
- Name the part labelled K (1 mark)
- State one function of each of the parts labelled
G...............(1 mark)
J................(1 mark) -
- What is the maximum number of eggs a hen can lay in a day? (1 mark)
- Give a reason for your answer in (c) (i) above. (1 mark)
- The diagram below illustrates a treatment practice for a cow's udder infected with mastitis.
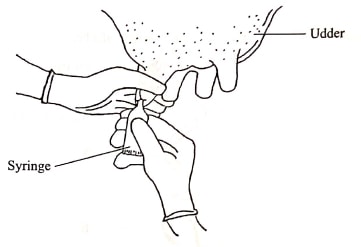
- Name the causal organism for mastitis. (1 mark)
- Explain the treatment practice illustrated. (1 mark)
- How is mastitis infection detected in a lactating cow? (1 mark)
- How is an infected cow handled during milking to prevent spread of the disease to other animals? (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a farm structure for storing grains
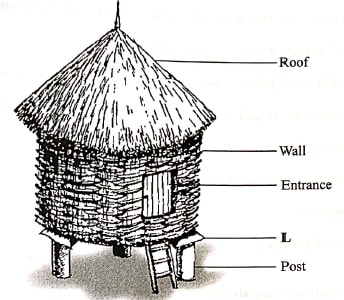
- Identify the farm structure. (1 mark)
- State the function of the part labelled L. (1 mark)
- State one disadvantage of the roofing material used on the farm structure. (1 mark)
- State two ways in which the structure is made ready for grain storage. (2 marks)
SECTION C (40 marks)
Answer any two questions from this section
-
- Describe milk fever disease under the following sub-headings:
- Animals affected. (1mk)
- Causal agent (1mk)
- Symptoms of attack (4mks)
- Control measures (4mks)
- Explain the factors to consider when selecting livestock for breeding. (10mks)
- Describe milk fever disease under the following sub-headings:
- Describe the management of a day old layer chick up to the end of brooding. (20mks)
-
- Describe the components of a cooling system of a tractor. (10mks)
- Outline five care and maintenance practices of a tractor battery. (5mks)
- State five uses of solar energy. (5mks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section
- State four effects of fleas in poultry.(2 marks)
- Irritation
- Anaemia
- Wounds damage on the skin
- Damaged raffled feathers
- Retarded growth
- Name two breeds of dairy cattle with the highest
- butter fat content (1 mark)
- Jersey
- Guernsey
- milk yield (1 mark)
- Fresian
- Aryshire
- butter fat content (1 mark)
- State four ways in which vaccines are administered to livestock. (2 marks)
- Through injections
- Orally through the mouth
- Through the nose/inhalation
- through the cloaca
- State four characteristics of animals which require a high maintenance ration. (2 marks)
- large animals
- young animals
- more active animals
- highly productive(yielding)animals
- State four microbial activities that occur in the rumen. (2 marks)
- Food fermentation
- Synthesis of vitamins
- Synthesis of amino acids
- Breakdown of proteins, amino acids and ammonia
- Breakdown of cellulose and carbohydrates to carbon (IV) oxide and volatile fatty acids
- Name four pests that attack bees. (2 marks)
- Honey badger
- Bee louse
- Wax moth
- Ants
- Name four mineral deficiency livestock disorders. (2 marks)
- Milk fever
- parakeratosis
- Goitre
- Enzootic noenatal ataxia(sway back in lambs)
- Anaemia
- Hypomagnesemia(Grass staggers)
- State four control measures for fowl typhoid. (2 marks)
- Kill and properly dispose infected birds
- Maintain proper hygiene
- Regular vaccination
- Obtain chicks from reliable sources
- Treatment using sulphur drugs
- State the function of each of the following:
- mallet (½ mark)
- Driving wood chisel
- trocar and canula(½ mark)
- Removal of accumulated gases which cause bloat in ruminants
- garden line (½ mark)
- Setting straight lines, measuring distances
- stock and die (½ mark)
- Cutting threads on pipes
- mallet (½ mark)
- State four maintenance practices carried out on a wheelbarrow. (2 marks)
- Greasing the moving parts
- Repairing broken parts
- Replacing worn out parts
- Cleaning after use
- Proper storage
- State four limitations of biogas as a source of power on the farm. (2 marks)
- High initial capital is required to construct the digester.
- Require high skilled labour
- It requires rearing of livestock to sustain gas production
- It is laborious in refilling with dung
- State four functional differences between disc and mouldboard ploughs. (2 marks
Disc Plough Mouldboard plough- Rolls over obstacles Rigid and slides along:
- Does not completely invert furrow slices. Completely inverts furrow slices
- Requires more secondary cultivations. Requires fewer secondary cultivations
- Ploughs at varying depths Ploughs at a uniform depth
- Not easily broken by obstacles Easily broken by obstacles.
- Requires less draft power. Requires more draft power.
- State four advantages of the Kenya Top Bar Hive (K.T.B.H.) over the log hive. (2 marks)
- Top bars can be removed and replaced to inspect the combs.
- Honey combs are harvested without disturbing the brood.
- Good quality honey is harvested without brood combs.
- More wax is harvested because combs are not returned to the hive
- It is easy to construct and repair.
- Utilizes queen excluder to separate honeycombs from the brood combs.
- Is cheap to construct and extract honey
- Distinguish between the following practices as used in livestock production:
- tupping and serving (1 mark)
- Tupping: Act of mating in sheep and goats
- Serving: Act of mating in cattle and pigs,
- ringing and raddling (1 mark)
- Ringing: Trimming of wool around the sheath of the penis to facilitate mating in sheep
- Raddling: Is the fitting of rams with breeding chutes painted in different colours or painting of rams in different colours on the underside to identify sires of lambs, infertile ewes and ewes with repeated heat
- tupping and serving (1 mark)
-
- Name the causal organism for East Coast Fever. (½ mark)
- Protozoa: Theirelia pava
- State three ways in which infectious diseases spread from one animal to another. (1½ marks)
- Through contact
- Through inhalation;
- Through ingestion;
- Name the causal organism for East Coast Fever. (½ mark)
SECTION B (20 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- The diagram below illustrates a practice in poultry rearing.
- Identify the practice. (1 mark)
- Artificial incubation
- Name the part labelled
E................... Thermometer(1 mark)
F.................... Source of heat(1 mark) - Explain two activities not shown in the illustration but very important for the practice to succeed. (2 marks)
- Egg turning to prevent chicks from sticking on shells
- Cleaning and disinfection to ensure proper hygiene/destro diseases agents
- Egg candling to remove infertile, broken and abnormal eggs
- Identify the practice. (1 mark)
- The diagram below shows the reproductive system of a hen.
- Name the part labelled K (1 mark)
- Uterus/shell gland
- State one function of each of the parts labelled
G............... Site of fertilization; addition of chalazae(1 mark)
J................ Addition of thick albumin; addition of water and mineral salts; addition of shell membarane(1 mark) -
- What is the maximum number of eggs a hen can lay in a day? (1 mark)
- one
- Give a reason for your answer in (c) (i) above. (1 mark)
- It takes 24 hours for an egge to form
- What is the maximum number of eggs a hen can lay in a day? (1 mark)
- Name the part labelled K (1 mark)
- The diagram below illustrates a treatment practice for a cow's udder infected with mastitis.
- Name the causal organism for mastitis. (1 mark)
- Bacteria-Streptococcus agalatiae / Staphylococcus urens:
- Explain the treatment practice illustrated. (1 mark)
- Alter milking, the infected teat/quarter is infused with antibiotics to destroy/kill the bacteria:
- How is mastitis infection detected in a lactating cow? (1 mark)
- By stripping milk into a strip cups, before actual milking starts.
- Watery milk/bloody milk/clot/pus/ on the strip cup indicate mastitis infection
- How is an infected cow handled during milking to prevent spread of the disease to other animals? (2 marks)
- Milk the infected animal last: milk the infected quarter last and discard the milk:
- Use Separate udder cloths for each animal:
- Name the causal organism for mastitis. (1 mark)
- The diagram below shows a farm structure for storing grains
- Identify the farm structure. (1 mark)
- Traditional granary
- State the function of the part labelled L. (1 mark)
- Prevent entry of rats into the store
- State one disadvantage of the roofing material used on the farm structure. (1 mark)
- Prone to damage by insects; fire risk; less durable
- State two ways in which the structure is made ready for grain storage. (2 marks)
- Cleaning
- Dusting:
- Clearing the vegetation around the granary:
- Repairing/replacing worn out broken parts:
SECTION C (40 marks)
Answer any two questions from this section
- Identify the farm structure. (1 mark)
-
-
- Animals affected
- Dairy cows
- Dairy goats
- Ewes
- Sows (any 1x1 = 1mk)
- Low calcium level in blood / hypocalcaemia. (1mk)
- Symptoms
- Muscular twitching causing animal to tremble.
- Staggering as the animal moves.
- Animal lies down on its side / unable to stand.
- Neck twisted to one side / sternal recumbency.
- Slow and weak breathing.
- Fall in body temperature.
- General paralysis.
- Milk production ceases / stops.
- Stomach contents are drained into the mouth which later cause lung fever when breathing.
(any 4x1 = 4mks)
- Control measures
- Feed animals on a diet rich in calcium.
- Give intra venous injection of calcium - 3 days before calving.
- Cows with past cases of milk fever should be partially milked for the first 10 days.
- Cull susceptive animals. (any 4x1 = 4mks)
- Animals affected
-
- Good animals on the basis of high yielding cows.
- Select animal with good health / free from any disease attack.
- Animals of high fertility.
- Good body conformation.
- Adaptability of breed to climate / area.
- Good mothering ability.
- Temperament / behaviour.
- Deformities / abnormalities.
- Good offspring performance.
- Age of the animal – young animals.
- Quality of products.
- Disease resistance.
(Explain any 10 x 1 = 10mks)
-
-
- Ensure the brooder is ready and functional 2 – 3 days before chicks arrive.
- The brooder house and brooder equipment should be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected before chicks arrive.
- Newspapers should be spread on the floor of the brooder to prevent chicks from eating the liter.
- Spread some feed on the Newspapers and place some in the feeders.
- Remove the newspapers once the chicks learn to eat from the feeders.
- Provide chicks with water mixed with glucose if they appear weak or stressed on arrival.
- Feed chicks on chick mash which is 20 – 22% DCP for the first 8 weeks.
- Keep the feed as clean and fresh as possible.
- Provide chicks with plenty of clean water.
- Check and adjust the temperatures of the brooder regularly for the first two weeks.
- Vaccinate against (gumboro) after 2 weeks, New Castle at 3 – 4 weeks and fowl typhoid at 7 weeks of age.
- Dust the chicks with the recommended insecticide to control external parasites.
- Control coccidiosis by giving coccidiostats to chicks through water or feed.
- Provide roosts for chicks to perch in the 6th week.
- Provide grit (sand to help in the digestion of feed.
- Introduce growers mash gradually in the 7th week at the ratio of 1:3, growers mash to chick mash.
- Remove the chicks from the brooder at the eight week.
- Feed growers mash only by the 9th week.
- Take the growers to the main poultry house in the 9th week.
- Provide enough floor space, roosts, feeders and water to the growers.
- There should be litter on the of the house about 15cm deep.
- Provide plenty of water to the growers.
- Control parasites and diseases.
- Provide green vegetables at various points to keep birds busy.
- Ensure the litter is dry to prevent caking / rake litter once every two weeks / throw grains on the liter for the birds to scratch.
- Oyster shell (soluble grit) should be provided at 12 weeks of age.
- Feed birds adlib.
- Introduce layers mash gradually at 16 weeks. (20 x 1 = 20mks)
-
-
- Radiator – it has fins or coiled pipes which help to cool hot water from the engine.
- Head tank – holds water for cooling.
- Water pump – pumps water from the radiator through the pipe system into the engine to cool it.
- Fans – blow air to the radiator grills and plates to assist in cooling water inside it.
- Water jacket – allow water to flow around the engine cooling it.
- Thermostat – it controls the engine temperature by either putting the fans on or off.
- Temperature gauge – it indicates the engine temperature to the driver.
- Filter cap – seals the inlet of the head tank making the system air tight.
- Upper hose – it carries hot water from the engine to the head tank.
- Bottom hose – carries cool water from the radiator to the engine water jacket. (any 5x2 = 10mks)
-
- The level of electrolyte should be kept just above the plate by topping with distilled water.
- Corroded terminals should be scrapped clean and smeared with grease.
- The battery should be fitted correctly on the tractor.
- Should be charged regularly and periodically.
- Owing long storage, the battery should be emptied and the battery kept upside down.
- The generator fan belt should always be functional to ensure the battery is always charged.
-
- Drying farm produce.
- Pumping water.
- Heating of water.
- Operating refrigerators.
- Generating electricity.
- Sterilizing milking utensils and equipment.
- Used by green plants for photosynthesis.
-
Download AGRICULTURE PAPER 2 - 2019 KCSE TAP TRIAL MOCK EXAMS (QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

