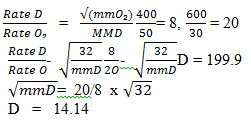INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL questions in the space provided.
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and no question are missing.
- Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid was left exposed in air for a few days .after a few days the level of the acid had risen.
- Why did the level of acid in the container raise? (1 mk)
- How is property useful in the laboratory (1 mk)
- The empirical formulae of a hydrocarbon is C2H3S has a molecular mass of 54.(C= 12, H=1.0)
- Determine the molecular formula of S. (1 mk)
- Name and draw the structural formula of two isomers of S (2 mks)
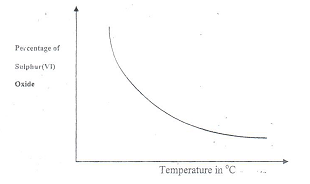
- The chemical equation below represents a reaction stage in the contact process
2SO2(g) + O2(g)2SO3 (g)
The percentage of sulphur (VI) Oxide in the equilibrium varies with temperature as illustrated in the sketch graph below- How does the percentage of sulphur (VI) Oxide in the equilibrium mixture vary as temperature increase? (1 mk)
- Is the forward reaction in equilibrium
2SO2 (g) + O2(g)2 SO3(g)
Exothermic or endothermic? Give a reason for your answer. (2 mks)
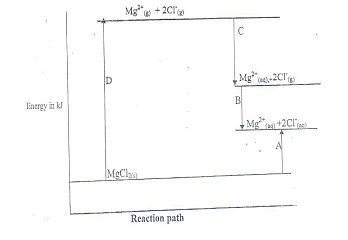
- Study the energy level diagram below and answer the question
- Which letters (A,B,C, of D) represents hydration energy for magnesium chloride(2mks)
- According to the diagram ,is the heat of solution for magnesium chloride exothermic process
- Suppose the lactice for magnesium chloride is -2493kj/mole, hydration energy of Mg 2+ and Cl- ions are – 1891 and – 840kj/mole respectively calculate the heat solution for MgCl2
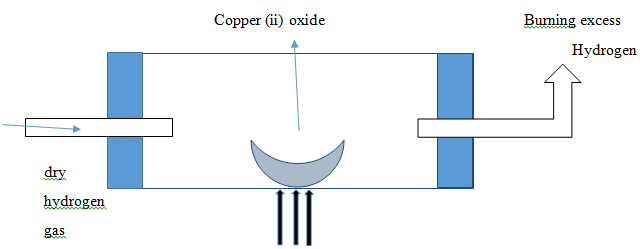
- Use the set up below to answer the question that follow.
- Excess hydrogen burns at the end of the combustion tube ,give reason (1 mk)
- What type of reaction is occurring in the combustion tube?
- State one industrial use of hydrogen gas (1mk)
- When chlorine is bubbled through colf dilute sodium hydroxide solution, the resulting solution acts as bleaching agent
- write a chemical equation for the reaction that produces the bleaching agent. (1 mk)
- Name the bleaching compound and show how it bleaches using the equation (1 mk)
- Distinguish between isomers from isotopes.
- A solution was made by dissolving 10g sodium hydroxide containing inset impurities in water and making it to 250cm3 of solution. If 20 cm3 of this solution is neutralized exactly by 15cm3 of 1m hydrochloric acid, calculate the percentage purity of sodium hydroxide . (3 mks) (Na = 23, O=16, H=1)
-
- Determine the oxidation state of sulphur in sodium thiosuphate (Na2S 2O3) (1 mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction of sodium thiosulphate and dilute hydrochloric (1mk)
- Of what use is the reaction in “b” above in our school laboratory (1mk)
- The flow chart below shows the preparation of ethanol by the hydrolysis of ethane
- Identify substances R and T (2mks)
- Write the equation for the reaction between ethanol and concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid room temperature (1 mk)
-
- what property of concentrated sulphuric (vi) acid is illustrated by its action in
- Sugar
- Copper metal
- Write equation for the reaction of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid with copper metal. (1mk)
- what property of concentrated sulphuric (vi) acid is illustrated by its action in
- The electron arrangement of the icons P+ ,Q+,R+ and T+ are 2:8, 2:8:8,2:8 and 2:8:8 Respectively .
- Write the electron arrangement of the elements P, Q, R, and T. (2mks)
- Write the formula of the compound that would be formed between Q and T (1mk)
- Write the formular of the compound formed when element P is burnt in excess are (1mk)
- The table below shows the first ionization energies of element D and E
ELEMENT
IONIZATION ENERGY IN KJ/MOLE
D
495
E
750
What do these values suggest about the reactivity of D compared to that of E. Give a reason for your answer. (2mrks)
- The table below gives the solubilities of salt L and K at 100 C and 40 0C. When the aqueous mixture containing 80g of L and 10 of K in 100 g of water at 50 C was cooled to 100 C
Salt
Solubility in g/ 100g of water
At 100 C
At 400 C
l
60
75
K
20
32
- Identify the salt that crystals were obtained. (1 mk)
- Define solubility ( 1 mk)
- suggest on industrial application of the method (1mk)
- Write equation to show the effects of heat on each of the following ( 3 mks)
- Potassium hydrogen carbonate.
- Silver nitrate
- Anhydrous iron (II)
-
- State Charles law ( 1mk)
- A certain mass of gas occupies 146cm3 at 240C and 98.31 Kpa ,.What will be its temperature if its volume is reduce to 135cm at 101.325 Kpa (2 mks)
- The elements X and Y belong to period 3 of the periodic table .there oxide are X2 O and YO2 respectively .compare the pH values of oxides when dissolved in water (2mks)
-
- Distinguish between strong and concentrated acid ( 1mk)
- A solution of ammonia in methylbenzene has no effects on red litmus paper while a solution of ammonia in water turns red litmus paper blue. Explain (1 mk)
- 150cm of ethane was mixed with 60cm3 of oxygen and the mixtures exploded to complete reaction .What is the volume of each of the remaining gases at room temperature and pleasure? (2 marks)
- Using dot (.) and cross (x) to represent election show bonding in the substance formed below.
- Ammonium ion (2 marks)
H = 1, N = 7 - Carbon (II) Oxide
C = 6, O =8
- Ammonium ion (2 marks)
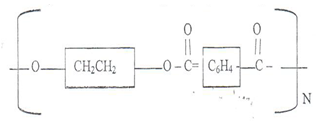
- Identity the monomers in the given polymer of terylene.
- The table below shows the pH values of solution I to IV
SOLUTION
1
II
III
IV
PH
2
7
11
14
- Which solution is likely to contain the highest concentration of hydroxide ions? ( 1 mk)
- Select the solutions in which a sample of aluminium oxide is likely to dissolve. Give a reason for your answer. ( 2 mks)
- The product formed by the action of heat in nitrates of A, B and C are shown below.
Nitrate
Product formed
A
Metal oxide + Nitrogen (iv) Oxide + Oxygen
B
Metal + Oxygen + Nitrogen (iv) Oxide
C
Metal nitrite + Oxygen
- Arrange the metals in order of increasing reactivity . ( 1 mk)
- Which substance forms a soluble carbonate? ( 1mk)
- Copper (II) sulphate solution was electrolysed using inert electrodes
- State two observation made (2mks)
- Write the equations of reaction at anode and cathode (2 mks)
-
- State Graham’s law of diffusion. (1 mk)
- 400cm3 of gas D diffuse from a porous 50 seconds while 600cm3 of oxygen gas diffuses from the same apparatus in 30 seconds. Calculate the relative molecular mass of gas D. O = 16. ( 2 mks)
- Use the information below to answer the question that follow.
Ca (s) + ½ O2 →CaO (s) Δ H = - 635kJmol
C (s) + O2 →CO2 (g) Δ H = -394kJ/mol
Ca(s) + C(s) + 3 /2 O2 (g)→CaCO3(s) ΔH = 1207kj/mol
Calculate enthalpy for the reaction ( 3 mks)
CaO (s) + CO2 →CaCO2 (s)
- Describe how a sample of lead (II) chloride can be prepared using the following reagents dilute nitric (V) acid, dilute hydrochloric acid and lead (II) Carbonate. ( 3 mks)
- When a current of 1.5 amperes was passed through cell containing M2+ ions for 15 minutes, the mass of the cathode increased by 0.26g ( IF = 96500 C)
- Calculate the quantity of electricity used. ( 1 mk)
- Determine the relative atomic mass of metal M. (2mks)
- A solution of silver nitrate was put in a container made of metal Q for one day. Given that
Q2+ (aq) + 2 eQ (s) , Eθ = +0.13V
Ag+ (aq) + eAg (s) , Eθ = + 0.80V
Determine whether or not a reaction occurred between silver nitrate and metal Q (2 mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- It absorbed moisture from air
- Used as a drying agent
-
- (C2H3)n = 54 27n = 54 n = 2
(12 x 2) + (1 x 3 )n = 54 MF C4 H6 - H – C = C – C - C – H But -1
- (C2H3)n = 54 27n = 54 n = 2
-
- it decreases as temperature increases
- Exothermic, as the volume of SO3 decreases in temperature increases.
-
- C and D
- Endothermic
- heat of solution = lattice energy + hydration energy
+ 2493 + -1891 + (-840 x 2)
+2493 - 3571
-1078kj/mol
-
- Its explosive if ignited in air
- Reduction
- Manufacture of Ammonia
Manufacture of Hydrochloric acid.
-
- 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) →NaCl(aq) + naOCl(aq) + H2O(l)
- sodium chlorate (l)
NaOCl(aq) + dye →Nacl(aq) + (dye + O)
- Isomers are compound with the same molecular formula but different structure formula white isotopes are atoms with same atomic no. but different mass number.
- (NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
20cm3 15cm3, 1m
Moles of HCl= 15 x 1 = 0.015moles
1000
Mole ratio NaOH; HCl 1 : 1
Mole of NaOH = 0.015moles
0.015 moles = 20cm3
250cm3
250 x 0.015= 0.1875
20
2fm of NaOH = 23 + 176 + 1 = 40
Press = 40 x 0.1875 = 7.5g
Percentage 7.5 x 100 = 75%
10
-
- (+1 x 2) + 25 + (-2 x 3) = 0+ 2 + 25 – 6 = 0
25 = +4
5 = +2 - Na2S2O3 + 2HCl(aq) = 2Nacl + SO2 + S(S) + s + H2O(l)
-
- Preparation of Cathodesulphur
- Determining reaction rate
- (+1 x 2) + 25 + (-2 x 3) = 0+ 2 + 25 – 6 = 0
-
- R - concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
T - ethyl hydrogen sulphate - CH3CH2OHL+ H2SO4 = CH3CH2OSO3H(a) + H2O(l)
- R - concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
-
-
- sugar = Dehydrating agent
- Copper metal = Oxidising agent
- Cu + 2H2SO4(l) → CUSO4(aq) + SO2 + 2H2O(l)
-
-
- P 2 : 8 : 1 R 2 : 8 : 3
Q 2 : 8 : 8 : 1 T 2 : 8 : 6 - Q2 T
- 2P(s) + O2(g) → P2O2(s)
- P 2 : 8 : 1 R 2 : 8 : 3
-
- D is more reactive than E
Reason.
D requires less energy to lose electron from the outmost energy level
- D is more reactive than E
-
- Max mess of a solute that dissolves in 100g of water at a particular temperature
- Extraction of sodium chloride in Magadi
-
- 2KHCO3(s) → K2CO3(s) + CO3(s) + CO2 + H2O(l)
- 2AgNO3(s) → 2Ag(s) + 2NO2(g) + SO3(g)
-
- Charles Law
The volume of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to absolute temperature at constant pressure. - P1 V1 = P2V2
T1 T2
98.31 x 146 = 13.5 x 101.32J
297 T2
T2 =297 x 135 x 101.325
98.31 x 146
T2 = 283K Or 100C
- Charles Law
- The PH of X2O in water is higher than YO2 since it forms a basic solution while YO2 forms on acidic solution.
-
- Strong acid ionizes completely in solution while concentrated acid contain high number of acid molecules per given volume.
- Ammonia in water dissociate to produce hydroxide ion while in methybenze it remain in molecular form.
- 2C2 H6 + 7O2(g) →4CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
150cm3 60cm3
60cm3 7
2 x 60
7
= 17.14cm3 of ethane required.
Volume of CO2formed = 34.28cm3
Volume of excess ethane = 132.86cm3
-
- Ammonium ion
H = 1, N= 7
NH4+
- Ammonium ion
-
- IV
- I and IV Al2 O3 is amphoteric
-
- B A C
- C
-
- -The blue colour of solution fades
-A brown solid deposited at Cathode - Anode 4OH-aq →2H2O + O2 + 4E
Cathode Cu2+ + 2E→CU(s)
- -The blue colour of solution fades
-
- The rate of diffusion of a given volume of a gas is inversely proportional to square not of its density at constant temperature and pressure.
-
- Ca + 3/2 O2 + C △H4 CaCO3
O2△H O2△H2△H3
CaOs+ CO2
△H4 = △H1 + △H2 + △H3
- 1207 = -635 _ -394 + △H3
-1207 + 635 + 394 = △H3
△H3 = -178kj/mol
- Add excess lead (II) carbonate to dilute nitric (v) acid Filter the mixture to obtain lead (II) nitrate as filtrate. Add dilute hydrochloric acid to filtrate and filter. Rinse the residue with distilled water and dry between filter paper.
-
- Q = it
Q = 1.5 x 15 x 60 = 1350C - (96500 x 2 )
1350C
96500 x 2 x 0.26= 37.17
1350
- Q = it
- Q(s) + 2Ag+ ↔ Q2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Q(s) ↔ Q(aq) - 2e - 0.13V
2Ag+ + 2e → Ag + 0.8Q
Q(s) + 2Ag+(aq) ↔ Q2+ (aq) +Q2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) + 0.67V
The reaction will occur.
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 - 2019 KCSE TAP TRIAL MOCK EXAMS (QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students