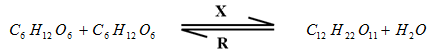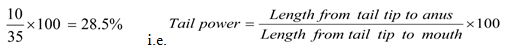INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL the questions in this question paper.
- All answers must be written in the spaces provided after each question.
- Candidates should answer all the questions in English.
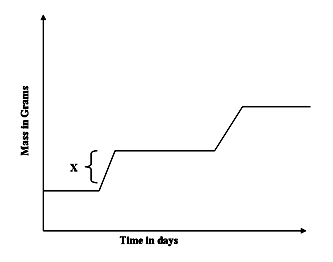
- The graph below represents the growth pattern of animals in a certain phylum.
- Name the type of growth curve shown above. (1 mark)
-
- Identify the process represented by X. (1 mark)
- Name the hormone responsible for the process in b(i) above. (1mark)
- State the importance of the growth of a pollen tube to a plant. (1 mark)
-
- What is the function of Sodium hydrogen Carbonate that is added to test solution of non-reducing sugar. (1 mark)
- The equation below represents a process X which is controlled by enzymes.
- Name the process X and enzyme R
Process X ……………………………………………………… (1 mark)
Enzyme R ………………………………………………………. (1 mark)
- Name the process X and enzyme R
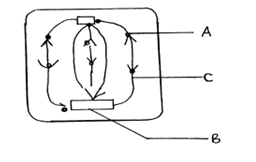
- The diagram shows an epidermal cell undergoing mitotic cell division.
- Name the stage of mitosis it represents (1 mark)
- Name the structures
A (1 mark)
C (1 mark)
- What is the effect of gibberellins on the shoots of plants? (4 marks)
-
- Give two forms in which carbon (IV) oxide is transported in human blood. (2 marks)
- Name the enzyme that enhances the loading and off – loading of carbon (IV) oxide in the human blood. (1 mark)
-
- What is the importance of the counter current flow in the exchange of gases in a fish?
- State two ways in which the tracheoles of an insect are adapted to their functions. (2 marks)
- The equation below represents a reaction that occurs during respiration in a cell.
K + Phosphate →Adnenosine triphosphate- Identify the compound K. (1 mark)
- State two differences between K and ATP. (2 marks)
- Name the organelle responsible for the production of energy in a cell muscle. (1 mark)
- Explain how crops grown along roads can be a source of lead poisoning to human beings. (2 marks)
- Explain why plants growing in low altitude areas grow faster than those in high altitudes.(3 marks)
- List down four phenotypic characteristics that have been selected for the production of strains suitable for modern agricultural purposes. (4 marks)
- Name the type of eye defects that can be corrected by;
- Use of bifocal lens (1 mark)
- Use of artificial lens (1 mark)
- Use of concave lens (1 mark)
-
- The length from the tail tip to the anus of a certain tilapia fish is 10 cm. The length from the tail tip to the mouth is 35cm. Calculate the tail power of the fish. (Show all your working).(2 marks)
- What is the significance of high tail power in fish? (1 mark)
- List down three differences between the endocrine system and nervous system. (3 marks)
Endocrine system
Nervous system
i.
ii
iii
i.
ii
iii
- Distinguish between the struggle for existence and survival for the fittest as used in the theory of natural selection. (2 marks)
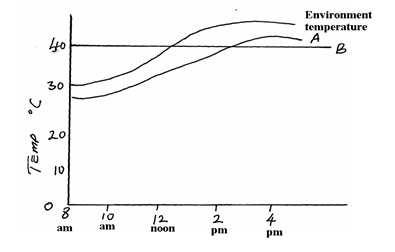
- The body temperatures of two animals A and B varied as below with environmental Temperature
- Which of the animals is;
- Endothermic …………………………………………………….. (1 mark)
- Ectothermic ……………………………………………………… (1 mark)
- With a reason, state which of the animals is likely to be widely distributed.(2 marks)
- Which of the animals is;
- State three roles of oestrogen during the menstrual cycle (3 marks)
- State three characteristics of cells at the zone of cell division in an apical meristem.
- Below are diagrams of three leaves A, B and C. Construct a two step dichotomous key which can be used to identify each of them. (4 marks)
-
- Name two mutagenic agents. (2 marks)
- Identify the type of gene mutations represented by the following pairs of words.
- Shirt instead of skirt (1 mark)
- Hopping instead of shopping (1 mark)
- Liver damage leads to impaired digestion of fats. Explain this statement. (2 marks)
- Explain why several lateral buds sprout when a terminal bud in a young tree is removed.(3 marks)
-
- State two structural adaptations that make xylem vessels suitable for transport of water and mineral salts. (2 marks)
- List any three adaptations of the root hair cells to their functions (3 marks)
- Define the following terms:- (2 marks)
- Species
- Binomial nomenclature
- What is the significance of active transport in the human body? (3 marks)
- Explain how the biceps and triceps muscles bring about the movement at the hinge joint of the elbow in man. (2 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Intermittent growth curve;
-
- Growth;
- Ecdysone/ mounting hormone;
- Results in fertilization by conveying the male gametes to the female gamete;
-
- Neutralise excess acid (HCl);
- X – Condensation;
R – Sucrase/ invertase;
-
- Anaphase
- A – Chromatids;
C – Spindles;
- Promote cell division/ cell elongation; initiates fruit formation without fertilization/ parthenocarpy; formation of side branches of stem; inhibits growth of adventitious roots; promotes dormancy in buds; Activates enzymes during germination; (4mks)
-
- – (Weak) carbonic acid ; acc bicarbonate ions/hydrogen carbonates
- Carbamino haemoglobin; - Carbonic anhydrase;
- – (Weak) carbonic acid ; acc bicarbonate ions/hydrogen carbonates
-
- Maintains a steep concentration gradient across the respiratory surface; ensuring maximum extraction of oxygen from water to the blood; (2mks)
- Thin epithelium for faster/ quick diffusion of gases; Have tracheole fluid/ moist surface to dissolve gases in solution before diffusing; Highly branched to increase surface area for gaseous exchange; (mark first two)
-
- Adenosine Diphosphate/ ADP
- K – has two phosphate molecules
ATP - has three phosphate molecules
K – has less stored energy
ATP – has more stored energy - Mitochondrion rej; Mitochondria
- Absorb lead from car exhaust fuses and pass it to animals and humans through the food chain.
- Low altitude areas have favourable temperature for working of enzymes; faster metabolic process leading to faster growth; high concentration of Co2 hence high rate of photosynthesis; High Co2 concentration in low altitude leads to increased rate of respiration to generate energy for faster growth;
-
- Resistance to diseases.
- Early maturity
- Adaptations to local conditions
- High yields
- Increased length of production
-
- Old sight/ presbyopia; (1mk)
- Cataract; (1mk)
- Myopia/ short sightedness; (1mk)
-
-
- To create a high propulsive force/ thrust
-
- Endocrine system Nervous system
- Uses hormones to relay impulses
- Uses electrical charges caused by chemical concentration
- Hormones transmitted through the
- Impulse transmitted through nerve cells; blood
- Hormones reach all parts of the body
- Nerve impulses are transmitted through nerve cells to specific parts of the body;
- Effects are long lasting
- Effects are rapid and short lived;
- Responses usually slow
- Responses usually fast;
- Struggle for existence – environmental pressure on the population in order to survive; Survival for the fittest – advantageous variations an individual possesses to make it survive;
-
-
- B 1
- A 1
- B1 – because it can keep its temperature constant despite variations in the environment 1
-
-
- Stimulates repair and healing of endometrium 1
- Stimulates production of LH 1
- Stimulates development of female secondary sexual characteristics 1
-
- Thin cell walls 1
- Nerval cytoplasm 1
- No vacuoles 1
- 1a; Simple leaf……………………………. Go to 2 1
1b; Compound leaf ……………………….. C 1
2a; With parallel variation…………………. B 1
2b; With network variation………………… A 1
Gramma rays 1
Mustard gas 1 -
- Substitution1
- Deletion 1
- Lack of bile salts; which emulsify fats;
- High auxin concentration produced by terminal bud/ apical meristem, inhibits lateral buds growing into branches; removal of terminal bud/ apical bud lowers the concentration of auxins/ lowers the inhibition effect (hence sprouting of lateral buds;
-
- - Its cells (vessels) have no transverse walls thereby forming a long hollow tube running from roots to leaves (through which water and mineral salts can easily be transported);
- Have dead cells lacking nucleus and other cell contents (organelles) which might have otherwise retarded / restricted the movement of mineral salts and water from the soil through the roots and up the plant;
- The cells are longitudinally joined to each other to enhance easy movement of water and mineral salts up the plant;
- The cells have side walls coated with light deposits which prevent leakage of water and also strengthen the walls preventing them from collapsing;
- The xylem vessels are narrow to facilitate capillarity; OWWTTE - - The epidermis is one cell thick for faster movement of water and mineral salts into the plants body;
- They are thin and flexible to easily penetrate through the soil particles.
- The root hairs are many to increase the surface area for diffusion of material into the plant;
- Have semi-permeable membrane for selective movement of materials into the plant;
- - Its cells (vessels) have no transverse walls thereby forming a long hollow tube running from roots to leaves (through which water and mineral salts can easily be transported);
-
-
- A group of organisms that can naturally/ freely interbreed to produce viable fertile young ones; (offspring) (1mk)
- (A scientific system of double naming) naming organisms using the generic/ genus and specific/ species names; OWWTTE (1mk)
-
- - Sodium pump mechanism in nervous system;
- Reabsorption of useful materials in blood stream from tissue fluid;
- Excretion of waste products from body cells;
- Absorption of digested food/ mineral salts/ vitamins from alimentary canal;
- Reabsorption of glucose / (some) salts in the kidney/ by kidney tubules;
- When biceps contract it pulls the fore arm and the arm bends; the triceps relaxes to bring about balanced movement; when triceps contract the biceps relaxes and the fore arm stretches/extends;
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download BIOLOGY PAPER 1 - 2019 KCSE STAREHE MOCK EXAMS (QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students