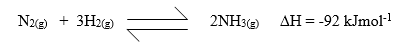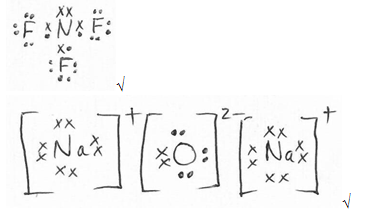INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- KNEC Mathematical tables and silent non-programmable electronic calculators may be used.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary
- Candidates should check the question paper to ensure that all pages are printed as indicated and no questions are missing.
- Candidates should answer all the questions in English.
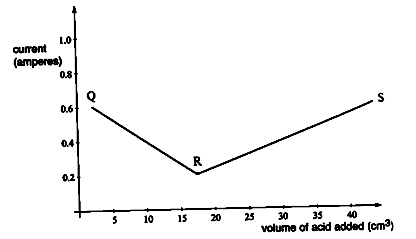
- The electrical conductivity of barium hydroxide solution was measured after each addition of 1.0 cm3 of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid from a burette. The graph below was obtained.
- Write the chemical equation of the reaction that took place. (1 mark)
- Explain the graph between,
- Q and R (1 mark)
- R and S (1 mark)
- A mass of 14.2 g sodium nitrate saturated 32.1 cm3 of water at 32 oC. Determine the solubility of sodium nitrate at 32 oC. (Density of water = 1g/cm3). (2 marks)
- Explain why sulphur is a solid while oxygen is a gas at room temperature. (2 marks)
- Study the electrode potential in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
E volts
Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) +0.34
Mg2+ (aq) + 2e- → Mg(s) -2.38
Ag+ (aq) + e- → Ag (s) +0.80
Ca2+ (aq) + 2e- → Ca (s) -2.87- Identify the strongest reducing agent. (1 mark)
- What would be observed when magnesium ribbon is dipped in solution of copper (II) sulphate. Explain. (2 marks)
- In a reaction, 0.65 g of impure zinc oxide reacted with 100 cm3 of 0.15 M nitric (V) acid.
- Write equation of the reaction. (1 mark)
- Calculate percentage purity of the zinc oxide sample. (2 marks)
(Zn = 65, O = 16)
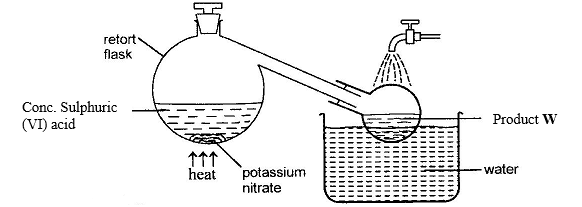
- The set up below can be used for the laboratory preparation of product W.
- Write chemical equation for the reaction that takes place in the retort flask. (1 mark)
- Explain why product W appears yellow in colour. How is the colour removed? (2 marks)
- The table below shows information of four elements A, B, C and D. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Element
Electronic arrangement
Atomic radius
Ionic radius
A
2.8.2
0.136
0.065
B
2.8.7
0.99
0.181
C
2.8.8.1
0.203
0.133
D
2.8.8.2
0.174
0.099
- Which two elements have similar properties? (1 mark)
- Explain why B ionic radius is larger than its atomic radius. (2 marks)
- The production of ammonia gas involves a reversible reaction as shown.
- What condition is necessary for the chemical equilibrium to be established? (1 mark)
- Suggest two conditions that are likely to shift the equilibrium from right to left. (2 marks)
- Describe how chloride ions are tested in a solution. (2 marks)
- The empirical formula of X is CH2Br. Given that 0.235 g of X occupies a volume of 56 cm3 at 546 K and 1 atmosphere pressure, determine its molecular formula.
(H = 1.0, C = 12.0, Br = 80.0, molar gas volume at STP = 22.4 dm3) (3marks)
- When a piece of sodium metal is place in cold water in a beaker it melts producing a hissing sound, as it moves on the surface of the water. Explain these observations. (3 marks)
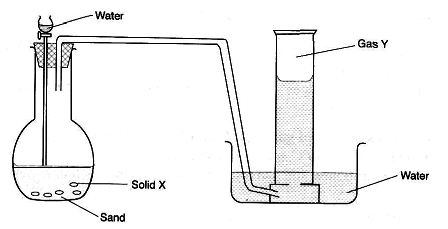
- The set-up below was used to prepare a hydrocarbon. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify solid X and gas Y.
Solid X (1 mark)
Gas Y (1 mark) - Write a chemical equation for the complete reaction between gas Y and bromine vapour. (1 mark)
- Identify solid X and gas Y.
-
- When excess chlorine gas is bubbled through cold, dilute sodium hydroxide solution, the resulting solution acts as a bleaching agent. Using an equation, explain how the resulting solution acts as a bleaching agent. (1 mark)
- What is observed when chlorine gas is bubbled through a solution of potassium bromide? Explain. (2 marks)
-
- Explain why the pH of 1.0 M hydrochloric acid is 1 while that of 1.0 M ethanoic acid is 5.0. (1 mark)
- How can a precipitate of barium sulphate be distinguished from that of barium sulphite? (2 marks)
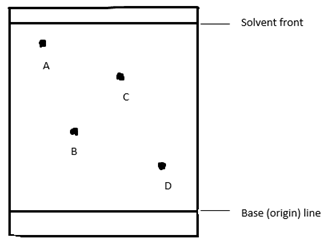
- A, B, C and D are dyes present in a mixture. In a given solvent, C is more soluble than B and A is more soluble than C. D is the least soluble. Draw an ascending paper chromatogram showing how they would appear when separated using the solvent. (2 marks)
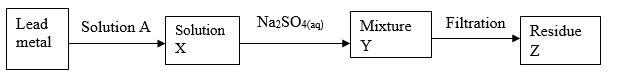
- The reaction below refers to the preparation of lead (II) sulphate starting with lead metal.
- Name solution A(1 mark)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction in (a) above. (1 mark)
- Explain why it is not possible to prepare residue Z using lead metal and dilute sulphuric acid. (1 mark)
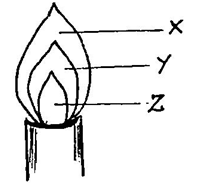
- The diagram below represents a Bunsen burner flame. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Under what condition is the represented flame produced? (1 mark)
- Which of the regions shown represents the hottest part of the flame? (1 mark)
- Name region Y (1 mark)
- A typical electrolysis cell uses a current of 40,000 amperes. Calculate the mass in kilograms of aluminium produced in one hour. (Al = 27, 1 Faraday = 96,500 coulombs) (3 marks)
-
- Distinguish between endothermic and exothermic reaction. (1 mark)
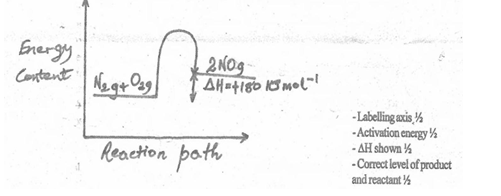
- Nitrogen reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen (II) oxide according to the following reaction
N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g) ∆H = +180 kJmol-1
Draw an energy level diagram for this reaction including the activation energy. (2 marks)
-
- When a compound T was heated, a brown gas and a residue which was yellow when hot and white when cold were formed. Identify the:
- Brown gas (1 mark)
- Residue (1 mark)
- Name a suitable drying agent for ammonia gas. (1 mark)
- When a compound T was heated, a brown gas and a residue which was yellow when hot and white when cold were formed. Identify the:
- Give the structural formula of the following organic compounds.
- 2-Methylbutane
- Pent-2-ene
- Ethylpropanoate
- When iron and steam are heated in a closed container, a dynamic equilibrium is reached.
- Define the dynamic equilibrium. (1 mark)
- What is the effect on equilibrium if magnesium is added? Explain. (2 marks)
- State and explain the observations that would be made when burning magnesium is lowered into a gas jar of sulphur (IV) oxide. (3 marks)
- A mixture contains barium sulphate, calcium chloride and dry ice. Describe how the components can be separated. (3 marks)
- In the redox reaction below:
2H+(aq) + Cr2O72-(aq) + 3SO2(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3SO42-(aq) + H2O(l)
Identify the reducing agent. Explain. (2 marks) -
- Explain why aluminium utensils do not corrode as easily as iron utensils although aluminium is higher than iron in the reactivity series. (1 mark)
- State two uses of aluminium other than utensils making. (2 marks)
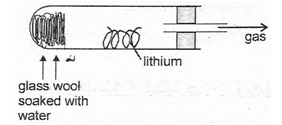
- The diagram below represents a set up that was used to react lithium with steam. Study and answer the question that follows.
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place. (1 mark)
- Why is it not advisable to use potassium metal in place of lithium in the above set-up? (1 mark)
- The gas produced above is used for welding. Which other gas is combined with it? (1 mark)
- Using dots (.) and crosses (×) to represent valence electrons, show bonding in:
- Nitrogen trifluoride (N = 7, F = 9) (1 mark)
- Sodium oxide (Na = 11, O = 8) (1 mark)
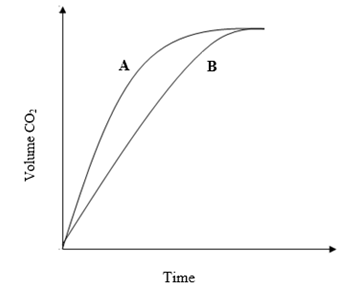
- The graphs below were drawn by measuring the volume of hydrogen produced with time when excess zinc metal in different physical states were reacted with 50 cm3 of 2 M hydrochloric acid.
- Which curve corresponds to the reactions involving powdered zinc? (1 mark)
- Both curves eventually flatten out at the same level of hydrogen. Explain. (1 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- H2SO4(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) → BaSO4(s) + H2O(l)
-
- Conductivity decreases because Ba2+ and OH- ions are converted to insoluble BaSO4(s) and H2O(l) which do not conduct electricity.
- Conductivity increases due to the increase of H2SO4(aq) beyond the neutralization point or equivalence point.
- Mass of water = 32.1 cm3 × 1 g/cm3 = 32.1 g √
32.1 g of water = 14.2 sodium nitrate
100 g of water = 100 × 14.2 = 44.24 g √
32.1
- Oxygen is above sulphur in group six, √ the intermolecular force of attraction between molecules increases down the group with increases in size of the molecule. √
-
- Ca / calcium √
- The blue colour of copper (II) sulphate will fade; √½ brown solid will be deposited on magnesium ribbon.√½
Magnesium reduces the copper (II) ions (blue) to copper metal (brown) and itself oxidised to colourless magnesium ions √ or
Mg(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Cu(s)
-
- ZnO(s) + 2HNO3(aq) → Zn(NO3)2(aq) + H2O(l) √
- mol HNO3 = 0.15 × 100/1000 = 0.015 √½
mol ZnO 0.015/2 = 0.0075 √½
g ZnO = 0.0075 × 76 = 0.57 √½
% ZnO = 0.57/65 = 87.7 √½
-
- KNO3(s) + H2SO4(l) → KHSO4(s) + HNO3(l) √
- Because of dissolved NO2 (g) √ (formed from thermal decomposition of HNO3); the colour can be removed by bubbling air through the acid. √
-
- A and D √
- B ion has an extra electron√ which reduces the overall nuclear attraction.√
-
- Reaction be carried out in a closed system or vessel √
- -Increase in temperature √
-Reduction in pressure √
- To the solution, add a few drops of lead nitrate solution. √ A white ppt that dissolves on heating confirms Cl- ions √ or add a few drops of silver nitrate and a white ppt is formed.
- (1 × 56)/546 = (1 × V2)/273
V2 = 28 cm3 √
28 cm3 = 0.235 g
22400 cm3 = (22400 ×0.235)/28 = 188 g √
n = 188/94 = 2
MF = (CH2Br)2 or C2H4Br2 √
- - Melting: reaction is exothermic. √1
- Hissing sound: due to hydrogen gas evolved. √1
- Moving on the surface: sodium is less dense than water and gets propelled by escaping H2 gas. √1
-
- Solid X-Calcium carbide / CaC2 √, Gas Y-Ethyne / C2H2 / CH≡CH √
- CH≡CH(g) + 2Br2(g) → CHBr2CHBr2(l) √
-
- NaOCl(aq) + dye → NaCl(aq) + dye-O (colourless compound) √
- Colourless solution turns brown √; Chlorine being more reactive than bromine oxidises bromide ions to bromine.√
-
- As a strong acid, hydrochloric acid is completely dissociated giving a high concentration of H+ ions while ethanoic acid is a weak acid and is partially dissociated. √1
- Sulphite dissolves in dilute hydrochloric acid or nitric acid with evolution of sulphur (IV) oxide √ while the sulphate does not dissolve.√
-
Diagram = 1 mark, Labelling = 1 mark
-
- Nitric (V) acid √
- Pb2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → PbSO4(s) √
- An insoluble coating of PbSO4(s) would prevent contact of the metal with the acid and stop further reaction. √
-
- Produced when air-hole is open √
- X √
- Green-blue region√
- Quantity of electricity = 40,000 × 60 × 60 √
3 × 96,500 coulombs produce 27 g of Al √
= 13.43 kg √
-
- Endothermic reaction- absorbs heat from the surrounding √½
Exothermic reaction- releases heat to the surrounding √½ -
- Endothermic reaction- absorbs heat from the surrounding √½
-
-
- Nitrogen (IV) oxide /NO2 √
- Zinc oxide/ZnO √
- Calcium oxide √
-
-
- CH3─CH2CHCH3 √
│
CH3 - CH3CH2CH═CHCH3 √
- O
║
CH3CH2C─O─CH2CH3 √
- CH3─CH2CHCH3 √
-
- The forward and backward reactions takes place at the same rate.√
- Backward reaction is favoured or equilibrium shift to the left √; Magnesium reacts with steam lowering the concentration which is replaced through backward reaction.√
- Magnesium continues to burn for some time, √½ white fumes √½ and yellow specks or solid are formed√½. Heat produced by burning magnesium decomposes sulphur (IV) oxide to sulphur (yellow solid) and oxygen √½. Magnesium burns in the oxygen √ ½ to form magnesium oxide (white fumes). √½
- Heat the mixture √½, dry ice sublimes √½, add water to the mixture √½, filter √½, and filtrate is calcium chloride, residue is barium sulphate √½, heat the filtrate to saturation and then cool to allow crystals of calcium chloride to form. √½
- Reducing agent SO2 √
Oxidation number of S has increased from +4 in SO2 to +6 in SO42-.
OS of S in SO2
S + 2(-2) = 0
S = +4 √½
OS of S in SO42-
S + 4(-2) = -2
S= +6 √½
-
- Aluminium form a protective layer of aluminium oxide on the surface which prevents further oxidation whereas iron does not.√
-
- Food packaging
- Head lamp reflectors
- Overhead electrical cables
- Construction of aircrafts and ships (Duralumin alloy)
- Reducing agent in thermite process
- Abrasive (corundum or emery)
Any two = 2mks
-
- 2Li(s) + H2O(g) → Li2O(s) +H2(s) √
- K is highly reactive and the reaction would be more vigorous and explosive.√
- Oxygen gas√
-
-
- Curve A
- In both cases, hydrochloric acid has been used up in the reaction and the total amount of hydrogen produced is the same. √
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 - 2019 KCSE STAREHE MOCK EXAMS (QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students