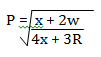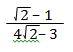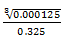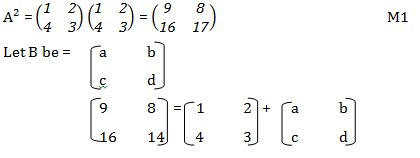SECTION I (50Mks)
Attempt ALL Questions from this section
- Make x the subject of the formula 3mks
- P varies partly as the square of v and partly as the cube of v. when V=2, P = -20 and when v = -3, P=135. Find the relationship between P and v. 3mks
- Expand (1 + 2x)7 up to x³, hence use the expansion to estimate the value of (1.02)7 correct to four decimal places. 3mks
- Simplify the following by rationalizing the denominator. 3mks
- The diagram below represents a field ABC.
- Draw the locus of points equidistant from sides AB and AC 2mks
- Draw the locus of points equidistant from points A and C. 2mks
- A coin is lost within a region which is nearer to point A than to point C and closer to side AC than to side AB. Shade the region where the coin can be located. 2mks
- Given x = 13.4cm and y=4.3cm. calculate the percentage error inx/y correct to 4 d.p3mks
- If matrix A=
Find B given that A² = (A +B). 3mks
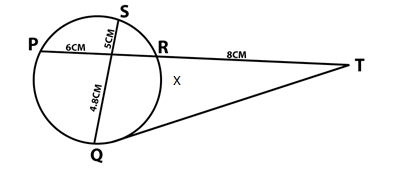
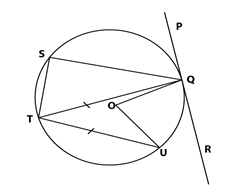
- In the figure below QT is a tangent to a circle at Q. PXRT and QXS are straight lines. PX = 6cm, RT = 8cm, QX= 4.8CM
Find the length of- XR 2mks
- QT 2mks
- A circle whose equation is (x -1)² + (y – k)² = 10 passed through point (2,5). Find the coordinates of the two possible centresof the circle. 3mks
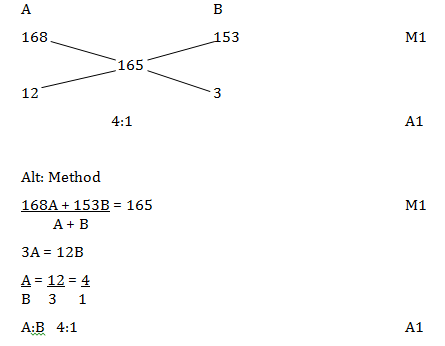
- A blender mixes two brands of juice A and B to obtain 70mls of the mixture worth Ksh. 165 per litre. If brand A is valued at Kshs. 168 per litre and brand B at Ksh. 153 per litre bottle, calculate the ration in which the brands A and B are mixed. (2mks)
- Without using logarithm tables solve the equation log(5x – 4) = log(x + 2) + 1/3 log 27. 3mks
-
- Use reciprocal tables to find the value of = 1 / 325 1mk
- Hence, evaluate 1mk
- The G.C.D of three numbers is 45 and the LCM is 18900. Two of the numbers are 675 and 540. Find the other possible numbers. 3mks
- solve for given that is acute and sin (3θ - 50⁰) – Cos (20 + 10⁰) = 0 3mks
- A container of height 90cm has a capacity of 4.5L. What is the height of a similar container of volume 9cm³. 3mks
- A point R divides a line PQ internally in the ration 3:4. Another point S, divides the line PR externally in the ratio 5:2. Given that PQ = 8cm, calculate the length of RS, correct to 2 decimal places. 3mks
SECTION II (50mrks)
Attempt any FIVE questions from this section
- Complete the table below for the function
- y=x² + 12/x – 15 for 0.5≤ x ≤4
X
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
y
9.25
-5
-4
- Draw the graph of y=x² + 12/x – 15 for 0.5≤x≤4. using a scale of 2cm rep 1 unit on the x – axis and 2cm for 5 units on the y – axis. 3mks
-
- from your graph, state the range of values of x for which y=x² + 12/x ≤ 18 3mks
- By adding a suitable straight line to your graph, solve the equation y = x² + 12/x – 5x + 20 3mks
- y=x² + 12/x – 15 for 0.5≤ x ≤4
- The product of the first three terms of a geometric progression is 64. If the first term is a and the common ratio is r.
-
- Express r in terms of a 3mks
- Given that the sum of the three terms is 14,
- Calculate the values of a and r and hence write down two possible sequences each up to the 4th 5mks
- Find the product of the 50th terms of the two sequences 2mks
-
-
A tax relief of Kshs. 1162 per month was allowed. In a certain month of the year, an employee’s taxable income in the fifth band was Ksh. 2108.Monthly income in Kenya Shillings (Kshs)
Tax rate in each shillings
0 – 10164
10%
10165 – 19740
15%
19740 – 29316
20%
29317 – 38892
25%
Over 38892
30%
- Calculate
- Employees total income in that month 2mks
- The tax payable by the employee in that month. 5mks
- The employee’s income includes a house allowance of Ksh. 15,000 per month. The employees contributed 5% basic salary to a cooperative. Calculate the employee net pay for that month. 3mks
- Calculate
- The following table shows the distribution of marks obtained by 50 students in a test.
By using an assumed mean of 62, calculateMarks
45-49
50-54
55-59
60-64
65-69
70-74
75-79
No. of Students
3
9
13
15
5
4
1
- The mean 5mks
- The variance 3mks
- The standard deviation 2mks
- A red and black dice are rolled and the events x, y and z are defined as follows.
X = the red die shows a 4
Y = the sum of the scores of the two dice is 6
Z = the black dice shows a 3- Which event is mutually exclusive to x 1mk
- The probability of events x and y 3mks
- Find the probability of event x 2mks
- Which event is independent of x 2mks
- The probability of event Y 2mks
- Complete the table below 2mks
-
Draw the graphs of y=sin(x-30) and y=-Cos x on the same axes, for 0⁰≤x≤360⁰ (5mks)X
0
30⁰
60⁰
90⁰
120⁰
150⁰
180⁰
210⁰
240⁰
270⁰
300⁰
330⁰
360⁰
- Cos x
-1
-0.5
0.5
0.87
0.87
-0.5
0.87
Sin(x-30⁰)
0.0
0.5
0.87
0.5
-0.5
-0.87
-0.5
- Use your graph to solve the equation sin(x - 30⁰) + Cos x = 0 (3mks)
- in the figure below, O is the centre of the circle, PQR is the tangent to the circle at Q, Angle PQS=28⁰, angle UTV = 54⁰ and UT = TQ
Giving reasons, determine the size of- Angle STR 2mks
- Angle TQU 2mks
- Reflex angle TQS 2mks
- Reflex angle UOQ 2mks
- Angle TQR 2mks
- The cost c of producing n items varies directly as n and partly as the inverse of n to produce two items it costs Ksh. 135 and to produce three items it costs Ksh. 140. Calculate
- The constant of proportionality and hence write the equation connecting c and n. 5mks
- The cost of producing 10 items 2mks
- The number of items produced at a cost of Ksh. 756. 3mks











MARKING SCHEME
- p² = x + 2w
4x + 3R M1
4p²x + 3p²R = x + 2w
4p²x – x = 2w – 3p²R
X(4p² - 1) = 2w – 3p²R M1
X = 2w – 3p²R²
4p² - 1 A1
- p = av² + bv³ : 4a + 8b = -20 M1
9a – 27b = 135
36a + 72b = -180
36a – 108b = 540
180b = -720 M1
B= -4
-20 = 4a +32
4a = -52
a = -13
p= -13V² + 4V³ A1
- (1+2x)7 = 1 + 7 (I)6(2x)1 + 21(1)5 + 35(1)4(2x)3 B1
= 1 + 14x + 84x² + 280x³ + _ _ _ _
(1.02)7 = (1 + 0.02)7 = (1 + 2x)
2 x = 0.02 —› x = 0.01
Subst x = 0.01
(1.02)7= 1 + 14(0.01) + 84(0.01)² + 280(0.01)³ M1
= 1 + 0.14 + 0.0084 + 0.00028
= 1.14868
= 1.1487 (to 4d.p) A1
- √2 – 1 x 4√2 + 3 = √2(4√2 + 3) – 1(4√2 + 3) M1
4√2 – 3 4√2 + 3 4√2(4√2 + 3) -3(4√2 + 3)
= 8 + 3√2 - 4√2 – 3
32 + 12√2 - 12√2 – 9 A1
= 5 - √2
23 A1
- Max val of x 13.45min 35 B1
Max val of Y 4.35 min 4.25
Max vals of x 13.45 = 3.164y
4.25
Min value of x13.35 = 3.069
Y 4.35
Actual value of x13.4 = 3.1163 B1
y 4.3
Absolute error = 3.1642 – 3.069 = 0.04785
2
Percentage error = 0.04785 x 100 = 1.5355% A1
3.1163
a + 1 = 9 a = 8
b + 2 = 8 b = 6 M1
c + 4 = 16 c = 12
d + 3 = 17 d = 14A1
-
- 6 x R = 4.8 x 5 M1
XR = 4.8 x 5
6
= 4 A1 - QT² = 18 x 8 = 144 M1
Qt = 12cm A1
- 6 x R = 4.8 x 5 M1
- (2-1)² + (5 – K)² = 10
1 – 25 – 10K + 1K² = 10
K² - 10K + 16 = 0
(K-2)(K – 8) = 0
K = 2 or 8
Centre (1,2) and (1,8)
- Log 5x – 4 = Log 3 M1
x + 2
5x – 4 = 3 M1
x + 2
5x – 4 = 3x + 6
2x = 10
x = 5 A1
-
- 1 x 10
3.25 = 0.3077 x 10 = 3.077 B1 - 0.05 x 3.077 M1
= 0.1539 A1
- 1 x 10
- Sin(30 - 50⁰) = Cos (20 + 10⁰)
30 – 50 + 20 + 10⁰ - 90⁰
50 - 40⁰ = 90⁰
50 = 130⁰
0 = 26⁰
- 5L = 4.5 x 10³cm³
9m³ = 9 x 10cm³
v.s.f 4.5 x 10³ : 90 x 106
1 : 2000
l.s.f 3√1 : 3√2000
1 : 12.6
90cm = x
h= 90 x 12.6
1134cm
PR: RQ = 3:4
PS : SR = 5: -2
PQ = 8CM
RS = 2/7 PQ
= 2/7 x 8
= 2.29cm
-
-
y = 2² + 12/x – 1515 ≤ x ≤ 2.75 B2X
1
1.5
3
3.5
4
Y
-2
-4.75
-2
0.6
4
y = x² + 12/x - 5x + 20 M1
y = -5x + 5
M1X
0
1
y
5
0
x = 2 or 0.8 A1
-
-
- 1st three terms are a, ar, ar² M1
Product a x ar x ar² = 64
a³r³ = 64 A1
r³ = 64/a³
r = 4/a
sum a + ar + ar² = 14
but R = 4/a
(a +a) 4/a) + a (4/a)2 = 14 M1
A + 4 + 16/q – 14
a² - 10a + 16 = 0
a² - 2a – 8a + 16 = 0 M2
a(a-2) – 8(a – 2) = 0 A1
a = 8 or a = 2
when a = 2, r = 2 when a = 8, r =½ B1
for a = 2 : Sequence 2, 4, 8, 16
For a = 8 : Sequence 8,4,2,1 A1
50thterm are ar49 and ar49 M1
2(2) 49 and 8(½) 49
Product 2(2)49 x 8(½)49 A1
= 16
- 1st three terms are a, ar, ar² M1
-
-
- Taxable income 38892 + 2108 – Shs. 41,000 M1A1
- 10164 x 10/100 = 1016.40
9576 x 15/100 = 1436.40 M1
9576 x 20/200 = 1915.21
9576 x 25/100 = 2394.00 M1
Rem 2108 x 30/100 = 632.40 M1
7394.40 M1
Less relief 1162.00
Kshs. 6232.40 A1
- Total deductions 41,000
15,000
Basic solar 26,000 M1
5/100 x 26000 = 1300 + payee
1300 + 6232.40 = 7532.40 M1
Net pay 41000 = 7532.40
Kshs 33,476.60 A1
-
- Let A = 62
Mean x = A + EfMarks
f
x
D=x-A
fd
d²
fd² 45-49
3
47
-15
-45
225
675
50-54
9
52
-10
-90
100
900
55-59
13
57
-5
-65
25
325
60-64
15
62
0
0
0
0
65-69
5
67
25
25
25
125
70-74
4
72
40
40
100
400
75-79
1
77
15
15
225
225
F = 50
Efd - 120
=2650
62 + -120 / 50 M1
= 62 – 2.4 = 59.6 A1- v = Efd² - Efd ² M1
Ef Ef
= 2560 - 120 ² = 53 – 5.76 M1A1
50 50 - s.d= Efd² - Efd
Ef Ef M1
47.24
= 6.873 A1
10
1/6 x1/6 = 1/36P = (x) = 1/6 M11 1 2 3 4 5
2 3 4 5 6
2
3
4
5
6
3 4 5 6 7
4 5 6 7 8
5 6 7 8 9
6 7 8 9 10
7 8 9 10 11
- P(x and z) = p(x) x p(2) M1A1
- Event Y B1
- Event Z B1
- P(Y) = 5/36 M1A
- <STQ = <PQS = 28⁰ B1
- v = Efd² - Efd ² M1
- Angles in alternative segment. A1
- <TQU = 180 – 54 = 63⁰ A1
2 - Base angles of an isosleles triangle B1
<TQS = 63 – 28 = 35⁰ M1
<TUQ is alternative to <PQT = 63 B1 - <UOQ = 54 x 2 = 108⁰
Angle subtended at the centre is twice that at the circumference by the same chord UQ B1
Reflex<UOQ = 360 - 108⁰ A1 - <TQR = <TSQ
= 180 – (28 + 35) = 117 B1 - Angles in alternative segment are equal A1
- <TQU = 180 – 54 = 63⁰ A1
-
- C = n + 1/n
C = kn + c/n M1
135 = 2k + c/2- (i)
140 = 3k + c/3- (ii) M1
270 = 4k + c - - (i)
420 = 9k + c + (ii)
-150 = -5k
K = 30
270 = (4x30) + C M1
270 = 120 + C
C = 150 A1 correct value K & C
.·.C = 30n + 150/11 A1 - C = (30 x 10) + 150/10 M1
= Shs. 315
756 = 30n + 150/n
756n = 30n² + 150 M1
30n²= 756n + 150 = 0
15n² - 378n + 75 = 0 ac = 1125 -375 and -3 M1
15n² - 375n – 3n + 75 = 0 b = 378
15n(n – 25) -3 (n – 25)
(15n – 3) (n – 25) = 0
N = 25 A1
- C = n + 1/n
Download MATHEMATICS PAPER 2 - KAPSABET BOYS 2019 TRIAL MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students