QUESTIONS
- You are provided with:
- Solution A: 0.10 M solution of a monobasic acid A;
- Solution B: Sodium hydroxide solution:
- Solution C: containing 10.0g of acid C per litre of solution.
You are required to: - Standardise solution B using solution A;
- Determine the number of moles of sodium hydroxide that react with one mole of acid C.
PROCEDURE I
Fill the burette with solution A. Using a pipette and pipette filler, place 25.0cm of solution B into 250 ml conical flask. Titrate solution B with solution A using phenolphthalein indicator and record your results in Table 1. Repeat the titration and complete Table 1.
- Table 1
(3 marks)I II III Final burette reading Initial burette reading Volume of solution A used, cm3 - Calculate the:
- average volume of solution A used. (1 mark)
- number of moles of solution A in the average volume used. (1 mark)
- number of moles of sodium hydroxide (N) in 25.0cm of solution B. (1 mark)
- concentration of sodium hydroxide in moles per litre. (1 mark)
PROCEDURE II
Clean the burette and fill it with solution C. Using a pipette and pipette filler, place 25.0cm of solution B into a 250 ml conical flask.
Titrate solution B with solution C using phenolphthalein indicator and record your results in Table 2. Repeat the titration and complete Table 2.
- Table 2
(3 marks)I II III Final burette reading Initial burette reading Volume of solution A used, cm3 - Calculate the:
- average volume of solution Cused. (1 mark)
- concentration in moles per litre, of solution C, given that the relative formula mass of acid C is 210.0. (1 mark)
- number of moles of acid C in the average volume used. (1 mark)
-
- Write the ratio of moles of acid Cto moles of sodium hydroxide (N) in the 25.0cm of solution B. (1 mark)
- Determine the number of moles of sodium hydroxide that react with one mole of acid C. (1 mark)
- You are provided with solid D.
You are required to determine the freezing point of solid D.
PROCEDURE- Fill a 250 ml beaker with about 200 cm3 of tap water and heat the water until it boils.
- Place all solid D provided in a dry test tube and insert a thermometer into the solid.
- Place the test tube in the boiling water and allow the solid to heat until it all melts.
- When the temperature of the melted solid is approximately 90°C, remove the test tube, wipe the sides with tissue paper and then place the test tube into an empty 250 ml beaker
- Start the stop watch or clock when the temperature of the melted solid is 85.0°C.
- As the solid cools, measure and record its temperature every 30 seconds and complete Table 3.
- Table 3
(4 marks)Time, s 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 Temperature, °C - On the grid provided, plot a graph of temperature (vertical axis) against time. (3 marks)
- Using the graph in (b), determine the freezing point of solid D. (1 mark)
- Table 3
- You are provided with solid E. Carry out the following tests and record your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Place all the solid E in a boiling tube. Add about 10 cm of dilute nitric(V) acid, warm the mixture and then allow to stand until all the solid dissolves. Add about 10 cm of distilled water to the solution and shake. Retain the solution for tests (b) and (c)
Observations Inferences (2 marks) (1 mark) - Use about 2 cm3 portions of the solution obtained in 3(a) for each of the following tests.
- To the first portion add 2 or 3 drops of aqueous barium nitrate,
Observations Inferences (1 marks) (1 mark) - To the second portion add 2 or 3 drops of aqueous lead(II) nitrate.
Observations Inferences (1 marks) (1 mark) - To the third portion add aqueous sodium hydroxide dropwise until in excess.
Observations Inferences (1 marks) (1 mark) - Place about 3 cm of aqueous ammonia in a test tube. To the fourth portion, add all the aqueous ammonia from the test tube dropwise.
Observations Inferences (1 marks) (1 mark)
- To the first portion add 2 or 3 drops of aqueous barium nitrate,
- To the remaining solution of solid in the boiling tube, add all the solid providedn
Shake the mixture for about 2 minutes. Filter the mixture into a boiling tube. Retain the filtrate for tests (i) and (ii) below.
Observations Inferences (1 marks) (1 mark) - To about 2 cm portion of the filtrate, add aqueous ammonia dropwise until in excess
Observations Inferences (1 marks) (1 mark) - To about 2 cm portion of the filtrate add 2 or 3 drops of dilute hydrogen peroxide solution.
Observations Inferences (1 marks) (1 mark)
- To about 2 cm portion of the filtrate, add aqueous ammonia dropwise until in excess
- Place all the solid E in a boiling tube. Add about 10 cm of dilute nitric(V) acid, warm the mixture and then allow to stand until all the solid dissolves. Add about 10 cm of distilled water to the solution and shake. Retain the solution for tests (b) and (c)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
24.0 CT 1 I II III D1 Final burette reading A1 Initial burette reading PA1 Volume of solution A used, cm3 FA1 -
- Correct working
correct ans (b)(i) - =correct ans (b)(i) x 0.1 = correct ans (b)(ii)
1000 - Ratio A:N b1:1
ans (b) (iii) - =1000 x ans (b)(iii) = ans (b)(iv)
25
- Correct working
-
PROCEDURE II
- Table 2
16.5 CT1 I II III D1 Final burette reading A1 Initial burette reading PA1 Volume of solution A used, cm3 FA1 -
- Correct working
correct ans (d)(i) - = 10/210 = 0.0476
- =correct ans (d)(i) x 0.0476 = correct ans (d)(iii)
1000
- Correct working
-
- ans (d)(iii) : ans(b)(iii)
- =ans(b)(iii) = ans (e)(ii)
ans(d)(iii)
- Table 3
-
Time, s 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 Temperature, °C 85.0 82.0 80.5 78.0 75.5 72.0 69.0 69.0 69.0 67.5 65.0 -
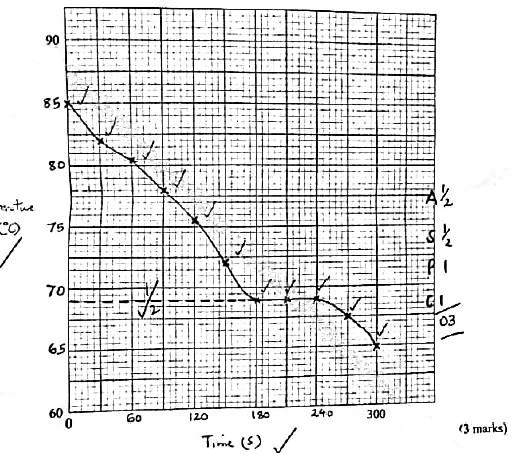
- showing
correct reading
-
-
-
Observations Inferences No effervescence
E dissolves to form a blue solution
(1 marks)CO32-/ SO32- absent
Cu2+ present
(1 mark) -
-
Observations Inferences No white ppt formed SO42- absent -
Observations Inferences No yellow ppt formed
No white ppt formedI- absent
Cl-/Br- absent -
Observations Inferences Blue ppt formed insoluble in excess Cu2+ present -
Observations Inferences Blue ppt formed that dissolves in excess to form a deep blue solution Cu2+ present
-
-
Observations Inferences Blue solution changes to green
Brown residue
Green filtrate
Boiling tube becomes warmCu2+ displaced by G/G is more reactive than Cu/G is oxidized by Cu2+ /Cu2+ are reduced by G/ Cu2+ are displaced by Fe -
Observations Inferences Green ppt formed insoluble in excess Fe2+ -
Observations Inferences Green solution changes to brown/Yellow
EffervescenceFe2+ oxidized to Fe3+
Fe3+ formed
-
-
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers - KCSE 2021 Past Papers.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
