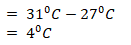INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
- This paper has two sections A and B.
- Answer ALL the questions in section A. In section B answer questions 6 and any other TWO questions.
SECTION A: 25 MARKS
Answer ALL questions in this section
- Describe the formation of planet earth according to the passing star theory. (5 marks)
-
- Give two examples of sedimentary rocks. (2 marks)
- State three characteristics of sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
-
- Differentiate between weathering and mass wasting. (2 marks)
- State three causes of landslides. (3 marks)
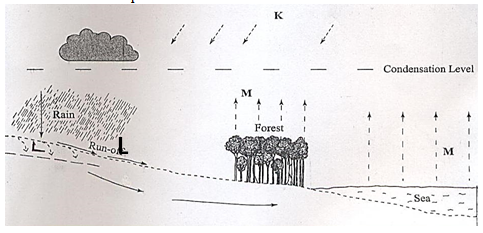
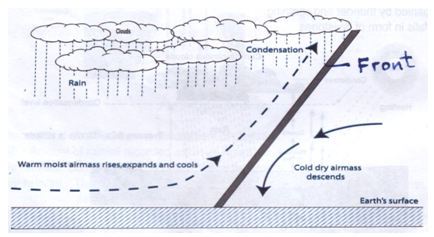
- The diagram below shows the hydrological cycle. Study and use it to answer the question that follows.
- Identify the processes marked K and L. (2 marks)
- State three characteristics of a flood plain. (3 marks)
-
- State two reasons why wind erosion is dominant in arid areas. (2 marks)
- Describe how a Bajada is formed. (3 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
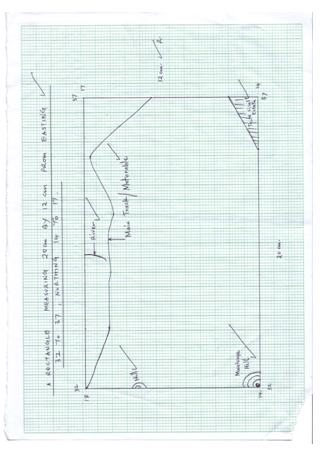
- Study the map of Taita hills, 1:50,000 sheetprovided and answer the question that follow.
-
- What is the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of Taita Hills map extract? (2marks)
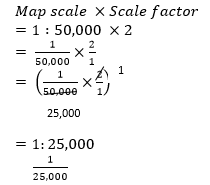
- Convert the ratio scale of the map into statement. (2marks)
- Citing evidence from the map, identify four social activities in the area covered by Taita Hills. (4 marks)
-
- Draw a rectangle 20cm by 16cm from Easting 32 to 37 Northings 14 to 18. (2 marks)
- On the rectangle mark and name; (4 marks)
- Taita sisal estate
- Hills
- Main track/motorable
- River
- Calculate the new scale of the drawn rectangle. (2 marks)
- Citing evidence, explain three ways how relief has influenced the distribution of settlement in Taita Hills. (6 marks)
- Describe the vegetation in the area covered by the map. (3 marks)
-
-
- Name two instruments kept in a Stevenson screen. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a weather measuring instrument. Use it to answer the questions below.
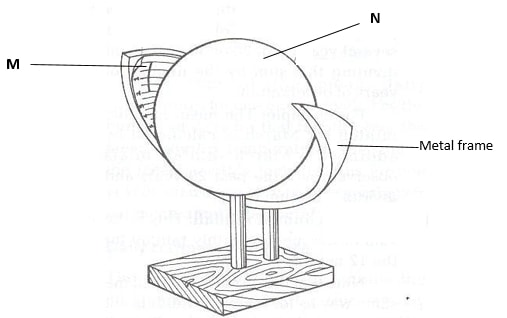
- Name the parts marked M and N. (2 marks)
- Describe how the instrument works. (4 marks)
- The table below shows climatic figure for station Q. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
Months
J
F
M
A
M
J
J
A
S
O
N
D
Temp in 0C
30
31
31
29
27
27
28
29
28
28
27
30
Rainfall in mm
257
246
231
234
207
201
218
227
234
240
235
230
- Calculate the annual range of temperature for station Q. (2 marks)
- Give four characteristics of climate for station Q. (4 marks)
- With the aid of a well-labelled diagram, describe the formation of cyclonic rainfall. (6 marks)
- You intend to carry out a field study of a weather station in your school.
- Give two methods of recording data that you are likely to use. (2marks)
- State three reasons why the recording of data at a school weather station may be inaccurate. (3 marks)
-
- Distinguish between a fault and a fold. (2 marks)
- Give three factors that influence folding. (3 marks)
- Describe how isostatic adjustment cause earth movement. (5 marks)
- Describe how plate tectonic movements cause fold mountain formation. (5 marks)
-
- Name two features resulting from faulting. (2 marks)
- Explain how faulting influences drainage of an area. (8 marks)
-
- Distinguish between soil profile and soil catena. (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence soil formation:
- The parent rock (4 marks)
- Relief (2 marks)
- Describe laterization process of leaching. (4 marks)
- State three importance of soil structure. (3 marks)
- Give two characteristics of Azonal soils. (2 marks)
- Explain four causes of physical soil degeneration. (8 marks)
- Define the term Moraine. (2 marks)
- State three conditions necessary for the formation of ice. (3marks)
- Describe how ice moves through the following:-
- Basalslip (3 marks)
- Extrusion flow (3 marks)
- Describe how an arete is formed. (6 marks)
- Explain the four Significance of lowland glaciated features to human activities. (8 marks)
- Define the term Moraine. (2 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
- Describe the formation of planet earth according to passing star theory. (5 marks)
- A star with greater gravitational force passed near the sun.
- The star pulled large volume of gaseous materials from the sun.
- The materials exploded and split into portions which cooled and condensed to form planets.
- The gravitational force of the sun set planets on their orbits.
- The smaller gaseous materials formed smaller heavenly bodies such as planetoids natural satellites and comets, all of which revolves around the sun.
- Planet earth is one of those planets that were formed in this process.
-
- Give two examples of sedimentary rocks. (2 marks)
- Sandstone
- Claystone
- Mudstone
- Shale
- Breccia
- Grit
- Siltstone
- Loess
- Conglomerate
- Boulder clay
(Consider other correct responses)
- State three characteristics of sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
- They are formed from sediments of pre-existing rocks.
- They are stratified.
- Some have plant and animal remains.
- They are non-crystalline.
- They have bedding planes.
- Give two examples of sedimentary rocks. (2 marks)
-
- Differentiate between weathering and mass wasting. (2 marks)
- Weathering is the breakdown/disintegration/decomposition of rocks at or near surface of the earth in situ by physical/chemical processes while mass wasting is displacement/movement of weathered materials down a slope under the influence of gravity.
- State three causes of landslides. (3 marks)
- The gradient of the slope.
- Nature of the materials on the slope.
- The amount of precipitation.
- Occurrence of earth movements such as earthquakes.
- Rise in temperature in glaciated highlands.
- Clearing of vegetation cover on the steep
- Human activities on steep slopes such as mining and construction.
- Differentiate between weathering and mass wasting. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows the hydrological cycle. Study and use it to answer the question that follows.
- Identify the processes marked Kand L. (2 marks)
- K-Solar insolation/Radiation
- L-Infiltration
- State three characteristics of a flood plain. (3 marks)
- It has a gently sloping gradient.
- It is made up of thick alluvial deposit.
- It has natural levees.
- It has marshes.
- It has braided channels.
- It has differed tributaries.
- It has river bluffs at the edge of the valley.
- It has pronounced meanders and ox-bow lakes.
- Identify the processes marked Kand L. (2 marks)
-
- State two reasons why wind erosion is dominant in arid areas. (2 marks)
- Presence of scanty or no vegetation cover which exposes the land to wind erosion.
- Presence of strong winds which erode the bare surfaces.
- Presence of loose unconsolidated materials which are easy to erode.
- Describe how a Bajada is formed. (3 marks)
- During heavy rains, temporary rivers move through dry valley from uplands into lowlands.
- The rivers carry fine rock materials which are deposited where the dry valley enter a lowland.
- As water reduces speed, the deposited materials form a cone-shaped depositional feature known as alluvial fan.
- Due to more deposition, adjacent alluvial cones may join.
- This leads to formation of a gentle sloping depositional surface called a bajada.
- State two reasons why wind erosion is dominant in arid areas. (2 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
- Study the map of Taita hills, 1:50,000 sheetprovided and answer the question that follow.
-
- What is the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of Taita Hills map extract? (2marks)
- Latitudinal extent is from 3014' South t 3030'
- Longitudinal extent is from 38016' East to 38030'
- Convert the ratio scale of the map into statement. (2marks)
Ratio scale 1: 50,000
1 km = 100,000cm
50000 = 0.5 km or ½
100000
Statement scale ⇒ 1 cm represents 0.5km/½ km
1cm represents ½ km
- What is the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of Taita Hills map extract? (2marks)
- Citing evidence from the map, identify four social activities in the area covered by Taita Hills. (4 marks)
Social activity Evidence
- Administration/security - Wundanyi DC’s office
- Chiefs office (2923) - Religious services - Church (2824)
- Mosque (2818) - Education - Schools
- Youth polytechnics (2025) - Health services/Medical services - Health centre (2718)
- Dispensary (2313) - Correctional services - Presence of a prison (2922)
- Water supply services - Water supply (2919)
-Water pipe line/Reservoir
-Pump house (2918)
- Administration/security - Wundanyi DC’s office
-
- Draw a rectangle 20cm by 16cm from Easting 32 to 37 Northings 14 to 18. (2 marks)
- On the rectangle mark and name;
- Taita sisal estate
- Hills
- Main track/motorable
- River
- Calculate the new scale of the drawn rectangle. (2 marks)
- Draw a rectangle 20cm by 16cm from Easting 32 to 37 Northings 14 to 18. (2 marks)
- Citing evidence, explain three ways how relief has influenced the distribution of settlement in Taita Hills. (6 marks)
- Rugged slopes/steep slopes evidenced by closely by closely packed contours in the western part have dense/Many settlement because the area is well drained.
- Gentle slopes evidenced by widely spaced contours in the eastern part have few settlement since the area is poorly drained/dry.
- River valleys along the rivers have few settlement since the areas are prone to flooding.
- Describe the vegetation in the area covered by the map. (3 marks)
- Forests are found in the western part of the map.
- Thicket vegetation found to the East of the area covered by the map.
- Scrub vegetation is found to the West of the map.
- Some scattered trees are found to the North of hemap.
- Some woodland vegetation is found to the South East of the area covered by the map.
-
-
- Name two instruments kept in a Stevenson screen. (2 marks)
- Hygrometer
- Maximum thermometer
- Minimum thermometer
- The six’s thermometer
- The diagram below shows a weather measuring instrument. Use it to answer the questions below.
- Name the parts marked M and N. (2 marks)
M - Sensitized card
N - Cylindrical glass lens - Describe how the instrument works. (4 marks)
- The glass sphere focusses the sun’s rays on a sensitized card which is graduated in hours and minutes.
- The heat burns the paper/card as the sun moves across the sky.
- The unburnt sections in the card indicates when there was cloud cover.
- At the end of the day, the card is removed and the number of hours that the sun shined are obtained by adding the burnt sections on the card.
- Name the parts marked M and N. (2 marks)
- The table below shows climatic figure for station Q. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Calculate the annual range of temperature for station Q. (2 marks)
- Outline four characteristics of climate in station Q. (4 marks)
- The station experiences high temperatures.
- Highest temperature is 310C/the lowest temperature is 270C.
- The annual range of temperature is 40C/the station has a low range of temperature.
- The station experiences high rainfall/2760mm.
- The station experiences rainfall throughout the year/there is no dry month.
- Lowest rainfall is experienced in May and July when temperature is also lowest.
- The station has one rainfall maxima.
- Calculate the annual range of temperature for station Q. (2 marks)
- With the aid of a well-labelled diagram, describe the formation of cyclonic rainfall. (6 marks)
- It occurs along the temperature front.
- It is the meeting point of cold, heavy dry polar easterlies and warm, light and moist north/south westerlies.
- The meeting of the air masses forms a front.
- When the two air masses meet along the front, the warm lighter westerly, winds rises over the cold polar air.
- Since it is moist, the air condenses forming clouds.
- The clouds become heavy enough, eventually falling as rain through the cold air.
- This is cyclonic/frontal rainfall.
- You intend to carry out a field study of a weather station in your school.
- Give two methods of recording data that you are likely to use. (2marks)
- Filling in questionnaires
- Labelling of samples
- Note taking
- Taking photographs
- Sketching diagrams
- Tabulation
- State three reasons why the recording of data at a school weather station may be inaccurate. (3 marks)
- Human error.
- Interference with the instruments by animals and people.
- Poor siting of a weather station.
- Extreme weather conditions.
- Natural calamities i.e. landslides.
- Use of defective instruments.
- Give two methods of recording data that you are likely to use. (2marks)
- Name two instruments kept in a Stevenson screen. (2 marks)
-
-
- Distinguish between a fault and a fold. (2 marks)
- A fault is a fracture or crack in the earth’s crust along which displacement of rocks has occurred while a fold is a download or an upward bend in the crustal rocks caused by tectonic forces.
- Give three factors that influence folding. (3 marks)
- Intensity/strength of compression forces.
- Nature/Elasticity of the crustal rocks.
- Type of earth movement.
- Amount of temperature within the rocks.
- Distinguish between a fault and a fold. (2 marks)
- Describe how isostatic adjustment cause earth movement. (5 marks)
- A reduction in weight occurs on the continental sial rock mass through erosion in melting of ice on the continents.
- The eroded material are deposited on the oceanic sima crusts.
- The sediments adds extra weight on the oceanic floor.
- The ocean flow undergoes isostatic sinking while the continental sial crust undergoes isostatic uplifting.
- The isostatic sinking and uplifting causes earth movements.
- Describe how plate tectonic movement cause fold mountain formation. (5 marks)
- The earth curst is made up of blocks called plates or tectonic plates.
- The plates float on the molten mantle.
- The plates move away from each other causing magma to fill the spaces between them.
- Some plates may move towards each destroying the materials between them; while others may move past each other restoring the material between them.
- When the plates melt there is subduction where sediments on the sea floor are compressed to form Fold Mountains.
- When the continental plates meet they are also compressed into Fold Mountain.
-
- Name two features resulting from faulting. (2 marks)
- Fault scarps/Escarpments
- Fault steps
- Fault blocks/block mountains/horst mountains
- Rift valleys/Graben
- Tilt blocks
- Explain how faulting influences drainage of an area. (8 marks)
- Faulting causes depressions which may be filled with water to form rift valley lakes.
- Faulting causes fault-guided drainage pattern.
- Faulting causes oozing of water to form springs.
- Faulting causes cracks/fault lines which may cause rivers to disappear underground.
- Faulting may cause rivers to change their direction of flow/reversed drainage.
- Vertical faulting across a river may cause a waterfall.
- Name two features resulting from faulting. (2 marks)
-
-
- Distinguish between soil profile and soil catena. (2 marks)
- Soil profile refers to the vertical arrangement of soil in layers from the surface to the bedrock while solid catena refers to the regular horizontal arrangement of soil particles on the hill slope from top to the bottom.
- Explain how the following factors influence soil formation:
- The parent rock (4 marks)
- It determines the time taken and the type of soil formed.
- It influences the rate of weathering. Hard rocks weathers slowly while soft rocks weather faster to form soils.
- It determines the soil texture. Coarse grained rocks produce coarse gained soils while fine grained rocks produce fine grained soils.
- It determines the soil mineral composition. Minerals in the parent rock determines the mineral composition of the soil.
- Rock texture determines soil structure which in turn determine the soil water holding capacity and permeability.
- Relief (2 marks)
- The general appearance and nature of landscape determine the rate of weathering.
- It influences the drainage, surface run off, erosion and aspect.
- Steep slopes have weathering but more erosion thus forming thin immature soils.
- Gentle slopes have moderate weathering forming deep-well developed and mature soils with a clear profile.
- Valley bottom have deep soil due to deposition of weathered materials.
- Flat areas may be waterlogged which slows down soil formation to form peat soils due to poor drainage.
- Aspects – slopes facing the sun has more weathering to form soils due to more heating.
- The slope gradient influence the arrangement of soils popularly known as soil profile.
- The parent rock (4 marks)
- Describe laterization process of leaching. (4 marks)
- Takes place in areas with warm humid climate with a wet and dry season.
- During the wet season, the base minerals on top layer dissolve in rain water and percolates in solution form from top soil to sub soil.
- The dissolved minerals precipitates and get deposited in horizon B.
- Insoluble minerals precipitates and get deposited in horizon B.
- This makes the top soil to harden and from a reddish-brown soil with a hard crust known as laterite/latosols or marram.
- State three importance of soil structure. (3 marks)
- It determines the soil water holding capacity.
- It determines the soil aeration.
- It determines the types of soil.
- It determines physical generation of soil.
- Give two characteristics of Azonal soils. (2 marks)
- They are immature and skeletal soils without a well-developed profile.
- Has horizon A and C but no horizon B.
- They are young soils and have not undergone full soil formation process.
- Have not had enough time to develop.
- They are found on steep slopes and therefore thin soils.
- Some form on valley bottoms with alluvial deposits.
- Explain four causes of physical soil degeneration. (8 marks)
- Overgrazing which leads to removal of vegetation cover exposing soil to agents to erosion which removes the top fertile soil.
- Continuous irrigation which causes leaching of soil nutrients making the top soil deficient of soluble minerals or leading to accumulation of dissolved minerals salts which makes the soils saline.
- Frequent ploughing which:
- Weakens the soil structure and makes it easy for the agents of soil erosion to carry away the fertile top soil.
- Leads to increased oxidation which results in loss of organic matter.
- Compacts the soil which reduce porosity thus making the soil poor.
- Increases water percolation and leaching of minerals making the soil poor.
- Ploughing up and down the slopes which creates channels for surface run-off which takes away some nutrients.
- Over-use of agro-chemicals which leads to change in soil pH thus making the soils poor.
- Monoculture/over cropping which exhausts the mineral nutrients in the soils thus making the soil to lose fertility.
- Burning the crop remains/burning the bush to clear land which destroys the organic matter and micro-organisms thus making the soil to lose fertility.
- Shifting cultivation: Which makes the abandoned land open to erosion and loss of fertility.
- Distinguish between soil profile and soil catena. (2 marks)
-
-
- Define the term Moraines. (2 marks)
- Rock materials/fragments carried by a moving glacier.
- State three conditions necessary for the formation of ice. (3 marks)
- Nature of underlying rocks.
- The speed of the glacier.
- Thickness and weight of the ice.
- Availability of debris.
- Define the term Moraines. (2 marks)
- Describe how ice moves through the following:-
- Basal slip (3 marks)
- Weight of the ice makes ice layers beneath to melt slightly.
- This creates water which acts as lubricant between the ice and the rock surfaces.
- The force of gravity then causes the ice to slip and slide over the underlying rocks.
- Extrusion flow (3 marks)
- Ice accumulates in lowlands with very low gradient
- Ice moving from upslope accumulates in lowland and builds to great thickness at the centre
- This results in great pressure build up at the centre
- The resultant weight compresses the layers of ice beneath
- This causes the ice to spread outwards to where there is low pressure thus resulting in extrusion flow
- Basal slip (3 marks)
- Describe how an arete is formed. (6 marks)
- Snow accumulates on two adjacent shallow pre-existing depressions on the mountain.
- Snow accumulates in the two adjacent shallow depressions and are compacted into ice.
- Freeze – thaw action occurs in the depression.
- This deepens the depression and more ice occupy them to form large cirque glacier.
- The ice moves downslope and erode the depression by plucking and abrasion to form adjacent cirques.
- Further plucking and abrasion enlarge and deepen the cirques.
- Plucking of the walls leads to back walls leads to recession of the cirque.
- Eventually a very steep knife-edged ridge separating the cirques forms called an arete.
- Explain four significances of lowland glaciated features to human activities. (8 marks)
- Out wash plains, boulder plains comprises of sand and gravel which are used as materials for building and construction are sometimes fertile hence promoting crop farming.
- Some glacial lakes are natural waterways promoting transportation.
- Erratic, kames, drumlins form beautiful scenery promoting tourism.
- Glacial tillprovide fertile soils for arable farming
- Ice sheets in there scouring effects reduce lands surface and depth to expose mineral seams which become easy to mine
-
Download GEOGRAPHY PAPER 1 - 2019 MOKASA II MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students