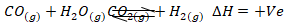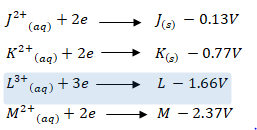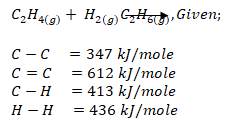INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name, admission number, date and school in the spaces provided.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Scientific calculators may be used.
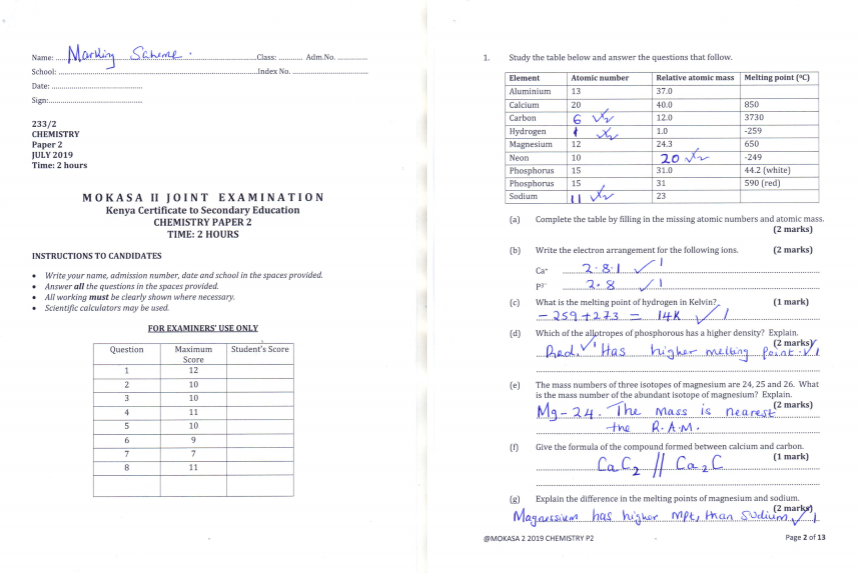
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Element
Atomic number
Relative atomic mass
Melting point (0C)
Aluminium
13
37.0
Calcium
20
40.0
850
Carbon
12.0
3730
Hydrogen
1.0
-259
Magnesium
12
24.3
650
Neon
10
-249
Phosphorus
15
31.0
44.2 (white)
Phosphorus
15
31
590 (red)
Sodium
23
- Complete the table by filling in the missing atomic numbers and atomic mass. (2 marks)
- Write the electron arrangement for the following ions. (2 marks)
Ca+ ………………………………………………………………………………………………………
P3- ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… - What is the melting point of hydrogen in Kelvin? (1 mark)
- Which of the allotropes of phosphorous has a higher density? Explain. (2 marks)
- The mass numbers of three isotopes of magnesium are 24, 25 and 26. What is the mass number of the abundant isotope of magnesium? Explain. (2 marks)
- Give the formula of the compound formed between calcium and carbon.(1 mark)
- Explain the difference in the melting points of magnesium and sodium. (2 marks)
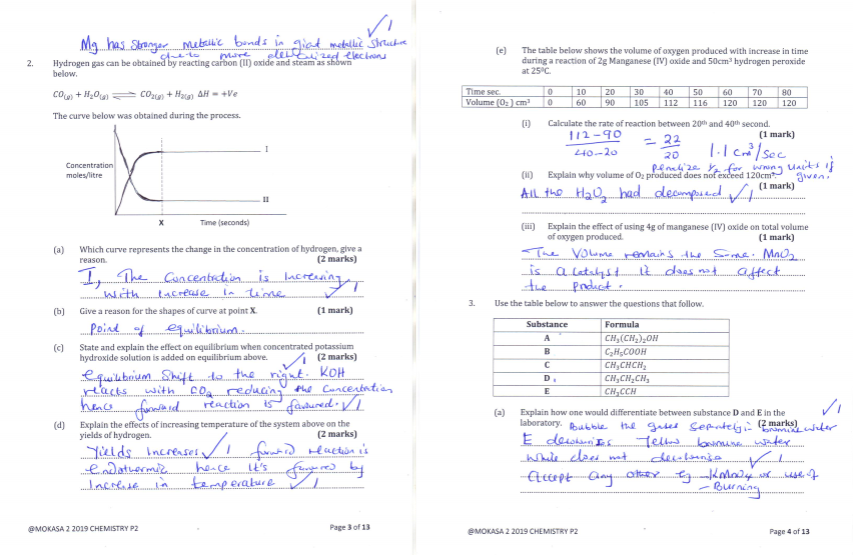
- Hydrogen gas can be obtained by reacting carbon (II) oxide and steam as shown below.
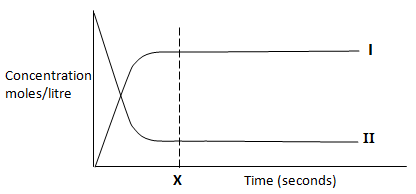
The curve below was obtained during the process.- Which curve represents the change in the concentration of hydrogen, give a reason. (2 marks)
- Give a reason for the shapes of curve at point X. (1 mark)
- State and explain the effect on equilibrium when concentrated potassium hydroxide solution is added on equilibrium above. (2 marks)
- Explain the effects of increasing temperature of the system above on the yields of hydrogen. (2 marks)
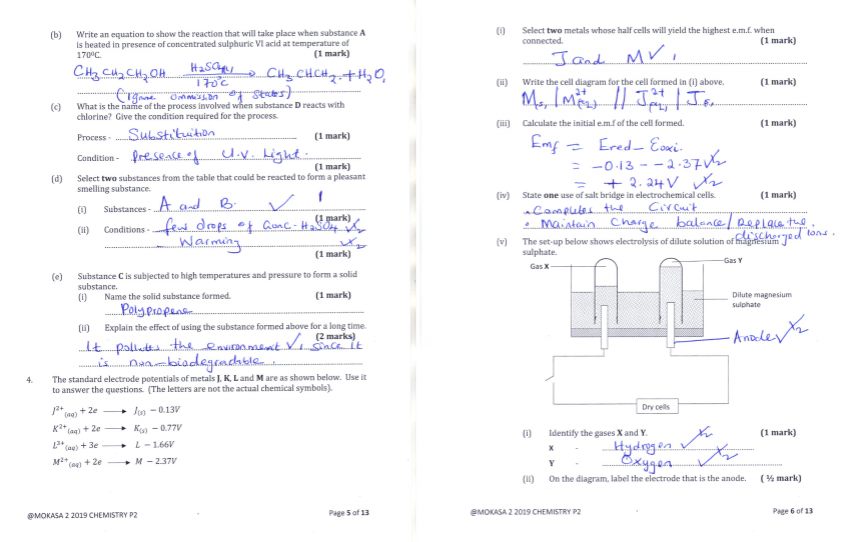
- The table below shows the volume of oxygen produced with increase in time during a reaction of 2g Manganese (IV) oxide and 50cm3 hydrogen peroxide at 250
- Calculate the rate of reaction between 20th and 40th (1 mark)
- Explain why volume of O2 produced does not exceed 120cm3. (1 mark)
- Explain the effect of using 4g of manganese (IV) oxide on total volume of oxygen produced. (1 mark)
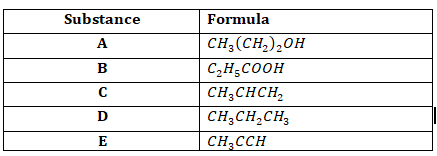
- Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
- Explain how one would differentiate between substance D and E in the laboratory. (2 marks)
- Write an equation to show the reaction that will take place when substance A is heated in presence of concentrated sulphuric VI acid at temperature of 1700C. (1 mark)
- What is the name of the process involved when substance D reacts with chlorine? Give the condition required for the process.
Process - ……………………………………………………………………….. (1 mark)
Condition - …………………………………………………………………………………………… (1 mark) - Select two substances from the table that could be reacted to form a pleasant smelling substance.
- Substances - ……………………………………………………………………………………. (1 mark)
- Conditions - …………………………………………………………………………………….. (1 mark)
- Substance C is subjected to high temperatures and pressure to form a solid substance.
- Name the solid substance formed. (1 mark)
- Explain the effect of using the substance formed above for a long time. (2 marks)
- The standard electrode potentials of metals J, K, L and M are as shown below. Use it to answer the questions. (The letters are not the actual chemical symbols).
- Select two metals whose half cells will yield the highest e.m.f. when connected. (1 mark)
- Write the cell diagram for the cell formed in (i) above. (1 mark)
- Calculate the initial e.m.f of the cell formed. (1 mark)
- State one use of salt bridge in electrochemical cells. (1 mark)
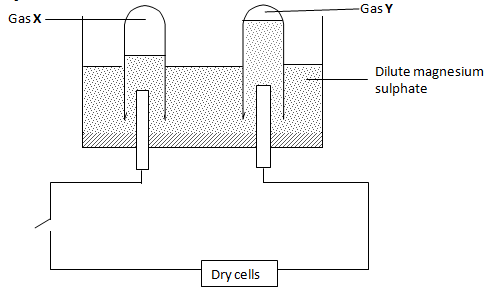
- The set-up below shows electrolysis of dilute solution of magnesium sulphate.
- Identify the gases X and Y. (1 mark)
X - ……………………………………………………………………….
Y - ………………………………………………………………………. - On the diagram, label the electrode that is the anode. ( ½ mark)
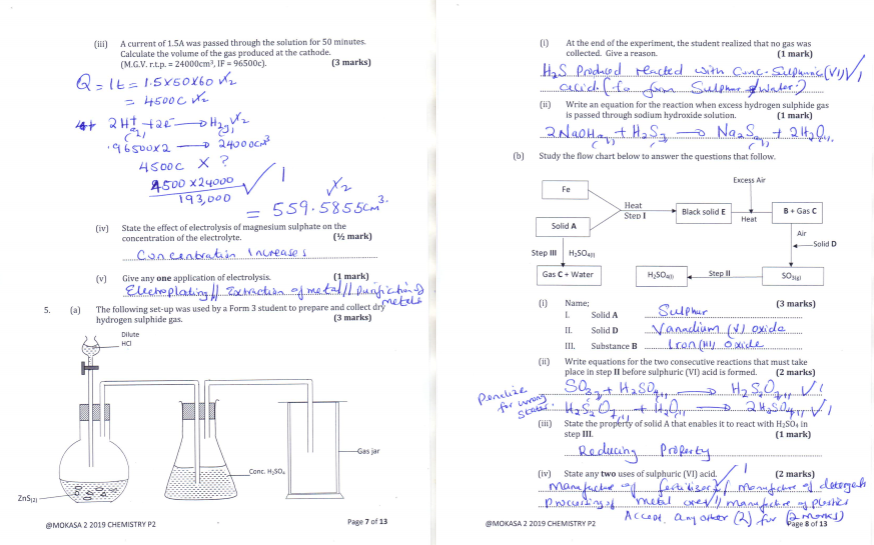
A current of 1.5A was passed through the solution for 50 minutes. Calculate the volume of the gas produced at the cathode.
(M.G.V. r.t.p. = 24000cm3, IF = 96500c). (3 marks) - State the effect of electrolysis of magnesium sulphate on the concentration of the electrolyte. (½ mark)
- Give any one application of electrolysis. (1 mark)
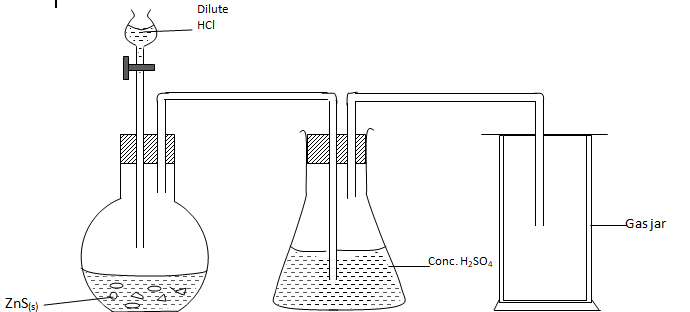
- The following set-up was used by a Form 3 student to prepare and collect dry hydrogen sulphide gas. (3 marks)
- At the end of the experiment, the student realized that no gas was collected. Give a reason. (1 mark
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Write an equation for the reaction when excess hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through sodium hydroxide solution. (1 mark
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- At the end of the experiment, the student realized that no gas was collected. Give a reason. (1 mark
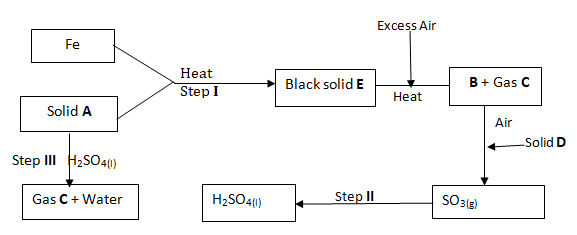
- Study the flow chart below to answer the questions that follow.
Name; (3 marks)
Solid A ………………………………………………………………
Solid D ………………………………………………………………
Substance B ……………………………………………………………… - Write equations for the two consecutive reactions that must take place in step IIbefore sulphuric (VI) acid is formed. (2 marks
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - State the property of solid A that enables it to react with H2SO4 in step III. (1 mark)………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- State any two uses of sulphuric (VI) acid. (2 marks)……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Study the flow chart below to answer the questions that follow.
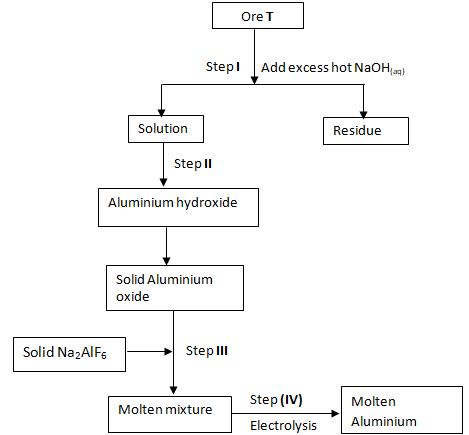
- Study the flow chart below and answer questions that follow.
- Name ore T. (1 mark)………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- Explain why the ore is dissolved in excess NaOH(aq). (1 mark)
- Name compound present in:- (1 mark)
- Solution ……………………………………………………………………………….
- Residue ……………………………………………………………………………….
- Name the process that takes place in step II. (½ mark)
- Why are sodium and fluoride ions not discharged in step IV? (½ mark)
- Write the equation for reaction in step IV. (1 mark)
- Why should the anode be replaced from time to time? (1 mark)
- State any two uses of aluminium. (1 mark)
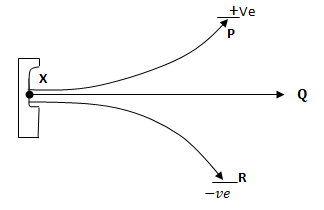
- The figure below shows the behavior of emissions by radioactive isotope X. Use it to answer questions that follow.
- Explain why isotope X emits radiation. (½ mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. - Name radiations P, Q and R. (1 ½ marks)
- Explain why isotope X emits radiation. (½ mark)
- State Hess’s law. (1 mark)
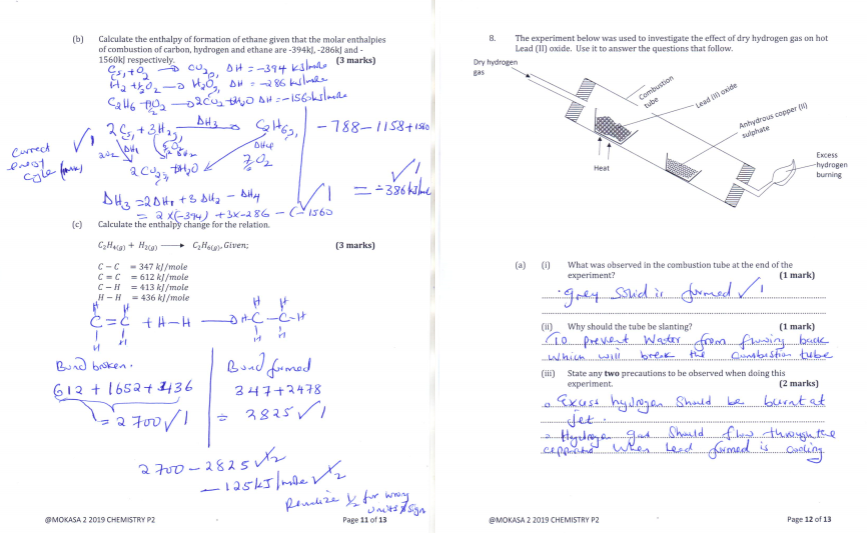
- Calculate the enthalpy of formation of ethane given that the molar enthalpies of combustion of carbon, hydrogen and ethane are -394kJ, -286kJ and -1560kJ respectively. (3 marks)
- Calculate the enthalpy change for the relation. (3 marks)
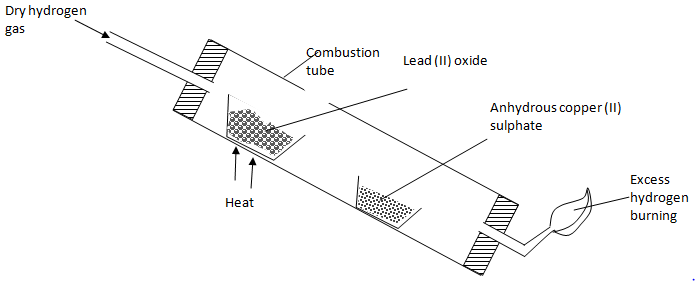
- The experiment below was used to investigate the effect of dry hydrogen gas on hot Lead (II) oxide. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- What was observed in the combustion tube at the end of the experiment? (1 mark)
- Why should the tube be slanting? (1 mark)
- State any two precautions to be observed when doing this experiment. (2 marks)
- If 2.07g of lead (II) oxide was reduced by certain amount of hydrogen gas during experiment. Calculate the mass of hydrogen gas that reduced 2.07g of lead (II) oxide. (Pb = 207, O = 32, H = 1) (3 marks)
- Calculate the mass of the residue in the combustion tube. (2 marks)
- Calculate the volume of hydrogen gas used at r.t.p. (MGV = 24L). (2 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 - 2019 MOKASA II MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students