SECTION A: 25 MARKS
Answer ALL questions in this section
-
- What is the relationship between Geography and Demography? (2 marks)
- State three reasons why it is important to study Geography. (3 marks)
- Describe the deep shaft method of mining. (5 marks)
-
- Apart from draining swamps, name two other methods of land reclamation in Kenya. (2 marks)
- State three aims of setting up the Perkerra irrigation scheme. (3 marks)
-
- Give two problems facing river transport in African. (2 marks)
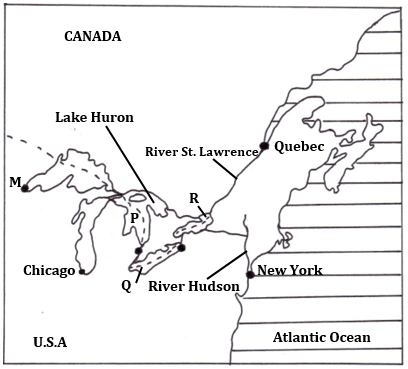
- The diagram below shows the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence sea way. Use it to answer the questions below.
Name the lakes P, Q and R.
-
- What is a Cottage Industry? (2 marks)
- Give three problems facing the Jua Kali industries in Kenya. (3 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
- Study the photograph below and use it to answer question (a).
-
- Identify the type of photograph shown above. (1 mark)
- Describe the characteristics of the forest shown on the photograph. (4 marks)
- Draw a rectangle measuring 15 cm by 10 cm. On it, sketch and label five main features shown on the photograph. (5 marks)
-
- Name two indigenous softwood tree species in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Explain three problems facing forestry in Kenya. (6 marks)
- State three factors favouring the development of softwood forests in Canada. (3 marks)
- Give four differences between softwood forests in Kenya and Canada. (4 marks)
-
-
-
- Identify three maize growing counties in Kenya. (3 marks)
- State four physical conditions that favour growth of maize in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Describe the stages of maize cultivation from land preparation to harvesting. (6 marks)
- State four problems facing plantation farming in tropical regions. (4 marks)
-
- Name two exotic dairy breeds reared in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Explain three measures that the government of Kenya has taken to promote dairy farming. (6 marks)
-
-
- What is fish farming? (2 marks)
-
- Identify three types of fishing. (3 marks)
- Describe the purse seining method of fishing. (4 marks)
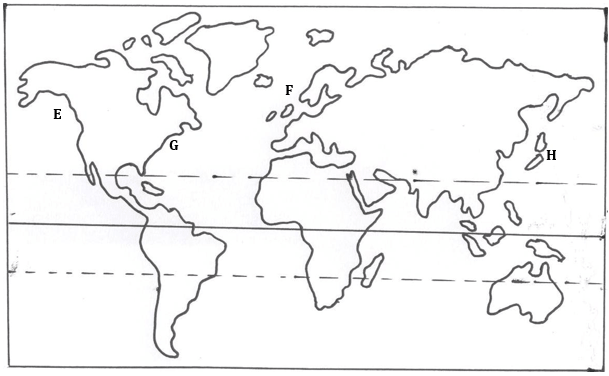
- The map below shows the fishing grounds of the world. Use it to answer the questions below.
- Name the fishing grounds marked E, F, G and H. (4 marks)
- Explain three physical factors which influence fishing in the fishing Ground marked H. (6 marks)
- Why is fresh water fishing more developed in Kenya than marine fishing? (6 marks)
-
-
- What is population growth? (2 marks)
- Explain three factors that have contributed to high population growth rate in Kenya. (6 marks)
- State four reasons why it is important for a country to carry out a population census. (4 marks)
- Explain how the following factors have influenced population distribution in East Africa.
- Pests and diseases. (2 marks)
- Government policy. (2 marks)
-
- Apart from Eldoret, name three other agriculture collecting towns in East Africa. (3 marks)
- Explain three factors that have led to growth of Eldoret as a major town in Kenya. (6 marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between management and conservation of environment. (2 marks)
- State three reasons for management and conservation of the environment. (3 marks)
-
- Apart from floods, name three other natural hazards. (3 marks)
- Give three causes of floods in the Kenyan lowland areas.(3 marks)
- Explain three measures that the government of Kenya has taken to control floods. (6 marks)
- Your Geography class undertook a field study on environmental pollution in a major urban centre in Kenya.
- Name three types of pollution that you may have observed. (3 marks)
- Give three effects of pollution you may have identified. (3 marks)
- Give two methods of collecting data you may have used. (2 marks)
-

Marking Scheme
SECTION A: 25 MARKS
-
- What is the relationship between Geography and Demography? (2 marks)
Population geography uses demographical information to explain the relationship between population distribution/trends and utilization of both natural and human resources on the earth surface. - State three reasons why it is important to study Geography. (3 marks)
- It prepares one for career opportunities
- It helps learners to develop skills /critical thinking.
- Enables learners to understand/appreciate different environmental influences.
- It teaches learners time management (through fieldwork and drawing of time schedules.)
- It creates awareness about the country and the rest of the world/It promotes international understanding.
- It promotes awareness on the sustainable use of resources.
- It helps learners develop important social values such as cooperation and patience as they work in groups.
- It promotes awareness on the sustainable use of resources.
- What is the relationship between Geography and Demography? (2 marks)
- Describe the deep shaft method of mining. (5 marks)
- Vertical shafts are sunk into the earth’s crust to reach the layer with the mineral.
- Horizontal tunnels/galleries are dug from the vertical shaft to reach the vein of the mineral bearing rock.
- The mineral bearing rock is blasted loose by explosives and then transported along the shaft by light railway or conveyer belt.
- It is then bought to the surface by a type of a crane or lift called cage.
- The galleries are supported by timber pit props or steel concrete beams which support the roof to prevent it from collapsing. It should be well ventilated and kept free from water.
-
- Apart from draining swamps, name two methods of land reclamation in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Irrigation
- Control of pests/Tsetse fly
- Afforestation/Planting trees
- Planting of drought resistant crops in marginal areas
- State three aims of setting up the Perkerra irrigation scheme. (3 marks)
- To utilize the detainee labor./Settle detainees and pastoralists.
- To develop land for Agricultural production
- To control the seasonal flooding of river Perkerra
- To utilize the excess water of river Perkerra that used to go to waste.
- Apart from draining swamps, name two methods of land reclamation in Kenya. (2 marks)
-
- Give two problems facing river transport in Africa. (2 marks)
- Inadequate capital to develop waterways, ports and for the purchase of vessels.
- Fluctuation of water levels which makes sailing difficult as a result of rivers passing through dry areas.
- Presence of rapids and waterfalls which hinders the vessels’ movement.
- Siltation of rivers which makes their channels shallow hence hindering movement of vessels.
- Presence of floating vegetation or swamps which makes it difficult for vessels to sail due to narrowing of the river channel.
- Most rivers pass through unproductive zones hence its uneconomical to develop river transport.
- Rivers flow across political boundaries which may require negotiation in order for the countries involved to use them for transport.
- Some rivers meander through their flood plains which increase the distance.
- Some rivers originate/pass through areas that experience long periods of drought leading to changes in the river regime.
- The diagram below shows the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence sea way. Use it to answer the questions below.
Name the lakes P, Q and R.
P - Lake Huron
Q - Lake Erie
R - Lake Ontario
- Give two problems facing river transport in Africa. (2 marks)
- What is a Cottage Industry? (2 marks)
- It is a type of industry which people work from their homes making products using their hands and simple tools/machines.
- It is a small scale industry which uses local raw materials and require little capital to start and operate.
- Give three problems facing the Jua Kali industries in Kenya. (3 marks)
- Difficulty in obtaining raw materials at affordable prices.
- Shortage of capital as most of the artisans have little access to modern banking facilities/low income.
- Competition from other industries making similar products.
- Exploitation of the artisans by the middlemen when they sell raw materials to them at high prices.
- Poor marketing skills /and strategies.
- What is a Cottage Industry? (2 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
- Study the photograph below and use it to answer question (a).
-
- Identify the type of photograph shown above. (1 mark)
- Ground obligue photograph
- Describe the characteristics of the forest shown on the photograph.(4 marks)
- The forest has mixed species of trees.
- The forest in the foreground is dense/trees are close to each other.
- The forest in the foreground is natural.
- The forest has some shrubs/undergrowth.
- Trees are of different height.
- Some part of the forest has been cleared.
- Draw a rectangle measuring 15 cm by 10 cm to represent the area by the photograph.On it sketch and label the main features shown on the photograph. (5 marks)
- Identify the type of photograph shown above. (1 mark)
-
- Name two indigenous softwood tree species in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Podo
- Cedar/African pencil
- Explain three problems facing forestry in Kenya. (6 marks)
- Rapid population increase has led to encroachment into the forested areas for settlement/agriculture leading to reduction of land under forest cover.
- Illegal logging by unlicensed timber merchants have led to depletion of indigenous tree species leading to their extinction.
- Prolonged drought have led to death of some tree species.
- Attack by pests/diseases have caused the destruction of valuable tree species.
- Occurrence of forest fires have led to destruction of large areas under forest cover.
- Excision of forest land by the government for settlement/human activities have led to reduction of land under forest cover.
- State three factors favouring the development of softwood forests in Canada. (3 marks)
- The cool/cold climate/low temperature.
- Rugged/steep landscape in British Columbia
- Low population density
- Heavy rainfall on the windward slopes of the mountain ranges of British Columbia.
- Extensive land in Canada is available for the forest to grow.
- Name two indigenous softwood tree species in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Give four differences between softwood forests in Kenya and Canada. (4 marks)
- In Kenya harvesting of trees is done throughout the year while in Canada harvesting is done in winter and early spring.
- In Kenya harvesting is done selectively while in Canada clear/indiscriminate cutting of trees is done.
- In Kenya forest products are mainly sold locally while in Canada are mainly for export.
- Species: Most Kenyan softwoods are exotic while in Canada softwoods are indigenous.
- Areas where they are found: Most softwood forests are found mainly in the highlands while in Canada they are found both in the highlands and lowlands
- Maturity: Softwoods in Kenya grow faster due to the warm tropical climate while softwoods take longer to reach maturity due to the cool temperate climate.
-
-
-
- Identify three maize growing counties in Kenya. (3 marks)
- Uasin Gishu
- Nakuru
- Trans Nzoia
- Laikipia
- Narok
- Bungoma
- Kakamega
- Nandi.
- State four physical conditions that favour growth of maize. (4 marks)
- Presence of warm conditions/moderate to high temperatures/100c – 300c.
- Presence of moderate to high rainfall.
- A hot/dry period for ripening/harvesting.
- Deep /and well drained volcanic soils/light loamy/black cotton
- Presence of gently sloping land
- Describe the stages of maize cultivation from land preparation to harvesting. (6 marks)
- Land is cleared, ploughed using tractors to make the soil loose.
- Holes are dug in lines using jembes for small scale farming and seeds and fertilizers are then applied in the holes and holes covered with soil/for large scale farming, tractor planters are used to make furrows where it places seeds and fertilizers and then cover them with soil as it moves in lines.
- Weeding/spraying with herbicide is done to control weeds
- Spraying against pests is done regularly.
- Top dressing is done with nitrogenous fertilizers when the maize attains a knee-height.
- Different maize varieties take different durations to mature.
- Mature maize is left to dry on the stalks.
- The stalks are cut and piled in pyramidal heaps.
- Maize cobs are plucked from their husks using human labour/combine harvesters.
- The maize is dried and then put in store.
- The dry maize is then shelled from the cobs using machines.
- The grain maize is then sifted and impurities removed.
- Maize is then weighed and put in 90kgs sacks.
- It is sold to middlemen, maize millers, NCPB and for domestic use.
- State four problems facing plantation farming in tropical regions. (4 marks)
- Crops may be destroyed by climatic hazards thus reducing production.
- There is high expenditure in maintaining plantations
- There is increasing subdivision of some plantations to provide land for the landless shareholders who bought them causing decline in output from plantations.
- Huge losses are incurred in events whereby the crop is destroyed by pests or diseases.
- There is rapid deterioration of soil due to monoculture, soil erosion due to complete weeding and most crops not providing sufficient soil cover.
- Fluctuations of world prices causes farmer to suffer great losses as they have no other crop to supplement their income.
- Poor management whereby managers misuses funds and shareholders fight over management leaving plantations unattended.
- Identify three maize growing counties in Kenya. (3 marks)
- Name two exotic dairy breeds reared in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Friesian/Holstein
- Alderney
- Jersey
- Swiss Brown/Brown Swiss
- Arshire
- Fleck-Vieh
- Guernsey
- Explain three measures taken by the government of Kenya to promote dairy farming. (6 marks)
- It constructs the cattle dips to control tick borne diseases
- It provides credit facilities through agricultural finance cooperation (AFC) for farmers to buy farm inputs.
- It encourages farmers to form dairy cooperatives to assist in milk collection, transportation and marketing.
- It improves road networks to help farmers milk reach the market in the shortest time hence avoiding losses.
- The government has up of cooling and processing plants in the milk producing areas to buy milk from the farmers.
- The government carries out research through Kenya Research Agricultural Institute (KARI) to help improve cattle breeds as well as fight pests which transmits animal diseases.
- The government sets up field days to educate farmers on good dairy management methods for realization of more production hence profits.
- Has set up demonstration projects such as Emali livestock multiplicity project of high quality bulls.
- The government provide veterinary services to control the spread of diseases.
- The government encourages farmers to attend agricultural shows to learn advancement of dairy farming.
- Carrying out vaccination programmes for dairy cattle in an effort to control diseases.
- Declaration of quarantine especially where there are disease outbreaks/saving the animals from death.
- Name two exotic dairy breeds reared in Kenya. (2 marks)
-
-
- Define fish farming. (2 marks)
- It is the rearing of fish in ponds for commercial or subsistence purposes - Identify three main types of fishing. (3 marks)
- Pelagic fishing
- Demersal fishing
- Inshore fishing
- Fresh water fishing
- Describe the purse seining method of fishing. (4 marks)
- Method is used to catch pelagic and anadromous/migratory fish which swim in shoals.
- A bag like nets with small meshes (seine) attached to two boats on each end is cast into the sea.
- Its kept open and held in position by floats on top and weights at the bottom.
- Fish move towards the net and get trapped.
- The net is hauled over and fish emptied onto the ship or the net is hauled to the shore (haul seining).
- Identify three main types of fishing. (3 marks)
- The map below shows the fishing grounds of the world. Use it to answer the questions below.
- Name the fishing grounds marked E, F, G and H. (4 marks)
E - North East Pacific.
F - North East Atlantic
G - North West Atlantic
H - North West Pacific. - Explain three physical factors which favour fishing in the fishing ground marked H. (6 marks)
- Broad continental shelf which favors plankton growth leading to more fish.
- Convergence of cold Oya Siwo and warm Kuro Siwo currents which result in coll well oxygenated and ice free waters ideal for fishing throughout the year.
- Numerous islands, bays and sheltered inlets which favour fish breeding and provide good fishing ports.
- Mountanious landscape especially in Japan which hinders development of agriculture making fish an alternative source of food and income.
- The cool waters are ideal for fish breeding because of abundant supply of planktons/fish food.
- The highly indented coastline provides secure fish breeding grounds/fishing ports/ villages.
- Name the fishing grounds marked E, F, G and H. (4 marks)
- Why is fresh water fishing more developed in Kenya than marine fishing? (6 marks)
- There are more inland fresh water fishing grounds but very few marine fishing grounds.
- Inadequate capital to by modern equipment to be used in the marine fishing grounds.
- Fresh water fishing is done using simple fishing equipment.
- There is a high demand for fresh water fish while there is a very low demand for the fish from the sea.
- Narrow continental shelf which limits the growth of planktons thus inhibiting the growth of fish.
- Very few sea inlets to provide sheltered areas for fish breeding.
- the tropical location makes the ocean water to be warm, thus making it unconducive for the growth of fish.
- Define fish farming. (2 marks)
-
-
- What is population growth? (2 marks)
- It refers to an increase or decrease in the number of people in a country. - Explain three factors that have contributed to high population growth rate in Kenya. (6 marks)
- Early marriages; many people in Kenya get married early and this allow them a longer period of fertility resulting in many children.
- Improved medical care; this leads to increased chances of survival for both mother and children/infants thus high population growth.
- Improved nutrition; this leads to better improved health for the entire population hence reducing mortality rate.
- Cultural belief; some culture encourage large families due to preference of one gender to the other/some culture discourage the use of contraceptives and family planning leading to couples having many children.
- What is population growth? (2 marks)
- State four reasons why it is important for a country to carry out a population census. (4 marks)
- It helps to know the growth of her population.
- It helps in planning for the resources in the country.
- It helps to know the number of people living in an area.
- It helps to show the composition of the population in terms of sex, age and regional distribution.
- It helps to know the number of males and females.
- It provides information on trends and levels of mortality and fertility. That helps the government to plan for provision of basic facilities to the people.
- It is used to create administrative divisions/boundaries.
- It helps to determine the dependency ratio.
- It shows the level of illiteracy that can be used be used to distribute education facilities.
- It shows ethnicity and nationality.
- Explain how the following factors have influenced population distribution in East Africa. (2 marks)
- Pests and diseases.
Areas infested by pests and diseases carrying vectors discourage settlements hence the conditions are unhealthy for human beings leading to low population. - Government policy
- It can attract or discourage population, creation of settlement and resettlement schemes to settle the landless and to resettle people from densely populated areas.
- The government may discourage people from settling in water catchment areas thus leading to low population in such areas.
- Pests and diseases.
-
- Apart from Eldoret, name three other agriculture collecting towns in East Africa. (3 marks)
- Nakuru
- Kisii
- Mbarara
- Mbale
- Kabale
- Mbeya
- Songea
- Iringa
- Karatina.
- Explain three factors that have led to growth of Eldoret as a major town in Kenya. (6 marks)
- Eldoret has a rich agricultural hinterland that provides farm produce/raw materials to industries/which has led to its growth as an agricultural collecting/processing center.
- It is located in an area that experiences cool and wet climate which is ideal for settlements.
- The terrain of the land is a plateau/undulating which allows room for expansion of town and industries
- The modern infrastructure such as Eldoret international airport has led to the expansion of the town.
- The high population in the surrounding regions provides market for agricultural/manufactured goods/provide labour for the industry.
- It is a county head quarter for Uasin-Gishu County and this has attracted administrative services in the town.
- Establishment of many educational institutions e.g. Moi University, university of Eldoret has attracted many settlements within.
- Availability of social ameneities e.g Moi Teaching and Referral Hospital which has attracted a large population.
- Apart from Eldoret, name three other agriculture collecting towns in East Africa. (3 marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between management and conservation of environment. (2 marks)
- Environmental management refers to the effective planning and controls used for sustainable exploitation and improvement of the environment while environmental conservation is the preservation and protection of natural environment from destruction through careful use and improvement of the environment. - State three reasons for management and conservation of environment. (3 marks)
- It helps to maintain soil fertility for sustainable food production.
- It helps to preserve generic resources for future generation.
- It helps to preserve aesthetic value and provide recreational facilities which promotes tourism.
- It helps to sustain raw materials for some manufacturing industries that produce goods for trade.
- It helps reduce the pollution that cause diseases to animals and plants to ensure good health.
- It helps to maintain natural habitats for both plants and wild animals.
- It helps in protecting the water catchment areas and sustain the hydrological cycle.
- It helps prevent desertification which destroys environmental resources.
- It helps to ensure proper utilization of available natural resources without destruction.
- It helps to sustain human life with required resources and by preventing pollution.
- Differentiate between management and conservation of environment. (2 marks)
- Apart from floods, name three other natural hazards. (3 marks)
- Desertification
- Landslides
- Hailstorms
- Heat waves
- Lightning and thunderstorms
- Dust storms and windstorms.
- Pests and diseases/Epidemics
- Drought
- Earthquakes
- Volcanic eruptions
- Give three causes of floods in Kenyan lowland areas. (3 marks)
- Presence of low gradient/lowlying areas which causes rain water to spread over wide areas.
- Occurrence of torrential rainfall in the adjacent highlands which releases large volumes of water into rivers causing them to over flow their banks.
- Deposition of silt on the river beds making them shallow hence water spills over wide areas.
- Presence of clay soils which is non-porous thus causing waterlogging.
- Rise in the water level of Lake Victoria due to heavy rainfall in adjacent highlands causing water to overflow and flood surrounding lowlands.
- Presence of rivers with wide flood plains at old stage which allows water spread over wide areas.
- Breaking of dams constructed across river valleys releasing water water in the reservoirs to overflow thus causing flooding in the downstream valley side.
- Explain three measures used by the Kenyan government to control floods. (6 marks)
- Construction of check dams across the rivers to hold the excess water in order to reduce river volume.
- Construction of artificial levees/dykes long the river banks to increase their height and prevent water from overflowing into the flood plain/to restrict the rivers within their channels.
- Construction of drainage channels to make them hold excess water from the land.
- Dredging and widening the river channels to make them hold excess water.
- Planting trees/reafforestation in the catchment areas to increase water infiltration /and reduce surface run off.
- Redirecting some river tributaries to other rivers to reduce the water volume of the main river.
- Straightening of a river to control its wild flow
- Apart from floods, name three other natural hazards. (3 marks)
- Your Geography class undertook a field study on environmental pollution in a major urban centre in Kenya.
- Name three types of pollution they may have identified. (3 marks)
- Water pollution
- Air pollution
- Land/soil pollution
- Noise/sound pollution
- Radiation pollution
- Thermal pollution
- Give three effects that may arise from the pollutions name in ‘i’ above. (3 marks)
- Water pollution may lead to outbreak of diseases such as cholera.
- Air pollution through smoke and gases such as carbon IV oxide may lead to development of respiratory diseases in human beings.
- Noise pollution may lead to loss of hearing ability of some people/headache.
- Land pollution may lead to development of ugly scenes which are an eyesore /blockage of drainage channels leading to flooding during rainy season.
- Dumped metals/glasses can cause accidents.
- Oil spills/industrial wastes leads to destruction of aquatic life.
- Air pollution causes foul smell/respiratory ailments.
- Garbage cause foul smell/eyesore
- Give two methods of collecting information they may have used. (2 marks)
- Taking photographs/tape recording/filming
- Administering questionnaires.
- Interviewing respondents orally.
- Observing.
- Measuring.
- Counting
- Conducting experiments.
- Collecting samples.
- Name three types of pollution they may have identified. (3 marks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 - 2020 MOKASA JOINT MOCKS EXAMINATION (QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students