SECTION A. (25 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section.
-
- State three main characteristics of minerals. (3Marks)
- Name two areas where diamond is mined in Tanzania. (2Marks)
-
- Give two reasons why hardwood tree species in Kenya is in danger of extinction? (2Marks)
- State three differences between the softwood forest of Kenya and those of Canada. (3Marks)
-
- Name two horticultural crops grown in Kenya. (2Marks)
- State three reasons why horticulture is more developed in the Netherlands than Kenya (3Marks)
-
- Differentiate between nomadic pastoralism and transhumance pastoralism. (2Marks)
- Give three measures taken by the government to improve life of nomads in Kenya (3Marks)
-
- Name two ways in which land may be reclaimed. (2Marks)
- List three land reclamation projects in Kenya. (3Marks)
SECTION B: (75 MARKS)
Answer Question 6 and any other two questions in this section.
- Study the photograph below and answer the questions that follow:
-
- Name the type of photograph. (1Mark)
- State the natural hazard depicted in the photograph above? (1Mark)
- Name three regions in Kenya where this photograph may have been taken. (3Marks)
-
- Outline five causes of the natural hazard shown in the photograph? (5Marks)
- State four effects which may result from this hazard. (4Marks)
- Give three measures that can be taken to control this hazard. (3Marks)
- Identify two sources of water pollution. (2Marks)
- Explain three effects of water pollution. (6Marks)
-
-
-
- Name two areas where coffee is grown on large scale in Kenya. (2Marks)
- Give five physical factors that favour coffee growing in Kenya. (5Marks)
- State four benefits of coffee growing in Kenya. (4Marks)
- Explain four ways through which the government of Kenya assists small-scale coffee farmers. (8Marks)
- Explain three ways by which the Brazilian government responds to the problems facing coffee industry in Brazil. (6Marks)
-
-
-
- Identify three characteristics of pelagic fish. (3Marks)
- State three reasons why marine fishing is not developed in Kenya. (3Marks)
- Give four reasons why should the Government of Kenya encourage fish farming? (4Marks)
-
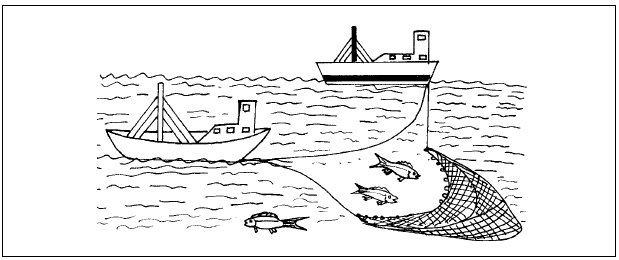
- Identify the fishing method shown below. (1Mark)
- Describe how the above method is used in Lake Victoria. (4Marks)
- State two problems facing fishing in Japan. (2Marks)
- Identify the fishing method shown below. (1Mark)
- Explain factors that favour fishing in the pacific fishing grounds. (8Marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between primary and secondary industry. (2Marks)
- Identify two examples of agricultural non-food processes sing industries in Kenya. (2Marks)
-
- State five characteristics of cottage industry in India. (5Marks)
- State four problems facing cottage industry in Kenya. (4Marks)
- Give four reasons why development of Jua Kali industry is encouraged in Kenya (4Marks)
- Explain four problems facing Jua Kali industry in Kenya. (8Marks)
-
-
-
- Apart from the sun, name three other sources of energy (3Marks)
- State four advantages of using solar energy (4Marks)
- Give four ways in which Kenya has benefited from hydroelectric power scheme (4Marks)
- Explain five factors favouring development of Hydroelectric power projects (10Marks)
- Explain two impacts of energy crisis in the society. (4Marks)
-

Marking Scheme
-
- State 3 main characteristics of minerals
- Chemical composition
- Hardness
- Crystal shape
- Specific gravity
- Colour
- Transparency
- Texture
- Lustre
- Cleavage
- Fracture
- Streak
- Tenancy
- Taste
Should begin with either (Minerals have different/minerals have a different degree of :) Any 3x1=3mks
- Name two areas where diamond is mined in Tanzania.
- Mwadui
- Shinyanga Any 2x1=2mks
- State 3 main characteristics of minerals
-
- Why hardwood tree species in Kenya is in danger of extinction
- High demand for hardwoods which has led to overexploitation.
- Rate of harvesting of hardwood is higher than the rate at which they mature.
- Population pressure on land has led to increased cutting of trees to provide land for farming. Any 2 x 1 = 2mks
- Differences between the softwood forest of Kenya and those of Canada
- In Kenya softwood is planted while in Canada they grow naturally.
- In Kenya softwood cover a relatively small area of the country while in Canada they are extensive.
- Most softwood in Kenya are exotic while in Canada they are indigenous.
- In Kenya there is a limited variety of tree species while in Canada there is a wider variety of tree species.
Any 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Why hardwood tree species in Kenya is in danger of extinction
-
- Horticultural crops grown in Kenya.
- Vegetables – Tomatoes/onions/carrots
Allow any correct vegetable max 1mk - Fruits – oranges, pineapples, plums, mangoes
Allow any correct fruit max 1mk
- Vegetables – Tomatoes/onions/carrots
- Why horticulture is more developed in Netherlands than Kenya
- Netherlands has a higher urban population than Kenya/ there is high demand both local and foreign for horticultural crops products in Netherlands while in Kenya is less
- Farmers in Netherlands have more access to the capital needed for horticultural farming while in Kenya is less.
- Netherlands unlike Kenya has highly skilled labour for production and handling of agricultural products.
- There is more advanced horticultural farming related research in the Netherlands than in Kenya.
- Netherlands unlike Kenya has well organized marketing procedures/co-operatives/auction markets which are conducive for horticultural farming. Any 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Horticultural crops grown in Kenya.
-
- Differentiate between nomadic pastoralism and transhumance pastoralism
- Nomadic pastoralism is the keeping of large number of livestock by communities who constantly move from one place to another with their stock in search of water and pasture while transhumance refers to seasonal movement of people with their livestock during seasons like winter and summer. Any 2x1=2mks
- Give three measures taken by the government to improve life of nomads in Kenya
- The government has set up demonstration ranches to educate pastoralists on better ways of keeping livestock /cattle dips to control pests
- Extension services are provided to give advice to the pastoralists.
- Boreholes and dans have been constructed to provide water for the livestock.
- Roads have been constructed to enable pastoralists to transport their produce to markets.
- Through formal education the pastoralists have learnt the advantages of keeping manageable sizes of herds.
- The government encourages group ranching to enable the pastoralists to view livestock keeping as a commercial undertaking. Any 3x1=3mks)
- Differentiate between nomadic pastoralism and transhumance pastoralism
-
- Name two ways in which land may be reclaimed
- Through irrigation
- Draining water bodies and swamps
- Controlling tsetse flies
- Afforestation and re-afforestation programmes. Any 2 x 1 = 2mks
- List three land reclamation projects in Kenya
- Mwea Tebere - Kibirigwi - Hola (Galole)
- Labwe valley - Rupinganzi - Turkwell
- Bura / Galole - Ishara - Ahero pilot Scheme
- Lower Yala - Mtonguu -Kibwezi
- Pekerra - Kunai
Any 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Name two ways in which land may be reclaimed
-
-
- Name the type of photograph.
- Ground close-up
- State the natural hazard depicted in the photograph above?
- Floods
- Name three regions in Kenya where this photograph may have been taken
- The lower Tana River in Tana River District
- Kano Plains of Kisumu District
- Bunyala Division in Busia District
- Budalangi in Busia Any 1x3=3mks
- Name the type of photograph.
-
- Outline five causes of the natural hazard shown in the photograph.
- Floods result from a continuous heavy downpour. This causes water in the streams to spill over the banks into the adjacent farm land.
- Floods also occur when the soil cannot absorb all the water from the rains.
- Floods have also been aggravated by the destruction of forests.
- Rising lake levels
- Occurrence of Tsunamis which are triggered off by an earthquake occurring on the sea bed
- Poor urban drainage.
Any 5x1=5mks
- State four effects which may result from this hazard.
- Destruction on property
- Outbreak of diseases
- Loss of lives
- Uproot plants, especially on higher slopes
- Bring about shortages of food lead to famine
- Destruction of infrastructure
- Displacement of people
Any 4x1=4mks
- Give three measures that can be taken to control this hazard.
- Building of dams across rivers to hold back excess water
- Building of dykes, like in the case of the Netherlands, to hold back sea water.
- Construction of levels along river banks.
- Embarking upon afforestation programmes to check the speed of water flow.
- Deepening of river channels
Any 3x1=3mks
- Outline five causes of the natural hazard shown in the photograph.
- Identify two sources of water pollution
- Garbage dumping in urban centres.
- Careless disposal of industrial wastes
- Spraying of plants with care-chemicals
- Burning of vegetation during law preparation
- Poor disposal of non- bio-degradable material. Any 2x1=2mks
- Explain three effects of water pollution
- Leads to death of aquatic plants and animals hence loss
- Polluted water when consumed may lead to death of people, domesticated and wild animals
- High incidences of diseases e.g. cholera and typhoid lead to deaths
- Corrosion of water vessels making their maintenance prohibitive.
- Beaches become filthy with waste materials affecting tourism.
Any 3x2=6mks
-
-
-
- Name counties where coffee is grown on large scale in Kenya
Nyeri, Muranga, Kiambu, Kirinyaga, Meru, Embu, Kisii and Nyamira
Any 2x1=2mks - Give five physical factors that favour coffee growing in Kenya
- Moderate to high temperature/ 14o- 26o c
- High rainfall/ 1000-2030 mm well distributed throughout the year
- High altitude from 1000-2000m above sea level
- Deep, well drained volcanic soils
- Undulating landscape
- Tree or banana shades to shelter them from direct sunlight
- Two months of dry period to allow flowering and ripening and picking of the crop
Any 5x1=5mks
- Name counties where coffee is grown on large scale in Kenya
- State four benefits of coffee growing in Kenya
- Coffee is exported earning foreign exchange money used to improve other sectors.
- Employment opportunities - those employed in the coffee industry improve their standard of living/earn income.
- Related industries have been established which creates employment to people
- Roads/railway/water transport have developed hence improved accessibility.
- Has led to urbanization/growth of towns from coffee sector related activities.
- Schools and medical centers have been established from earnings from coffee or setting up coffee factories in certain areas.
- Coffee farming has offered direct income to the farmers hence raising their living standards.
Any 4x1=4mks
- Explain four ways through which the government of Kenya assists small-scale coffee farmers.
- The government conducts research to establish the kind of coffee strains that is best suited for different areas, coffee disease and control
- The government arranges for marketing of coffee through Marketing Board of Kenya
- Advance payment to KPCU, which in turn advances payment to farmers/ loans to enable them continue farming
- Conducts regular education for coffee farmers on crop production through field days/ agricultural shows/ demonstrations
- Provision of extension officers who educate the farmers
- Coffee co-operatives have been set up to enable the farmer’s pool their resources together e.g. capital machinery and technology
- Improvement of transport means e.g. roads, railway and water transport to facilitate transport of coffee and its products
Any 4x2=8mks
- Explain three ways by which the Brazilian government responds to the problems facing coffee industry in Brazil.
- The government has encouraged crop diversification by introducing annual crops such as sugarcane, cotton to reduce over independence on coffee.
- The government buys coffee from farmers and stores it, thus stabilizing the prices for the farmers to solve the problem of over production.
- The government lobbies for higher quota in the international market.
- The government has established an Institute for Permanent Defense of coffee which manipulates coffee output released to the world market to create artificial shortage consequently maintaining high prices.
- Prohibiting new plantings by the government.
- It manipulates the amount of coffee released to the international market thus creating artificial shortages hence maintaining higher prices.
Any 3x2=6mks
-
-
-
- Characteristics of Pelagic fish.
- Live near the water surface / live at shallow depths.
- Live in large groups.
- They are small in size
- They move in shoals.
Any 3x1=3mks
- Reasons why Marine fishing is not developed in Kenya.
- Inadequate capital.
- Low fish-eating culture among the local communities
- Small market along the coast /sparse population.
- Stiff competition from foreign fishermen.
- Use of small boats discourages deep sea fishing/ poor technology.
- Warm waters of the tropics discourage fish breeding.
- Narrow continent shelf.
- Shallow waters due to the presence of coral reefs.
Any 3x1 =3mks
- Characteristics of Pelagic fish.
- Reasons the government of Kenya should encourage fish farming.
- Allows better and maximum utilization of land and water resources especially swamps/dams with no agricultural use.
- It is less exposed to dangers of deep sea or fishing-storms, drowning
- It assists in the conservation of rare species, which face the danger of depletion or extinction.
- It occupies less space.
- Creates job opportunities.
- Some fish from the ponds are exported to earn foreign exchange.
- May lead to the development of fish related industries.
- It is free from territorial disputes and conflicts.
- Fish is a source of food/supplement animal protein.
Any 4x1=4mks
-
- Identify the fishing method shown below.
- Seining Any 1x1= 1mks
- Describe how the above method is used in Lake Victoria
- Fishing boat with the help of another boat (Dory) spread out the seine net in the Lake.
- Nets are held in position using floats.
- Nets are tied to some weights at the bottom to keep it in water.
- The Net is attached to the boats which surround a shoal of fish and allowed to get trapped into the net.
- The net is pulled from both ends.
- Once the net is full, the net is hauled over and fish emptied onto the ship
Any 4x1=4mks
- Problems facing fishing in Japan
- Restrictions imposed on Japanese fleets by her neighbours.
- Depletion of some fish species due to overexploitation as a result of high demand for them locally and abroad.
- Overfishing due to use of highly advanced technology.
- Water pollution through oil spillages from fishing vessels lead to reduction of fish species.
Any 2x1 =2mks
- Identify the fishing method shown below.
- Factors favouring fishing in the North west pacific grounds
- Availability of large internal/external market/labour due to high Asian population
- Well-developed water transport/road/railway facilities.
- The mountainous landscape hinder agriculture making fishing the only alternative source of food
- Broad, shallow and extensive continental shelf that favours the growth of planktons
- Convergence of the cold Oyasiwo and warm Kurosiwo currents that makes the coast ice free allowing fishing all year round (warm Kurosiwo), provides ideal conditions for plankton growth (cold Oyasiwo)
- Indented North East Asian coastline with numerous islands, bays and sheltered inlets that favour fish breeding and development of fishing ports.
- Advanced technology especially in Japan has encouraged the development of fishing and facilitated transport of fish e.g. through ship building and refrigeration of ships.
-
-
-
- Differentiate between primary and secondary industry
- Primary industry involves exploitation of natural resources to provide raw material while secondary involves the changing of raw materials into finished goods
(Any 2x1=2mks)
- Primary industry involves exploitation of natural resources to provide raw material while secondary involves the changing of raw materials into finished goods
- Identify two examples of agricultural non-food processing industries in Kenya
- Cotton ginnery
- Bata Shoe Company
- British America Tobacco
- Pyrethrum Board of Kenya factory (Any 2x1=2mks)
- Differentiate between primary and secondary industry
-
- State five characteristics of cottage industry in India
- Owned by individual families or groups
- They are rural based
- Work is carried out manually/its labour intensive
- Industries operate in homes or small workshops
- They are found almost throughout the country
- Small capital is invested
- Simple tools and machinery are used
- Uses locally available raw materials
- Most products are sold in the local market/few are exported.
(Any 5x1=5mks)
- State four problems facing cottage industry in India
- Inadequate funds
- Stiff competition for market from the same producers
- Shortage of labour
- Difficulties in marketing goods produced by artisans as they get raw materials from dealers at high prices
(Any 4x1=4mks)
- State five characteristics of cottage industry in India
- Give four reasons why development of Jua-Kali industry is encouraged in Kenya
- Requires less capital to establish
- It creates employment opportunities
- Goods produced are mainly for local market
- It encourages decentralization of industries
- It uses local available skills
- Successfully uses materials that would otherwise be disposed
- Saves the country foreign revenue as they reduce the imports
- Earns the country foreign exchange as some are exported to COMESA countries
(Any 4x1=4mks)
- Explain four problems facing Jua Kali industry in Kenya
- Stiff competition from large scale manufacturing industries. They need a lot of support from the government more so in giving contracts to the artisans to do the supplying to government offices.
- Traders lack adequate skills to produce high quality goods that can compete well in the open market
- The Jua Kali traders lack a patent law to protect their innovations from ending up in developed countries
- The traders are exploited by middle men especially those dealing with soap stones, clothes, extra.
- They lack modern machinery and equipment.
- There cost of raw materials needed in industries is high
(Any 4x2=8mks)
-
-
-
- Apart from the sun, name three other sources of energy
- Water, Wind, Wood, Tides, Biomass
(Any 3x1=3mks) - State four advantages of using solar energy
- Cheap source of energy
- Available almost every where
- It can be stored and used later
- Environmentally friendly
- Inexhaustible source of energy.
(Any 4x1=4mks)
- Apart from the sun, name three other sources of energy
- State four ways in which Kenya has benefited from hydroelectric power scheme
- Provision of electricity
- Foreign exchange
- Fishing grounds
- Modified the local climate
- Control of floods
- Improvement of transport and communication. (Any 4x1=4mks)
- Explain five factors favouring development of Hydroelectric power projects
- Hard basement rocks to provide a firm foundation for dam construction
- Presence of waterfalls to provide a massive hydraulic force head for power generation
- Regular/large volume of water to ensure continuous power generation
- Non porous rocks to prevent water loss/seepage underground
- Presence of a deep narrow valley/gorge to provide a large reservoir behind the dam/reduce cost of building embankments
- Government policy – availability of land/space for setting up the plant
- Market to buy the produced HEP
- Adequate capital to set up the project since it involves high capital outlay
(Any 5x2=10mks)
- Explain two impacts of energy crisis in the society
- Is a situation where the demand for oil is higher than supply, leading to high oil prices
- Increased transport cost
- Increase in price of oil, increases price of other commodities
- Affect balance of trade
- Agriculture inputs such as fertilizers would become more expensive
(Any 2x2=4mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Kapsabet Mocks 2020/2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students