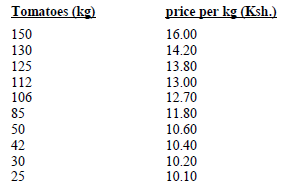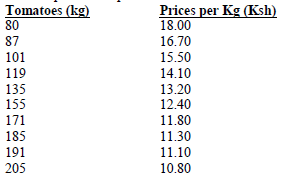SECTION A (30MARKS)
Answer All questions in this section.
- State four disadvantages of monocropping in crop production (2 marks)
- Give four soil factors that influence soil productivity (2marks)
- State two benefits of optimum soil temperature in crop production (1mark)
- State four reasons for deep ploughing during land preparation (2marks)
-
- State three factors to be considered before deciding on an irrigation in crop production (11/2 marks)
- List three surface water sources found in a farm (11/2 marks)
- List four types of a financial books a farmer should keep (2marks)
-
- What is increasing returns in production (1mark)
- What are three classification of farm credits according to the repayment periods (11/2 marks)
- Name one physiological disease in tomatoes (1/2 mark)
-
- State two criteria in which weeds can be classified (1mark)
- State four factors that contribute to competitive ability of weed? (2marks)
- Give the reasons of carrying out the following (1mark)
- Pricking out
- Seed inoculation
-
- Outline the ideal characteristics of green manure crop ( 11/2mark)
- What is the function of top soil in the preparation of compost manure) (1/2 mark)
- Give two ways in which cover crop help to conserve water in the soil (1mark)
- Name two ways in which land consolidation helps to improve farm management . (1mark)
-
- Explain the difference between fixed and variable costs in farming (1mark)
- Give four variable costs in production of coffee in an established field of coffee (2marks)
-
- Calculate the amount of K2O contained in 400kg of compound fertilizer 25:10:5(2marks)
- State four importance of irrigation in farming (2marks)
SECTION B (20MARKS)
Answer all questions in the spaces provided
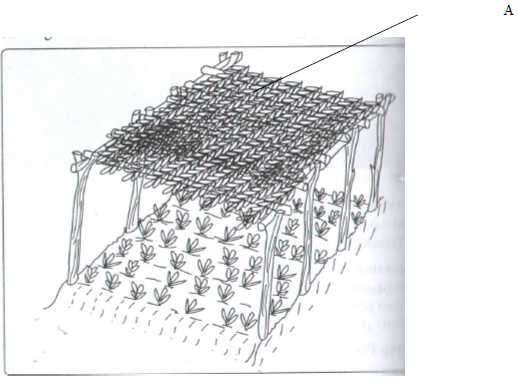
- The following is crop production structure. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow:
- Identify the structure ( 1mark)
-
- Explain how practices which are carried out when the seedlings are being prepared for transplanting is done. (2marks)
- What is the recommended height of the crop structure ( ½ mark)
- What is the purpose of the part labeled A? (2marks)
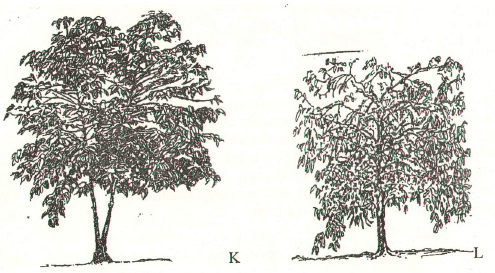
- Below are diagram K and L showing coffee plants established using two different formative pruning systems. Study them and answer the questions that follow:-
- Name the systems of pruning illustrated in the diagram labeled K and L (2marks)
- Describe the procedure of carrying out the system labeled K. (3marks)
- The following is a farm record for Mrs. Kamau had kept as at 30th June 2014. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow:-
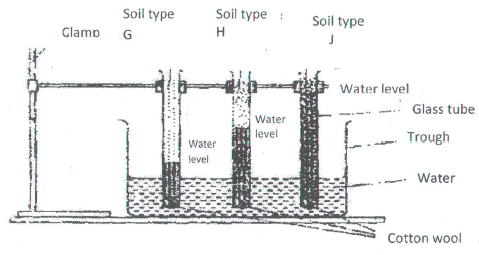
Prepare balance sheet from the above information for Mrs. Kamau’s farm. (5marks) - The diagram below shows an experiment set up using soil types G, H and J and observation made after 24hours. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow:-
- What is the experiment above designed to study? (1mark)
- Name the three soil types G, H and J (11/2marks)
- What is the characteristic feature of soil types G and J (1mark)
- State how a farmer would improve the structure of soil type G (1mark)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions in this section
-
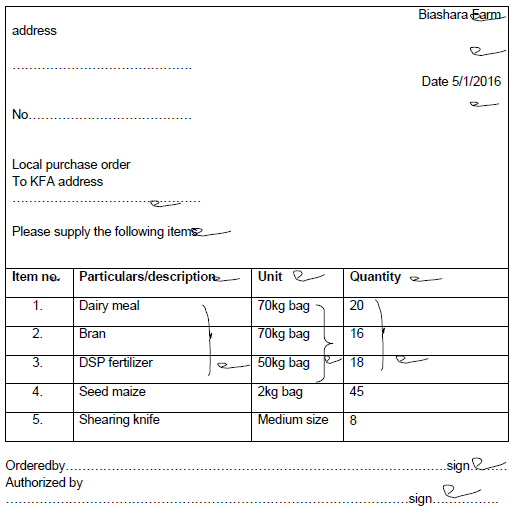
- On 5th January 2016 Biashara farm purchased the following items on credit from a KFA shop.
20 bags of dairy meal, 70kg each @ sh. 11oo per bag , 16bags of bran, 70kg each @sh. 700 per bag, 18 bags of DSP fertilizer, 50kg @ sh. 1,500 per bag 45 bags of maize seeds each 2kg @ sh. 300 per bag, 8 shearing knives (small sized @ sh. 300 per knife.- Prepare a purchase order that Biashara farm made to KFA (6marks)
- Calculate the value of each item purchased and the total value of the order (3marks)
- Explain how various practices carried in the field help to control crop diseases . (8marks)
- Explain three advantages of budgeting in a farm business (3marks)
- On 5th January 2016 Biashara farm purchased the following items on credit from a KFA shop.
-
- Explain eight factors that can encourage soil erosion (8marks)
- Explain the ways farmers use to overcome risk and uncertainties in farming business (7marks)
- Describe harvesting of tea (5marks)
-
- The tables below gives information on supply and demand schedules for tomatoes in a local market
Table 1 prices and quantities of tomatoes supplied
Table 2: prices and quantities of tomatoes demanded- Using the above data, plot supply and demand curves on the same axes. (8marks)
- Determine the price at which 120kg of tomatoes were supplied on the market. (1mark)
- How many kilograms of tomatoes were bought at a market price of Ksh. 13.00 (1mark)
- What was the equilibrium price for tomatoes on the market (1mark)
- Explain five advantages of mulching in crop production (5marks)
- Outline activities that may be undertaken in organic farming (4marks)
- The tables below gives information on supply and demand schedules for tomatoes in a local market

Marking Scheme
-
- High risk of total loss incase of crop failure
- under utilization of some nutrients
- build up of specific crop pest/diseases/weeds
- only specific mineral nutrients are absorbed/exhaustion of certain mineral nutrients from soil
- results in soil erosion in crops with poor coverage
- faster spread of pests and diseases
- leads to destruction of soil structure
- loss of soil fertility
(4X1/2 =2)
-
- Soil depth/drainage/aeration
- Water holding capacity
- Level of nutrients/cat ion exchange
- Soil PH/ soil borne pests and diseases
(4X1/2 = 2)
-
- Enhance seed germination
- Enhance plant growth
- Enhance soil microbial activities
- Improves quality of crops e.g Tea, pineapple
(2x1/2 = 1)
-
- Facilitates aeration
- Facilitates drainage
- Breaks hard pans/facilitates water infiltration
- Brings up previously leached nutrients
- Facilitates development of deep rooted crops
- Exposes soil borne pests and diseases agents
- Removes deeply rooted weeds.
(4x1/2 = 2)
-
-
- Type of soil
- Types of crop to be growth
- Source of water/water availability/rainfall pattern/quality of water
- Size of land to be irrigated
- Capital availability/costs involved
- Profit ability of irrigation/viability of enterprise
- Topography
(3X1/2 =11/2)
-
- River/streams
- Lakes
- Dams
(3x1/2 = 1 ½ )
-
-
- Journal
- Cash book
- Ledger
- Inventory
(4x1/2 = 2)
-
- This is the production in which each additional unit of input results to a larger increase in output than the proceeding unit of input (OWTTE) (1x1=1)
-
- Short term credit
- Medium term credit
- Long term credit
(4x1/2 = 2)
- Blossom end rot (1/2)
-
-
- Leaf size (broad and narrow leafed)
- Growth cycle (annual, Biannual and perennial)
- Habitat (aquatic and Terrestrial)
(2x1/2 = 1)
-
- Ability to produce large quantities of seeds
- Ability of seeds to remain viable in the soil for a long period of time
- Easy and successful dispersal mechanism of most weed seeds
- Ability to survive even under adverse conditions
- Ability to complete life cycle in a short time
- Elaborate root system
` (4x1/2 = 2)
-
-
- Reduce competition/ensure healthy seedlings
- Promote nitrogen fixation
-
-
- Rapid growth rate
- Production of abundant foliage
- Rich in plant nutrient /leguminous /rich in nitrogen
- Ability to decay rapidly
- Adaptable to wide range of condition/hardy
(3x1/2 = 1 ½ )
- Introduces micro – organism necessary for decomposition of organic material (1x ½ = ½ )
-
-
- Reduce surface run off/increase water infiltration
- Reduce evaporation
(2x1/2 = 1)
-
- saves time and money
- Makes it easy to have a sound farm plan e.g rotation programme
- Eases soil conservation measures
- Eases supervision as enterprise are at one place
- Facilitates mechanization/economical to mechanise
(2x1/2 = 1)
-
- Fixes costs are costs that do not change with the level of production while variable costs are costs that change with the level of production (1mk)
Mark as a whole -
- casual labour costs
- Fertilizer / manure costs
- cost of chemicals e.g pesticides
- Fuel costs
- cost of repair of machinery
(4x1/2 = 2)
- Fixes costs are costs that do not change with the level of production while variable costs are costs that change with the level of production (1mk)
-
- 5/100 x 400kg = 20kg
- A mark for formulae
- A mark for answer with units
-
- It makesit possible for crops to be produced during the dry season
- It makes it possible to reclaim land for agricultural production/grow crops in arid and semi arid areas
- It supplements rainfall
- Sustains proper growth of crops which require plenty of water e.g rice.
- Created favourable temperature for proper plant growth
- Facilitate fertigation
- Crops can be grown under special structure e.g green house (4x1/2 = 2)
- 5/100 x 400kg = 20kg
-
-
- Direct nursery bed/nurserybed/nursery ( 1 mk)
- 0.6M. (Ref without units) ( ½ mk)
-
- reduce light intensity
- regulate temperature
- intercepts rain drops/hailstones (2x 1= 2)
-
- reduction of watering
- Gradual removal of shade (1mk)
-
-
-
- K – multiple stem pruning
- L – Single stem pruning
-
- Cut the main stem of seedling to allow growth of suckers
- Select two health suckers and allow to grow
- remove the other remaining suckers (3x 1= 3)
-
- Balance sheet for Mrs. Kamau as at 30th June 2014
Assets Liabilities Fixed assets Ksh. Long term liabilities Ksh. Buildings 50,000 Disc ploughs 16,000 loan 50,000 Working tools 12,000 Land 80,000 Cattle 40,000 Current assets Current liabilities Cash in hand 20,000 Bank over draft 24,000 Cash in bank 66,000 Creditors 20,000 Debtors 1,600 Total liabilities 94,000 Net worth/Net capital 206,000 TOTAL 300,000 300,000
Title of the Account – 1mk
Correct label of columns – 1mk
Correct entries of Assets – 1mk
Correct Network value – 1mk Total 5mks -
- Capillarity in different soils ( 1 x 1 = 1mk
- G- Sandy soil
H – Loam soil
J – Clay soil
(3X1/2 =11/2) - G – Rough/coarse texture J – fine texture ( 2x1/2 =1)
-
- Addition of organic manure
- Addition of lime (1x1= 1)
-
- Purchase order from Biashara farm to KFA
- Dairy meal 1100/= x 20 = 22,000/= (1/2mk)
Bran 700/= x 16 = 11,200/= (1/2mk)
Dsp fertilizer 1,500 x 18 = `27,000/= (1/2mk)
Seed Maize 300 x 45 = 13,500/= (1/2mk)
Knives 300/= x8 = 2,400/= (1/2mk)
Total = 76,100/= (1/2mk)
-
- Crop rotation helps to break life cycle of disease causing organism
- rogueing infected crop stops the disease from spreading
- Use of certified seeds/disease free plants prevent introduction of pathogens into the field.
- Close season breaks life cycle of pathogens
- Early planting/timely planting crops establish faster before attack.
- Proper spacing creates unfavourable micro –climate for some pathogens.
- Weed control prevents harbouring of some pathogens
- Weed control prevents harbouring of some pathogens
- Use of resistant varieties prevents attack by pathogens
- Application of appropriate chemical kills pathogens
- Use of clean equipment reduces chances of contamination with disease causing organisms.
- Quarantine prevents introduction of pathogens into the farm.
- Heat treatment kills micro – organism
- Pruning gives unfavorable micro-climate for some pathogens.
- Control vectors to control spreading of pathogens
- Proper nutrition helps plant to withstand plant diseases/control deficiency diseases.
- Destruction of crop residues to kill pathogens.
(8 x 1 = 8)
-
- help farmer to predict the profitability of an enterprise
- enables farmer to detect problems easily so that correction is done in good time before losses occur
- Assist the farmer to make management decisions
- makes farmer to make effective changes in the organization
- Ensures periodic analysis of the farm business
- helps to estimate required production resources e.g labour
- Helps when negotiating for Agricultural credit
- enhances efficiency to meet targets
- Helps in controlling various aspects of production in the farm
- For future reference
(3x1 = 3)
-
-
- lack of ground cover exposes soil to agents of soil erosion
- Steep slopes increases the speed of surface ran off hence erositive power of work
- Light/sand soils are easily carried away by agents of erosion.
- Shallow soils are easily Saturated with water and carried away
- High rainfall intensity leads to Saturation of soils hence increases in soil erosion/surface run off.
- Frequent cultivation/over cultivation pulverizes the soil making it easy to detach and carry away
- Over stocking leads to overgrazing this destroys ground cover exposing it to agents of erosion.
- Burning /Deforestation destroy vegetation cover and exposes soil to agent of erosion.
- Ploughing up and down the slope creates channels.
- Cultivation of river banks destroys riverine vegetation and destroys soil structure exposing it to agents of erosion.
- Cultivation the soil when too dry destroy soil structure making it easy to be eroded
- Long slopes increases volume and speed of runoff hence increasing erosive power.
(Factor with explanation to score) (8x 1 = 8mks)
-
- Diversification; so that if one enterprise fails the farmer has something to rely on;
- Insurance against losses; so that incase of failure the enterprises are covered
- Strategic farming/inventing marketing; keeping farm products and selling at a time when prices are high.
- Carrying out flexible enterprises engaging in enterprises that can be stopped & started early as conditions change
- Rationing of inputs/using just sufficient input; so that incase of losses the costs are not too high.
- Using of more certain husbandry practices; using practices that the farmer is surer of and has used in the past.
- Contract marketing/edging; making arrangement with marketing agencies in advance so that changes in prices after the arrangement do not change the prices of the farmer’s produce.
- Selecting more certain enterprises; selection of enterprises that have done well in the area/tried through research.
- Maintain high liquidity; for use in case of any eventuality.
- Adopting modern methods of production/modern technology; Adopting risk reducing techniques of farming e.g vaccination irrigation, disease resistant varieties etc.
½ mk for mentioning factor
½ mk for explanation
(7x1 = 7)
-
- Leaves are picked selectively for the highest quality
- Pluck top two leave and a bud for fine plucking /3 leaves and a bud for coarse plucking
- Use plucking stick to maintain plucking table
- Pluck at 5-7 days interval in rains and 10-14 days in dry periods/cold periods
- Put plucked tea in woven buskets to facilitate air circulation/prevent fermentation
- Do not compress the leaves in the basket to prevent heating up/ browning
- Put plucked tea in cool and shaded places
- Deliver to the factory on the same day
(5 x 1 = 5)
-
-
-
-
- Heading (H) = 1mk
- Smooth curves (SC) = 2X1 = 2mks)
- Curve identified (CI) = 2 x ½ = 1mk
- Curve plotting (CP) = 2x1 = 2mks
- Scale (S) = 2 x ½ = 1mk
- Labeling axes (A) = 2 x ½ = 1mk
( 8mks)
- Ksh. 13.40 ᶤ 10cts (13,30- 13.50)
- 140 ᶤ 1kg (139 – 141 kg)
- Ksh 13. 80 ᶤ 10cts (13.70 – 13. 90)
-
-
- Has an insulating effect thus modifies /regulates soil temperature
- Prevents water evaporation therefore moisture is retained in the soil for the plant to use
- Controls soil erosion by intercenting rain drops before they hit the soil reducing the speed off surface runoff and increasing water infiltration
- Organic mulch decomposes into humus thereby improving soil structure/water holding capacity/water retention.
- After decomposition improves soil fertility by releasing nutrients
- After decomposition organic mulch it buffers soil PH/ increase cat ion exchange capacity
NB/ explanation must come out for score)(5x1 = 5mks)
-
- Mulching
- Application of organic manure/organic fertilizers
- Crop rotation
- Use of medicinal plant products to control diseases and parasites
- Rearing of livestock on natural feed staff/organic growth feedstuffs
- Physical/cultural/Biological pest/weed/parasite and disease control/accept specific control measure given (4 x 1 = 4)
-
-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Kapsabet Mocks 2020/2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students