Instructions to candidates.
- This paper consist of two sections; A and B.
- Answer all the questions in section A and question 6 and any other two questions in section B.
SECTION A. Answer all the questions.
-
- Give any two ways in which minerals occur. (2 mks)
- State three problems facing soda ash exploitation in Magadi. (3 mks)
-
- Define the term agroforestry. (2 mks)
- State three reasons why agroforestry is being encouraged in Kenya. (3 mks)
-
- Apart from land pollution name two other types of environmental hazards. (2mks)
- State three ways through which land pollution can be controlled. (3 mks)
-
- Apart from a telephone, state two other forms of communication (2mks)
- Mention three problems facing railway transport in Africa (3mks)
-
- Apart from the common market for Eastern and southern Africa (COMESA) identify two other trading blocks in Africa. (2 mks)
- Give three benefits of COMESA to member states. (3 mks)
SECTION B. Answer question 6 compulsory and only other two questions from the remaining questions.
- Study the photograph below and answer questions that follow

-
- Identify the type of photograph shown above (1 mk)
- Draw a rectangle measuring 15cm by 10cm to represent the area covered by the Photograph (1 mk)
- On the rectangle, sketch and label four main features (4 mks)
-
- Which type of farming is shown on the photograph (1 mk)
- Give three physical conditions favouring tea farming in Kenya (3 mks)
- Describe the stages of tea processing (5 mks)
-
- State two areas in Kenya where maize is grown on large – scale (2 mks)
- Explain four problems facing maize farmers in Kenya (8 mks)
-
-
- Differentiate between Land Reclamation and Rehabilitation. (2 mks)
- Give three methods used to reclaim land in Kenya. (3mks)
- State two methods that are used to control tse tse fly in Kenya. (2 mks)
- Explain three benefits of perkerra irrigation scheme. (6 mks)
-
- What is a polder? (2 mks)
- Name two crops grown in the polders. (2 mks)
- Outline the stages through which land is reclaimed from the sea in the Netherlands. (8 mks)
-
-
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries. (2 mks)
- State two categories of fish. (2 mks)
- Apart from Trawling, name two other methods of fishing. (2 mks)
- With the aid of a diagram, describe trawling method of fishing. (6 mks)
- Explain four problems experienced by Kenyan fishermen in Lake Victoria. (8 mks)
- The world map below shows major fishing grounds.
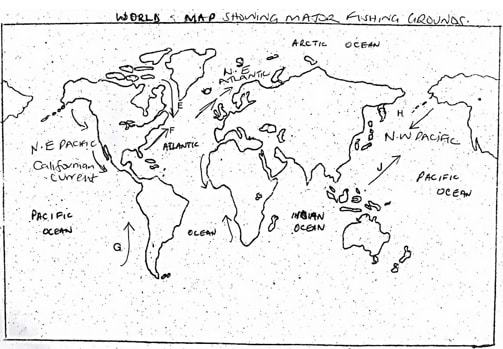
Use it to answer the following questions.- Name the ocean currents marked: (5 mks)
E –
F –
G –
H –
J – - Explain three factors that favour fishing in Japan. (6 mks)
- Name the ocean currents marked: (5 mks)
-
-
- Define wildlife. (2 mks)
- Distinguish between a game sanctuary and a game ranch. (4 mks)
- Study the following map of East Africa and answer the questions below.
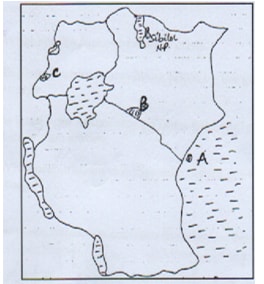
- Name national parks marked A, B and C. (3 mks)
- Explain four factors showing the future of tourism industry in Kenya. (8 mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence wildlife.
- Vegetation.(4 mks)
- Altitude (4 mks)
-
- What is energy conservation? (2 mks)
- Identify three non-renewable sources of energy. (3 mks)
- State three advantages of Hydroelectric power as a source of energy. (3 mks)
-
- What are the causes of energy crisis? (4 mks)
- Explain four measures being taken by the government to conserve energy. (8 mks)
- Students from your school carried out a field at Olkaria Geothermal Power Generation station.
- What preparations did they take before going out for the field study. (3 mks)
- Identify the secondary sources of data they would use to prepare for the study. (2 mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Two ways in which minerals occur
- veins / lodes
- beds / seams
- alluvial deposits
- placer deposits
- weathering and leaching products (2 mks)
- Problems facing soda ash exploitation in Magadi
- located in remote areas with poor transport and communication links
- there is inadequate fresh water supply for use in the factory and domestic purposes
- the area has no permanent inhabitants to provide the factory with reliable labour
- competition from large soda ash mining countries in USA, China and Israel
- low prices in salt has demoralized operators (3 mks)
- Two ways in which minerals occur
-
- Define Agroforestry
- It is a land use system where there is growing of trees and crops on the same piece of land at the same time
- Reasons why Agroforestry is encouraged in Kenya
- reduce importation of forest products
- create employment opportunities
- protect the soil from erosion
- improve the scenic beauty
- to maintain the hydrological cycle (3 mks)
- Define Agroforestry
-
- Apart from land pollution, name two other types of environmental hazards (2 mks)
- Wind stroms
- Pest and disease
- Lightening
- Floods
- Fire out breaks
- Earthquakes
- State three ways through which land pollution can be controlled (3 mks)
- Burning waste
- Digging pit for throwing rubbish / waste disposed.
- Educating the public on the effect of land pollution
- Recycling waste materials
- Minimizing use of harmful chemicals
- Legislation against dumping
- Setting up garbage collection/ provision of bins
- Apart from land pollution, name two other types of environmental hazards (2 mks)
-
- Apart from a telephone, state two other forms of communication (2 mks)
- Internet/computer
- Telex/telefax
- Pagers
- Cell phone/mobile phone
- Fibre cable network (2 mks)
- Mention three problems facing railway transport in Africa (3 mks)
- There is insufficient capital to expand the railway network in some Africa countries
- It is difficult to connect the railway line of one country with another because of different gauges.
- Different ideologies and political instability in some African countries hinder efforts to construct railway lines to link them.
- Many parts of Africa are in productive, it would be uneconomical to construct railway lines.
- There is poor management of the sector leading to many railway lines and train left unserviced making the mode of transport unreliable.
- African countries produce similar goods hence there is limited trade between them, this does not warrant construction of railway line. (3 mks)
- Apart from a telephone, state two other forms of communication (2 mks)
-
- Apart from the common market for eastern and southern Africa (COMESA) identify two other trading blocks in Africa
- Southern African development community (SADC)
- Economic community of west Africa states (ECOWAS) (2 mks)
- Give three benefits of (COMESA) to the members states
- Has created a large market for each country
- Has promoted regional peace
- Has led to expansion of industries and agriculture to cater for the wide market
- Has reduced tariffs
- Has expanded market for goods hence promoting industrial development as demand increases (3 mks)
- Apart from the common market for eastern and southern Africa (COMESA) identify two other trading blocks in Africa
SECTION B:
-
-
- Identify the type of photograph above Ground general view (1 mk)
- Draw a rectangle measuring 15cm by 10cm to represent the area covered by the photograph (1 mk)
- On the rectangle, sketch and label four main features shown on the photograph (4 mks)

-
- Which type of farming is shown on the photograph (1 mk)
- Mixed crop farming
- Give three physical conditions favouring tea farming in Kenya
- Requires rainfall of about 1500cm per annum/well distributed
- Cool to warm temperatures of between 15°C – 30°C
- Fertile, deep, well drained acidic and well aerated soils/volcanic soils
- It grows well between 1500 – 2200 metres above sea level
- It should be sheathered from strong wind and sunshine (3 mks)
- Describe the stages of the processing (5mks)
- In the factory, tea leaves are weighed and spread out on long wire trays
- Leaves are dried by blasting warm air from underneath to remove any moisture.
- Leaves are rolled mechanically between steel rollers to break up fibres.
- Chopped leaves are placed in containers for fermentation to reduce tannic acid by half and changing the colour to gre brown
- Leaves are roasted and dried over fire until they are black in colour
- Leaves are sieved to eliminate stems and other unwanted particles
- The finished product is graded and packed for export.
- Which type of farming is shown on the photograph (1 mk)
-
- State two areas in Kenya where maize is grown on large scale (2 mks)
- Uasin Gishu
- Trans-Nzoia
- Nakuru
- Bungoma
- Explain four problems facing maize farmers in Kenya (8 mks)
- Farm inputs are expensive, reducing farmers profit margins
- The prices in the market keep on fluctuating making it hard for the farmers to plan, or recover their inputs.
- Adverse weather conditions/unfavourable weather/prolonged drought destroy the crop leading to low yields/low income for the farmer.
- Pests and diseases e.g. stalk bores, army worms, aphids, weevils, etc destroy the crop leading to loss for the farmers
- Inadequate storage facilities, hence post harvest losses/low income for the farmers.
- Stiff competition in the market/flooded market with cheap imports from foreign countries.
- Poor transport and communication networks in the growing areas affecting marketing
- Shortage of capital to buy inputs, discouraging farmers
- Maize grow encourages monoculture. Soils are easily exhausted and requires regular application of fertilizer/manure making this farming venture expensive.
- State two areas in Kenya where maize is grown on large scale (2 mks)
-
-
- Differentiate between land reclamation and rehabilitation.
- Land reclamation is the process of converting less productive land into a more productive state for agricultural or settlement purposes while land rehabilitation is the process of restoring degraded land back to useful state. (2 mks)
- Give three methods used to reclaim land in Kenya.
- Draining
- Irrigation
- Planting of draught resistance vegetation
- Control of tse tse fly. (3 mks)
-
- State two methods that are used to control Tse Tse flies in Kenya.
- Bush clearing of tse tse fly infested areas
- Use of traps
- Construction of buffer zones
- Spraying using insecticides. (2 mks)
- Explain three benefits of perkerra irrigation scheme.
- Made use of unproductive semi- arid land into productive land.
- Created employment opportunities for local population.
- Raised the standards of living of many farmers.
- Supplied agricultural produce to the local market. (6 mks)
- State two methods that are used to control Tse Tse flies in Kenya.
-
- What is a polder?
- A polder is a low-lying area reclaimed from a sea. (2 mks)
- Name two crops grown in polders.
- Barley
- Oats
- Sugar beets
- Rye (2 mks)
- Outline the stages through which land is reclaimed from the sea in the Netherlands.
- Parts of the low lying land covered by sea water is enclosed using strong walls / dykes.
- Ring canals are constructed to lead water to pumping station.
- The water is pumped out using wind mills.
- Ditches are then dug to drain excess water from the enclosed area/ land.
- Reeds planted to suck up water and reduce salinity.
- Chemicals are added to the soil to reduce salinity / fresh water is flashed into the enclosed land to reduce salinity.
- Oats, rye and sugar beets are planted to improve the pH of the soil and reduce the water.
- The land is dry and ready for use.
- The land is sub-divided and leased to farmers. (8 mks)
- What is a polder?
- Differentiate between land reclamation and rehabilitation.
-
-
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries.
- Fishing refers to all activities involved in the exploitation of fish and other aquatic resources for commercial purposes while fisheries are water bodies where aquatic organisms/ fish are found or reared for exploitation. (2 mks)
- State two categories of fish.
- Pelagic fish
- Demersal fish
- Anadromours fish (2 mks)
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries.
-
- Apart from trawling, name two other methods of deep sea fishing.
- Long line / lining
- Drifting
- Purse seine net / seining (2 mks)
- With the aid of a diagram, describe trawling method of fishing.
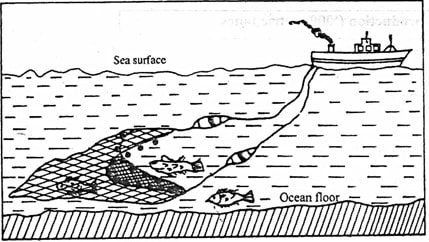
- A bag shaped net is attached to a trawler ship.
- The net is thrown into the water by the trawler ship
- The upper part of the net is kept afloat by corks or floats.
- The lower part of the net has weights to make it sink to the sea bed.
- The net mouth is kept open by outer boards/ head beams.
- The trawler drags or pulls the net along the sea bed.
- After sufficient fish have been caught, the net is hauled into the trawler to empty the fish. (6 mks)
- Apart from trawling, name two other methods of deep sea fishing.
- Problems experienced by Kenyan fishermen in L. Victoria.
- Occurrence of strong winds or thunderstorms which lead to high waves that cause accidental / drowning and destruction of fishing vessels and nets.
- Poor fishing equipments or motor boat engines which are inefficient leading to low catch and delayed landing of fish.
- Poor shortage or preservation facilities which result in deterioration of fish.
- Floating of vegetation like water hyacinth entangle and tear fishing nets which results in loss to fishermen or hinders movement of boats.
- Swampy or marshy parts of the lake shores which make the landing of the fishing boats difficult.
- Insecurity or theft of fishing equipment discourages fishermen.
- Conflict with neighbouring countries makes Kenyan fishermen get arrested which hinders fishing e.g Migingo Island conflict with Uganda. Any 4 x 2 = 8 mks
- The world map below shows major fishing grounds. Use it to answer the following question.
- Name the ocean currents marked:
- E – Cold Labrador Current
- F – Warm Gulf stream current
- G – Cold Peruvian current
- H – Cold Oyashio current
- J – Warm Kuroshio Current Any 1 x 5 = 5 mks
- Explain three factors that favour fishing in Japan.
- The mountainous or rugged nature of the country hinders agricultural activities hence fishing is an alternative economic activity.
- Japan has a large population which provides ready market for fish.
- The Japanese have a long history of sea farming thus they are highly experienced in fishing which promotes the fishing culture.
- The shallow continental shelf allows sunlight to penetrate to the bed for growth of plankton.
- The many off shore islands provide sheltered inlets ideal for the establishment of fishing ports and villages. Any 4 x 2 = 8 mks
- Name the ocean currents marked:
-
-
-
- Define wildlife.
- Wildlife refers to undomesticated animals and plants(fauna and flora) found in their natural habitats. Any 2 x 1 = 2mks
- Distinguish between a game sanctuary and a game ranch.
- A game sanctuary is an area set aside for protection of specific animals or birds/endangered species from extinction while a games ranch is a protected large tracts of land for rearing specific kinds of animals for meat game products.
NB: Both definitions must be correct for the student to score. (4 mks)
- A game sanctuary is an area set aside for protection of specific animals or birds/endangered species from extinction while a games ranch is a protected large tracts of land for rearing specific kinds of animals for meat game products.
- Define wildlife.
-
- Name national parks marked A, B and C.
- A – Kisite Marine park
- B – Amboseli.
- C – Ruwenzori. (3 mks)
- Four factors showing the future of tourism industry in Kenya.
- Aggressive promotion by ministry of Tourism through KTB through exhibitions abroad to promote Kenya as a tourist destination and also marketing is being done within, targeting domestic tourists.
- Lowering of tariffs in hotels, games parks and airports taxes so as to encourage more tourists visits Kenya.
- Strength of the Kenyan shillings depreciation will attract more tourists since most will find it cheaper to visit Kenya.
- Opening up of new areas with untapped attraction potential e.g. around lakes like Baringo, Bogoria, Turkana etc.
- Developing of sustainable tourism e.g. Eco-tourism i.e. tourism that involve conservation of the environment.
- Formation of Kenya National tourism master plan to underscore the need to diversity tourist sources, attractions and opening up of new avenues. Any 4 x 2 = 8 mks
- Explain how the following factors influence wildlife.
- Vegetation
- Different plants and animals are found in different vegetation zones.
- Natural forests are habitat for elephants gorillas, baboons, monkeys, variety of birds and insects.
- Savannah grasslands with acacia trees host a lot of herbivores e.g gazelles, wild beasts.
- Woodland savannah is a home for many animals like gazelles, bees and the carnivores as well as they shelter in the bushes.
- Semi deserts and desert vegetation support hardy animals which can withstand dry conditions e.g. hartebeest, grant gazelle. Any 2 x 2 = 4mks
- Altitude
- Determines the climate and vegetations type.
- Very high mountains e.g. Mt. Kenya and Kilimanjaro are too cold, hence absence of animals.
- Different plant formation are therefore found at different altitudes hence also determine type of animals present there.
- Savannah is found near the base then the forest, bamboo forest and health and moon land. Any 2 x 2 = 4mks
- Vegetation
- Name national parks marked A, B and C.
-
-
-
- What is energy conservation?
- This involve the use of available energy resources in the most efficient manner in order to ensure no wastage. (2 mks)
- Identify three non-renewable sources of energy.
- Petroleum
- Coal
- Natural gas.
- Uranium Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks
- Three advantages of Hydroelectric power as a source of energy.
- Clean and environmentally friendly.
- Is inexhaustible.
- Can be transmitted over long distance using cables.
- Can be put into many use.
- Relatively easy to use i.e. operate from a switch.
- Can be adjusted to any fraction depending on the need.
- Viable source of energy because it has significant production levels.
- Can be used almost throughout the world.
- Construction of dam lead to creation of lakes used for irrigation/recreation/supply of water/fishing etc. Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks
- What is energy conservation?
-
- What are the causes of energy crisis?
- Over-reliance on petroleum and its products.
- High oil prices due to sharp se in oil demand.
- Economic and political sanctions.
- Uncertainties in oil supplies to consumers.
- Rapid depletion of oil reserves.
- Conflict in the Middle East especially between Israel and Palestine.
- Mismanagement of energy.
- Oil production limits set by OPEC.
- Artificial shortages by countries like Russia and USA relying on oil from other countries while conserving their own. Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks
- Explain four measures being taken by the government to conserve energy.
- Developing other alternative sources of energy to reduce overdependence on petroleum especially for industrial and domestic use.
- Creating awareness on the need to conserve energy and use of energy saving devices.
- Increase exploration and exploitation/prospecting by encouraging foreign investors to invest which has several exploitation in Northern Kenya and coast.
- Improve the state of the roads to reduce traffic jams and high consumption.
- Developing and improving public transport reducing the need to use personal vehicles.
- Encouraging the use of other means of transport e.g. motorcycles, bicycles or walk over short distances. Any 4 x 2 = 8 mks
- What are the causes of energy crisis?
- Students from your school carried out a field at Olkaria Geothermal Power Generation station.
- What preparations did they take before going out for the field study.
- Seeking permission from relevant authorities.
- Formulate objectives and hypothesis.
- Conduct a reconnaissance.
- Divide into groups/hold ground discussion.
- Assemble necessary equipment.
- Prepare a questionnaire.
- Prepare a work schedule.
- Read more on the topic.
- Determine methods of collecting and recording data. Any 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Identify the secondary sources of data they would use to prepare for the study.
- Text books.
- Past research papers.
- Photographs
- Journals/magazines. Any 2 x 1 = 2 mks
- What preparations did they take before going out for the field study.
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Murang'a County Mocks 2020/2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

