SUKELLEMO JOINT MOCK
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education
GEOGRAPHY
PAPER 2
2 ¾ HOURS
Instructions to Candidates
- This paper has TWO sections: A and B.
- Answer ALL the questions in section A. In section B answer QUESTION 6 and any other TWO questions from the section.
SECTION A
Answer all the questions from this section
-
- What is Mining? (2mks)
- State three ways in which mining derelicts can be reclaimed. (3mks)
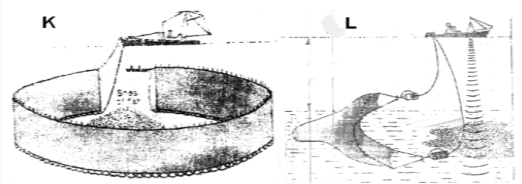
- The diagram below represents some commercial fishing methods
- Name the fishing method marked K and L (2mks)
- Give three reasons why marine fishing is not well developed in the Kenyan coast. (3mks)
-
- Name three marine national parks in Kenya. (3mks)
- Outline three ways game reserves are of benefit to the communities living near them. (3mks)
-
- Apart from air pollution list three other types of pollution. (3mks)
- State two factors which favoured growth of Kisumu as an urban centre. (2mks)
- Highlight four problems that arise from population decline. (4mks)
SECTION B
Answer Question 6 and any other Two from this section.
- Use the photograph provided to answer the questions
-
- Name the activity in the photograph. (1mk)
- Citing evidence, state the time of the day when this photograph was taken. (2mks)
-
- Draw a sketch of the photograph given. On the sketch mark and name the main features. (5mks)
- State three physical conditions that favour the growing of the crop shown in the photograph. (3mks)
-
- Name two counties in Kenya where Coffee is grown in large scale. (2mks)
- Describe systematically the processing of Coffee until it is ready for the market. (6mks)
- Explain how Coffee growing in Kenya and Brazil differ under the following sub-headings;
- Size of land (2mks)
- Land tenure (2mks)
- Marketing (2mks)
-
-
-
- Apart from coniferous forest, name two other types of natural forests. (2mks)
- State two characteristics of coniferous which favour their exploitation. (2mks)
- Explain three factors that favour the growth of natural forests on the slopes of Mt. Kenya. (6mks)
- Use the map of Kenya below to answer questions (i) and (ii).
- Name the forest reserves marked H, J and K. (3mks)
- Explain three factors that favour the growth of natural forest in the area marked L. (6mks)
- Explain three problems facing forestry in Kenya. (6mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between Pelagic fish and Demersal fish. (2mks)
- Name three types of pelagic fish. (3mks)
-
- Describe three conditions for planktons to survive. (3mks)
- Define Fish farming. (2mks)
- Explain four reasons why the government of Kenya is encouraging fish farming. (8mks)
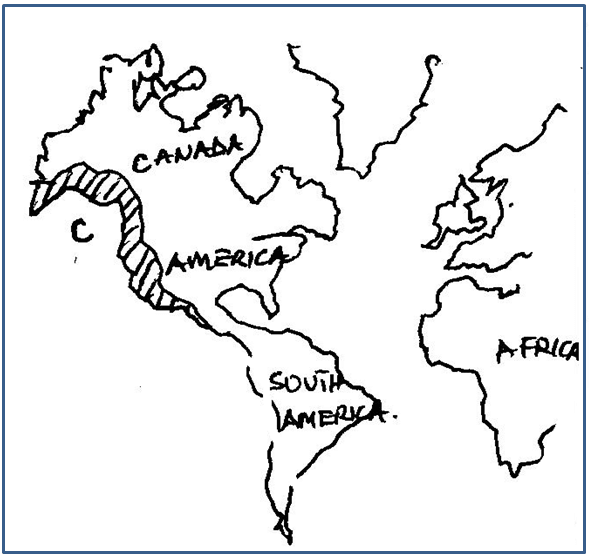
- Use the map below to answer question (i) and (ii).
- Name the fishing ground marked C. (1mk)
- Explain three physical conditions that have favoured the fishing ground named above. (6mks)
-
-
-
- Define Biomass. (2mks)
- Give three examples of Biomass except Biogas. (3mks)
- Give four reasons why the use of Biogas is not widespread. (4mks)
-
- Give four reasons why Nuclear Power is lacking in developing countries. (4mks)
- Explain three basic physical requirements of siting a Hydro Electricity project. (6mks)
- You have been asked to carry out a field study in Loyangalani Wind Power Project.
- How did you prepare for the field study? (3mks)
- State 3 benefits of the project to the surrounding community. (3mks)
-
-
-
- What is Transport? (2mks)
- Identify three modes of transport. (3mks)
-
- Give four advantages of Standard Gauge Railway (SGR) to Kenya. (4mks)
- Name four navigable rivers in Africa. (4mks)
- Explain four problems facing river transport in Africa. (8mks)
-
- Name two canals in Africa. (2mks)
- Define the term Containerisation. (2mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
Answer all the questions from this section
-
- What is Mining? ( 2mks)
- The process of extracting valuable minerals within the rocks of the crust
- The process of extracting valuable minerals within the rocks of the crust
- State three ways in which mining derelicts can be reclaimed.
- Legislation- the government should set up laws to enforce mining companies to
rehabilitate derelict land and ensure proper dumping of waste materials - Government should set up dumping grounds away from human settlements to
maintain land beauty - Introduction of aqua-culture in the open pits
- Fill up the open pits with soil and create agricultural land or landscaping of the
land for homes or settlements - Plant vegetation or trees to make recreation parks and nature trails that attract
tourists e.g. Haller park
- Legislation- the government should set up laws to enforce mining companies to
- What is Mining? ( 2mks)
- The diagram below represents some commercial fishing methods
- Name the fishing method marked K and L (2mks)
- K. Purse Seining
- L. Trawling
- Give three reasons why marine fishing is not well developed in the Kenyan coast (3mks)
- Inadequate capital /high competition by well-established foreign fishing
companies - Insecurity / fear of attack by Somali insurgents / pirates
- Straight coastline does not encourage good fish breeding .
- Pollution by transport ships.
- Limitations of international boundaries.
- Low level of technology / inadequate research.
(3 x 1 =3 marks)
- Inadequate capital /high competition by well-established foreign fishing
- Name the fishing method marked K and L (2mks)
-
- Name three marine national parks in Kenya. (3mks)
- Watamu
- Kisite
- Mpunguti
- Diani
- Malindi
(3 x 1= 3 marks)
- Outline three ways game reserves are of benefit to the communities living near
them. (3mks)- Construction of road networks enable them transport their goods to markets.
- Tourists attracted expand their market for their goods / services earning them
income. - Employment is created earning people incomes
- Social amenities created provided services such as health care and help the local communities.
- Wildlife also give aesthetic value to the environment e.g. elephant
(3x1)=Marks
- Name three marine national parks in Kenya. (3mks)
-
- Apart from air pollution list three other types of pollution. (3mks)
- Water pollution
- Land / soil pollution
- Noise pollution
- Radiation pollution
- State two factors which favoured growth of Kisumu as an urban centre. (2mks)
- Location at the shores of Lake Victoria made if grow as a port .
- Building of Uganda railway made it a terminus thus influx of settlers and traders .
- Kisumu was a regional administrative centre in the
colonial period. - The rich hinterland with mineral / agriculture resources provided raw materials.
- The nearby rivers and Lake Victoria provide fresh water for the industrial / domestic
needs - Well developed means of transport / roads/ airport makes the town easily accessible.
(2 x1= 2 mks)
- Apart from air pollution list three other types of pollution. (3mks)
- State four problems that arise from population decline. (4mks)
- Labour shortages.
- High cost of maintaining ageing population.
- Low market / demand for goods and services.
- Rural depopulation.
- Inadequate use of natural resources.
- Environmental degradation in the neglected regions.
( 4 x 1 = 4 marks)
SECTION B
Answer Question 6 and any other Two from this section.
- Study the photograph provided and use it to answer the questions (a)
-
- Name the activity in the photograph. (1mk)
- Harvesting of wheat.
- Harvesting of wheat.
- Citing evidence, state the time of the day when this photograph was taken. (2mks)
- During midday
- Bright /clear sky
- Short shadows at the bottom of objects
- Name the activity in the photograph. (1mk)
-
- Draw a sketch of the photograph given. On the sketch mark and name the main features. (5mks)
- Frame 1mk- must be the same size as the photograph.
Features - Wheat crop -1mk
- Harvester - 1mk
- Truck/lorry - 1mk
- Farm house/ store-1mk
- Trees - 1mk
- Sky – 1mk
(Any 4 named features and correctly placed =4mks)
- Frame 1mk- must be the same size as the photograph.
- State three physical conditions that favour the growing of the crop in the photograph in Kenya. (3mks)
- The areas receive moderate rainfall/305-1015mm which is sufficient for wheat growing.
- Moderate temperatures between 15-200C to allow maturity of the crop/wheat.
- A warm dry sunny period for ripening and harvesting.
- Deep well drained volcanic soils to provide anchorage for the wheat stalks.
- Gently sloping slopes for proper drainage and mechanization.
- Wheat growing areas are of high altitude to provide cool conditions.
- Draw a sketch of the photograph given. On the sketch mark and name the main features. (5mks)
-
- Name two counties in Kenya where Coffee is grown in large scale. (2mks)
- Kiambu
- Nyeri
- Meru
- Embu
- Kericho
- Muranga
- Kirinyaga
- Kisii/Nyamira
- Describe systematically the processing of Coffee until it is ready for the market.(6mks)
- From the collection centres the good berries are taken to the factory.
- At the factory berries are weighed again, and then put in large tanks with water to remove the outer cover- pulping.
- The beans are heaped in a tank to ferment for 12-24hrs
- After that beans are washed in clean water.
- They are then put on wire mesh in the open sun for curing for almost one week. This reduces moisture between12-13%.
- The beans are put in a drying machine that reduces moisture to optimum of 10%
- After curing the beans are put in a machine that peels off the two layers of the inner husks.
- The beans are then winnowed and graded.
- The beans are the sorted according to size and quality and then packed in 60kgs bags for shipment.
- Name two counties in Kenya where Coffee is grown in large scale. (2mks)
- Explain how Coffee growing in Kenya and Brazil differ under the following subheadings;
- Size of land (2mks)
- In Kenya, the Coffee is grown smaller farms both in large-scale and small-scale while in Brazil it is grown in large extensive farms.
- The large-scale farms in Kenya are called plantations/estates while in Brazil the large-scale called fazcendas.
(Any 1x2=2mks)
- Land tenure (2mks)
- In Kenya the farms are owned by individuals and family members and casual labourers provide labour while in Brazil the fazcendas are owned by rich land owners but tenants work for the rich owners. (1x2=2mks)
- In Kenya the farms are owned by individuals and family members and casual labourers provide labour while in Brazil the fazcendas are owned by rich land owners but tenants work for the rich owners. (1x2=2mks)
- Marketing (2mks)
- In Kenya marketing is done by cooperatives and agents while in Brazil marketing is done by companies.
- In Brazil the marketing system is efficient with financial stability while in Kenya the marketing system is less efficient and depends on auctions.
- Co-operatives sell coffee to the Kenya Planters Cooperative Union (KPCU) who passes to Coffee Board of Kenya (CBK) while in Brazil companies sell directly to world market.
- CBK sells coffee through organized auction system while in Brazil; the Brazillian Speciality Coffee Association auctions the coffee through the internet in conjunction with Speciality Coffee Association of America.
- In Kenya coffee is exported to Britain, Germany, and Norway Japan & North America while in Brazil coffee is sold to same countries and also sold locally within Brazil.
(Any 1x2=2mks)
- Size of land (2mks)
-
-
-
- Apart from coniferous forest, name two other types of natural forests. (2marks)
- Tropical hardwood forests
- Temperature hardwood forests
- Mixed forests
- Bamboo / montane forests
- Tropical monsoon forest
- Mangrove forests
- Mediterranean forest
- State two characteristics of coniferous which favour their exploitation. (2marks)
- the trees are light in weight
- the trees occur in pure stand
- there is little undergrowth
- the trees have straight trunk
(Any2x1=2mks)
- Apart from coniferous forest, name two other types of natural forests. (2marks)
- Explain three factors that favour the growth of natural forests on the slopes of Mt. Kenya. (6marks)
- The area receives high rainfall 1000- 22000 mm throughout the year which encourages continuous growth of trees.
- The area has deep fertile volcanic soils that allow the roots to penetrate deep into the ground to support the trees
- The area has well drained soil thus there is no water logging which can choke plants and interfere with their growth
- The area has moderate cool condition/ climate is ideal for the growth of a variety of trees.
- The area is a gazzetted forest reserve/ settlement and cultivation are prohibited hence allowing forests to grow without interference
- The steep slopes discourages human activities thus enabling forests to thrive well
(Explanation 1 mk, Factor 1 mk)
- Use the map of Kenya below to answer questions (i) and (ii).
- Name the forest reserves marked H, J and K. (3 marks)
- H-Mt. Elgon
- J- Mt Kenya
- K-Arabuko sokoke
- Explain three factors that favour the growth of natural forest in the area marked L. (6 marks)
- The area receives high rainfall that encourages growth of trees
- The area has deep well drained soils that allow the roots to penetrate deep into the ground
- The area has moderate to high temperatures /that allow growth of variety of trees.
- The area is gazette forest hence the settlement /cultivation is prohibited
- Some areas are steep which discourages settlement and allow forest growth
- Enforcement of laws allow re-establishment of forests
- Name the forest reserves marked H, J and K. (3 marks)
- Explain three problems facing forestry in Kenya. (6 marks)
- Rapid increase in population has led to encroachment into forest land hence destruction of forests
- Occurrence of forest fires which have led to the destruction of large areas under forest
- Illegal logging/indiscriminate cutting of trees thereby reducing /depleting indigenous tree species
- Attacks by pest/diseases has led to destruction of valuable tree species
- Some wild animals debark/ trample /damage trees
- At times, the government allocates land to private developers /degazzetment thus reducing
- land under forest
- Prolonged drought leads to drying of some trees
-
-
-
- Differentiate between pelagic fish and demersal fish. (2mks)
- Pelagic fish live near the surface or shallow depth seas while demersal fish live at or close to the bottom of the sea.
- Pelagic fish live near the surface or shallow depth seas while demersal fish live at or close to the bottom of the sea.
- Name three types of pelagic fish. (3mks)
- herring
- mackerel
- tuna
- sardines
- Differentiate between pelagic fish and demersal fish. (2mks)
-
- Describe three conditions which favour planktons to survive best. (3mks)
- shallow water
- this will allow high to penetrate for planktons to survive.
- cool waters
- where warm and cold current meet is ideal conditions for plankton
- Land derived mineral
- minerals like salts from land favour plankton growth
- Define fish farming. (2mks)
- is the artificial rearing or breading of fish of desired species in a controlled area e.g ponds, dams rice fields
- is the artificial rearing or breading of fish of desired species in a controlled area e.g ponds, dams rice fields
- Describe three conditions which favour planktons to survive best. (3mks)
- Explain four reasons why the government of Kenya is encouraging fish farming. (8mks)
- Provides food security because it contributes to meeting demand for food rich in protein
- Fish farms create employment opportunities; hence source of income which improves standard on living
- Fish caught may be exported thus earning foreign exchange which is invested in other sectors
- Fish farms lead to the establishment of related industries such as fish feeds, net making, fertilizers, canning etc leading economic growth
- They assist in the conservation of rare species which might face danger of depletion
- Fish farms are easier to manage and exhaustion can be controlled through restocking hence no damage of depletion
-
- Name the fishing ground marked c. (1mk)
- North East Pacific fishing ground
- North East Pacific fishing ground
- Explain three physical conditions that have favoured the fishing ground named abo (6mks)
- cool conditions
- the cold California current verges upon the warm North Pacific current resulting to cool temperatures for plankton
- the coast has many fields which provides good breeding ground or sheltered coasts for ports
- the coastal region is a rugged landscape that discourages Agric making fishing the alternative economic activity
- large continental shelf provides enough sunlight for plunktons to flourish
Any 3 x 2 = 6 mks
- Name the fishing ground marked c. (1mk)
-
-
-
- Define Biomass. (2mks)
- Energy derived from organic matter e.g trees crop residue waste etc
- Energy derived from organic matter e.g trees crop residue waste etc
- Give three examples of Biomass except Biogas. (3mks)
- Fuel wood
- Charcoal
- Alcohol
- Give four reasons why the use of Biogas is not widespread. (4mks)
- it is restricted to areas where zero grazing is practised due to availability of the raw material
- it is tedious work
- costs a lot to install thus discouraging many
- animals graze over a wide area hence it is not possible to collect dung
Any 4 x 1 = 4mks
- Define Biomass. (2mks)
-
- Give four reasons for lack of nuclear power in developing countries. (4mks)
- inadequate skilled personnel in nuclear energy
- limitation and supervision by big nuclear power producers
- nuclear plants require heavy capital investment
- concerted efforts made by conservationists have helped check proliferation of nuclear stations
- nuclear plants take too long to built
- nuclear reactors have a short life span of 25 years
Any 4 x 1 = 4mks
- Explain three basic physical requirements of siting a Hydro Electricity project.(6mks)
- a large volume of water sufficient and constant to enable continuous production of electricity
- sleep gradient to provide a high head to turn the turbines
- a firm rock base to provide a strong foundation to support the dam
- a deep gorge to provide a large space for a reservoir
- presence of a narrow gorge behind the dam which minimizes the cost of construction of the dam
- presence of impervious rocks to prevent water see page
- Give four reasons for lack of nuclear power in developing countries. (4mks)
- You have been asked to carry out a field study in Loyangalani wind power project.
- How did you prepare for the field study. (3mks)
- ask for permission
- carry out a reconnaissance
- draw the objectives and the hypothesis
- hold discussion
- Identify suitable methods of collecting data
- Read relevant material
- draw a route map
- collecting relevant material
- prepare the work schedule
- prepare a questionnaire
- State 3 benefits of the project to the surrounding community. (3mks)
- they are able to get cheap power
- the energy is clean so does not pollute the environment
- land between the mills can still be used for other purposes e.g Agriculture
Any 3 x 1 = 3mks
- How did you prepare for the field study. (3mks)
-
-
-
- What is Transport? (2mks)
- The physical carriage and movement of goods and people from place to place
- The physical carriage and movement of goods and people from place to place
- Identify three modes of transport. (3mks)
- land
- water
- air
- What is Transport? (2mks)
-
- Give four advantages of stand Gauge Railway (SGR) to Kenya. (4mks)
- less prone to accidents
- more efficient because it operates on fixed time schedules thus enable passengers to plan their time
- has a large carrying capacity hence suitable to transport heavy and bulky goods which less expensive
- follows a fixed schedule hence is not affected by traffic congestion
- has low maintenance cost because once constructed it does not require frequent repairs like roads
Any 4 x 1 = 4mks
- Name four Navigable rivers in Africa. (4mks)
- R- Nile
- Ogoowe
- parts of Congo river
- upper sections of R. Niger
- parts of R. Gambia
- Give four advantages of stand Gauge Railway (SGR) to Kenya. (4mks)
- Explain four problems facing river transport in Africa. (8mks)
- silting at the river mouths hinder the development of ports and make rivers shallow
- presence of floating vegetation e.g sudd in Sudan hinders movement of boats
- presence of Rapids and water falls hinder the vessels
- shallow narrow fast flowing water is not suitable for navigation
- season fluctuation of water in the rivers as they pass through different climatic regions hinders movement
- some rivers pass through unproductive areas hence it is uneconomical to develop
- inadequate technology hinders the process of developing river transport
-
- Name two canals in Africa. (2mks)
- Tonglei Canal in Sudan
- Suez Canal in Egypt
- Define the term containerisation. (2mks)
- The packing of goods in large standard sized box-like metallic structures in factory sealed and transported to the consumers
- Name two canals in Africa. (2mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Sukellemo Joint Mock 2020/2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students