INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
- This paper has two sections A and B
- Answer ALL the questions in section A. In section B answer questions 6 and any other TWO questions.
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section.
-
- What is agroforestry? (2 marks)
- Give three reasons why agroforestry is encouraged in Kenya. (3 marks)
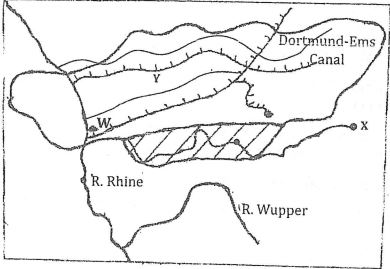
- Study the map of the Ruhr industrial region and use it to answer the questions that follow,
-
- Name the river marked X. (1 mark)
- The canal marked Y. (1 mark)
- State three factors which influenced the location of the iron and steel industry in Ruhr region of Germany. (3 marks)
-
-
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation. (2 marks)
- State three ways in which the government of Kenya is trying to control locust invasion in Kenya.(3 marks)
-
- Name two renewable sources of energy. (2 marks)
- State three conditions necessary for the formation of petroleum. (3 marks)
- State five factors that have led to the growth of Thika as an industrial town. (5 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
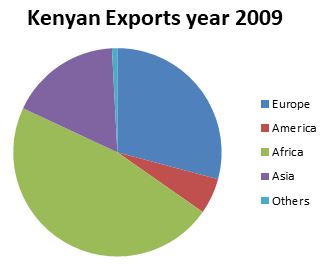
- The table below shows Kenyan exports by destination in Ksh. Million between 2008 - 2010. Use it to answer question (a).
Region/year 2008 2009 2010 Europe 94,685 100,975 109,422 America 22,055 18,961 24,380 Africa 116,995 162,732 188,914 Asia 57,241 59,236 81,600 Others 206 3,044 5,225 -
- In which year was Kenya's exports highest? (1 mark)
- Using a radius of 5cm, draw a pie-chart to represent the data on Kenya's exports in 2009.(8 marks)
- State two advantages of using pie charts to represent data. (2 marks)
- Give reasons why horticultural farming is more developed in the Netherlands than in Kenya.
(6 marks) - Explain the measures that the government of Kenya has taken to promote horticultural farming in Kenya. (8 marks)
-
-
- Name two by-products obtained when crude oil is refined. (2 marks)
- State three ways in which mining derelicts can be rehabilitated. (3 marks)
-
- Give two uses of Gold. (2 marks)
- Identify three problems facing gold mining in South Africa.[3 marks)
- Describe the processing of gold in South Africa. (5 marks)
-
- Name two alluvial mining methods. (2 marks)
- Explain four ways in which soda ash mining contributes to the economy of Kenya.
(8 marks)
-
- Name two counties in Kenya where wheat is grown in large scale. (2 marks)
- State five physical conditions that favour wheat growing in the Kenya. (5 marks)
-
- Describe coffee growing in Kenya from planting to harvesting. (6 marks)
- State four problems facing coffee farming in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Explain four measures taken by the government of Kenya to improve beef cattle farming.
(8 marks)
-
- Define the term fisheries. (2 marks)
-
- Give three methods used to preserve fish. (3 marks)
- State five ways in which the Government of Kenya is promoting the fishing industry in the country. (5 marks)
-
- Describe drifting method of fishing. (4 marks)
- Explain three human factors which have favoured the fishing industry in Japan. (6 marks)
- Give five differences between fishing in Kenya and Japan. (5 marks)
-
-
- Define international trade. (2 marks)
- Explain four benefits that Kenya derives from international trade. (8 marks)
-
- State five reasons why common market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) was formed. (5 marks)
- List two major imports to Kenya from China. (2 marks)
- Explain four problems facing trade in Kenya. (8 marks)
-

Marking Scheme
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section.
-
- What is agroforestry? (2 marks)
- It is the deliberate growing of trees and crops/ keeping of animals on the same piece of land.
- Give three reasons why agro-forestry is encouraged in Kenya. (3 marks)
- To ensure continuous supply of wood fuel/ to conserve forests
- provide raw materials for industries
- To provide fruits/food for human consumption
- To provide fodder for animals
- Trees are a source of income to farmers when converted to timber.
- Trees act as windbreakers/provide shade for young plants.
- For medicinal value
- Create micro-climate.
- What is agroforestry? (2 marks)
- Study the map of the Ruhr industrial region and use it to answer the questions that follow,
-
- Name the river marked X. (1 mark)
- River Ruhr
- The canal marked Y. (1 mark)
- Rhine-Herne Canal
- Name the river marked X. (1 mark)
- State three factors which influenced the location of the iron and steel industry in Ruhr region of Germany. (3 marks)
- Availability of coal/iron ore/limestone in the Rhine valley.
- River Rhine/Ruhr/ Wopper/lippe/Emscher provided water for cooling machines in industries.
- The region is served by navigable rivers /Rhine/Ruhr/Emscher/ Lippe provided cheap means of transporting bulky raw materials and finished products.
- Presence of rich companies/Kruff families provided capital for the development of the industry.
- The dense/affluent population in Central and Western Europe provided ready market for iron and steel.
- The large local population had acquired skills on iron working.
-
-
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation. (2 marks)
- Land reclamation is the process of converting less productive land into more productive state for agricultural or settlement purposes while Land rehabilitation is the process of restoring damaged land back to a useful state.
- State three ways in which the government of Kenya is trying to control locust invasion in Kenya.(3 marks)
- Use of pesticides/bio-pesticides/chemical control
- Remote sensing/satellite imagery for easy location of locust breeding areas /infestation.
- Training of specialists to conduct surveys and control infestation
- Scaring the locusts through shouting
- Trapping the locusts for food/feeding
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation. (2 marks)
-
- Name two renewable sources of energy. (2 marks)
- Wind
- Wood
- Biogas
- Water
- Geothermal steam
- Sun
- Draught animals
- State three conditions necessary for the formation of petroleum. (3 marks)
- Compression of the remains of flora and fauna due to folding of the layers of rocks
- Deposition of other layers of rocks/non-porous/over the remains of flora and fauna.
- Presence of porous rocks
- Presence of flora and Fauna over a long period of time.
- Name two renewable sources of energy. (2 marks)
- State five factors that have led to the growth of Thika as an industrial town. (5 marks)
- Expansive flat land for setting industries
- The government policy of decentralization of industries has encouraged the growth.
- Nearness to Nairobi has led to industrial interdependence/ ease of access to supplies.
- The rich agricultural winter land has provided raw materials for industries
- The high population around Thika provides ready market for the industrial products.
- The abundant supply of water from river Chania which is used for industrial purposes
- The roads( Thika Super Highway)/ railway links/ accessibility have made it easy to receive raw materials and sell the industrial products
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
- The table below shows Kenyan exports by destination in Ksh. Million between 2008 - 2010. Use it to answer question (a).
Region/year 2008 2009 2010 Europe 94,685 100,975 109,422 America 22,055 18,961 24,380 Africa 116,995 162,732 188,914 Asia 57,241 59,236 81,600 Others 206 3,044 5,225 -
- In which year was Kenya's exports highest? (1 mark)
- 2010
- Using a radius of 5cm, draw a pie-chart to represent the data on Kenya's exports in 2009.(8 marks)
Total = 100,975 + 18,961 + 162,732 + 59,236 + 3,044
=344,948
Europe 100,975 × 360° =105.38 =105°
344,948
America 18,961 × 360° =19.78 =20°
344,948
Africa 162732 × 360° =169.83 =170°
344,948
Asia 59236 × 360° = 61.82 =62°
344,948
Others 3044 × 360° =3.17 =3°
344,948
Title-1
Calculation-3
Segment-3 - State two advantages of using pie charts to represent data. (2 marks)
- Easy to read/interpret.
- Allows for comparison to be made.
- Easy to draw/ construct
- Clear visual impression.
- In which year was Kenya's exports highest? (1 mark)
- Give reasons why horticultural farming is more developed in the Netherlands than in Kenya.
(6 marks)- Well organized marketing systems/ cooperatives which are favourable for Horticultural farming
- Netherlands has a higher urban population which is also affluent than Kenya, thus higher demand for both local and foreign horticultural crops than in Kenya
- Farmers in Kenya have more access to capital needed for horticultural farming than in Kenya
- There is more advanced and appropriate technology in Netherlands which has enhanced horticultural farming than in Kenya.
- Netherlands has highly skilled labour force for the production and handling of horticultural products than in Kenya resulting in high production.
- Explain the measures that the government of Kenya has taken to promote horticultural farming in Kenya. (8 marks)
- Setting up the Kenya Horticulture Development Project to help the farmers with advice as well as market their crops.
- Setting up a Horticultural Research station to improve on crops in order to increase yields
- The government has trained and posted extension officers to the horticultural -crop growing areas to assist the farmers with advice.
- The government has entered into trade agreements with foreign countries especially European Union in order to ensure market for the Kenyan products.
- Has improved air transport, thus enhancing the transported goods.
- The Government has improved the roads in the Rural areas where horticulture is practised in order to ensure crops are transported in time, thus reduce wastage.
- Has set up Export Promotion Council to help market the Country's horticultural products.
- Maintained good relation with foreign government who consequently assist the horticultural farmers with finances and technical advice (e,g Germany)
-
-
- Name two by-products obtained when crude oil is refined. (2 marks)
- Bitumen/Tar/Asphalt
- Lubricant/grease
- Sulphur
- Wax
- Resin/petro-chemicals
- State three ways in which mining derelicts can be rehabilitated. (3 marks)
- Planting tress
- Creating a park to attract tourists
- Introducing aquaculture
- Refilling the holes
- landscaping for settlement/farming
-
- Give two uses of Gold. (2 marks)
- Used in dentistry as Gold teeth fillings and tooth caps
- Used to make medals
- Used to make jewellery/ornaments
- Used as a basis of the world currency/medium of exchange
- Used in chemical factories to make compounds for photographic materials
- Used to make gold paint for cookery such as spoons
- Identify three problems facing gold mining in South Africa.[3 marks)
- Expensive to mine for lying deeply.
- large capital is required to start mines
- Problem of removal of underlying water
- Inadequate supply of fresh water on the surface in the mining areas
- Accidents resulting from collapsing of mine roofs
- Low gold content in the ore.
- Complication of mining by folds and faults in the crust.
- Industrial unrest.
- Describe the processing of gold in South Africa. (5 marks)
- Ore is crushed to a fine powdery dust
- Ore is mixed with water until it becomes fluid mud
- Cyanide is added to dissolve gold.
- The fluid is runoff with gold dissolved leaving behind waste salts.
- Zinc dust is added to filter gold for solidification.
- Gold sinks as it is dense.
- Gold is smelted and cast ingots/bows
- Give two uses of Gold. (2 marks)
-
- Name two alluvial mining methods. (2 marks)
- Panning
- Dredging
- hydraulic mining
- Explain four ways in which soda ash mining contributes to the economy of Kenya.
(8 marks)- Soda ash is exported to earn foreign exchange which is used in the economic development of a country.
- It creates employment opportunities to Kenya, which raises the standard of living of the people/earn more income.
- Soda ash provides raw materials to the manufacturing industries leading to industrialization/glass manufacture.
- It has led to the development of social amenities in the area/hospitals and schools hence inproving the living standards.
- Has lead to the development of Magadi town.
- It has supported pastoralists by providing water for their animals/domestic use.
- It provides revenue for the country through taxation.
- Has led to the growth of local and foreign tourism.
- Has led to the development of infrastructure e.g railway line from Konza to Lake Magadi.
- Name two alluvial mining methods. (2 marks)
- Name two by-products obtained when crude oil is refined. (2 marks)
-
- Name two counties in Kenya where wheat is grown in large scale. (2 marks)
- Uasin Gishu County
- Transzoia County
- Narok county
- Laikipia County
- Nakuru County
- State five physical conditions that favour wheat growing in the Kenya. (5 marks)
- Moderate rainfall/500 mm to 1270mm to enhance the growth
- Warm conditions/15°C to 20°C to facilitate growth /maturity of wheat.
- Gentle sloping /undulating landscape for mechanized cultivation.
- A warm/dry/sunny spell for ripening and harvesting
- Volcanic soils to sustain high production
- Well drained soils
- Frost free conditions.
- High altitude
-
- Describe coffee growing in Kenya from planting to harvesting. (6 marks)
- Coffee seeds are planted in a nursery where they germinate and left to stay for 6 months.
- The seeds are watered regularly.
- Shade is erected above the nursery bed.
- Holes are dug in the field 3m apart.
- Seedlings are transplanted for about 6 months to 1 year.
- Manure is applied.
- Mulching is also done by laying dry leaves around the stem.
- The seedlings are pruned annually.
- Regular weeding/herbicides are applied.
- Spraying of pesticides to control pests is done regularly.
- From the 5th year, the trees attain maturity and the coffee beans are ready for harvesting.
- Harvesting involves manual plucking of red/ ripe berries leaving the green ones to ripen.
- State four problems facing coffee farming in Kenya. (4 marks)
- The crops is attacked by pests e.g ladybird.
- Diseases e.g leaf rust/ coffee berry disease/leaf rot.
- Fluctuation of coffee prices in the world market.
- Poor road network causing delays in transporting of yields.
- Mismanagement of coffee cooperatives.
- Inadequate rainfall in some seasons hence low yield.
- Inaccessibility to credit/inadequate capital.
- Expensive pricess of farm inputs/fertilizers/pesticides.
- Delayed payments hence demoralizing the farmers.
- Poor marketing strategies.
- Low payment hence discouraging the farmers.
- Describe coffee growing in Kenya from planting to harvesting. (6 marks)
- Explain four measures taken by the government of Kenya to improve beef cattle farming.
(8 marks)- The government encourages the cross breeding of traditional cattle breeds with exotic ones thus improve the quality of the beef cattle.
- It has constructed and improved roads to make services accessible to farmers/ make transportation of beef cattle to markets easier.
- It strengthens community education to teach beef cattle farmers better livestock management.
- It has sunk boreholes/ dug wells/ constructed dams to provide water for the beef cattle.
- Kenya Meat Commission has been revived. This helps to buy beef cattle from farmers for slaughter.
- It encourages the replacement of the course grass with nutritious pasture to improve the quality of the beef cattle.
- Name two counties in Kenya where wheat is grown in large scale. (2 marks)
-
- Define the term fisheries. (2 marks)
- Fisheries are water bodies where aquatic organisms/fish are reared for exploitation.
-
- Give three methods used to preserve fish. (3 marks)
- Salting.
- Canning.
- Sun drying.
- Smoking.
- Freezing.
- State five ways in which the Government of Kenya is promoting the fishing industry in the country. (5 marks)
- Discouraging entry of foreign fishermen into the Kenyan waters.
- Encouraging formation of fishing cooperatives.
- Restocking overfished areas.
- Encouraging fish farming/facilities/finances establishments of fish farms in different parts of the country.
- Banning of indiscriminate fishing/enforcing the use of standardized nets/ seasonal ban on fishing to allow breeding/licensing.
- Formation/establishing research stations.
- Controlling water hyacinth.
- Dredging of salted lakes.
- Controlling water pollution.
- Establishment of ministry of fisheries.
- Out lawing use of poor fishing methods.
- Give three methods used to preserve fish. (3 marks)
-
- Describe drifting method of fishing. (4 marks)
- A drift net is used.
- The net is attached to drifter by use of rope /warp rope.
- The net is kept vertically in the sea like tennis net to a few meters below water surface.
- The net is fixed with floaters on the upper edge and weight below to help it stretch.
- The net is cast in the sea from the drifter and placed a few meters below the water surface where the fish swim in large shoals.
- As the fish attempts to swim through the net, They are entangled by their gills hence unable to move backwards/forwards.
- After sufficient fish has been caught, the net is hauled onto the drifter to empty the fish.
- Explain three human factors which have favoured the fishing industry in Japan. (6 marks)
- Japanese have advanced technology that is used in fish processing /preservation of fish.
- Japan has a large population which provides ready local market for fish
- Japanese have a long history of sea fishing thus are highly experienced in fishing.
- Adequate capital which has enabled Japan to purchase modern fishing equipment needed for deep sea fishing.
- Highly developed research in fish breeding techniques has lead to high quality fish species.
- Describe drifting method of fishing. (4 marks)
- Give five differences between fishing in Kenya and Japan. (5 marks)
- In Japan, extensive research on fishing has been done while in Kenya little research on fishing has been done.
- Japan has cool climatic factors hence preservation is efficient while Kenya has hot climate thus preservation is poor.
- Japan use well developed and advanced fishing methods e.g ships while Kenya use traditional methods of fishing and vessels e.g canoes.
- Japan has more than 3000 islands or fishing villages while Kenya has about 300 fishing villages.
- Japan has expensive fishing waters while Kenya has limited fishing waters.
- In Japan fishing vessels are owned by large co-operatives while in Kenya mostly fishing vessels are owned by individuals.
- In Japan, inland fishing is seasonal while in Kenya inland fishing is full time in some areas.
- In japan both marine and inland fishing are well developed while in Kenya, marine fishing is yet to be developed and contributes only about 10% of the total catch.
- In Japan there is large market within the country and from abroad while in Kenya, there is small market from within and from abroad.
- Japan has extensive continental shelf,shallow waters and presence of cold and warm currents hence rich in planktons while Kenya has a narrow continental shelf and the offshore areas of the Indian Ocean are too deep for the growth of plankton.
- Japan has indented coastline with many natural harbours while the Kenyan coastline is fairly straight with few indentation and hence unideal for fishing.
- Define the term fisheries. (2 marks)
-
-
- Define international trade. (2 marks)
- Is the exchange of goods and services between different countries.
- Explain four benefits that Kenya derives from international trade. (8 marks)
- Kenya earns foreign exchange which enables it to import goods from other countries.
- Kenya gets a ready market for its surplus goods.
- Kenya is able to import what it needs from other countries to satisfy its people.
- Trade encourages specialization which leads to production of high quality goods in some industries in Kenya hence earn high income.
- Trade has enhanced co-operation between Kenya and the trading partners through interaction.
- Employment opportunities have been created in the micro functioning service industries that handle imports and exports.
- Transport and communication network in Kenya has been improved to facilitate the movement of trade goods.
- Demand for Kenya's exports have led to the expansion of the industries that produce those goods.
- Define international trade. (2 marks)
-
- State five reasons why common market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) was formed. (5 marks)
- To promote trade among member state.
- To establish a larger market for the goods produced in the region.
- To acquire greater, higher bargaining power with other trading blocks in the niche.
- To encourage member countries to reduce duties charged on goods entering their countries from COMESA member states.
- To remove trade barriers among member states.
- To create regional specialization in order to improve the quality of goods.
- To create political co-operation among member states
- List two major imports to Kenya from China. (2 marks)
- machinery/electronic appliances.
- Expatriates
- Pharmaceuticals.
- Textiles
- Soya beans
- Crude oil
- Iron ores.
- Petroleum gas
- Gold.
- State five reasons why common market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) was formed. (5 marks)
- Explain four problems facing trade in Kenya. (8 marks)
- Insecurity in the country discourages investors/traders incur great losses.
- The high fuel prices increase production/transport costs leading to increased prices of goods/low demand for goods.
- Exports are mainly raw material agricultural products which are lowly priced hence earning little revenue for the country.
- Cheap imported goods create unfair competition for some local products leading to reduction in the production of such goods/closure of some industries.
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Moi Kabarak High School Mock 2020/2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students