SUKELLEMO JOINT MOCK
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education
BUSINESS STUDIES
PAPER 1
2 HOURS
Instructions to Candidates
- This paper consists of six questions
- Answer any five questions. All questions carry equal marks
-
- Outline five differences between a public limited company and a parastatal(10 marks)
- The following details were ectractred from the books of Juhudi Retailers
Invoices Issued:
Prepare Journal entries and show the posting of the totals to the relevant ledger accounts(10 marks)2017 Sh July 1 Mwango 120,000 July 4 Nyambura 60,000 July 10 Mwango 150,000 July 25 Nyambura 80,000 Invoices Received: 2017 Sh July 1 Ndaru 220,000 July 3 Ndaru 90,000 July 14 Omari 40,000 July 28 Ndaru 110,000 Credit Notes Sent 2017 Sh July 8 Mwango 20,000 July 26 Nyambura 16,000 Credit Notes Received 2017 Sh July 11 Ndaru 30,000 July 27 Ndaru 10,000
-
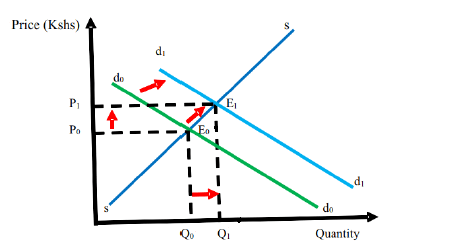
- By use of a diagram show the effect of a shift of the demand curve from the left to right on equilibrium price and quality. (10 marks)
- Discuss five benefits of filing office documents to an organization. (10 marks)
-
- Give five limitations of using per capita income to compare the standard of living in different countries. (10 marks)
- Explain five ways in which a country may suffer as a result of being a member of a trading bloc. (10 marks)
-
- Explain five benefits Kenya would derive from a well-drawn development plan. (10 marks)
- Highlight five reasons why the government may find it necessary to participate in business activities. (10 marks)
-
- On 1st January 2013, Chui has Sh. 35,000 in cash and a bank overdraft Sh. 12,00. During the month, the following transaction took place:
Jan 2 Sold goods for Sh. 8,000 cash.
Jan 5 Received a cheque for Sh. 40,000 from Mwirigi Enterprises
Jan 8 Paid Sh. 6,000 cash to Bundi.
Jan 10 Deposited Sh. 13,000 into the bank from cash till
Jan 14 Withdrew Sh. 5,000 from bank for personal use.
Jan 15 Paid wages Sh. 4,000 in cash.
Jan 18 Received Sh. 25,000 cash from Kazure.
Jan 24 Cash sales paid directly into the bank Sh. 45,000
Jan 26 Paid wages Sh. 2,400 in cash
Jan 27 Withdrew Sh. 21,000 from bank for business use
Jan 28 Bought furniture Sh. 19,000 in cash.
Jan 29 Paid insurance Sh. 17,000 by cheque.
Jan 30 Deposited all the cash into the bank leaving a balance of only Sh.3,000
Prepare a two-column cashbook and balance it off. (10 marks) - Explain five circumstances under which a buyer would prefer buying goods under credit purchase rather than hire purchase terms. (10 marks)
- On 1st January 2013, Chui has Sh. 35,000 in cash and a bank overdraft Sh. 12,00. During the month, the following transaction took place:
-
- Give four ways in which an entrepreneur contributes to produce goods.(8 marks)
- The following trial balance was extracted from the books of Baite Traders as at 31st August 2015
Additonal information:Dr Cr Sh Sh Sales 350,000 Purchases 160,000 Cash at the bank 290,000 Returns inwards 5,000 Carriage inwards 20,000 Carriage outwards 14,000 Salaries and wages 10,000 Debtors 56,000 Creditors 90,000 Stock 35,000 Machinery 265,000 Rent 25,000 Discounts received 18,000 Light and heating 12,000 Buildings 240,000 Advertising 13,000 Drawings 30,000 Capital 667,000 1,150,000 1,150,000 - Stock on 31st August 2015 was valued at Sh. 50,000
- Prepare trading, profit and loss account for the year ended 31st August 2015 and a balance sheet as at that date.(12 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Outline five differences between a public limited company and a parastatal(10 marks)
Public Limited Company Parastatal -Owned by private people who own shares
-Directors are elected by shareholders
-Main objective is to make profit
-Profit realised belongs to shareholders
-Initially financed through issues of shares.-Fully owned by government
-Directors are appointed by government
- Main objective is to offer essential goods and services
-Profit realised belongs to the state.
-Initially financed by state or though state guarantee - The following details were ectractred from the books of Juhudi Retailers
Invoices Issued:
Prepare Journal entries and show the posting of the totals to the relevant ledger accounts(10 marks)2017 Sh July 1 Mwango 120,000 July 4 Nyambura 60,000 July 10 Mwango 150,000 July 25 Nyambura 80,000 Invoices Received: 2017 Sh July 1 Ndaru 220,000 July 3 Ndaru 90,000 July 14 Omari 40,000 July 28 Ndaru 110,000 Credit Notes Sent 2017 Sh July 8 Mwango 20,000 July 26 Nyambura 16,000 Credit Notes Received 2017 Sh July 11 Ndaru 30,000 July 27 Ndaru 10,000
Sales Journal Date Details Invoice No. l.f Amount 20 -7
July 1
July 4
July 10
July 25
July 31
Mwango
Nyambura
Mwango
Nyambura
total posted to G.L(Cr)SH
120,000
60,000
150,000
80,000
410,000
Purchases Journal Date Details Invoice No. l.f Amount 20 -7
July 1
July 3
July 14
July 28
July 31
Ndanu
Ndanu
Omari
Ndanu
Total posted to G.LSh
220,000
90,000
40,000
110,000
460,000
Returns Inwards Journal Date Details Invoice No. l.f Amount 20 -7
July 8
July 26
July 31
Mwango
Nyambura
Total posted to G.L(dr)Sh
20,000
16,000
36,000
Returns Outwards Journal Date Details Invoice No. l.f Amount 20-7
July 11
July 27
July 31
Ndaru
Ndaru
Total posted to G.L(cr)Sh
30,000
10,000
40,000
Sales Account Dr Cr . . . . . . 20-7
July 31
Sundry DebtorsSh
410,000
Purchases Account Dr Cr 20 -7
July 31
Sundry creditorsSh
460,000. .
. . . .
Returns Outwards Account Dr Cr . . . . . . 20-7
July 31
Sundry creditorsSh
40,000
Returns Inwards Account Dr Cr 20 -7
July 31
Sundry debtorsSh
36,000. . . . . .
- Outline five differences between a public limited company and a parastatal(10 marks)
-
- By use of a diagram show the effect of a shift of the demand curve from the left to right on equilibrium price and quality. (10 marks)
- Discuss five benefits of filing office documents to an organization. (10 marks)
- Filing of documents in an office makes it tidy, otherwise it would make an office disorganised if documents are thrown all over the place without any order.
- It makes it possible for an organization to make references when necessary. In case the documents are not kept, it may be difficult for information to be accessed when needed at some future date.
- Documents can easily get lost or stolen if not filed. Filing ensures that documents are kept in secure places which minimises loss, theft or misplacement.
- It takes a shorter time to access documents than when they are not filed which would waste a lot time trying to look for them.
- It saves spaces otherwise documents that are not filed and kept end up taking a lot of space.
- By use of a diagram show the effect of a shift of the demand curve from the left to right on equilibrium price and quality. (10 marks)
-
- Give five limitations of using per capita income to compare the standard of living in different countries. (10 marks)
- Inequality in income distribution. Per capita income in one country may be high but in the hands of very few people yet another country may have low per capita income, which is evenly distribution.
- Inappropriate application of national income. Per capita income in one country may be high but used in a way that does not benefit citizens while in the other country, it may be used to finance projects that directly benefits the masses.
- Effect in people’s health. High per capita income in one country could be achieved at the expense of the people’s health
- Different interpretations of national income. One country may interpret her national income as gross domestic product at market price while another may interpret hers as net national product at factor cost.
- Non-marketed output. A country heavily relying on subsistence sector may appear to have low per capita income because of un-marketed output compared with another where such as sector insignificant.
- Price structure. Price structure may be different in difference countries e.g. food stuffs may be cheaper in one country compared to another.
- Inequality in income distribution. Per capita income in one country may be high but in the hands of very few people yet another country may have low per capita income, which is evenly distribution.
- Explain five ways in which a country may suffer as a result of being a member of a trading bloc. (10 marks)
- Loss of government revenue as no duty is imposed on goods to and from member countries.
- Closing down of local industries due to unhealthy competition with goods from more established industries from member countries.
- Unemployment for locals as they are not able to compete with more qualified people from member countries.
- Limits consumer choice. Citizens may have a limited choice as they may get goods produced within the trading block due to barriers placed to non-member countries.
- Compromising a country’s political ideology as the country adjusts itself to fit in the trading block.
- Give five limitations of using per capita income to compare the standard of living in different countries. (10 marks)
-
- Explain five benefits Kenya would derive from a well-drawn development plan. (10 marks)
- Allocation of available resources enables the government to allocate the available resources in the best way possible. This would ensure that there are neither idle resources nor some being used in the wrong manner.
- Project evaluation. Plan acts as a standard in which projects can be evaluated. Where there are deviations, they may analysed and corrective measures taken before it is too late.
- Equitable distribution of income. Development plans enables government to distribute equitably income thorugh fair allocation of resources regionally.
- Negotiation with donors. The government may use a development plan to convince donors that funds being sought would be put into proper use.
- Stimulating effort. A well-drawn and explained development plan may make the masses exert more effort in national development.
- Avoiding duplication. Through proper planning, different industries are set in different parts of the country thereby ensuring balanced development in the country.
- Highlight five reasons why the government may find it necessary to participate in business activities. (10 marks)
- To provide goods and services that are too sensitive to be left in the hands of the private sector.
- To attract foreign investment by initiating major development projects
- To prevent exploitation of consumers by private business people especially in provision of essential goods and services
- To provide essential goods and services which private individuals are not able to due to large amount of capital required.
- To stimulate economic development in the country
- To ensure equitable distribution of essential goods and services
- To provide unprofitable but essential goods and services
- Explain five benefits Kenya would derive from a well-drawn development plan. (10 marks)
-
- On 1st January 2013, Chui has Sh. 35,000 in cash and a bank overdraft Sh. 12,00. During the month, the following transaction took place:
Jan 2 Sold goods for Sh. 8,000 cash.
Jan 5 Received a cheque for Sh. 40,000 from Mwirigi Enterprises
Jan 8 Paid Sh. 6,000 cash to Bundi.
Jan 10 Deposited Sh. 13,000 into the bank from cash till
Jan 14 Withdrew Sh. 5,000 from bank for personal use.
Jan 15 Paid wages Sh. 4,000 in cash.
Jan 18 Received Sh. 25,000 cash from Kazure.
Jan 24 Cash sales paid directly into the bank Sh. 45,000
Jan 26 Paid wages Sh. 2,400 in cash
Jan 27 Withdrew Sh. 21,000 from bank for business use
Jan 28 Bought furniture Sh. 19,000 in cash.
Jan 29 Paid insurance Sh. 17,000 by cheque.
Jan 30 Deposited all the cash into the bank leaving a balance of only Sh.3,000Prepare a two-column cashbook and balance it off. (10 marks)
Dr Two-column Cash Book Cr Date Particulars Cash Bank Date Particulars Cash Bank 20 -8 Sh Sh 20-8 Sh Sh Jan 1 Balance b/d 35,000 Jan 1 Balance b/d 12,000 Jan 2 Sales 18,000 Jan 8 Bundi 6,000 Jan 5 Mwirigi Entr 40,000 Jan 10 Bank 13,000 Jan 14 Drawings 5,000 Jan 10 Cash 13,000 Jan 15 Wages 4,000 Jan 26 Wages 2,400 Jan 18 Kazure 25,000 Jan 27 Cash 21,000 Jan 28 Furniture 19,000 Jan 24 Sales 45,000 Jan 29 Insurance 17,000 Jan 27 Bank 21,000 Jan 30 Bank 51,600 Jan 31 Bal c/d 3,000 94,600 Jan 29 Cash 51,600 99,000 149,600 99,000 149,600 - Explain five circumstances under which a buyer would prefer buying goods under credit purchase rather than hire purchase terms. (10 marks)
- Where there is need to own the goods as under hire purchase ownership remain with the seller until the last instalment is paid.
- Where there is need to sell the goods as goods under hire purchase cannot be sold before all instalments are paid.
- Where there is need to benefit from lower price as hire purchase term is higher.
- Where there is need to avoid good being repossessed as it is the case in hire purchase terms.
- Where buyer is buying non durable goods which cannot be sold under higher purchase terms.
- Where buyer is intending to pay in one instalment and avoid periodic instalment which are required under hire purchase terms.
- On 1st January 2013, Chui has Sh. 35,000 in cash and a bank overdraft Sh. 12,00. During the month, the following transaction took place:
-
- Give four ways in which an entrepreneur contributes to produce goods.(8 marks)
- Provides the capital required in the production process
- He assembles other factors of production
- He makes decisions on how the business should run
- Pays fro other factors of production
- Bears risk
- Identifies the viable business opportunity
- The following trial balance was extracted from the books of Baite Traders as at 31st August 2015
Additonal information:Dr Cr Sh Sh Sales 350,000 Purchases 160,000 Cash at the bank 290,000 Returns inwards 5,000 Carriage inwards 20,000 Carriage outwards 14,000 Salaries and wages 10,000 Debtors 56,000 Creditors 90,000 Stock 35,000 Machinery 265,000 Rent 25,000 Discounts received 18,000 Light and heating 12,000 Buildings 240,000 Advertising 13,000 Drawings 30,000 Capital 667,000 1,150,000 1,150,000 - Stock on 31st August 2015 was valued at Sh. 50,000
- Prepare trading, profit and loss account for the year ended 31st August 2015 and a balance sheet as at that date.(12 marks)
Baite Traders
Trading, Profit and Loss A/C
For the period ended 31st August 20-5Sh Sh SH Sh Opening stock 35,000 Sales 350,000 Add: Purchases 160,000 Less: Return inwards 50,000 345,000 Carriage inwards 20,000 180,000 COGAFs 215,000 Less: Closing stock 50,000 Cos 165,000 G.P c/d 180,000 345,000 345,000 Carriage outwards 14,000 G.P b/d 180,000 Sal/wages 10,000 Rent 25,000 Light & heat 12,000 Discount Received 18,000 Advert 13,000 NP c/d 174,000 223,000 223,000
Biate
Balance sheet
As at 31st August 20-5Assets
Machinery
BuildingsSh
265,000
240,000Capital + Liabilities
Capital
Less: DrawingsSh
667,000
30,000Sh
637,000 Stock
Bank
Debtors50,000
290,000
56,000Add Net Profit
Creditors174,000 811,000
90,000901,000 901,000
- Give four ways in which an entrepreneur contributes to produce goods.(8 marks)
Download Business Studies Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Sukellemo Joint Mock 2020/2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students