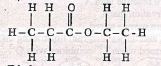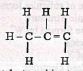CHEMISTRY
PAPER 2
TIME: 2 HOURS.
Instructions to candidates
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided.
-
- An element S has an atomic number of 38 and belongs to period 5.
- What name is given to the group to which the element belongs? (1mk)
- Write the electronic configuration of the element (1mk)
- The table below gives information about some ions of certain elements. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Ion Ionic
ConfigurationIonic
Radius
(nm)Atomic
radii
(nm)Q2- 2:8 0.136 0.072 T3+ 2:8 0.050 0.143 W+ 2:8 0.095 0.186 X+ 2 0.066 0.152 - Name the nature of the oxide formed when T3+ forms an oxide (1mk)
- Identify the ion of the most electronegative element (1mk)
- Compare the reactivity of elements forming ions W+ and X+ (1mk)
-
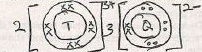
- Draw a 'dot' and 'cross' diagram illustrating on the compound formed when T3+ combines with Q2- (1mk)
- Name the type of structure formed (1mk)
- Name the charge carries would be present in:
- Chloride formed by W+ (1mk)
- Element of X+ (1mk)
- Two elements R and S belong to group VII of the periodic table with atomic numbers 17 and 53 respectively.
- State the electronic configuration of the ion R (1mk)
- S is a solid while R is a gas. Explain (1mk)
- An element S has an atomic number of 38 and belongs to period 5.
-
- If chlorine gas is passed over heated iron fillings and the product dissolved in water, a yellow solution is formed.
- What would be observed if aqueous ammonia is added to the yellow solution (1mk)
- Write the ionic equation for the reaction above in (i) (1mk)
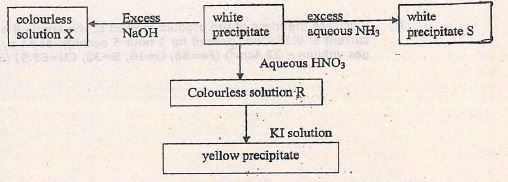
- Study the reaction scheme below and answer the questions that follow.
- Write the ionic equations for the formation of
- Colourless solution X (1mk)
- Yellow precipitate (1mk)
- What observations are made when white precipitate S is heated strongly (1mk)
- Hydrogen sulphide gas was passed through colourless solution R. Write the equation for the reactions that took place (1mk)
- Write the ionic equations for the formation of
-
- A student was required to prepare a sample of copper metal using crystals of copper II sulphate and iron fillings. Describe how the student would obtain copper metal (3mks)
- The solution obtained in (i) above was electrolysed using inert electrodes.
- Name the product at cathode. (1mk)
- Calculate the mass of the product formed at the anode if a current of 0.15A was passed for 1 hour 5 seconds at s.t.p. (molar gas volume - 22.4cm3) (Fe=56, O=16, S=32, CU=63.5) (3mks)
- If chlorine gas is passed over heated iron fillings and the product dissolved in water, a yellow solution is formed.
- The table below gives reduction potentials obtained when half cells for the following metals; J, K, L, M and N were connected to a copper half cell as reference electrode.
metals reduction potentials
(volts)J- -1.10 K -0.47 L 0.00 M +0.45 N +1.16 -
- What is metal L likely to be (1mk)
Give a reason (1mk) - Which metal cannot be displaced from its salt by any other metal in the table (1mk)
- What is metal L likely to be (1mk)
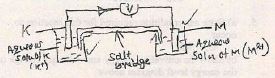
- If metal Kand M were used as electrodes to form an electrochemical cell
- Draw a well labeled diagram of this cell and the direction of the electrons flow (3mks)
- Write the reaction of the cell (1mk)
- Calculate the e.m.f. of the cell (1mk)
- During electrolysis of dilute CUSO4 solution, 0.5 amperes was passed for 3 hours
- Write the reactions that took place at the cathode and at the anode (2mks)
- Cathode
- Anode
- Calculate the amount of the solid deposited at the cathode and the amount of Gas liberated at the anode at s.t.p
- Solid (2mks)
- gas (2mks)
- Write the reactions that took place at the cathode and at the anode (2mks)
-
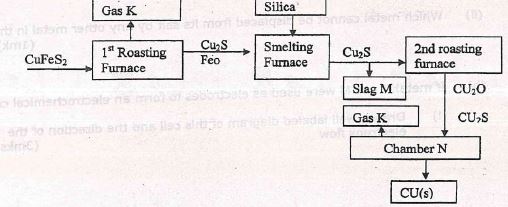
- The flow chart below outlines some of the process involved in extraction of copper from pyrites
-
- Name-gas K (1mk)
- Write an equation for reaction taking place in the 1st roasting furnace. (1mk)
- Name the slag (1mk)
- What name is given to the reaction taking place in chamber N? (1mk)
- Write the reaction (1mk)
- Copper obtained above is not pure. Draw a well labeled diagram to show the set up you would use to refine the copper. (3mks)
- Given that the mass of copper obtained from the above extraction was 210kg. Determine percentage purity of the copper pyrite if 810kg of it was fed to the 1st roasting furnace (4mks)
(CU=64, Fe=56, S=32)
-
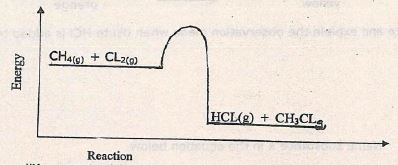
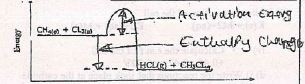
- Below is an energy level diagram for the reaction
- Reaction State one condition required for this reaction to occur. (1mk)
- Show the activation energy and enthalpy change on the energy level diagram above. (2mks)
- Give the following bond energies
C-C - 347 Kj/Mol
C-H - 413 Kj/Mol
CL-CL - 242Kj/Mol
H-CL - 431 Kj/Mol - Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction rate of the above (3mks)
- What is the effect of increasing pressure on the reaction rate of the above reaction. Explain (2mks)
- Study the reversible reaction below
2CrO42-(aq) + 2H+(aq)Cr2O72-(aq) + H2O(l)
yellow orange
State and explain the observation made when dilute HCl is added to the reaction (3mks)
-
- Name substance x in the equation below
C10H22 → X + C2H4
X _______________________(1mk) - What is the name of the process (1mk)
- Name and write the formula of 3 isomers of hexane (2mks)
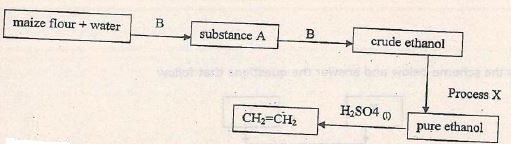
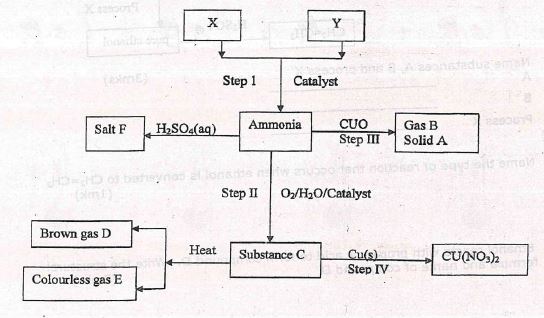
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name substances A, B and process X (3mks)
A ____________________________
B ____________________________
Process X ____________________________ - Name the type of reaction that occurs when ethanol is converted to CH2=CH2 (1mk)
- Ethanol reacts with propanoic acid to form compound D. Write the structural formula and name of compound D (2mks)
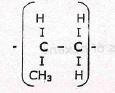
- Alkenes can polymerise
Deduce and name the structural formula of the monomer for the structure of the polymer shown above (2mks)
- Name substances A, B and process X (3mks)
- Name substance x in the equation below
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow
- Identify the catalyst used in step I (1mk)
- Describe the chemical test of gas E (1mk)
- Name the optimum conditions for the production of ammonia gas (2mks)
- Identify X and Y and their sources (2mks)
X________________Source________________
Y________________Source________________ - Write a chemical equation of the reaction between substance c and copper metal (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- An element S has an atomic number of 38 and belongs to period 5.
- What name is given to the group to which the element belongs? (1mk)
- Alkaline earth metals
- Write the electronic configuration of the element (1mk)
- 2:8:18:8:2
- 2:8:18:8:2
- What name is given to the group to which the element belongs? (1mk)
- The table below gives information about some ions of certain elements. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Ion Ionic
ConfigurationIonic
Radius
(nm)Atomic
radii
(nm)Q2- 2:8 0.136 0.072 T3+ 2:8 0.050 0.143 W+ 2:8 0.095 0.186 X+ 2 0.066 0.152 - Name the nature of the oxide formed when T3+ forms an oxide (1mk)
- Amphoteric oxide
- Identify the ion of the most electronegative element (1mk)
- Q2-
- Compare the reactivity of elements forming ions W+ and X+ (1mk)
- W is more reactive than X
-
- Draw a 'dot' and 'cross' diagram illustrating on the compound formed when T3+ combines with Q2- (1mk)
- Name the type of structure formed (1mk)
- Giant Ionic Structure
- Giant Ionic Structure
- Draw a 'dot' and 'cross' diagram illustrating on the compound formed when T3+ combines with Q2- (1mk)
- Name the charge carries would be present in:
- Chloride formed by W+ (1mk)
- Mobile ions
- Element of X+ (1mk)
- Delocalized electrons
- Delocalized electrons
- Chloride formed by W+ (1mk)
- Name the nature of the oxide formed when T3+ forms an oxide (1mk)
- Two elements R and S belong to group VII of the periodic table with atomic numbers 17 and 53 respectively.
- State the electronic configuration of the ion R (1mk)
- 2:8:8
- 2:8:8
- S is a solid while R is a gas. Explain (1mk)
- Has larger molecules than R hence stronger Van der Waal forces of attraction
- State the electronic configuration of the ion R (1mk)
- An element S has an atomic number of 38 and belongs to period 5.
-
- If chlorine gas is passed over heated iron fillings and the product dissolved in water, a yellow solution is formed.
- What would be observed if aqueous ammonia is added to the yellow solution (1mk)
- A brown precipitate is formed
- A brown precipitate is formed
- Write the ionic equation for the reaction above in (i) (1mk)
- Fe3+(aq) + 3OH-(aq) → Fe(OH)3(s)
- Fe3+(aq) + 3OH-(aq) → Fe(OH)3(s)
- What would be observed if aqueous ammonia is added to the yellow solution (1mk)
- Study the reaction scheme below and answer the questions that follow.
- Write the ionic equations for the formation of
- Colourless solution X (1mk)
- Pb(OH)2(s) + 2OH-(aq) → [Pb(OH)]2+(aq)
- Pb(OH)2(s) + 2OH-(aq) → [Pb(OH)]2+(aq)
- Yellow precipitate (1mk)
- Pb(NO)3(aq) +2I-(aq) → PbI(s)
- Pb(NO)3(aq) +2I-(aq) → PbI(s)
- Colourless solution X (1mk)
- What observations are made when white precipitate S is heated strongly (1mk)
- Turns from white to orange/ red when hot then yellow on cooling or turns from white to yellow.
- Turns from white to orange/ red when hot then yellow on cooling or turns from white to yellow.
- Hydrogen sulphide gas was passed through colourless solution R. Write the equation for the reactions that took place (1mk)
- Pb(NO3)2(aq) + H2S(aq) → PbS(s) + 2HNO3(aq)
- Pb(NO3)2(aq) + H2S(aq) → PbS(s) + 2HNO3(aq)
- Write the ionic equations for the formation of
-
- A student was required to prepare a sample of copper metal using crystals of copper II sulphate and iron fillings. Describe how the student would obtain copper metal (3mks)
- Pass water to copper (II) sulphate crystals and stir to form CuSO, solution.
- Add iron fillings to the solution and stir.
- Continue adding iron fillings till the pale blue colour of solution just fades.
- Filter the mixture to obtain copper metals residue.
- Wash and dry the residue between filter papers.
- The solution obtained in (i) above was electrolysed using inert electrodes.
- Name the product at cathode. (1mk)
- Hydrogen gas
- Hydrogen gas
- Calculate the mass of the product formed at the anode if a current of 0.15A was passed for 1 hour 5 seconds at s.t.p. (molar gas volume - 22.4cm3) (Fe=56, O=16, S=32, CU=63.5) (3mks)
- Q = It
= 0.15A x 60 x 60 + 5)
= 0.15A x 3605
= 540.75C
4OH-(aq)
2H2O(l) + O2(g) + 4e-
(96500CX 4) yield 32g of O2
X = 540.75C x 32 = 0.0448g
96500C x 4
- Q = It
- Name the product at cathode. (1mk)
- A student was required to prepare a sample of copper metal using crystals of copper II sulphate and iron fillings. Describe how the student would obtain copper metal (3mks)
- If chlorine gas is passed over heated iron fillings and the product dissolved in water, a yellow solution is formed.
- The table below gives reduction potentials obtained when half cells for the following metals; J, K, L, M and N were connected to a copper half cell as reference electrode.
metals reduction potentials
(volts)J- -1.10 K -0.47 L 0.00 M +0.45 N +1.16 -
- What is metal L likely to be (1mk)
- Сорреr
Give a reason (1mk)
It is reference electrode hence Eº of 0.00
- Сорреr
- Which metal cannot be displaced from its salt by any other metal in the table (1mk)
- What is metal L likely to be (1mk)
- If metal Kand M were used as electrodes to form an electrochemical cell
- Draw a well labeled diagram of this cell and the direction of the electrons flow (3mks)
- Write the reaction of the cell (1mk)
- K(s) + M2+(aq) → K2+(aq) + M(s)
- K(s) + M2+(aq) → K2+(aq) + M(s)
- Calculate the e.m.f. of the cell (1mk)
- +0.45-0.47 = ±0.92V
- +0.45-0.47 = ±0.92V
- Draw a well labeled diagram of this cell and the direction of the electrons flow (3mks)
- During electrolysis of dilute CUSO4 solution, 0.5 amperes was passed for 3 hours
- Write the reactions that took place at the cathode and at the anode (2mks)
- Cathode
- Cu2+(aq) + 2e → Cu(s)
- Cu2+(aq) + 2e → Cu(s)
- Anode
- 4OH-(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2
- 4OH-(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2
- Cathode
- Calculate the amount of the solid deposited at the cathode and the amount of Gas liberated at the anode at s.t.p
- Solid (2mks)
- 0.5 x 3 x 60 = 90C
2 x 96500 - 63.5
90 = 63.5 x 90
2 x 96500
= 1.776688
- 0.5 x 3 x 60 = 90C
- gas (2mks)
- 4 x 96500C = 22.41
90 = 22.4 x 90
4 x 96500
= 0.00522 litres
- 4 x 96500C = 22.41
- Solid (2mks)
- Write the reactions that took place at the cathode and at the anode (2mks)
-
- The flow chart below outlines some of the process involved in extraction of copper from pyrites
-
- Name-gas K (1mk)
- SO2
- SO2
- Write an equation for reaction taking place in the 1st roasting furnace. (1mk)
- 2CuFeS2(s) + 4O2(g) → Cu2S(s) + 2FeO(s) + 3SO2(g)
- 2CuFeS2(s) + 4O2(g) → Cu2S(s) + 2FeO(s) + 3SO2(g)
- Name the slag (1mk)
- Iron (II) salicate (FeSiO3)
- Iron (II) salicate (FeSiO3)
- What name is given to the reaction taking place in chamber N? (1mk)
- Redox
- Redox
- Write the reaction (1mk)
- Cu2S(l) + 2Cu2O(l) → 6Cu(l)+ SO2(g)
- Cu2S(l) + 2Cu2O(l) → 6Cu(l)+ SO2(g)
- Name-gas K (1mk)
- Copper obtained above is not pure. Draw a well labeled diagram to show the set up you would use to refine the copper. (3mks)
- Given that the mass of copper obtained from the above extraction was 210kg. Determine percentage purity of the copper pyrite if 810kg of it was fed to the 1st roasting furnace (4mks)
(CU=64, Fe=56, S=32)- 2CuFeS2 → Cu2S
Cu2S → Cu2O
Cu2O → 3Cu
Moles of Cu = 210000
64.
= 3.281
Moles of Cu = 3.28
3
=1.09375
Moles of Cu2S = 0.09375
Moles of CuFeS2 - 1.09375 x 2 = 2.1875
Mass of CuFeS2 = 2.1875 x 151 = 402.5
% purity = 402.5 x 100
810
= 49.69%
- 2CuFeS2 → Cu2S
-
- Below is an energy level diagram for the reaction
- Reaction State one condition required for this reaction to occur. (1mk)
- U.V light
- U.V light
- Show the activation energy and enthalpy change on the energy level diagram above. (2mks)
- Give the following bond energies
C-C - 347 Kj/Mol
C-H - 413 Kj/Mol
CL-CL - 242Kj/Mol
H-CL - 431 Kj/Mol- Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction rate of the above (3mks)
- H = (413 +242) - (346+ 431) = -122kJ
- H = (413 +242) - (346+ 431) = -122kJ
- What is the effect of increasing pressure on the reaction rate of the above reaction. Explain (2mks)
- Reaction rate increase - Increase in pressure brings reacting particles closer thus increasing the rate of effective collisions.
- Reaction rate increase - Increase in pressure brings reacting particles closer thus increasing the rate of effective collisions.
- Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction rate of the above (3mks)
- Study the reversible reaction below
2CrO42-(aq) + 2H+(aq)Cr2O72-(aq) + H2O(l)
yellow orange
State and explain the observation made when dilute HCl is added to the reaction (3mks)- HCl is added to the reaction
- Intensity of orange colour increases
- HCl increases H concentration hence equation shifts to the right, more Cr2O72- is formed.
- Reaction State one condition required for this reaction to occur. (1mk)
-
- Name substance x in the equation below
C10H22 → X + C2H4 (1mk)- X -Octane (C8H18)
- X -Octane (C8H18)
- What is the name of the process (1mk)
- Cracking
- Cracking
- Name and write the formula of 3 isomers of hexane (2mks)
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
|
CH3
2-methylpentane - CH3
|
CH3CCH2CH2CH3
|
CH3
2,2-Dimethyl butane - CH3CH2CHCH2CH3
|
CH3
3-methyl pentane
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name substances A, B and process X (3mks)
A - Glucose
B - yeast
Process X - Fractional distillation - Name the type of reaction that occurs when ethanol is converted to CH2=CH2 (1mk)
- Dehydration
- Dehydration
- Ethanol reacts with propanoic acid to form compound D. Write the structural formula and name of compound D (2mks)
Ethyl propanoate - Alkenes can polymerise
Deduce and name the structural formula of the monomer for the structure of the polymer shown above (2mks)
- Name substances A, B and process X (3mks)
- Name substance x in the equation below
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow
- Identify the catalyst used in step I (1mk)
- Iron
- Iron
- Describe the chemical test of gas E (1mk)
- Bring a glowing splint to the mouth of the test tube contravening gas E
- The glowing splints relights
- Name the optimum conditions for the production of ammonia gas (2mks)
- Iron catalyst
- 500 atmospheres
- 400°C to 500°C
- Identify X and Y and their sources (2mks)
X - Nitrogen Source - From fractional distillation acquired from air
Y - Hydrogen Source - from contracting of petroleum products - Write a chemical equation of the reaction between substance c and copper metal (1mk)
- Cu(s) + 4HNO3(l) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
OR
3Cu(s) + 8HNO3(aq) → 3Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 4H2O(l) + 2NO2(g)
- Cu(s) + 4HNO3(l) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
- Identify the catalyst used in step I (1mk)
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mang'u Mock 2020 Exam.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students