AGRICULTURE
PAPER 1
TIME: 2 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name, school and index number, in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of the examination in the spaces provided above.
- This paper consists of three sections: A, B and C.
- Answer all the questions in section A and B and any two questions from section C.
- All answers must be written in the spaces provided in this booklet.
For Examiner’s Use Only
|
SECTION |
QUESTIONS |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATES SCORE |
||
| A | 1-15 | 30 | |||
| B | 16-19 | 20 | |||
| C | 20 | ||||
| 20 | |||||
| Total Score | 90 | ||||

QUESTIONS
SECTION A (30 MRKS)
- Differentiate between olericulture and pomoculture as used in crop production .(1mrk)
- Give four method of farming (2mrks)
- Give two examples for each of the following types of cost incurred in broiler production .
a) Variable cost ( 2 marks)
b) fixed cost (2 marks) - Give four advantages of crop rotation .(2mrk)
- State four factors that that should be considered when classifying crop pest (2mrks)
- a) Name four pieces of information contained in a land title deed (2mks
b) Name two forms of collective land tenure system. (1mk - List four post – harvest practices that are carried out in maize production (2mks
- What is opportunity cost? (1/2 mk)
- Outline four ways of improving lab our productivity (2mks
- State four factors that can affect the efficiency of pesticides (2mks
- List four sites on which agro forestry trees can be established on a farm. (2mks
- Give four advantages of using seeds over vegetative materials. (2 mks)
- State four features that should be considered when choosing water pipes for use on the farm. (2 mks)
- Give three reasons why primary cultivation should be done early before the onset of the rains(1 ½ )
- Give four suitable characteristics of plants used as green manure. (2mks)
SECTION B: (20 marks)
Answer all the questions in the section in the spaces provided.
- The diagram below shows a pest and the damaged crop study it and answer the questions that follow.

a) Identify the pest illustrated above (1mk
b) Explain two ways of controlling the pest (2mks
c) State two ways in which the pest economically important. (2mks) - a) Distinguish between straight and compound fertilizers. (1mk
b) A farmer applied 200kg of C A N (20%N) per hectare maize crop. Calculate the amount of Nitrogen applied on his 5 hectare crop. Show your working (4mks - The diagram below shows a maize cob attacked by a certain disease. Study it and then answer the following questions.

a) Identify the disease (1 Mk)
b) Name two causal organism of the disease. (1 Mk)
c) State three cultural methods of controlling the disease. (3 Mks) - Below is a graphical representation of a law in agricultural economics. Study the graph carefully and answer the questions that follow.
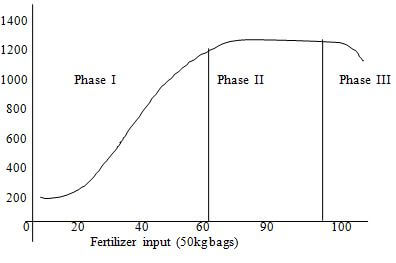
a) State the law illustrated by the graph (2mk
b) Explain how each additional unit of fertilizer input relates to the total output of maize in phases II and III .( 2 mks)
Phase II
........................................................................................................................................................................................................
Phase III (1mk
........................................................................................................................................................................................................
c) State the importance of the law identified in ( I ) above to the maize farmer (1mk
SECTION C ( 40MARKS)
Answer any two questions in this section in the spaces provided
- a) Explain five factors that should be considered in farm planning. (10 Mks)
b) Describe transplanting of tomatoes seedling. (10 Mks) -
- Describe paddy rice production under the following sub-headings.
i) Land preparation (2 Mks)
ii) Water control (2 Mks)
iii) Fertilizer application (2 Mks)
iv) Weed control (2 Mks) - Explain how each of the properties of rainfall and light influence crop production.
i) Rainfall (8 Mks)
ii) Light - Explain four factors that should be considered when sitting a vegetable nursery. (4mks)
- Describe paddy rice production under the following sub-headings.
- a) Describe six advantages of rotational grazing (6mrks)
b)Explain eight ways in which soil fertility can be maintained (8mrks)
c) Explain six reasons for pruning coffee.(6mrks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30 mks)
1. Difference between olericulture and pomoculture
- Olericulture –Growing of flowers
- Pomoculture –growing of fruits
2 .Methods of farming
- mixed farming
- Nomadic pastoralism
- shifting farming
- Organic farming
- agro-forestry
3. Variable and fixed cost in broiler production
- Variable cost
- cost of the feed
- cost of drug
- Fixed cost
- cost of feeders and waterers
- Cost of structure/Depreciation of poultry house
- Cost of chicks
4. Advantages of crop rotation (2mrks)
- Improve soil structure
- Control soil borne pest and diseases
- Ensure maximum utilization of farm labour (2mrks)
- Aids in weed control
- Improve soil erosion
- Security in case of failure on one crop
- Add nitrogen through N-fixation by Rhizobium bacterial when legume are included
5. Factors considered when classifying crop pests
- crop attacked /mode of felling
- whether field /storage pest/stage of attack (2mrks)
- Crop part attacked
- science classification e.g. insect mite, rodent
6 a)
- Name of the owner
- Size of the land
- Land title deed number
- Seal and signature of issuing officer
- Date of registration
b)
- Communal land tenure
- Co-operative land tenure
- State ownership
7.
- Drying
- Dusting/seed dressing
- Sorting and grading
- Processing
- Packaging
8.Refers to returns from the best alternative forgone
9.
- Supervision.
- Giving incentives
- Training
- Mechanisation
10.
- Concentration
- Weather conditions
11.
- Farm boundaries
- Homestead
- Terraces
- River bank/water catchment areas
- Slopes
- Within pasture land
12.Give four advantages of using seeds over vegetative materials. (2 Mks)
- Seeds are not bulky
- Seeds are easy to handle during planting
- Possible to mechanize operations when using seeds
- Seeds are easy to treat against soil borne pests and diseases
13.State four features that should be considered when choosing water pipes for use on the farm (2 Mks)
- Durability
- Strength/ability to withstand pressure
- Diameter/size of the pipe
- Workability
- colour
14..Reasons why primary cultivation should be done early before the onset of the rains.(1 ½ mrks)
- Give time for the soil organism to act on organic mater
- Allow gaseous exchange to take place thus carbon dioxide diffuses out of the soil .
- Allows other operations to take place in time .
15.
- Fast growth
- Fast to lot
- Leafy
- Preferably leguminous
- Able to grow in poor soil conditions.
SECTION B: (20 mrks)
16
- Cutworm / agrotis SPP.(1 mk)
-
- Early planting. For crop to establish first (2 mks)
- application of appropriate pesticide/insecticide/chemical to kill it.
- field hygiene to prevent transmission from previous crop residues
-
- It increases the cost of productionby buying the pesticides (2mks)
- It reduces the yield of the crops
17
-
- Straight fertilizer supply one of the fertilizer elements e.g N1 P1 or K
- Compound fertilizers supply two or three fertilizer elements.
- 100kg supply 20kg N
1 hectare = 200kg C.A.N
100kg = 20kg N
200kg = ?
200 × 20
100
= 40kg N
1 ha requires = 40kg N
5 ha = “ ?
40 x 5 = 200kg N
1
18
- Identify the disease 1 Mk)
- Maize smut
- Name causal organism of the disease. (1 Mk)
- Fungus Ustilago
- State three cultural methods of controlling the disease. (3 Mks)
- Crop rotation
- Field hygiene
- Use of certified seeds
- Planting resistant varieties
19.
- Law of diminishing returns which states that if successive units of work input are added to a fixed input a point is eventually reached where additional out put per addition unit of in put declines(2 mks)
- Phase II each additional unit of fertilizer input leads to a lower increase in total output of maize than the previous unit of fertilizer
Phase III each additional unit of fertilizer input leads to decrease in total output of maize (2 mks) - Helps the farmer to identify the level of optimum fertilizer application in the production of maize (1 mks)
SECTION C (40MARKS)
20.
- Explain five factors that should be considered in farm planning. (10 Mks)
- Environment factors
- Size of the farm
- Farmers objective and performance
- Government regulations/policy
- Availability and cost of farm inputs
- Security
- Trends in the labour market/skills
- Existing market conditions and price
- Communication and transport to ensure that produce reach markets and inputs are easily accessed.
- Possible production enterprises the farmer chooses that have low inputs with most profitable
- Describe two transplanting of tomatoes seedling. (10 Mks)
- Should be done when seedlings are pencil size thick (one month old)
- Nursery should be watered before for ease lifting of seedlings
- Use of garden trowel to ensure that seedlings are lifted with lump of soil around roots
- Applying appropriate pesticide on the planting holes and thoroughly mix with the soil
- Lift only healthy and vigorous seedlings
- Plant one seedling per hole at the same depth as was in the nursery
- Transplanting should be done in the evening or on cloudy day
- Provide temporary shade to the transplanted seedling
- Water the seedlings as necessary
- Plan the soul around the seedling and firm
- Holes dug are placed at 60 – 100 cm by 50 – 60 cm
- Transplant onset of rain
- Transport the seedlings carefully /use a wheelbarrow
- Plant holes should be dug at 15 cm deep
21.a). Describe paddy rice production under the following sub-headings.
- Land preparation (2 Mks)
- The rice field should be levelled and burels constructed around them for controlling water
- In small scale jembes are used in land preparation
- Water control (2 Mks)
- The level of water is increased to 5 cm at planting time gradually to a height of 15 cm by the time of seedling are fully grown
- Water should be allowed to flow slowly through the fields
- If the flow of water is not possible then old water should be drained and fresh water added every 2 – 3 weeks
- Fertilizer application (2 Mks)
- Sulphate or ammonia is applied at rate of 25 kg for each nursery unit of 18.5 m x 18.5 m before sowing.
- Double super phosphate is broadcasted in the field at the rate of 120 kg/ha before planting
- In the fields sulphate of ammonia is applied as a rate of 125 kg/ha before transplanting and 125 kg/ha about 4 days after transplanting.
- Weed control (2 Mks)
- Weeds are controlled by the flooding
- Use appropriate britachlor to control a few weeds
b) Explain how each of the properties of rainfall and light influence crop production.
- Rainfall (4 Mks)
- Rainfall reliability :Determines timing of land preparation and planting
- Amount of rainfall: Determines the type of crop to grow
- Rainfall distribution: Influences the type and variety of crops to grow in an area
- Rainfall intensity: High rainfall intensity damages crops and causes soil erosion
- Light (4 Mks)
- light intensity : the rate of photosynthesis increases with increase in light intensity
- Light duration: It determines the flowering hence the type of crop to grow i.e short day, long day or day neutral plants
- Light wavelength: Plants absorb light of specific wavelength making natural light more suitable for crop production
c)
- Near a water source for easy watering
- In a well sheltered place to prevent strong winds which can uproot seedlings and cause excessive evaporation.
- Security so as to protect them from theft and destruction by animals/birds
- On a gentle slope to prevent erosion through run off and to prevent flooding
- Type of soil, should be fertile and well drained
- Previous cropping. Avoid area where same crop family had been planted to avoid pest and disease attack/build up
- Near the seedbed/main field to minimize damage to seedlings during transplanting
- Accessibility for ease of movement
- Away from shading effect to allow sunshine
22a) Six advantages of rotational grazing (6mrks)
- The livestock make maximum efficient use of pasture.
- It reduces the buildup of pest and diseases.
- Animals waste is distributed evenly in all paddock or field
- Excess pasture can be harvested and conserved
- It is possible to apply fertilizers and control weeds , pest and diseases in the pasture that are not in use
- It allows a resting period for the pasture to regenerate before been grazed on again (6mrks)
b) Eighty ways in which soil fertility can be maintained. (8mrk)
- adding manure to the soil to enrich it with nutrients.
- using inorganic fertilizers which releases nutrients in forms that are readily available to plants.
- practicing crop rotational to ensure balanced nutrients use.
- using appropriate tillage, for instance minimum tillage.
- regulating soil ph though liming
- controlling soil erosion
- practicing a forestation and reforestation
- By irrigation which increases availability and uptake of plant nutrients and reclaims saline soil
- through mulching
- By weeding to reduce competition for nutrients.
- By practicing inter cropping preferably with legume to enhance nitrogen fixation.
c) Six reasons for pruning coffee (6mrks)
- To train the plant so that it can have the required shape
- To remove the diseased and the unwanted parts of a plant such as extra suckers ,leaves ,branches ,flowers or even stems
- To control cropping
- To facilitate picking to ease penetration of the s pray
- To control pest and diseases.
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Meru Central Cluster Exam 2020.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

