INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided.
- Answer all questions in the spaces provided
- KNEC mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used for calculations.
- All workings must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain all the pages are printed as indicated and no questions are missing.
- The diagram below shows a set up used by a student in an attempt to prepare collect oxygen gas
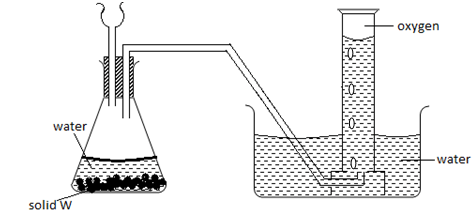
-
- Identify and correct the mistakes in the set up to enable the preparation and collection of the gas. (2mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Identify solid w. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Identify and correct the mistakes in the set up to enable the preparation and collection of the gas. (2mks)
- A piece of phosphorous was burnt in excess air. And the product dissolved in hot water to make a solution.
- Write an equation for the burning of phosphorous in excess air. (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - The solution obtained in (b) above was found to have a pH of 2.0. Give reasons for this observation. (1mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Write an equation for the burning of phosphorous in excess air. (1mk)
- Explain why cooking pots made of aluminium do not corrode easily when exposed to air. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - The reaction between sulphure (IV) Oxide and oxygen to form Sulphur (VI) Oxide is an exothermic reaction, which can be represented by the equation below;
2SO2(g) + O2(g)2SO3(g) H = -ve Δ
A factory manufacturing sulphuric (VI) acid by contact process produces 350kg of sulphur(VI)oxide per day (conditions for the reaction; catalyst, 2 atmospheres pressure and temperatures between 400 – 500ºC.)- What is meant by an exothermic reaction? (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - How would the yield per day of sulphur trioxide be affected if temperatures lower than 400ºC are used? Explain. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - All the sulphur (VI) Oxide produced was absorbed in concentrated sulphuric acid to form oleum.
SO3(g) + H2SO4(l) → H2S2O7(l)
Calculate the mass of oleum that was produced per day. (S = 32.0, O= 16: H = 1.0)(3mks)
- What is meant by an exothermic reaction? (1mk)
-
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow:
Compounds Melting point ºC Boiling points ºC C2H4O2 16.6 118 C3H6 -185.0 -47.7 C3H8O -127 97.2 C5H12 -130 36.3 C6H14 -95.3 68.7 -
- Which of the compounds is a solid at 10ᵒC. Explain (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - Choose two compounds which are members of the same homologous series and explain the difference in their melting points (3mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - The compound C3H8Ois an alcohol. How does its solubility in water differ from the solubility of C5H12 in water? Explain (2mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Which of the compounds is a solid at 10ᵒC. Explain (1mk)
- Complete combustion of one mole of a hydrocarbon produces four moles of carbon (IV) oxide and four moles of water.
- Write the formula of the hydrocarbon (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - Write the equation for the complete combustion (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Write the formula of the hydrocarbon (1mk)
-
- In a reaction, an alcohol “J” was converted to hex -1-ene. Give the structural formula of alcohol “J” (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….. - Name the reagent and conditions necessary for the reaction in C (ii) above ( 1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- In a reaction, an alcohol “J” was converted to hex -1-ene. Give the structural formula of alcohol “J” (1mk)
- Compound K reacts with sodium hydroxide as shown below
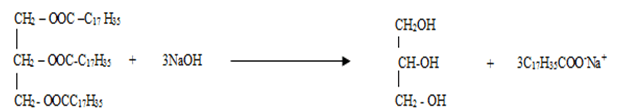
- What type of reaction is represented by the equation above (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - To what class of compound does “K” belong? (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
- What type of reaction is represented by the equation above (1mk)
- The following equations represent two different types of reactions
- nC4H8(g) → [C4H8]n(g)
- C2H6(g) + Cl2(g) → C2H5Cl(g) + HCl(g)
State the type of reaction represented by (i) and (ii) (1mk)- ……………………………………………
- ……………………………………………
-
-
- Give the name of one reagent which when reacted with concentrated hydrochloric acid produces chlorine gas (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - A student set out to prepare iron (lll) chloride using apparatus shown in the diagram below
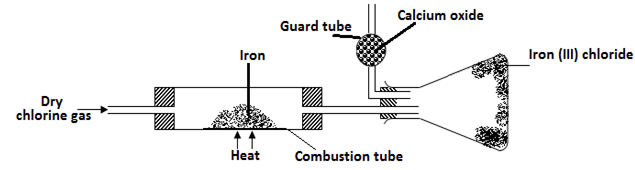
- Explain why it is necessary to pass chlorine gas through the apparatus before heating begins? (1mk)
..............................................................................................................................................................
………………………………………………………………………………………………………... - What property of iron (III) chloride makes it possible to be collected as shown in the diagram (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - The total mass of iron (III) chloride formed was found to be 0.5g. Calculate the volume of chlorine gas that reacted with iron. (Fe = 56, Cl = 35.5 and molar gas volume at r.t.p is 24,000 cm3) (3mks)
- Explain why it is necessary to pass chlorine gas through the apparatus before heating begins? (1mk)
- When hydrogen sulphide gas passed through a solution of iron (III) chloride the following observation was made;
The colour of the solution changed from reddish brown to green and yellow solid was deposited. Explain these observations (2mks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………… - State and explain the observations that would be made if a moist blue-litmus paper was placed in a gas jar full of chlorine gas (2mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….. - Study the information to answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Elements Atomic number Melting point (ºC) L 11 97.8 M 13 660 N 14 1410 C 17 -101 R 19 63.7 -
- Write the electron arrangement for the ions formed by elements “ M” and “C” (1mk)
M ……………………………………………..
C ………………………………………………. - State the type of the bond that will be formed when M and C react. (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - In which group and period of the periodic table does element “R” belongs? (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - Element R loses its outermost electrons more readily than “L”. Explain (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
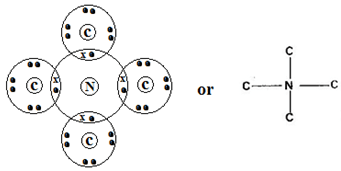
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - Using dots and crosses to represent electrons, show bonding in the compound formed between N and C. (2mks)
- Write the electron arrangement for the ions formed by elements “ M” and “C” (1mk)
-
- Give the name of one reagent which when reacted with concentrated hydrochloric acid produces chlorine gas (1mk)
- Study the energy level diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
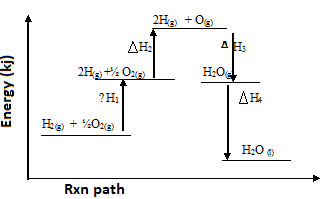
-
- Which H values have a positive sign. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Which H values have a negative sign (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………... - What chemical changes is being represented by (2mks)
ΔH1 ………………………………………………………………………..
ΔH4 ………………………………………………………………………..
- Which H values have a positive sign. (1mk)
- The hydration energy of Al3+ and Cl- are -4690 and -364kJmol-1 respectively. The heat of solution of alluminium chloride is -332kJ mol-1.
- Calculate the lattice energy of alluminium chloride (2mks)
- Draw an energy level diagram for dissolving of alluminium chloride (2mks)
- When one mole of butanol is burnt. 2676kJ are liberated
- Write a chemical reaction for combustion of butanol. (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Considering the following heats of combustion
ΔHθC (Graphite) = -393kJ mol-1
ΔHθC (H2) (g) = -286kJ mol-1
ΔHθC (Butanol) = -2676kJ mol-1
Draw an energy cycle for the above energy changes (2mks) - Calculate the heat of formation of butanol (2mks)
- Write a chemical reaction for combustion of butanol. (1mk)
-
-
- The equations below shows the standard reduction potential for four half cell. Study it and answer the questions that follow. Letters are not actual symbols of the element.
Eᶿ Volts
F2(g) + 2e- → 2F-(aq) + 0.54
G2+(aq) + 2e- → G(s) -0.44
H+2(aq) + 2 e- → H(s) + 0.34
2J+(aq) + 2e- → J2(g) 0.00- Write the equation for the reaction which takes place when solid “G” is added to a solution containing H2+ (ions) (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - Calculate the Eᶿ value for the reaction in (ii) above (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction which takes place when solid “G” is added to a solution containing H2+ (ions) (1mk)
- The diagram below shows the apparatus used to electrolyze acidified water to obtain hydrogen and oxygen gases. Study it and answer the questions that follows?
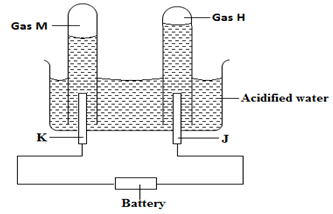
- Identify the electrodes marked K and J (1mk)
K ……………………………………………………………
J ……………………………………………………………. - Write the equation that led to the production of gas (1mk)
M ……………………………………………………………………………………
H …………………………………………………………………………………… - Explain why hydrochloric acid is not used to acidify the water (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Identify the electrodes marked K and J (1mk)
- During electrolysis of aqueous copper (II) sulphate 144750 columbus of electricity were used. Calculate the mass of copper metal that was obtained (Cu= 64, 1 Faraday = 96500 Columbus) (2mks)
- The equations below shows the standard reduction potential for four half cell. Study it and answer the questions that follow. Letters are not actual symbols of the element.
- The flow chart illustrates the extraction of zinc and preparation of Zinc (II) sulphate crystals. Study it and answer the questions that follow
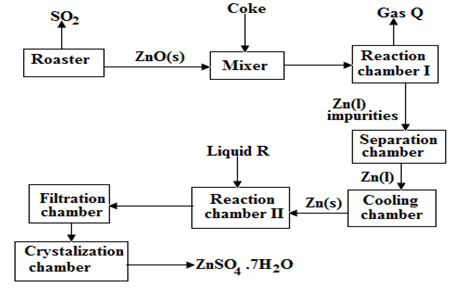
-
- Name
- Gas Q ………………………………………………………………. (1mk)
- Liquid R …………………………………………………………….. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in
Chamber I ………………………………………………………………………………… (1mk)
The Roster …………………………………………………………………………………. (1mk)
Chamber II ………………………………………………………………………………….(1mk) - Given that the zinc sulphide ore contain 45% of Zinc sulphide by mass, calculate
- The mass in grains of Zinc sulphide that would be obtained from 250 kg of the ore.(1mk)
- The volume of sulphur (IV) oxide (So2) that would be obtained from the above mass of zincsulphideat room temperature and pressure (S = 32.0, molar gas volume = 24 dm3). (2mks)
- The mass of zinc metalthat would be obtained in Iabove(Zn = 65.4) (1mk)
- Name
- In such an experiment sulphur (IV) Oxide may keep escaping to the atmosphere. Explain how this could affect the environment. (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………….. - Suggest one other manufacturing plant that could be set up near Zinc extraction plant. (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
-
-
- State the difference between chemical and nuclear reactions (1mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Below is a radioactive decay series starting from
214 206
Bi and ending at Pb. Study it and answer the questionsthat follows
83 82- Identify the particle emitted in step I and III. (2mks)
- ………………………………………………………….
- …………………………………………………………
- Write the nuclear equation for the reaction which takes place in step V (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Identify the particle emitted in step I and III. (2mks)
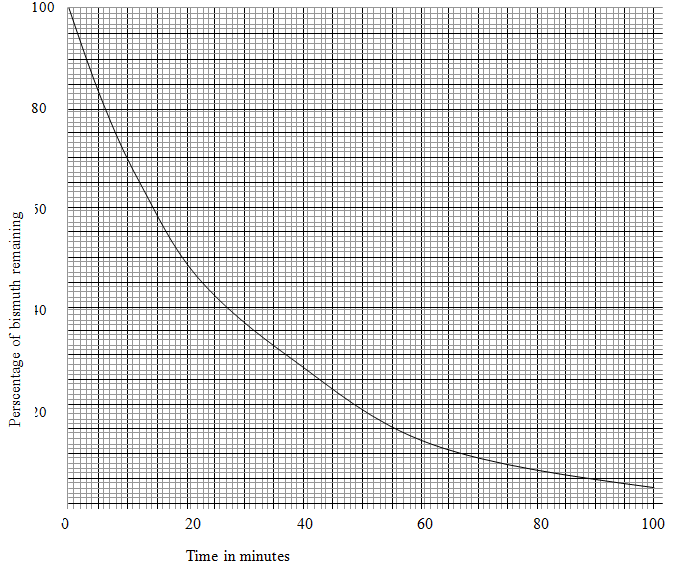
- The table below gives the percentage of radioactive isotope of Bismuth that remains after decaying at different times.
Time (mm) 0 6 12 22 38 62 100 Percentage of Bismuth 100 81 65 46 29 12 3 - On the grid provided below, plot a graph of the percentage of bismuth remaining (vertical axis) against time (3mks)
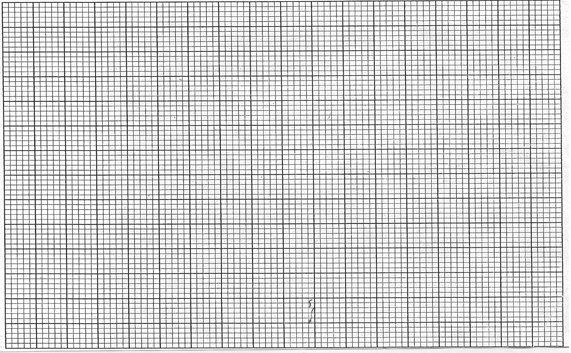
- Use the graph, determine the
- Half life of the Bismuth (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Original mass of bismuth isotope given that the mass remained after 70 minutes was 0.16g (1mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- Half life of the Bismuth (1mk)
- On the grid provided below, plot a graph of the percentage of bismuth remaining (vertical axis) against time (3mks)
- Give one use of radioactive isotope in medicine (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………...
- State the difference between chemical and nuclear reactions (1mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
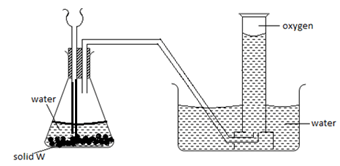
The thistle funnel has to dip inside the solution so that the gas does not escape through it.- Sodium peroxide Na2O2
-
- 4P(s) + 5O2(g) → 2P2O5(g)
- Phosphorous (V) oxide dissolves in water to form an acid (Phosphoric acid)
- A firm oxide (aluminium Oxide) is formed on the surface of the metal. This oxide protect aluminium from further attack
-
- A reaction which proceeds by production of heat i.e heat is lost to the surroundings.
- The yield will be lowered: through the Le- Chateliers principle, the yield is expected to increase. But lower temperatures will result into fewer particles attaining activation energy.
- RMM of SO3 = 32 + 48 = 80
Moles of SO3 used = 350 = 4.38 moles
80
Moles of H2S2O7 = 4.38 moles
RMM of H2S2O7 = 2 + 64 + 112 = 178
Mass of H2S2O7 = 4.38 x 178 = 779.6 kg
-
-
-
- C2 H4 O2 it melting point is higher than 100 C
- CH14 and C5H12
C6 H14 has a higher melting point since it is more bulky compared to C5H12; hence the vanderwaals force between the molecules of C6 H14 is abit stronger. - C3H8O is more soluble in water than C5H12: because it formshydrogen bonds with water molecules i.e it is polar due to the presence of (-OH) group.
-
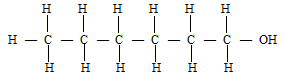
- C4H8
- C4H8(g) + 6O2(g) → 4O2(g) + 4 H2O(l)
-
Reagents- Concentrated sulphuric acid
Al2O3 or phosphoric acid (Catalyst)
Conditions
Heat (160-180ºC)
-
- Saponification/Hydrolysis
- Fats/ ester
-
- Polymerisation
- Substitution
-
-
-
- potassium manganate (vii)
- Lead (IV) oxide
- Manganese (IV) oxide
- Calcium chlorate (CaOCl2)
-
- to remove all the oxygen which would form iron (iii) oxide instead of iron (iii) chloride.
- CaO can absorb both Cl2 and moisture, CaCl2 can only absorb moisture.
- RMM FeCl3 = 162.5
Moles of FeCl3 = 0.5 = 0.003
162.5
Moles of Cl2 = 3 x 0.003 = 0.0045
Vol of Cl2= 0.0045 x 24000 = 110.8cm3
- Fe3+ is reduced to Fe2+; H2S is oxidized to sulphur
- Turns, red then white because chlorine is acidic and a bleaching agent inpresence of water.
-
- M 2:8
C 2:8:8 - Ionic bond
- Group one, Period 4
- “R” has a large atomic radius that “L”. The outermost electrons in “R” are not held tightly its nucleus.
- M 2:8
-
-
-
- ∆H1& ∆H2
- ∆H3& ∆H4
- ∆H1 – Atomisation
∆H4 – Condensation
-
- ∆H latt + -4690 + (3x -364) = 332
∆H latt – 5782 = -332
∆H latt - = 5450kJmol-1 - draw
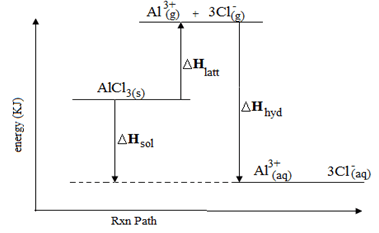
- ∆H latt + -4690 + (3x -364) = 332
-
- 2C4H9OH(l) + H3O2(g)8CO2(g)+ HOH2O(l)
- Draw
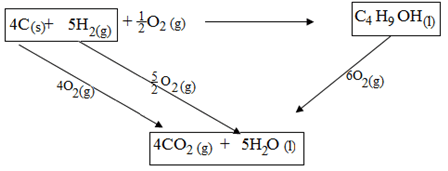
- ∆Hf + -2676 = (4 x -393) + (5 x -286)
∆Hf = -1572 + -1430 + 2676 = -326kJ mol-1
-
-
-
- G(s) + H2+(aq) → G2+(aq) + H(s)
- EMF = E0red – E oxi
+ 0.34 + 0.44 = + 0.78v
-
- K …. Cathode
J …… Anode - M – 4H+(aq) + 4e- 2H2(g)
H – 4OH-(aq) 2H2O(l)+ O2(g) + 4e- - HCl(aq)ions are readily discharged to chlorine gas hence there will be a mixture of two gases as the anode products (oxygen and chlorine gases)
- K …. Cathode
- 144750 Columbus = 144750 Faradays = 1.5F
96500
2 faradays gives 64g of copper
1.5 faradays give 1.5 x 64 = 48g
2
-
-
-
-
- Carbon (II) Oxide / Carbon (IV) Oxide
- Dilute Sulphuric acid
Chamber I
- ZnO(s) + C(s) CO(g) + Zn(s)
Roaster
2ZnS(s) + 3O2(g) SO2(s) + ZnO(s)
Chamber II
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g) -
- Mass of ZnS = 45 x250 = 112.5g
100 - 22 ZnS(s) + 3O2(g) 2SO2(g) + 2ZnO(s)
Moles of ZnS =112.5 = 1.16 moles
97.4
Volume of SO2 = 1.16 Moles
Volume of SO2 = 1.16 x 24 = 24.72 dm3 - 65.4 x 112.5 = 75.54g of Zn
97.4
- Mass of ZnS = 45 x250 = 112.5g
-
- Cause acidic rain
SO2 is poisonous - Contact process: SO2 (by product) can be used to manufacture sulphuric
-
-
-
Any pairNuclear reactions Chemical reactions Inolves protons and neutrons Involve valency electrons Reaction rate not affected by element changes Reaction rate is influenced by element changes Involve huge amount of energy Involve little amount of energy There is change in mass No change in mass -
- 1: Alpha II: beta
- 210 206 4
PoPb + He
84 82 2
-
-
- 120 minutes
- % value at 70 minutes = 9% 2
Mass = 0.16 x 100 = 1.778(g)
9±
-
- Treatment of cancer
- Sterlization of surgical equipment
- Treatment of leation of goiter
- Regulate heat pace makerAny one
- Detection of blood circulation disorders
- Measure of uptake of iodine.
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Lanjet Joint Mock Exams 2020.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

