INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name, index number and class in the spaces provided above.
- This paper consists of THREE SECTIONS, A, B and C.
- Answer all questions in sections A and B and two questions in section C.
- All your answers must be written in the spaces provided in this question paper.
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer all questions from this section
- What do the following terms mean? (1 ½ mks)
- Gross domestic product (G.D.P)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Gross national income (GNI)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Per capita income
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Gross domestic product (G.D.P)
-
- What does the term opportunity cost in farming mean? (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - State two situations when opportunity cost is nil or zero (2mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
- What does the term opportunity cost in farming mean? (1mk)
- List four advantages of individual owner tenure system (2mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - State two ways to show how check dams reduce soils erosion (1mks)
- Identify four soil constituents. (2mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Mention four ways of classifying herbicides (2mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. -
- List two ways of controlling smut disease in the field. (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Name any two pests that attack bean pods in the field (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
- List two ways of controlling smut disease in the field. (1mk)
- What four factors should a farmer consider for effective control of pests in the field
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. (2mks) - Mr. Wotsula Applied 150kg N.P.K 25:20:15 to his one hectare of groundnuts in his Kakamega farm. Calculate how many kilograms of each of the fertilizer element he applied. (3mks)
- State five marketing functions (2 ½mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - State five functions of cooperative societies (2½ mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - List three characteristics of green manure crops (1 ½ mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Name three types of water pumps to be used on the farm. (1 ½ mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Name four species of trees commonly used in agroforestry (2mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - List four factors that determine the competitive ability of weeds (2 mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
SECTION B: (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section
- The diagrams labeled A1, A2, A3, and B below illustrate materials and methods of vegetative propagation. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
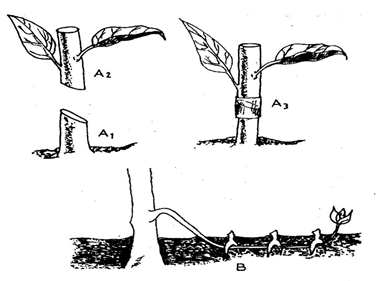
- Name the parts labeled A1, and A2 (2 mks)
A1 - ……………………………………………………………………………………………….
A2 - ………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Name the methods of propagation illustrated in diagrams A3 and B (2 mks)
A3 - …….…………………………………………………………………………………..….
B- ……………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Name the parts labeled A1, and A2 (2 mks)
- The diagram below illustrates some soil structures. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
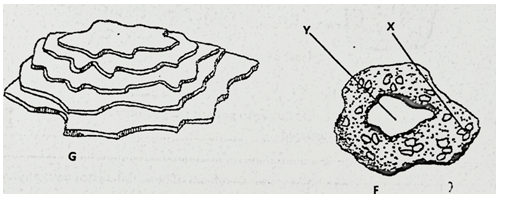
- Identify the soil structures F and G (2mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Name the parts labeled X and Y in diagram F (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Sate two ways through which structure G influences crop production (2mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Identify the soil structures F and G (2mks)
- Below is an illustration of a maize cob attacked by smut disease. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow:
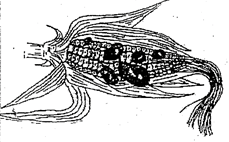
- Beside what is visible on the maize cob, state two other symptoms of the disease (2mks) …………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………. - State three control measures of the above disease. (3mks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Beside what is visible on the maize cob, state two other symptoms of the disease (2mks) …………………………………………………………………………………………….
- The diagram below shows a set up used to study an aspect of soil. The set up was left undisturbed for five hours. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
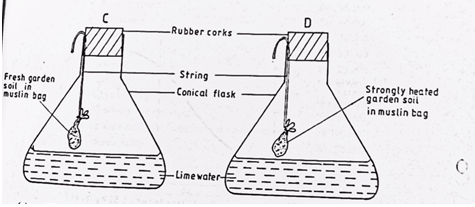
- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - State one observation that was made in each of the flasks labelled C and D (2mks)
C- …………………………………………………………….……………………….
D-………………………………………………………………………………………. - Give a reason for your answer in (b) above (2mks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Apart from the aspect under the study above, state any other soil component that could be studied (1mk)
……………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………….……………………………………………………………………………….
- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
SECTION C: (40 MARKS)
Answer any TWO questions from this section
- The following table shows an illustration of production of maize (in tons) using various levels of inputs
Units of variable input(Man hours) Total output of maize (Tons) Marginal Product Average product 0 0 1 6 2 18 3 33 4 40 5 45 6 48 7 48 8 40 - Work out the marginal product and average product and fill in the table (9mks)
- On the same graph paper, plot the graph showing total output, marginal product and average product against variable input (8mks)
- On the graph draw lines to show the following zones (3mks)
- Increasing return production function
- Decreasing return Production function
- Diminishing return production function
-
- Outline five benefits of trees and shrubs to the economic wellbeing of Kenyans (5mks)
- Explain 7 ways on how farmers overcome risks and uncertainties in a farming business (7mks)
- Explain the factors that influence the type of irrigation to be used in a farm (8 mks)
-
- State the principles involved in planning a crop rotation programme. (6mks)
- Discuss the production of maize under the following subheadings Maize
- Seedbed preparation (2mks)
- Planting (2mks)
- Weed control (2mks)
- Field management practices (2mks)
- Pests control (2mks)
- Disease control (2mks)
- Harvesting (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
- What do the following terms mean? (1½ mks)
- Gross domestic product (G.D.P)
- The sum total of goods and services produced by a country within one year.
- Gross national income (GNI)
- Total output from resources owned by the nationals of a country both within and outside the country within a year.
- Per capita income
- Gross national income divided by total population
- Gross domestic product (G.D.P)
-
- What does the term opportunity cost in farming mean? (1mk)
- Cost of the foregone alternative when we make a choice.
- Example is choosing to grow maize instead of wheat.
- Opportunity cost is the value of wheat
- Opportunity cost only exists where there are alternatives.
- State two situations when opportunity cost nil or zero (2mks)
- When supply is unlimited
- When goods are free
- When there are no alternatives
- What does the term opportunity cost in farming mean? (1mk)
- List four advantages of individual owner tenure system (2mks)
- deed used to secure loan credit
Independent production plan
Accessibility to agricultural advice
Earn income by leasing/renting land
High production of quality produce
Proper supervision of land (4 x ½ = 2mks)
- deed used to secure loan credit
- State two ways to show how check dams reduce soils erosion (1mks)
- Trap sediments/soil
Slow down the speed of run off
Reduce volume of run off (2 x ½ = 1mk)
- Trap sediments/soil
- Identify four factors that contribute to competitive ability of weeds (2mks)
- Produce large quantities of seeds
Seeds have a long viability
Propagate vegetatively
Extensive root system
Hardy/survive adverse weather and soil condition
Have a short life cycle
Gross feeders/heavy feeders (4 x ½ = 2mks)
- Produce large quantities of seeds
- Mention four ways of classifying herbicides (2mks)
- Mode of action
Time of application
Selectivity
Formation/physical form of herbicide (4 x ½ = 2mks)
- Mode of action
-
- List two ways of controlling smut disease in the field. (1mk) (1mk)
Rogueing/uproot and burn infected crop (reject rogueing alone)
Crop rotation
Plant resistant varieties of maize
Plant certified seeds
Avoid application of infected organic manure (2 x ½ = 1mk) - Name any two pests that attack bean pods in the field (1mk)
American bollworm (reject bollworm alone)
Flower thrips (2x ½ = 1mk)
- List two ways of controlling smut disease in the field. (1mk) (1mk)
- What four factors should a farmer consider for effective control of pests in the field (2mks)
- Nature of crop damage caused
Biology of pest/reproduction of pest/feeding habits
Weather conditions favoring pest attack
Whether pest has natural enemies
Population level of pest
- Nature of crop damage caused
- Mr. Wotsula Applied 150kg N.P.K 25:20:15 to his one hectare of groundnuts in his Kakamega farm. Calculate how many kg of each of the fertilizer element he applied. (3mks)
- N.P.K total ratio = 60
Nitrogen = 62.50 Kg
Phosphate = 50Kg
Potassium = 37.5Kg
- N.P.K total ratio = 60
- State five marketing functions (2 ½mks)
- Buying
- Selling
- Assembling by traders or middlemen
- Transportation i.e. distribution
- Standardization by grading and sorting out
- Storage facilities
- Processing
- Packing or packaging
- Advertising i.e. sales promotion
- Financing i.e. provide credit to farmers
- Risk bearing, Market research
- State five functions of cooperative societies (2 ½ mks)
- Marketing facilities
- Provision of inputs on credits
- Provide expert advice
- Storage of inputs and produce
- Giving loans all credit to farmers
- Educating for fair prices of inputs and produce
- Keep proper records of all activities
- Provide banking services to members.
- List three characteristics of green manure crops (1 ½ mks)
- Fast growth rate
- Preferably a legume
- Leafy / high foliage ratio
- Ability to rot rapidly
- Name three types of water pumps to be used on the farm. (1 ½ mks)
- Centrifugal / rotardynamic
- Semi-rotary
- Piston/ reciprocating pumps
- Hydram.
- Name four species of trees commonly used in agroforestry (2mks)
- Eucalyptus
- Cypress
- Grevillea
- Leukemia
- List four factors that determine the competitive ability of weeds (2 mks)
- Short life cycles
- Ability to produce many seeds
- Ability to propagate vegetatively
- Easy seed dispersal
- Seeds have long viability
- Extensive rooting system
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
-
- Name the parts labeled A1, and A2 (2 mks)
A1 -root stock
A2 -scion - Name the methods of propagation illustrated in diagrams A3 and B (2 mks)
A3 -Grafting
B- Trench layering
- Name the parts labeled A1, and A2 (2 mks)
-
- Identify the soil structures F and G (2mks)
G– Platy soil structure
F- Granular soil structure - Name the parts labeled X and Y in diagram F (1mk)
- Y- air space
- X- Humus with clay
- Sate two ways through which structure G influences crop production (2mks)
- Impedes root penetration.
- Hinders aeration
- Hinders drainage
- Hinders water infiltration
- Identify the soil structures F and G (2mks)
-
- Beside what is visible on the maize cob. State two other symptoms of the disease. (2mks)
- Severe dwarfness
- Increased tillering
- State three control measures of the above disease. (3mks)
- Planting resistant varieties
- Use of certified seeds
- Field hygiene
- Crop rotation
- Beside what is visible on the maize cob. State two other symptoms of the disease. (2mks)
-
- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
- To investigate the presence of living organisms in the soil
- State one observation that was made in each of the flasks labelled C and D (2mks)
C- Lime water turned milky
D- lime water remained clear - Give a reason for your answer in (b) above (2mks)
The living organisms in flask C respired and produced carbon dioxide which turned the lime water milky while heating in Flask D killed the microorganisms hence the lime water remained clear - Apart from the aspect under the study above, state any other soil component that could be studied (1mk)
- Soil water
- Soil air
- Soil organic matter
- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
| Units of variable input(Man hours) | Total output of maize (Tons) | Marginal Product | Average product |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 18 | 12 | 9 |
| 3 | 33 | 15 | 11 |
| 4 | 40 | 7 | 10 |
| 5 | 45 | 5 | 9 |
| 6 | 48 | 3 | 8 |
| 7 | 48 | 0 | 6.9 |
| 8 | 40 | -8 | 5 |
-
- On the same graph paper, plot the graph showing total output, marginal product and average product against variable input (8mks)
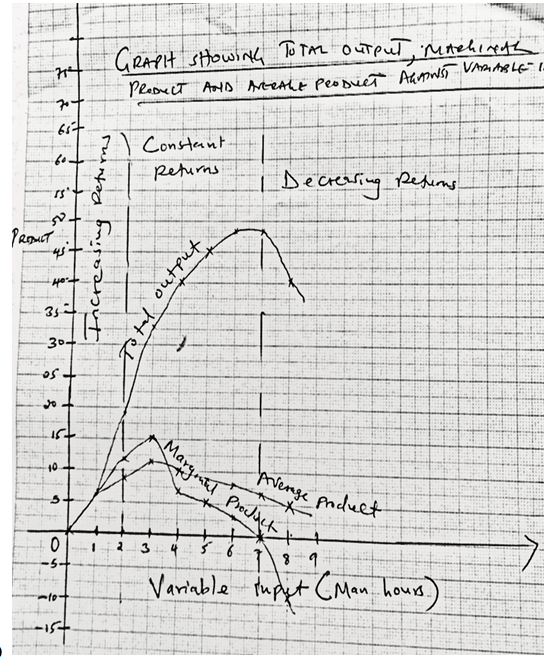
Plotting=3mks
Smooth curves=3mks
Correct scale =1mk
Correct labelling=2mks- On the graph draw lines to show the following zones (3mks)
- Increasing return production function
- Decreasing return Production function
- Diminishing return production function
- On the same graph paper, plot the graph showing total output, marginal product and average product against variable input (8mks)
-
- Outline five benefits of trees and shrubs to the economic wellbeing of Kenyans (5mks)
Some are used as cash crops
Some produce edible fruits which can be sold
Some are used for production of industrial products
Most are source of timber and poles
Their roots help to bind soil particles together which helps to prevent soil erosion
Some trees provide nectar and pollen which is used by bees
Some have medicinal value - Explain 7 ways on how farmers overcome risks and uncertainties in a farming business (7mks
Diversification/ growing a variety of crop or having various enterprises so that if one fails has something to rely on.
Insurance against losses/ taking insurance policy for farming activities so that in case of failure the enterprises are covered.
Inventory marketing/ strategic farming keeping farm product and selling at when prices are favorable
Flexible enterprises engaging in enterprises that can be stopped or started early as condition change.
Rationing of inputs using just sufficient inputs such that in case of losses the cost is not too high
Using more certain husbandry practices using practices that the farmer is sure of and has used in the past.
Hedging/ contract marketing making arrangements with marketing agencies in advance so that changes in price after the arrangement do not change the price of the farmer’s produce.
Selecting more certain enterprises selection of enterprises that the done well in the area/ tried though research (Any 7 x 1 = 7mks) - Explain the factors that influence the type of irrigation to be used in a farm
Topography,
Soil type
Type of crop to be irrigated.
Amount of water available.
Technology available.
Distance of the source of water to the field.
Capital available, skills available
Climate factors of the area.
(Relevant application to be given, 8 x 1 =8mks)
- Outline five benefits of trees and shrubs to the economic wellbeing of Kenyans (5mks)
-
- State the principles involved in planning a crop rotation programme. (6mks)
Shallow rooters should alternate with deep rooters.
Crop attacked by the same pests and disease should not follow each other.
Crops with high nutrient requirement should come first in a newly ploughed land.
Legumes should be included in the programme to increase nitrogen content of soil.
Fallow period / grass should be included in the rotation to build soil structure.
Crops which are hard to weed should alternate with those that are easy to weed. - Discuss the production of maize under the following subheadings Maize
- Seedbed preparation (2mks)
Clear land early before the rains
Harrow the land to medium tilth
Cultivate land to get rid of perennial weeds and allow vegetation to rot. - Planting (2mks)
Done at the beginning of rains
Dry planting is recommended
Spacing varies with variety i.e. 23-30 cm x 57 – 90 cm
Plant seed at 2.5 – 10 cm deep
Planting manually or mechanically
Apply DAP at 100 – 150 kg/ hectare in planting hole
Top dress with CAN at 200kg / hectare - Weed control (2mks)
Weed at early stage to reduce competition for moisture
Hand weeding done
Herbicides sometimes used e.g. simazine/ atrazine before germination and MCPA / 2-4- D after germination. - Field management practices (2mks)
Thinning done early to get consistent growth
Gapping done early - Pests control (2mks)
Scare birds e.g. quellea and weaver birds
Use appropriate control of pests e.g. aphids, army worm e.g. insecticides.
Disease control (2mks)
Use appropriate control e.g. fungicides for smut, rust and maize streak
Harvesting (2mks)
Depending on altitude and variety
Stock out maize or harvest cobs when dry in field
- Seedbed preparation (2mks)
- State the principles involved in planning a crop rotation programme. (6mks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Lanjet Joint Mock Exams 2020.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

