Instructions to candidates
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above.
- This paper consists of Two sections: Section I and section II.
- Answer ALL the questions in section I and only five questions from section II.
- All answers and working must be written on the question paper in the spaces below each question.
- Show all the steps in your calculations, giving your answers at each stage in the spaces below each question.
- Marks may be given for correct working even if the answer is wrong.
- Non-programmable silent electronic calculators and KNEC tables may be used.
For examiners use only
Section 1
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
Total |
Section II
|
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
Total |

QUESTIONS
SEC I: (50 marks)
Answer all questions in this section
- Without using a calculator evaluate. (3mks)
(-16) - 36 - 4(-17 + 5)
18÷(-6)-10 8 - Three metal rods of lengths 234cm, 270cm and 324cm were cut into short pieces all of the same length to make window grills. Calculate the length of the longest piece that can be cut from each of the rods and hence the total number of pieces that can be obtained from the rods. (3mks)
- A point P has the coordinates (1, 2, 3). If PQ = 5i + j + 2k , find.
- the coordinates of point Q. (2mks)
- the modulus of PQ. (1mk)
- The size of an exterior angle of a regular polygon is 3 1/2 times that of its exterior angle. Determine the sum of interior angles of the polygon. (4mks)
- Evaluate using square root, reciprocal and square tables only. (3 mks)
1 - 1
(√0.7235) 10.56 - Solve for x and y in the following equations (4mks)
2x + 3y =59
2 x+3 – 3y+2 = 13 - Solve the inequalities and represent the solution on number line. (3mks)
3x – 9 < 5x + 3 < 2x – 6 - A Kenyan bank buys and sells foreign currencies as shown below.
A businessman on a trip to Kenya had £50000 which he converted to Kenya shillings .While in Kenya he spent 80% of the money and changed the remaining amount to South African Rand.Calculate to the nearest Rand the amount he received. (3mks)Buying (ksh)
Selling (ksh)
1 Sterling pound (£)
130.10
130.54
1 South African Rand
9.52
9.58
- Simplify the expression (3mks)
2x2 - 3xy - 2y2
4x2 - y2 - The volumes of two similar cans are 125cm3 and 216cm3 respectively. If the base area of the smaller can is 75cm2, find the base area of the larger can. (3 marks)
- Find the perimeter of the figure belowto 4 s.f. (3 marks)
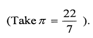
- Thirty men working at the rate of 10 hours a day can complete a job in 14 days. Find how long it would take 40 men working at the rate of 7 hours a day to complete the same job. (3mks)
- The curved surface area of a cylindrical container is 1980cm2. If the radius of the container is 21cm, calculate to one decimal place the capacity of the container in litres (3 mks)
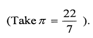
- In the figure below PQRS is a rhombus, ∠SQR = 55º, ∠QST is a right angle and TPQ is a straight line.
Find the size of the angle STQ. (3 marks) - From a viewing tower 30metres above the ground, the angle of depression of an object on the ground is 30º and the angle of elevation of an aircraft vertically above the object is 42º.Calculate the height of the aircraft above the ground to the nearest whole number. (3mks)
- Joan earns a commission of 3% on sales up to sh. 150000. She gets an additional commission of 1.5% on any sales above this. In one month she sells goods worth sh. 385000 at a discount of 2%. Calculate the amount of commission she received. (3mks)
SEC. II: (50 marks)
Answer ONLY FIVE questions from this section
- A straight line L1 passes through the points P (5, 2) and Q( 3, 4).
- Find the equation of L1 in the form ax +by+ c = 0where a, b and c are integers.(3 mks)
- A line L2 passes through a point R (0 ,3) and is perpendicular to L1.
- Find the equation of L2 in the form y= m x+ cwhere mand care constants. (2 mks)
- Determine the point of intersection between L1 and L2. (3 marks)
- Another line L3 is parallel to L1 and passes through R. Find the x – intercept of L3.(2 marks)
- The figure shows the cross-section of a cylindrical tank containing some oil and lying horizontally. The tank is 4m long. O is the centre of the circle, radius 14cm and ∠AOB=120°. (π=22/7)
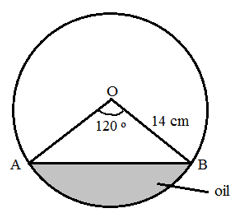
Calculateto 2 d.p:- The length of chord AB. (2 marks)
- The area of segment ACB. (3 marks)
- The volume of oil in the tank in m3. (2 marks)
- The area of the tank in contact with the oil in cm2. (3 marks)
- A bus travels from Nairobi to Kisumu a distance of 320 km at a speed of x km/hr.If the speed is reduced by 20km/hr the bus would take 48 minutes more.
- Form an equation to represent the given information and hence find the speed of the bus (5mks)
- Determine the time taken by the bus for the whole journey (1mk)
- Another car left Kisumu at 8.00 a.m.and travelled along the same road to Nairobi at an average speed of 80km/h.If the bus left Nairobi at 9.00 a.m, determine the time when the vehicles met. (4mks)
- Four towns P, R, T and S are such that R is 80km directly to the north of P and T is on abearing of 290° from P at a distance of 65km. S is on a bearing of 330° from T and a distance of30 km. Using a scale of 1cm to represent 10km, make an accurate scale drawing to show therelative position of the towns. (3mks)
Find:- The distance and the bearing of R from T (3mks)
- The distance and the bearing of S from R (3mks)
- The bearing of P from S (lmk)
-
- Triangle ABC has the vertices A(-2,-2),B(-2,-5) and C(-5,-4). Draw ∆ABC on the graph paper provided. (1 mark)
- ∆A'B'C'is the image of ∆ABC under reflection in the line x + y = 0. Draw triangle A'B'C' on the same axes and state its coordinates. (3 marks)
- ∆A''B''C''is the image of ∆A'B'C' under a positive quarter turn about the origin. Draw ∆A''B''C'' on the same axes and state its coordinates. (3 marks)
- ∆A'''B'''C'''is the image of ∆A''B''C'' under an enlargement centre (0,0) and scale factor -1. Draw ∆A'''B'''C''' and state its coordinates. (3 marks)
- Triangle ABC has the vertices A(-2,-2),B(-2,-5) and C(-5,-4). Draw ∆ABC on the graph paper provided. (1 mark)
- The figure below represents a model of a solid structure in the shape of a frustrum of a cone with a hemispherical top. The diameter of the hemispherical part and the top of the frustrum is 70cm. The frustrum has a base diameter of 28cm and slant height of 60cm.
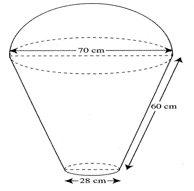
Calculate:- The area of the hemispherical surface. (2mks)
- The slant height of the cone from which the frustrum was cut. (2mks)
- The curved surface area of the frustrum. (2mks)
- The area of the base. (2mks)
- The total surface area of the model. (2mks)
- Fifty three seedlings were uprooted from a nursery and their heights measured to the nearest centimeter and recorded in the given table.
Calculate:Height (cm)
Frequency
13 -15
16- 18
19 – 21
22 – 24
25 – 27
28 – 30
31 – 33
4
7
11
15
6
5
2
-
- The mean height of the seedlings (3mks)
- The median height of the seedlings (3mks)
- Draw a histogram and hence a frequency polygon to represent the above data (4mks)

-
- In the figure below PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral. Given that TPX is a tangent at P and O is the centre of the circle. RQX is a straight line with angle RPQ = 50º, and angle PRS = 25º.
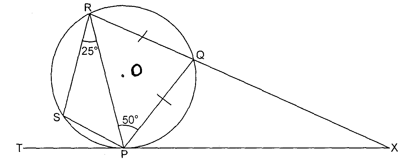
Giving reasons in each case, find:- Angle PRQ (2mks)
- Angle PSR. (2mks)
- Angle PXQ (2mks)
- Angle TPS (2mks)
- Angle POS (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
SEC I: (50 marks)
Answer all questions in this section
- Without using a calculator evaluate. (3mks)
(-16) - 36 - 4(-17 + 5)
18÷(-6)-10 8 - Three metal rods of lengths 234cm, 270cm and 324cm were cut into short pieces all of the same length to make window grills. Calculate the length of the longest piece that can be cut from each of the rods and hence the total number of pieces that can be obtained from the rods. (3mks)
- A point P has the coordinates (1, 2, 3). If PQ = 5i + j + 2k , find.
- the coordinates of point Q. (2mks)
- the modulus of PQ. (1mk)
- The size of an exterior angle of a regular polygon is 3 1/2 times that of its exterior angle. Determine the sum of interior angles of the polygon. (4mks)
- Evaluate using square root, reciprocal and square tables only. (3 mks)
1 - 1
(√0.7235) 10.56 - Solve for x and y in the following equations (4mks)
2x + 3y =59
2 x+3 – 3y+2 = 13 - Solve the inequalities and represent the solution on number line. (3mks)
3x – 9 < 5x + 3 < 2x – 6 - A Kenyan bank buys and sells foreign currencies as shown below.
A businessman on a trip to Kenya had £50000 which he converted to Kenya shillings .While in Kenya he spent 80% of the money and changed the remaining amount to South African Rand.Calculate to the nearest Rand the amount he received. (3mks)Buying (ksh)
Selling (ksh)
1 Sterling pound (£)
130.10
130.54
1 South African Rand
9.52
9.58
- Simplify the expression (3mks)
2x2 - 3xy - 2y2
4x2 - y2 - The volumes of two similar cans are 125cm3 and 216cm3 respectively. If the base area of the smaller can is 75cm2, find the base area of the larger can. (3 marks)
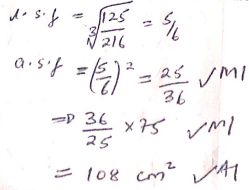
- Find the perimeter of the figure belowto 4 s.f. (3 marks)

p = (169 × 2 × 22 × 4.2) + 4.2 + 4.2
360 7
=12.39 + 8.4
=20.79 cm - Thirty men working at the rate of 10 hours a day can complete a job in 14 days. Find how long it would take 40 men working at the rate of 7 hours a day to complete the same job. (3mks)
M H D
30 10 14
40 7 ?
= 30 × 10 × 14
40 7
= 15 days - The curved surface area of a cylindrical container is 1980cm2. If the radius of the container is 21cm, calculate to one decimal place the capacity of the container in litres (3 mks)
2 × 22 × 21 × h = 1980
7
h = 15 cm
volume = 22 × 212 × 15
7
= 20790 cm3
= 20.79 L
≈ 20.8 L - In the figure below PQRS is a rhombus, ∠SQR = 55º, ∠QST is a right angle and TPQ is a straight line.
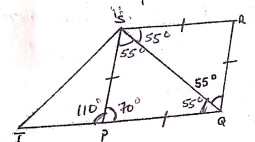
<TPS = 110º
<STQ = 180 - (110 + 35)
= 35º
<TSP = 35º
Find the size of the angle STQ. (3 marks) - From a viewing tower 30metres above the ground, the angle of depression of an object on the ground is 30º and the angle of elevation of an aircraft vertically above the object is 42º.Calculate the height of the aircraft above the ground to the nearest whole number. (3mks)
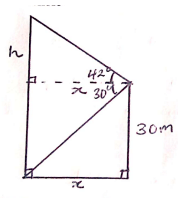
Tan 30º = 30
x
x = 30 = 51.96m
tan 30
h = 51.96 tan 42º
= 46.78 m
height of aircraft
= 30 + 46.78
= 76.78
≈ 77m - Joan earns a commission of 3% on sales up to sh. 150000. She gets an additional commission of 1.5% on any sales above this. In one month she sells goods worth sh. 385000 at a discount of 2%. Calculate the amount of commission she received. (3mks)
98 × 385 000
100
= sh.377300
3 × 150000
100
= sh 4500
4.5 × 277300
100
=sh 10228.50
total - 4500 + 10228.50
≈ sh.14728.50
SEC. II: (50 marks)
Answer ONLY FIVE questions from this section
- A straight line L1 passes through the points P (5, 2) and Q( 3, 4).
- Find the equation of L1 in the form ax +by+ c = 0where a, b and c are integers.(3 mks)
gradient = 4 - 2 = -1
3 - 5
= y - 2 = -1
x - 5
y - 2 = -x + 5
therefore x + y - 7 = 0 - A line L2 passes through a point R (0 ,3) and is perpendicular to L1.
- Find the equation of L2 in the form y= m x+ cwhere mand care constants. (2 mks)
m1m2 = -1 ⇒ m2 = 1
y - 3 = 1
x - 0
y - 3 = x
therefore: y = x + 3 - Determine the point of intersection between L1 and L2. (3 marks)
x + y - 7 = 0 .....(i)
y = x + 3 ..........(ii)
x + x + 3 - 7 = 0
x = 2
y = 5
therefore: point is (2,5)
- Find the equation of L2 in the form y= m x+ cwhere mand care constants. (2 mks)
- Another line L3 is parallel to L1 and passes through R. Find the x – intercept of L3.(2 marks)
m = 1
y - 3 = -1
x - 0
y - 3 = -x
y = -x + 3
therefore: x-intercept; x = 3
- Find the equation of L1 in the form ax +by+ c = 0where a, b and c are integers.(3 mks)
- The figure shows the cross-section of a cylindrical tank containing some oil and lying horizontally. The tank is 4m long. O is the centre of the circle, radius 14cm and ∠AOB=120°. (π=22/7)

Calculateto 2 d.p:- The length of chord AB. (2 marks)
sin 60º = NB
14
NB = 12.12cm
therefore: AB = 2 × 12.12 = 24.24 cm
ALT:
NB = 14
sin 60 sin 90
NB = 12.12cm
therefore: AB = 24.24cm - The area of segment ACB. (3 marks)
120 × 22 × 142 - ½ × 142 sin 120
360 7
205.33 - 84.87
=120.46 cm2 - The volume of oil in the tank in m3. (2 marks)
120.46 × 400
1000000
=0.05m3 - The area of the tank in contact with the oil in cm2. (3 marks)
120 × 2 × 22 × 14 × 400 + 2 × 120.46
360 7
= 11733.33 + 240.92
=11974.25cm2
- The length of chord AB. (2 marks)
- A bus travels from Nairobi to Kisumu a distance of 320 km at a speed of x km/hr.If the speed is reduced by 20km/hr the bus would take 48 minutes more.
- Form an equation to represent the given information and hence find the speed of the bus (5mks)
320 - 320 = 4
x - 20 x 5
1600x - 1600x + 32000 = 4x2 - 80x
4x2 - 80x - 32000 = 0
x2 - 20x - 8000 = 0
x2 - 100x + 80x - 8000 = 0
x(x - 100) + 80(x - 100) = 0
(x - 100)(x + 80) = 0
x = 100, x = -80 (ignore)
= x = 100km/h - Determine the time taken by the bus for the whole journey (1mk)
320 = 3.2hrs
100
or
3hrs 12min - Another car left Kisumu at 8.00 a.m.and travelled along the same road to Nairobi at an average speed of 80km/h.If the bus left Nairobi at 9.00 a.m, determine the time when the vehicles met. (4mks)
in 1 hour; x = 80 × 1
= 80kn
R.D = 320 - 80
=240km
R.S = 100 + 80 = 180km/h
time taken = 240 = 11/3
180
meeting time = 9.00am
1.20
=10.20am
ALT
320 - 80 = 240km
240 - x = x
100 80
100x = 19200 - 80x
180x = 19200
x = 106.67km
T.T = 106.67
80
= 11/3
meeting time = 10.20 am
- Form an equation to represent the given information and hence find the speed of the bus (5mks)
- Four towns P, R, T and S are such that R is 80km directly to the north of P and T is on abearing of 290° from P at a distance of 65km. S is on a bearing of 330° from T and a distance of30 km. Using a scale of 1cm to represent 10km, make an accurate scale drawing to show therelative position of the towns. (3mks)
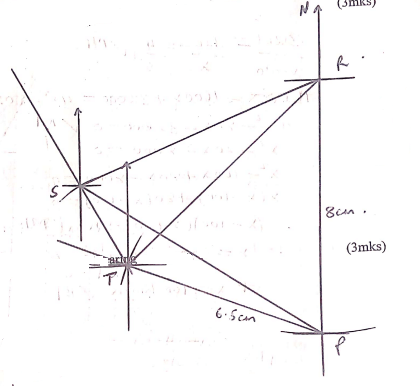
Find:- The distance and the bearing of R from T (3mks)
RT = 8.4 × 10
84km ± 1km
bearing of R from T = 045º ± 1º
OR
N45ºE - The distance and the bearing of S from R (3mks)
8.2 × 10
=82 km
247º or 567º W - The bearing of P from S (1mk)
124º
or S56ºE
- The distance and the bearing of R from T (3mks)
-
- Triangle ABC has the vertices A(-2,-2),B(-2,-5) and C(-5,-4). Draw ∆ABC on the graph paper provided. (1 mark)
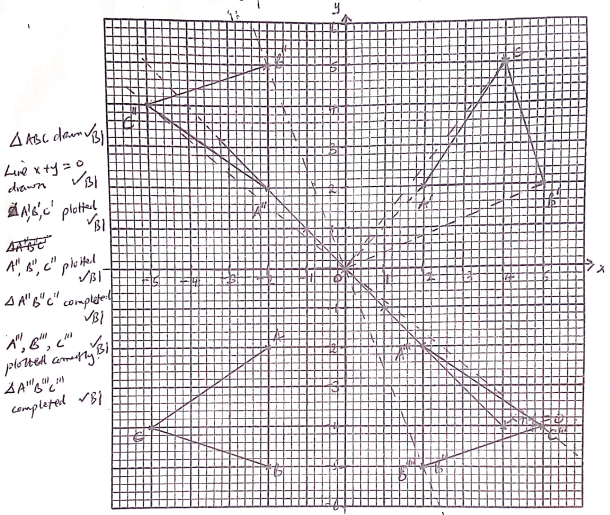
- ∆A'B'C'is the image of ∆ABC under reflection in the line x + y = 0. Draw triangle A'B'C' on the same axes and state its coordinates. (3 marks)
A'(2,2), B'(5,2), C(4,5) - ∆A''B''C''is the image of ∆A'B'C' under a positive quarter turn about the origin. Draw ∆A''B''C'' on the same axes and state its coordinates. (3 marks)
A''(-2,2), B''(-2,5), C''(-5,4) - ∆A'''B'''C'''is the image of ∆A''B''C'' under an enlargement centre (0,0) and scale factor -1. Draw ∆A'''B'''C''' and state its coordinates. (3 marks)
A'''(2,-2), B'''(2,-5), C'''(5,-4)
- Triangle ABC has the vertices A(-2,-2),B(-2,-5) and C(-5,-4). Draw ∆ABC on the graph paper provided. (1 mark)
- The figure below represents a model of a solid structure in the shape of a frustrum of a cone with a hemispherical top. The diameter of the hemispherical part and the top of the frustrum is 70cm. The frustrum has a base diameter of 28cm and slant height of 60cm.

Calculate:- The area of the hemispherical surface. (2mks)
2 × 22 × 352
7
= 7700cm2 - The slant height of the cone from which the frustrum was cut. (2mks)
α = 28
α + 60 70
70l = 28l + 1680
α = 40cm
L = 40 + 60
= 100cm - The curved surface area of the frustrum. (2mks)
22 × 35 × 100 - 22 × 14 × 40
7 7
= 11000 - 1760
= 9240 cm2 - The area of the base. (2mks)
22 × 142
7
= 616 cm2 - The total surface area of the model. (2mks)
= 7700 + 9240 + 616
= 17556 cm2
- The area of the hemispherical surface. (2mks)
- Fifty three seedlings were uprooted from a nursery and their heights measured to the nearest centimeter and recorded in the given table.
Calculate:Height (cm)
Frequency
(f)x fx c.f 13 -15
16- 18
19 – 21
22 – 24
25 – 27
28 – 30
31 – 334
7
11
15
6
5
214
17
20
23
26
29
3256
119
220
345
156
145
644
11
22
37
43
48
50-
- The mean height of the seedlings (3mks)
= 1105
50
=22.1 cm - The median height of the seedlings (3mks)
medidan class : 22 - 24
median = 21.5 + (25 - 22) × 3
15
= 22.1 cm
- The mean height of the seedlings (3mks)
- Draw a histogram and hence a frequency polygon to represent the above data (4mks)
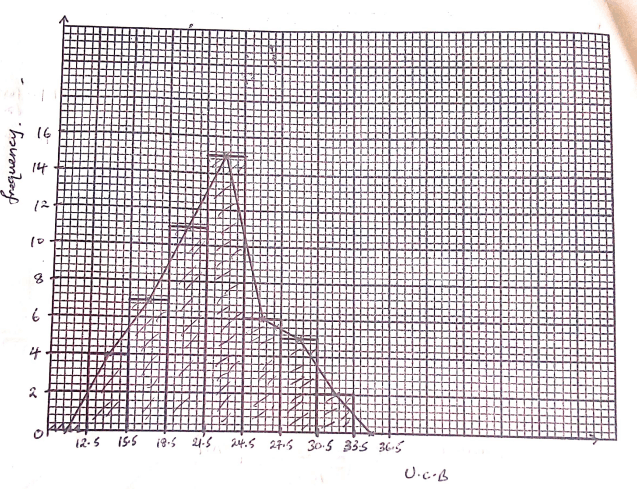
-
- In the figure below PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral. Given that TPX is a tangent at P and O is the centre of the circle. RQX is a straight line with angle RPQ = 50º, and angle PRS = 25º.
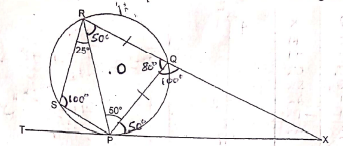
Giving reasons in each case, find:- Angle PRQ (2mks)
50º
base angles of isoscels triangle are equal - Angle PSR. (2mks)
100º
opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary - Angle PXQ (2mks)
180 - (100 + 50)
=30º
angle of sum of triangle up to 180º - Angle TPS (2mks)
25º
angle in the alteranate segment - Angle POS (2mks)
50º
angle at the centre is twice angle circumference
- Angle PRQ (2mks)
Download Mathematics P1 Questions and Answers - Nambale Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

