INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- You are NOT allowed to start working within the first 15 minutes of the 2 ¼ hours allowed for this paper. This time is to enable you read the question paper and make sure you have all the chemicals and apparatus that you may need.
- All working MUST be clearly shown.
- Mathematical tables and silent scientific calculators may be used.
- This paper consists of 7 printed pages.
- Candidates should check to ascertain that all papers are printed as indicated and that no questions are Missing
QUESTIONS
- You are provided with:
- 5.0g of solid X in a boiling tube
- Solution Y, which is acidified Potassium manganate (VII) containing 9.0g of Potassium manganate (VII), KMnO4, in 1000cm3 of solution.
You are required to determine:
- The solubility of solid X at different temperatures
- The number of moles of water of crystallization in solid X
Procedure
- Using a 10 cm3 measuring cylinder add 4cm3 of distilled water to solid X in the boiling tube. Heat the mixture while stirring with thethermometer to about 85ºC.When all the solid has dissolved allow the solution to cool while stirring with the thermometer.(You can occasionally immerse the boiling tube in a beaker of tap water).Note the temperature at which crystals of solid X first appear. Record this temperature in table 1.
- Add 2cm3 of distilled water to the contents of the boiling tube warm the mixture while stirring with the thermometer until all the solid dissolves. Allow the mixture to cool while stirring. Note and record the temperature at which crystals of solid X first appear.
- Repeat procedure (ii) three more times and record the temperature in the table 1. Retain the contents of the boiling tube for use in the procedure
-
- Complete table 1 by calculating the solubility of solid X at different temperatures.
Table 1
(6 marks)Volume of water (cm3) Temperature at which crystals(ºC) Solubility of solid X (g/100g of water) 4 6 8 10 12 - On the grid provided, plot a graph of solubility of solid X (vertical axis) against temperature. (3 marks)

- Using your graph, determine the temperature at which 100g of solid X would dissolve in 100cm3 of water. (1 mark)
Procedure II
- Complete table 1 by calculating the solubility of solid X at different temperatures.
-
- Transfer the contents of the boiling tube into a 250ml volumetric flask, rinse both the boiling tube and the thermometer with distilled water and add to the volumetric flask. Add more distilled water to make up to the mark. Label this solution X. Fill a burette with solution Y.
Using the pipette and pipette filler, place 25.0cm3 of solution X into a conical flask. Warm the mixture to about 60ºC. Titrate the hot solution X with solution Y until a permanent pink colour persists. Continuously shake the mixture during the titration. Record your readings in table 2.
Repeat the titration two more times and complete the table 2.
Table 2
(4 marks)Titration I II III Final burette reading (cm3) Initial burette reading (cm3) Volume of solution Y used (cm3) - Calculate the:
- average volume of solution Y used (1 mark)
- Number of moles of Solution Y, Potassium manganate (VII) used (K=39, Mn=55, O=16) (2 marks)
- Number of moles of X in 25cm3 of solution X given that 2 moles of potassium manganate (VII) react completely with 5 moles of X (1 mark)
- Number of moles of X in 250cm3 of solution (1 mark)
- Relative formula mass of X, (1 mark)
- The formula of X has the form X.nH2O. Determine the value of n in the formula given that the relative mass of X is 90.0
(O=16.0, H=1.0) (2 marks)
- Transfer the contents of the boiling tube into a 250ml volumetric flask, rinse both the boiling tube and the thermometer with distilled water and add to the volumetric flask. Add more distilled water to make up to the mark. Label this solution X. Fill a burette with solution Y.
- You have been provided with solid R. Carry out the tests below
- Transfer all the solid R to a boiling tube. Add about 6cm3 of distilled water and shake the mixture thoroughly. Allow to settle then carefully filter into another boiling tube. Retain the residue for part (b)
Divide the filtrate into three portions- To the first portion of the filtrate in a test tube, add few drops of 2M lead (II) nitrate solution and warm
Observations Inferences (1 mark) (1/2 mark) - To the second portion of the filtrate in a test tube, add 2M sodium hydroxide solution drop wise until in excess
Observations Inferences (1 mark) (1 mark) -
- Describe how you would carry out a flame test on the solution obtained.
Procedure Expected observation (1 mark) (1 mark) - On the third portion of the filtrate, carry out the flame test described above
Observations Inferences (1 mark) (1/2 mark)
- Describe how you would carry out a flame test on the solution obtained.
- To the first portion of the filtrate in a test tube, add few drops of 2M lead (II) nitrate solution and warm
-
- To the residue in a boiling tube add 2M hydrochloric acid provided drop wise until there is no more change. Test for any gas using a burning splint.
Divide the resultant solution into two portions
Observations Inferences (1 mark) (1/2 mark) - To the first portion, add 2M sodium hydroxide solution drop wise until in excess
Observations Inferences (1 mark) (1/2 mark) - To the second portion, add 2M ammonium hydroxide solution until in excess
Observations Inferences (1 mark) (1/2 mark)
- To the residue in a boiling tube add 2M hydrochloric acid provided drop wise until there is no more change. Test for any gas using a burning splint.
- Transfer all the solid R to a boiling tube. Add about 6cm3 of distilled water and shake the mixture thoroughly. Allow to settle then carefully filter into another boiling tube. Retain the residue for part (b)
- You are provided with solid H. Carry out the tests below. Write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Using a clean metallic spatula, heat about one third of solid H in a Bunsen burner flame.
Observations Inferences (1 mark) (1 mark) - Dissolve the remaining portion of solid H by adding about 6cm3 of distilled water and divide the solution into 3 portions.
- To the first portion, add two drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution
Observations Inferences (1 mark) (1 mark) - To the second portion, add two drops of bromine water
Observations Inferences (1 mark) (1 mark) - Determine the pH of the third portion using universal indicator paper
Observations Inferences (1/2 mark) (1/2 mark)
- To the first portion, add two drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution
- Using a clean metallic spatula, heat about one third of solid H in a Bunsen burner flame.
CONFIDENTIAL INSTRUCTIONS
Instructions to Schools:
The information contained in this paper is to enable the head of the school and the teacher in charge of Chemistry to make adequate preparation for the Chemistry Practical Examination.
NO ONE ELSE should have access to this paper or acquire knowledge of its content. Great care MUST be taken to ensure that the information herein does NOT reach the candidates either directly or indirectly. The teacher in charge of Chemistry should NOT perform any of the experiments in the SAME room as the candidates nor make the results of the experiment available to the candidates of give any information related to the experiments to the candidates. Doing so will constitute an examination irregularity.
In addition to the fittings and apparatus found in a Chemistry laboratory, EACH candidate will require:
- 100ml of Solution Y for each candidate
- Accurately weighed 5g of solid X supplied in a stoppered container.
- About 0.5g of Solid H supplied in a stoppered container.
- About 1g of solid R supplied in a stoppered container.
- One Burette, 0-50ml.
- One 25ml Pipette.
- Three 250ml Conical Flasks
- 250ml Volumetric Flask with a stopper.
- One complete Retort Stand
- One White Tile
- One Pipette Filler
- One Test-tube Rack
- Six Test-tubes (on a rack)
- Source of heat
- Tripod stand
- Wire gauze
- Clean metallic spatula
- Wooden splint
- Clean glass rod or Nichrome wire loop
- Thermometer with a range of -10ºC to 110ºC
- 200cm3 beaker
- Test tube holder
- One label
- Two Boiling tubes
- One Filter paper
- Filter funnel
- Measuring cylinder 10ml
- Wash bottle filled with distilled water
ACCESS TO
- Acidified Potassium Manganate (VII) supplied with a dropper.
- Universal indicator paper
- PH chart
- 2M Hydrochloric acid supplied with a dropper.
- 2M Sodium hydroxide solution supplied with a dropper.
- 2M Ammonia solution supplied with a dropper.
- 2M lead (II) nitrate supplied with a dropper.
- Bromine water supplied with a dropper.
NOTES
- Solution Y -Acidified Potassium Manganate (VII)prepared by dissolving 9g of solid Potassium Manganate (VII) in about 600cm3 of 2M Sulphuric (VI) acid and adding distilled water to make a litre of solution.
- Solid H is pure Maleic acid.
- Solid R is a 1g mixture of anhydrous calcium chloride and zinc carbonate in the ratio of 1:1
- Solid X is accurately weighed 5g of Oxalic acid

MARKING SCHEME
- You are provided with:
- 5.0g of solid X in a boiling tube
- Solution Y, which is acidified Potassium manganate (VII) containing 9.0g of Potassium manganate (VII), KMnO4, in 1000cm3 of solution.
You are required to determine:
- The solubility of solid X at different temperatures
- The number of moles of water of crystallization in solid X
Procedure
- Using a 10 cm3 measuring cylinder add 4cm3 of distilled water to solid X in the boiling tube. Heat the mixture while stirring with thethermometer to about 85ºC.When all the solid has dissolved allow the solution to cool while stirring with the thermometer.(You can occasionally immerse the boiling tube in a beaker of tap water).Note the temperature at which crystals of solid X first appear. Record this temperature in table 1.
- Add 2cm3 of distilled water to the contents of the boiling tube warm the mixture while stirring with the thermometer until all the solid dissolves. Allow the mixture to cool while stirring. Note and record the temperature at which crystals of solid X first appear.
- Repeat procedure (ii) three more times and record the temperature in the table 1. Retain the contents of the boiling tube for use in the procedure
-
- Complete table 1 by calculating the solubility of solid X at different temperatures.
Table 1
(6 marks)Volume of water (cm3) Temperature at which crystals(ºC) Solubility of solid X (g/100g of water) 4 79 125.000 6 67 83.333 8 55 62.500 10 52 50.000 12 48 41.667
- Accuracy(79±2ºC) - 1mk
- Decimal - 1mk
- Trend - 1/2 mk
- Complete table - 1
- Calculations (solubility column) - 2.5mks
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of solubility of solid X (vertical axis) against temperature. (3 marks)
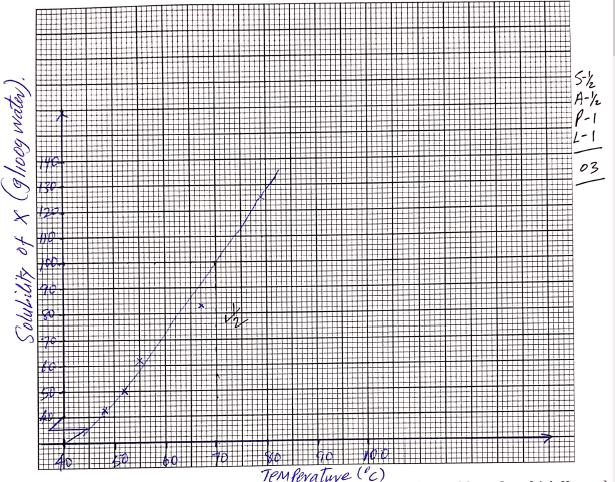
- Using your graph, determine the temperature at which 100g of solid X would dissolve in 100cm3 of water. (1 mark)
70ºC (Must be shown on graph)
Procedure II
- Complete table 1 by calculating the solubility of solid X at different temperatures.
-
- Transfer the contents of the boiling tube into a 250ml volumetric flask, rinse both the boiling tube and the thermometer with distilled water and add to the volumetric flask. Add more distilled water to make up to the mark. Label this solution X. Fill a burette with solution Y.
Using the pipette and pipette filler, place 25.0cm3 of solution X into a conical flask. Warm the mixture to about 60ºC. Titrate the hot solution X with solution Y until a permanent pink colour persists. Continuously shake the mixture during the titration. Record your readings in table 2.
Repeat the titration two more times and complete the table 2.
Table 2
(4 marks)Titration I II III Final burette reading (cm3) 27.4 27.4 27.4 Initial burette reading (cm3) 0.0 0.0 0.0 Volume of solution Y used (cm3) 27.4 27.4 27.4 - Calculate the:
- average volume of solution Y used (1 mark)
I + II + III = Ans bI e.g. 27.4 +27.4 + 27.4 = 27.4
3 3 - Number of moles of Solution Y, Potassium manganate (VII) used (K=39, Mn=55, O=16) (2 marks)
KMnO4 = 158
Molarity = 9/158
0.057M
Moles = (Ans bI x 0.057) ÷1000
= ans bII
e.g. 27.4 x 0.057 = 0.001561mol
1000 - Number of moles of X in 25cm3 of solution X given that 2 moles of potassium manganate (VII) react completely with 5 moles of X (1 mark)
MnO4:x = 2:5
Moles of x in 25cm3 = 5/2 x ans bII
=Ans bIII
e.g. 5/2 x 0.001561
=0.003902 - Number of moles of X in 250cm3 of solution (1 mark)
250 x Ans bIII
25
=Ans b(IV)
e.g. 5
0.03902
= 0.03902 - Relative formula mass of X, (1 mark)
5
Ans b IV
= Ans bIV
e.g 5
0.03902
= 128.1427
- average volume of solution Y used (1 mark)
- The formula of X has the form X.nH2O. Determine the value of n in the formula given that the relative mass of X is 90.0
(O=16.0, H=1.0) (2 marks)
x.nH2O = Ans b(v)
n = (Ans b(v) - 90) ÷ 18
= Ans (c)
e.g. 90 + 18n = 128.1427
18n = 128.1427 - 90
n = 38.1427 ÷ 18
= 2.12 ≈ 2
- Transfer the contents of the boiling tube into a 250ml volumetric flask, rinse both the boiling tube and the thermometer with distilled water and add to the volumetric flask. Add more distilled water to make up to the mark. Label this solution X. Fill a burette with solution Y.
- You have been provided with solid R. Carry out the tests below
- Transfer all the solid R to a boiling tube. Add about 6cm3 of distilled water and shake the mixture thoroughly. Allow to settle then carefully filter into another boiling tube. Retain the residue for part (b)
Divide the filtrate into three portions- To the first portion of the filtrate in a test tube, add few drops of 2M lead (II) nitrate solution and warm
Observations Inferences White ppt soluble on warming Cl-, Br- present
(penalize fully for contradiction) - To the second portion of the filtrate in a test tube, add 2M sodium hydroxide solution drop wise until in excess
Observations Inferences White ppt insoluble in excess Mg2+, Ca
2 - 1 mark
1 - 1/2 mark
0 - 0 mark -
- Describe how you would carry out a flame test on the solution obtained.
Procedure Expected observation Dip a clean glandrod,/nichome wire/metallis spatula into the solution
Heat the part with solution on a non-luminous flameFlame color in bright white or orange - On the third portion of the filtrate, carry out the flame test described above
Observations Inferences Orange flame Ca2+ (must have appeared in a (ii), procedure in 2(iii) must be correct.
Penalise fully for any contradiction
- Describe how you would carry out a flame test on the solution obtained.
- To the first portion of the filtrate in a test tube, add few drops of 2M lead (II) nitrate solution and warm
-
- To the residue in a boiling tube add 2M hydrochloric acid provided drop wise until there is no more change. Test for any gas using a burning splint.
Divide the resultant solution into two portions
Observations Inferences Bubbles of colorless gas
colorless solution formedCO32- (reject HCO3)
Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+ absent
Any 1 correct or pegged on correct observation - To the first portion, add 2M sodium hydroxide solution drop wise until in excess
Observations Inferences White ppt soluble in excess Zn2+, pb2+ present
2 - 1/2 mark
1 - 0 mark - To the second portion, add 2M ammonium hydroxide solution until in excess
Observations Inferences White ppt soluble in excess Zn2+ present
Must have appeared in b(iii) above
Penalise fully for any contradiction to 1/2 mark maximum
- To the residue in a boiling tube add 2M hydrochloric acid provided drop wise until there is no more change. Test for any gas using a burning splint.
- Transfer all the solid R to a boiling tube. Add about 6cm3 of distilled water and shake the mixture thoroughly. Allow to settle then carefully filter into another boiling tube. Retain the residue for part (b)
- You are provided with solid H. Carry out the tests below. Write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Using a clean metallic spatula, heat about one third of solid H in a Bunsen burner flame.
Observations Inferences Burns with yellow smoky/sooty flame 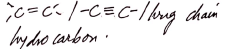
- Dissolve the remaining portion of solid H by adding about 6cm3 of distilled water and divide the solution into 3 portions.
- To the first portion, add two drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution
Observations Inferences People H+/Kmn 04 in decolorized 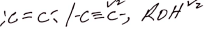
- To the second portion, add two drops of bromine water
Observations Inferences Yellow/orange decolorised 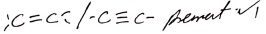
- Determine the pH of the third portion using universal indicator paper
Observations Inferences PH = 1,2,3 Strongly acidic
- To the first portion, add two drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution
- Using a clean metallic spatula, heat about one third of solid H in a Bunsen burner flame.
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers with Confidential - Kassu Joint Mock Examination 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

