QUESTIONS
- The table below shows concentration of some minerals inside the cells of a water plant and in the surrounding water.
Mineral Sodium Magnesium Calcium Cell sap 631 202 318 Surrounding water 28 293 47 - Name the process by which magnesium is taken up by the plant. (1mrk)
- Explain why maize plant take up calcium minerals quicker in well aerated soils than in water logged soil. (3mrks)
- Give a reason why a mature plant cell does not lose its shape even after losing water. (1mrk)
-
- State the function for co-factors in cell metabolism. (1mrk)
- Give one example of a metallic co – factor. (1mrk)
- Name the features that increase the surface area of the small intestines. (2mrks)
-
- Name three characteristics that are used to divide the members of phylum Arthropoda into classes. (3mrks)
- The diagram below represents a certain plant species.
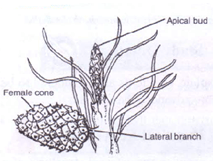
- State the class to which the plant belongs. (1mrk)
- State one observable xerophytic characteristic seen in the diagram above?. (1mrk)
- The chart below represents a simplified nitrogen cycle.
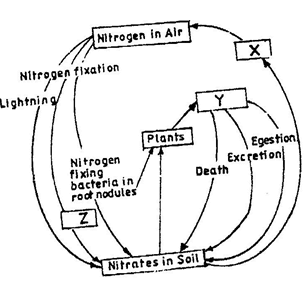
What is represented by X, Y and Z. (3mrks)
X……………………………………………………………………………………………
Y……………………………………………………………………………………………
Z……………………………………………………………………………………………. - People can die when they inhale gases from a burning charcoal stove in a poorly ventilated room. What compound is formed in the human body that lead to such deaths?. (1mrk)
- Explain why blood from a donor whose blood group is A cannot be transfused into a recipient whose blood group is B. (2mrks)
- In an experiment, a student covered one of the leaves of a potted plant on both upper and lower surfaces with blue cobalt chloride paper. The plant was exposed outside for 45 minutes.
Observation: The cobalt chloride on the undersurface of the leave changed into pink in the first 20 minutes only as the upper surface remained blue. However at the end of the experiment, after 45 minutes, the upper surface also turned pink.- State the aim of the experiment. (1mrk)
- Give one significance of the results obtained. (1mrk)
- When transplanting seedlings, it is advisable to remove some leaves. Explain ( 1mrk)
-
- Describe the path taken by carbon (IV) oxide released from the tissue of an insect to the atmosphere. (3mrks)
- Name two structures for gaseous exchange in plants. (2mrks)
- What is the effect of contraction of the diaphragm muscles during breathing in mammals?. (2mrks)
- The chart below shows the number of chromosomes before and after cell division and fertilization in a mammal.
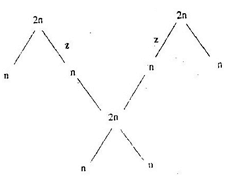
- What type of cell division takes place at Z. (1mrk)
- Where in the female body of humans does process Z occur?. (1mrk)
- Name the process that leads to addition or loss of one or more chromosomes. (1mrk)
- State three benefits of polyploidy in plants to a farmer. (3mrks)
- The diagram below represents human foetus.
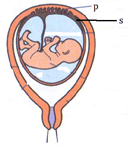
- Name the part labelled S (1mrk)
- Give the roles of structure P in; (2mrks)
- Nutrition.
- Protection.
- What is the function of the following in the human male reproductive system?. (2mrks)
- Epididymis.
- Scrotal sac.
- The diagram represents an experimental set up used by students to investigate a certain process.
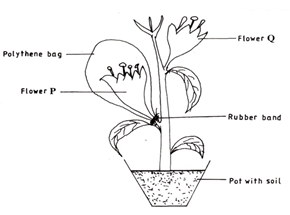
Flower Q produced seeds, while P did not. Account for the results (3mrks) - Name any two branches of microbiology. (2mrks)
- Which biological tool would a scientist require to collect rats to be used for study? (1mrk)
- Distinguish between magnification and resolution as used in microscopy. (1mrk)
- A group of students set up an experiment to investigate a certain physiological process. The set up was as shown below.
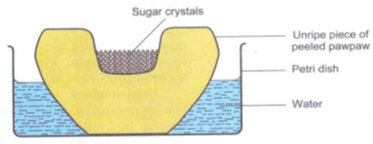
- Name the physiological process being investigated. (1mrk)
- Account for the formation and rise in the level of sugar solution at the end of the experiment. ( 3mrks)
- The scientific name of a blackjack is bidens pilosa. Identify two mistakes in the written name. (2mrks)
- State two advantages of natural selection to organisms. (2mrks)
-
- Give two ways in which sexual reproduction is important in the evolution of plants and animals. (2mrks)
- Explain why it is only mutations in genes of gametes that influence evolution (1mrk)
- The diagram below shows two fused bones of a mammal.
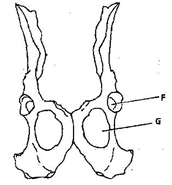
- Identify the fused bone. (1 mark)
- Name the
- Bone that articulates at the point labelled F. (1 mark)
- The hole labelled G. (1 mark)
- The chart below represents the result of successive crosses, staring with red- flowered plants and white flowed plants and in which both plants are pure breeding.
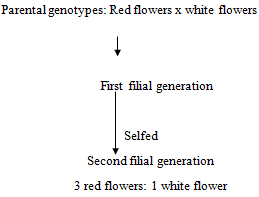
Phenotypic ratio 3: 1- What were the parental genotypes? Use letter R to represent the gene for red colour and r for white colour. (1mrk)
-
- What was the colour of the flowers in the first filial generation?. (1mrk)
- Give a reason for your answer in b (i) above. (1mrk)
- What is a test- cross?. (1 mark)
-
- Name two tissues in plants which are thickened with lignin. (2 marks)
- How is support attained in herbaceous plants? (1 mark)
- Name the type of response exhibited by; (2mrks)
- Euglena when it swims towards the source of light.
- Sperms when they swim towards the ovum.
- A person was able to read a book clearly at arm’s length but not at normal reading distance. (3mrks)
- State the defect the person suffered from?.
- Why was he unable to read book clearly at normal distance.
- How can the defect be corrected?.
- The photograph below shows the effects of certain pollutant in Nairobi dam. Study it carefully and use to answer the questions that follow.

- Suggest the main pollutant in the dam (1mark)
- What are the possible effects of pollution illustrated in the photograph (2mrks)
- Suggest one possible pollution control measure that can be put in place to save aquatic organisms in the dam. (1mark)
- State one structural and one functional difference between motor and sensory neurones. (2mrks)

MARKING SCHEME
- The table below shows concentration of some minerals inside the cells of a water plant and in the surrounding water.
Mineral Sodium Magnesium Calcium Cell sap 631 202 318 Surrounding water 28 293 47 - Name the process by which magnesium is taken up by the plant. (1mrk)
Active transport; - Explain why maize plant take up calcium minerals quicker in well aerated soils than in water logged soil.
More oxygen gas is available for respiration; to generate more energy; needed for uptake of calcium by active transport; (3mrks)
- Name the process by which magnesium is taken up by the plant. (1mrk)
- Give a reason why a mature plant cell does not lose its shape even after losing water.
Has a cellulose cell wall; (1mrk) -
- State the function for co-factors in cell metabolism.
Substances that activate enzymes; (1mrk) - Give one example of a metallic co – factor.
Metallic ions e.g. iron / mg / Zn / Cu /(accept correct iron forms)
Fe 2+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Mn2+, C02+ , Kl, mo2+, (Reject wrong charges). (1mrk)
- State the function for co-factors in cell metabolism.
- Name the features that increase the surface area of the small intestines. (2mrks)
Presence of villi and microvilli; must mention both to score
Long; -
- Name three characteristics that are used to divide the members of phylum Arthropoda into classes. (3mrks)
Number of body parts;
Number of jointed appendages;
Number of antennae; - The diagram below represents a certain plant species.
- State the class to which the plant belongs. (1mrk)
Coniferales; - State one observable xerophytic characteristic seen in the diagram above?. (1mrk)
Needle like leaves;
- State the class to which the plant belongs. (1mrk)
- Name three characteristics that are used to divide the members of phylum Arthropoda into classes. (3mrks)
- The chart below represents a simplified nitrogen cycle.
What is represented by X, Y and Z. (3mrks)
X- Denitrifying bacteria/ denitrification;
Y- Animals/ Herbivores; accept primary consumers;
Z- Nitrogen fixing bacteria (in soil) accept Azotobacter; - People can die when they inhale gases from a burning charcoal stove in a poorly ventilated room. What compound is formed in the human body that lead to such deaths?.
(1mrk) Carboxyhaemoglobin; - Explain why blood from a donor whose blood group is A cannot be transfused into a recipient whose blood group is B. (2mrks)
The recipient’s blood plasma produces a antibodies which react with the A antigens ; from the donor resulting in Agglutination; - In an experiment, a student covered one of the leaves of a potted plant on both upper and lower surfaces with blue cobalt chloride paper. The plant was exposed outside for 45 minutes.
Observation: The cobalt chloride on the undersurface of the leave changed into pink in the first 20 minutes only as the upper surface remained blue. However at the end of the experiment, after 45 minutes, the upper surface also turned pink.- State the aim of the experiment. (1mrk)
To compare the number of stomata in the upper and lower surface/ To show that the lower surface of the leaf has more stomata than the upper surface; - Give one significance of the results obtained. (1mrk)
It is an adaptation to reduce water loss through transpiration;
- State the aim of the experiment. (1mrk)
- When transplanting seedlings, it is advisable to remove some leaves. Explain ( 1mrk)
To reduce the number of stomata/surface area for water loss; -
- Describe the path taken by carbon (IV) oxide released from the tissue of an insect to the atmosphere. (3mrks)
CO2 diffuses into tracheoles; follows the trachea; then through spiracles; - Name two structures for gaseous exchange in plants. (2mrks)
Spongy mesophyll cells;
Cuticles;
Lenticels; - What is the effect of contraction of the diaphragm muscles during breathing in mammals?. (2mrks)
Muscles of diaphragm contract; causing the diaphragm to flatten (from dome position);The external intercostals muscles contract internal intercostals muscles relax pulling the ribcage upward/forward and outward in man;
- Describe the path taken by carbon (IV) oxide released from the tissue of an insect to the atmosphere. (3mrks)
- The chart below shows the number of chromosomes before and after cell division and fertilization in a mammal.
- What type of cell division takes place at Z. (1mrk)
Meiosis; - Where in the female body of humans does process Z occur?. (1mrk)
Ovary; - Name the process that leads to addition or loss of one or more chromosomes. (1mrk)
Non- disjunction;
- What type of cell division takes place at Z. (1mrk)
- State three benefits of polyploidy in plants to a farmer. (3mrks)
Resistance to diseases;
Draught resistance;
Early maturity;
Prolonged period of productivity;
Long shelf life; - The diagram below represents human foetus.
- Name the part labelled S (1mrk)
Chorion; - Give the roles of structure P in; (2mrks)
- Nutrition.
Allows passage of nutrients from the mother to the foetus; - Protection
It is a physical barrier preventing mixing of maternal and foetal blood;
Selectively allows some substances to pass through and not others;
- Nutrition.
- What is the function of the following in the human male reproductive system?. (2mrks)
- Epididymis.
Storage of sperms; - Scrotal sac.
Hold/protect the testis;
- Epididymis.
- Name the part labelled S (1mrk)
- The diagram represents an experimental set up used by students to investigate a certain process.
Flower Q produced seeds, while P did not. Account for the results (3mrks)
The flower is self-sterile/do not self pollinate;
Covering prevents pollination in flower P;
Flower Q received pollen grains from other plants/cross pollination;
Flower Q produced seeds, while P did not. Account for the results (3mrks)
The flower is self-sterile/do not self pollinate;
Covering prevents pollination in flower P;
Flower Q received pollen grains from other plants/cross pollination; - Name any two branches of microbiology. (2mrks)
Bacteriology;
Mycology;
Parasitology; - Which biological tool would a scientist require to collect rats to be used for study? (1mrk)
Bait trap; - Distinguish between magnification and resolution as used in microscopy. (1mrk)
Magnification is the number of times the image of an object has been enlarged while resolution is the ability of a microscope to distinguish between two objects that are very close to each other as distinct and separate entities; - A group of students set up an experiment to investigate a certain physiological process. The set up was as shown below.
- Name the physiological process being investigated. (1mrk)
Osmosis; - Account for the formation and rise in the level of sugar solution at the end of the experiment. ( 3mrks)
Sugar solution is hypertonic to the cell sap of the potato tissue;water molecules move through the potato into the sugar solution by osmosis; dissolves the sugar thus increasing the level of sugar solution;
- Name the physiological process being investigated. (1mrk)
- The scientific name of a blackjack is bidens pilosa. Identify two mistakes in the written name. (2mrks)
bidens starts in a small letter instead of a capital letter;
The two names have been underlined as one word but it should have been underlined separately; - State two advantages of natural selection to organisms. (2mrks)
Causes the elimination of disadvantageous characteristics/perpetuates advantageous characteristics;
Allow better adapted organisms to survive adverse changes in the environment/less adapted organisms are eliminated; -
- Give two ways in which sexual reproduction is important in the evolution of plants and animals. (2mrks)
brings about useful variations/desirable characteristics;
Variations make offspring better adapted for survival/more resistant to diseases;
May lead to origin of new species/ leads to speciation; - Explain why it is only mutations in genes of gametes that influence evolution (1mrk)
gametes form the new offspring;
- Give two ways in which sexual reproduction is important in the evolution of plants and animals. (2mrks)
- The diagram below shows two fused bones of a mammal.
- Identify the fused bone. (1 mark)
Pelvic girdle; - Name the
- Bone that articulates at the point labelled F. (1 mark)
Femur; - The hole labelled G. (1 mark)
Obturator foramen;
- Bone that articulates at the point labelled F. (1 mark)
- Identify the fused bone. (1 mark)
- The chart below represents the result of successive crosses, staring with red- flowered plants and white flowed plants and in which both plants are pure breeding.
Phenotypic ratio 3: 1- What were the parental genotypes? Use letter R to represent the gene for red colour and r for white colour. (1mrk)
RR, rr; -
- What was the colour of the flowers in the first filial generation?. (1mrk)
Red; - Give a reason for your answer in b (i) above. (1mrk)
Complete dominance/ gene for red colour is dominant over the gene for white colour;
- What was the colour of the flowers in the first filial generation?. (1mrk)
- What is a test- cross?. (1 mark)
A cross between an individual of unknown genotype with that of homozygous recessive;
- What were the parental genotypes? Use letter R to represent the gene for red colour and r for white colour. (1mrk)
-
- Name two tissues in plants which are thickened with lignin. (2 marks)
Schlerenchyma tissue;
Xylem vessels/ xylem tracheids; - How is support attained in herbaceous plants? (1 mark)
Turgidity of cells;
- Name two tissues in plants which are thickened with lignin. (2 marks)
- Name the type of response exhibited by; (2mrks)
- Euglena when it swims towards the source of light.
Phototaxis; - Sperms when they swim towards the ovum.
Chemotaxis;
- Euglena when it swims towards the source of light.
- A person was able to read a book clearly at arm’s length but not at normal reading distance.
(3mrks)- State the defect the person suffered from?.
Long sighted ness/ hypermetropia; - Why was he unable to read book clearly at normal distance.
Eye ball too short/ eye lens are unable to focus because they are flat/weak, unable to focus the image on the retina; eyes are unable to accommodate/ change their focal length; - How can the defect be corrected?.
By wearing convex / biconvex lenses; accept converging lenses;
- State the defect the person suffered from?.
- The photograph below shows the effects of certain pollutant in Nairobi dam. Study it carefully and use to answer the questions that follow.
- Suggest the main pollutant in the dam (1mark)
Domestic effluents; - What are the possible effects of pollution illustrated in the photograph (2mrks)
Reduction of light penetration into the water thus affecting the primary productivity which brings about the death of autotrophs;
Decomposers deplete oxygen from water, causing death of aquatic organisms; - Suggest one possible pollution control measure that can be put in place to save aquatic organisms in the dam. (1mark)
- Suggest the main pollutant in the dam (1mark)
- State one structural and one functional difference between motor and sensory neurones. (2mrks)
Structural differences: - The cell body of a motor neurone is terminal (at the end) and inside the central nervous system, while the cell body in sensory neurone is not terminal but has axons on both ends i. e it is bipolar;
Functional difference:-Motor neurone carry impulses from central nervous system (CNS) the effectors i. e muscles or glands, while sensory neurons carry impulses from receptors/senses;
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Kassu Joint Mock Examination 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

