INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- You are required to spend the first 15 minutes of 1 ¾ hours allowed for this paper reading the whole paper carefully before commencing your work.
- Candidates may be penalized for recording irrelevant information and for incorrect spelling especially of technical terms.
- You are provided with an unknown mixture labelled J
You are also provided with Benedict’s solution, dilute hydrochloric acid solution, iodine solution, Dichlorophenol-Indophenol (DCPIP) solution. Sodium hydrogen-carbonate solution, means of heating, test tubes, test tube holder and a test tube rack.- Using the reagent provided only, test for the food substances in mixture J. Record in the table below the chemical test, the procedure of the test, your observations and conclusions. 8mks
Chemical test Procedure Observations Conclusions - Which of the components of mixture J does not undergo digestion in the mammalian digestive system? 1mk
- Name a deficiency disease that may result from a deficiency of the component identified in (b) above. 1mk
- Name a common carbohydrate that could be present in mixture J. 1mk
- State the role of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydrogen carbonate in the experiment. 2mks
Hydrochloric Acid
Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
- Using the reagent provided only, test for the food substances in mixture J. Record in the table below the chemical test, the procedure of the test, your observations and conclusions. 8mks
- The photographs below show a flower specimen. Study it carefully and use to answer the questions that follow.

- On the photograph, label the following parts 3mks
- Stigma
- Style
- Staminal tube
-
- Classify the plant from which the flower was picked into the taxonomic groups listed below. 4mks
Kingdom
Division
Sub division
Class - Name three observable features from the photograph of the class you named in (a) (i) above. 3mks
- Classify the plant from which the flower was picked into the taxonomic groups listed below. 4mks
- Suggest the pollination agent of this flower. Give reasons for your answer.
Pollinating agent 1mk
Reasons 2mks
- On the photograph, label the following parts 3mks
- Below are photographs of two specimens, J and K. Both of them belong to the same Phylum and Class. Observe them carefully before you answer the questions that follow.
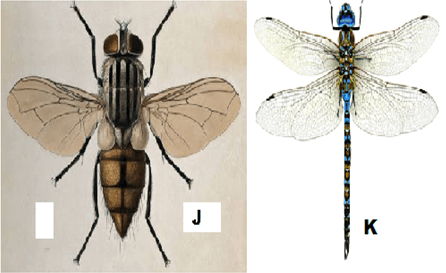
- Name the class to which J and K belong and support your answer with two reasons.
Class 1mk
Reasons 2mks - Suggest why the transport fluid in J and K has no haemoglobin. 2mks
- The actual length of specimen K is 8cm, given that both J and K are under the same magnification, determine the actual length of J 3mks
- Below is a diagram showing the life cycle of specimen J.
- Identify the stage labeled D. 1mk
- Name the hormone responsible for the change from D to A. 1mk
- Explain the differences in the change from C2 to C3 and from C3 to D. 2mks
C2 to C3
C3 to D - State the importance of the process illustrated above in the life cycle of the organism 2mks
- Name the class to which J and K belong and support your answer with two reasons.
CONFIDENTIAL
Candidates require the following in the working bench
QUESTION 1
- Mixture J: Solution containing a mixture of sucrose and vitamin C.
- Benedict’s solution,
- Dilute hydrochloric acid solution.
- Iodine solution
- Dichlorophenol – indophenol (DCPIP) solution,
- Sodium hydrogen – carbonate,
- Means of heating,
- 5 test tubes,
- Test tube holder
- Test tube rack
QUESTION 2
- Photograph Q: complete hibiscus flower (Each candidate should be provided with a real flower)
- Photograph Q: Half flower of hibiscus
- Scalpel / razor blade

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Mixture J: Solution containing a mixture of sucrose and vitamin C
- Benedict’s solution, dilute hydrochloric acid solution. Iodine solution Dichlorophenol – Indophenol (DCPIP) solution, sodium hydrogen – carbonate, means of heating, 5 test tubes, test tube holder and a test tube rack
- Photograph Q: complete hibiscus flower
- Photograph Q: Half flower of hibiscus
- Scarpel
- You are provided with an unknown mixture labled J
- You are also provided with Benedict’s solution, dilute hydrochloric acid solution, iodine solution, dichlorophenol-indophenol (DCPIP) solution. Sodium hydrogen-carbonate solution means of heating, test tubes, test tube holder and a test tube rack.
- Using the reagent provided only, test for the food substances in mixture J. Record the able below the food substance tested, the procedure of the test, your observations and conclusions. (12 mks)
Food Procedure Observations Conclusions Starch To about 2 ml of solution J add 3 drops of iodine and mix Yellow / brown colour. Colour of iodine solution Starch Reducing sugar To about 2 ml of solution J add an equal volume of Benedict’s solution, shake to mix and heat to boil Blue colour of Benedict’s solution remains Reducing sugar absent Non reducing sugar To about 2 ml of solution J add 6 drops dilute Hcl and heat. Cool and the add NaHCO3 solution drop wise until fizzing stops. Add about 2 ml Benedict’s solution and heat to boil Colour changes to yellow / orange / brown Non – reducing sugar present Vitamin C To about 2 ml of DCPIP add solution J dropwise. DCPIP is decourized Vitamin C present - Which of the components of mixture J does not undergo digestion in the mammalian digestive system. (1mk)
Vitamin C - Name a common carbohydrate that could be present in mixture J (1mk)
Sucrose - State the role of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydrogen carbonate in the experiment (2mks)
Hydrochloric acid hydrolyzes non-reducing sugar (s) into simple sugars / monosaccharides reducing sugars - Name a deficiency disease that may result from a deficiency of one of the substances present in mixture J. (1mk)
scurvy - Give one common symptoms of the disease you have stated in € (i) above.1mk)
bleeding gums
- Using the reagent provided only, test for the food substances in mixture J. Record the able below the food substance tested, the procedure of the test, your observations and conclusions. (12 mks)
- The photographs below show a flower specimen labelled M and a section of the same flower labelled M1.
- Classify the plant from which the flower was picked into the taxonomic groups listed below. (4mks)
kingdom plantae
division spermatophyte
sub division angiospermae / angiospermatophyta
class dicotyledonae - Name three observable features from the photographs of the class you named in (a) (i) above. (3mks)
Five petals: five stigmas; petals have network veins - State the plane through which the flower has been cut to obtain M1. (1mk)
Longitudinal section - Suggest the pollination agent of this flower. Give reasons for your answer (3mks)
Pollinating agent insect
Reasons brightly colouored petals
Large / conspicuous petals
For parts (d) and € below, an actual specimen is required - Examine one flower and describe the following parts. (8mks)
Calyc: five green sepals, fused in the lower half but free at the upper half pointed tips
Corolla: five large, brightly coloured petals which are separate and overlapping/ polypetalours corolla, petals have rounded ends and prominent nectary guides
Androecium many anthers each of which is attached to a short filament. The filaments fuse to form a stamen tube that encloses the style. Anthers lie below the stigma
Gynoecium a green superior / hypognours and syncapous ovary with several ovules. A long, white style that branches near the tip. Each style branch to supports a red, round stgma
- Classify the plant from which the flower was picked into the taxonomic groups listed below. (4mks)
- Below are photographs of two specimens, J and K. Both of them belong to the same phylum and class. Observe them carefully before you answer the questions that follow.
- Name the class to which J and K belong and support your answer with two reasons.
Class Insecta; 1mk Rej. insect
Reasons 2mks- Six legs; three body parts; two antennae; two compound eyes;
- Suggest why the circulatory fluid in J and K has no haemoglobin. 2mks
Haemoglobin used to transport oxygen/ carbon (IV) oxide in the body; oxygen is taken directly to tissues/ carbon (IV) oxide taken directly from tissues by tracheoles; - divergent evolution; 1mk
Reason one pair of wings in J reduced to halters/ are vestigial; but both are functional in K 2mks- pupa stage; 1mk
- Ecdysone; accept Moulting hormone
- 4mks
C2 to C3 – moulting hormone / Ecdysone induce moulting; but presence of juvenile hormone prevent formation of pupa;
C3 to D – moulting hormone / Ecdysone induce moulting; but abscence of juvenile hormone lead to formation of pupa;
- Name the class to which J and K belong and support your answer with two reasons.
Download Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Kassu Joint Mock Examination 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

