Instructions to Candidates
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of the examination in the spaces provided.
- This paper consist of six question.
- Answer any five questions in the spaces provided.
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and that no questions are missing.
QUESTIONS
-
- Discuss five factors that influence entrepreneurship in Kenya. (10 marks)
- Explain five monetary measures that can be taken to control inflation. (10 Marks)
-
- On 1st January 2018, Sunlight enterprise had Kshs.95000 cash in hand and Kshs.125000 at bank. During the month the following transactions took place;
2018
Jan 3rd; Cash sales kshs.9000 directly banked
- 5th ; Purchased goods worth kshs.19500 by cash
- 12th; Deposited kshs.25000 into the business bank account from private sources.
- 14th ; Obura a debtor settled his account of kshs.15000 by cash less 5% cash discount
- 17th; Paid James kshs.3900 by cheque in full settlement of his account less 2.5% cash discount.
- 20th; Sold goods worth kshs.13500 to Kim on credit.
- 23rd; Settled Kamau’s account of kshs.15000 by a cheque of kshs.13500.
- 24th; Received a cheque of kshs.28800 from Leeroy a debtor having allowed a cash discount of 4%.
- 25th ; Paid salaries by cheque kshs.36000
- 27th ; Bought stationery by cash Kshs.29600
- 28th; The cheque received from Leeroy on 24th was dishonoured.
- 30th; All cash was banked except Kshs.15000.
Required;
Prepare a dully balanced three column cash book. (10 Marks)
- Explain five differences between commercial banks and Non-Bank financial institutions. (10 Marks)
- On 1st January 2018, Sunlight enterprise had Kshs.95000 cash in hand and Kshs.125000 at bank. During the month the following transactions took place;
-
- With the aid of an appropriate diagram, Explain how the price of a commodity is determined in a free market. (10 Marks)
- Discuss five trends in forms of business units. (10 Marks)
-
- Katiba enterprise is a new firm which was established recently. Discuss five factors that the marketing manager should consider in order to choose an appropriate method of promoting their product. (10 Marks)
- Describe five features of economic resources. (10 Marks)
-
- The following information was extracted from the books of Chelule Traders for the year ended 31st December 2019.
Stock on 31st December 2019 was valued at Kshs.15,000ITEM KSHS. Capital 636,000 Salaries 95,000 Transport 16,000 Commission allowed 800 Commission received 2,800 Rent income 72,000 Gross profit 326,000 Insurance 92,000 Power & Lighting 2,500 Discount received 1,200 Machinery 800,000 Furniture 150,000 Debtors 35,000 Creditors 17,000 Cash at Bank 89,700 Cash in hand 74,000 Advertising 4,500 N.I.C Bank loan 320,000 Discount allowed 500
Required;
- Prepare Chelule Traders profit and loss account for the year ended 31st Dec 2019. (7 Marks)
- Extract a balance sheet as at 31st Dec 2019. (5 Marks)
- Poor services delivery in most counties is caused by inappropriate utilization of public resources, explain four principles that should guide public expenditure in order to improve service delivery. (8 Marks)
- The following information was extracted from the books of Chelule Traders for the year ended 31st December 2019.
-
- Discuss five characteristics of perfect competitive market . (10 Marks)
- Explain five reasons why some countries engage in trade restriction. (10 Marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Factors that influence entrepreneural practices
- Government policy. Some government policies may be favourable to the operations while others are unfavourable. Favourable government policies e.g. decrease in taxes may encourage entrepreneurial practices while unfavourable government policies discourage entrepreneurial activities.
- Level of infrastructure. Infrastructure refers to the basic systems and services that are necessary for efficient operation of businesses. Infrastructure may include transport network, water systems, electricity, communication etc. Availability of good infrastructure in an area encourages entrepreneurial practices while poor infrastructure discourages entrepreneurial practices.
- Levels of education and skills. Relevant knowledge and skills are essential for business success. Knowledge and skills on business can be acquired through education, training and experience. An entrepreneur who has appropriate knowledge and skills is likely to succeed in business than the one without appropriate skills and knowledge.
- Availability of markets. Availability of market determines the profitability of the business. Availability market encourages entrepreneurial activities whereas Inavailability of market discourages entrepreneurship.
- Availability of resources. For a business to start and run efficiently, resources are required. These resources may include; capital, labour, technology, finances etc. Availability of adequate resources enables the business produce high quality goods and services that will encourage more customers. Availability of adequate resources will therefore encourage entrepreneurial practices while lack of adequate resources discourages entrepreneurial practices.
- Culture. Culture refers to the norms, values and beliefs of a given community. Culture influences the kind of goods and services that people consume thereby determining the type of businesses to be established in a given area. E.g. Muslims don’t eat pork, therefore a business selling pork will not be suitable in an area with many Muslims.
- Level of competition. Competition is an attempt by businesses to out-do each other in their efforts to attract and retain available customers. A business will therefore do well where there is minimal competition hence lack of competition encourages entrepreneurship than presence of competition
- Political stability. Political stability gives a conducive environment for businesses to operate hence encouraging entrepreneurial activities. On the other hand, political instability increases the level of insecurity in a given area hence discouraging entrepreneurial activities.
- Natural factors. Natural factors such as rainfall, temperatures, earthquakes, pests, wind, drought etc. may influence the type of businesses that are carried out in a certain area. E.g. finishing is only possible in places with water bodies.
- Monetary policies of controlling inflation
- Selling of government securities in an open market operation (O.M.O). the selling of securities such as Bonds and Treasury bills mops money from the economy, reducing the amount of money being held by individuals
- Increasing the commercial banks cash/liquidity ratio. This reduces their ability to lend and release more money into the economy, reducing their customer’s purchasing power.
- Increase rate of interest of lending to the commercial banks. This forces them to increase the rate at which they are lending to their customers, to reduce the number of customers borrowing money, reducing the amount of money being added to the economy.
- Increasing the compulsory deposits by the commercial banks with the central banks. This reduces their lending power to their customers, which makes their customers to receive only little amount from them, reducing the amount of money in the economy
- Putting in place the selective credit control measures. The central bank may instruct the commercial bank to only lend money to a given sector of the economy which needs it most, to reduce the amount of money reaching the economy
- Directives from the central banks to the commercial banks to increase their interest on the money being borrowed, to reduce their lending rates
- Request by the central bank to the commercial banks (the moral persuasion) to exercise control on their lending rates to help them curb inflation.
- Factors that influence entrepreneural practices
-
- Three Column cash book
SUNLIGHT ENTERPRISE
THREE COLUMN CASH BOOK
FOR THE MONTH OF JAN 2018
½ x 20 = 10 marksDate Details F Discount allowed Cash Bank Date Details F Discount received Cash Bank 2018
Jan 1
3
12
14
24th
30Bal. b/d
Sales
Additional Investment
Obura
Leeroy
cashc
750
1200
195095000
14250
109250125000
900
25000
28800
94250
2828502018
Jan 12
17
23rd
25
27th
28
30
30Purchases
James
Kamau
Salaries
Stationery
Leeroy
Bank
Bal. c/dc
100
1500
160019500
29600
94250
15000
109250
3900
13500
36000
28800
199830
282050
N/B Award marks only if the details column is correct - Differences between Commercial banks and Non-bank financial institutions
Commercial banks Non-bank financial institution Provide finance that is not restricted to any sector
May provide foreign exchange services
Provide short term and medium term finance
provide all types of accounts i.e current, savings and fixed deposit account
They are under direct control of the central bank
May offer overdraft facilities as they operate current account
Provides facilities of safe keeping of valuable items
Provide finance mainly for working capitalProvide finance for a specific sector
Do not provide foreign exchange services
Mainly provide medium term and long term finances
Mainly offer savings and fixed accounts only
NBFI are not under direct control of the central bank
Do not offer overdraft facilities since they do not operate current savings account
Do not provide facilities for safe keeping of valuable
Provide finance mainly for capital development
- Three Column cash book
-
- Price determination in a free market
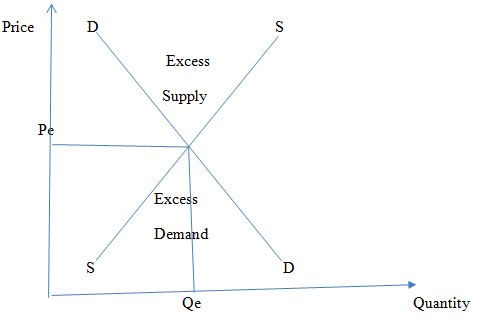
The price of a commodity is determined by the interaction of demand and supply curves. The resulting price is referred to as the equilibrium price and represents an agreement between sellers and consumers of the good. In equilibrium, the quantity of goods supplied equals the quantity demanded.
At any price below Pe, there will be excess demand, consumers will be forced to pay higher price in order to attract more supply therefore setting the price back to equilibrium. Similarly if a price is set above Pe, there would be excess supply sellers would be willing to lower their prices in order to clear their stock. The end result is a reduction in price back to the equilibrium point.
Award 6 marks for well drawn curves and 4 marks for the explanation - Trends in forms of business units
- Amalgamation- This is where two or more business organisation combine and form one new business. The merging companies ceases to exist
- Privatisation - This is where the government sells their shares to the public. It is the changing of state owned corporations into public limited companies
- Holding companies - This is where a company acquires 51% or more shares in one or more other companies.
- Franchising – This is where one company grants another the rights to manufacture, distribute or provide its branded products using the name of the business that has granted the right.
- Check off system - This is a system where members contribution to Saccos are deducted at source.
- Performance contract. These are contracts signed by employees in state corporations where they commit perform to set standards.
- Cartels - A cartel is a group of related companies that agree to work together in order to control output, price and markets of their products.
- Absorption ( take over)This is where a business buys all assets of another business
- Burial benevolent funds (BBF).This is a system mostly in SACCOs which is aimed at assisting their members financially during burials
- Front office savings account (FOSA).This is a service which used in SACCOs to enable their members conveniently deposit and withdraw.
- Price determination in a free market
-
- Factors to consider when choosing an appropriate method of product promotion
- Cost of the method of promotion method
A more affordable method of sales promotion should be chosen. - Nature of the product
Some products because of their nature require to be promoted by specific methods only. For example a product requiring demonstration is best promoted through personal selling. Therefore the firm should chose a method of product promotion that suits its products - Target group
The promoter should a method of promotion that reaches his/her target group so as to reduce wastage. - Objectives of the promoting firm
Sometimes, firms undertake product promotion in order to achieve certain objectives. For instance, if the objective is to correct the bad image of the firm, public relations should be preferred. A firm should therefore choose a method of sales promotion that will help meet the objectives of the firm. - Methods used by the competing firm
Firms should choose methods of promotion that enables them compete favourably with their competitors that is the firm should use a different method of promotion from the one the competitor is using - Government policy
A firm should use only those methods that are allowed by the law of the land - Geographical region
Some products may require countrywide coverage while others will require regional coverage. The firm should therefore choose a method that will cover the geographical area intended - Availability of the promotion method
Some methods of product promotion are easily available than others. A firm should therefore choose a method that is easily available
- Cost of the method of promotion method
- Characteristics of economic resources
- They are scarce in supply – economic resources are limited in supply. This means that resources are less in supply than what is required by human beings.
- Have money value – economic resources have value at which they can change ownership.
- Can be combined – Economic resources can be combined to produce other goods and services.
- Can change ownership - The ownership of economic resources can be shifted from one person to another through trade.
- Economic resources have utility - This resources have the ability of satisfying human wants.
- Have alternative uses - Economic resources can be put into different uses. Individual have to choose the most appropriate use for resources.
- Can be complimentary- different economic resources may be consumed together.
- Economic resources are unevenly distributed. Different places are endowed with different quantities of economic resources.
- Factors to consider when choosing an appropriate method of product promotion
-
- CHELULE TRADERS
PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
FOR THE PERIOD ENDED 31/12/2019
DR CR Ksh
Salaries 95,000
Transport 16,000
Commission allowed 8,000
Insurance 92,000
Power & lightning 2,500
Advertising 4,500
Discount allowed 500
Net profit c/d 190,700
402,000
½ x 14 = 07 marksKsh
Commission received 2,800
Rent income 72,000
Gross profit 326,000
Discount received 1,200
402,000
CHELULE TRADERS
BALANCE SHEET
AS AT 31/12/2019
Assets Sh. Sh
Fixed assets
Machinery 800,000
Furniture 150,00 950,000
Current assets
Stock 15,000
Debtors 35,000
Bank 89,700
Cash in hand 74,000 213,700
1,163,700
½ x 10 = 05 marksCapital + liabilities Sh Sh
Capital 626,000
Add profit 190,7000 826,700
Long term liabilities
N.I.C Bank loan 320,000
Current liabilities
Creditors 17,000
1,163,700 - Principles of public expenditure
- principle of maximum social benefit. Any expenditure by the county should ensure that majority of the population will benefit out of any spending in development projects.
- Sanctions. The principle requires approval of any expenditure by the relevant authority e.g county assembly approvals.
- Proper financial management .County funds should be well managed. This should be facilitated by proper financial recording.
- Economy. Any expenditure by the country government should minimize wastage at all costs.
- Flexibility /elasticity-The policy on public expenditure should be flexible enough to meet prevailing economic situations i.e. it should be possible to increase or decrease the expenditure on projects depending on the prevailing circumstances e.g. during drought, it should be possible to spend on famine relief.
- Productivity-The biggest proportion of public expenditure should be spent on development projects and less on non-development projects.
- Equity-Government expenditure should be distributed equitably to all sectors of the economy in order to reduce income and wealth inequalities.
- Surplus-Surplus revenue collected should be saved for emergencies or for when collection of revenue is below projections.
- CHELULE TRADERS
-
- Features of perfectly competitive product market
- There is wider knowledge about the market. Consumers in a perfectly competitive product market have adequate knowledge about price, quality and other market conditions. This therefore enables them to make a rational decision on the product to buy
- The products are homogenous. This implies that the units produced are similar and therefore buyers have no preference between different units.
- There is no transport cost. This ensures that products are charged the same price irrespective of the regional difference.
- Large number of buyers and sellers. This widens consumer’s choice on where to buy his/her product. It also ensures that no player in this market structure can influence the market.
- Free entry and exit of firms into the market. This ensures that all firms are given equal opportunities to trade
- No excess supply or demand. This promotes price stability. Therefore the buyers can budget his expenditure.
Students to be awarded 2 marks only if he/she gives the significance of the feature otherwise award only 1 mark for starting the feature
- Reasons for protectionism
- Protection of local infant industries. Trade restriction protects local infant industries from unfair competition from established foreign industries which are able to sell goods at a cheaper price hence controlling the market
- Promote self-reliance. Through trade restriction, local producers may be encouraged to increase their productivity in order to ensure a constant supply of goods and services so as to avoid over-reliance on imports which may not be available during times of emergencies
- Protection of strategic industries. Strategic industries are the very important industries to the country such as those providing security. The country needs to protect these industries to ensure they don’t over depend on foreigners. To do this, the government has to restrict foreign trade
- Expansion of market for local products. Discouraging imports increases demand for local products.
- Discourage dumping. Dumping refers to a situation where a country disposes its products cheaply in another country. Dumping brings about unfair competition to local industries hence has to be discouraged.
- Creation of employment. Discouraging imports encourages local industries to emerge in order to produce goods that could have been imported. These industries will contribute to employment creation.
- Preservation of the balance of trade. Discouraging imports ensures the balance of trade is always favourable.
- Protection of cultural and social values. Trade restriction controls the adoption of harmful cultures from foreign countries through interaction during trade activities.
- Features of perfectly competitive product market
Download Business Studies Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Kassu Joint Mock Examination 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

