QUESTIONS
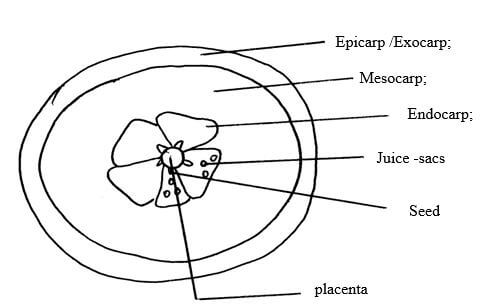
- You are provided with specimen labeled E, examine specimen E
- Giving reasons, identify the type of the fruit? (2mks)
- Cut a transverse section through specimen E, make a well labeled diagram (5mks)
- State the type of placentation of E (1mk)
-
- Name the agent of dispersal for E (1mk)
- State how E is adapted to its mode of dispersal (2mks)
- Squeeze out the juice from specimen E into test tubes and using the regents provided carry out food test and fill in the table below (6mks)
Food test
Procedure
Observation
- Study the photographs and answer the following questions.

- The photograph in Plate 5 shows the germination process in a species of legume.
-
- Name the type of germination shown in the photograph. (1 mark)
- Give a reason for your answer. (1 mark)
- Other than germination the seedling has shown some responses.
- Name two responses shown in the photograph. (2 marks)
- State one survival value of each of the response named above. (1 mark)
-
- Examine the photograph in Plate 6 and Plate 7 which show different essential parts of a flower of a species on two different plants.
- Name the flower parts shown in Plate 6 and Plate 7. (2 marks)
-
- Name the phenomenon described in the statement above. (1 mark)
- Explain the significance of the phenomena stated in (a)(i) above. (1 mark)
-
- State the mode of pollination of the flower shown in the photograph. (1 mark)
- Give a reason for your answer. (1 mark)
- The photograph in Plate 5 shows the germination process in a species of legume.
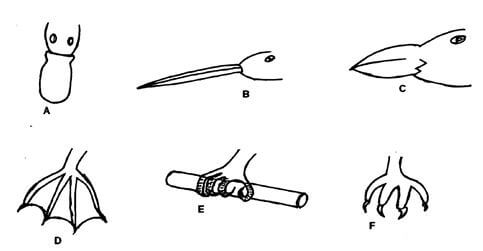
- The diagrams below represent body parts of some organisms (animals). Study them and answer the question that follow.
-
- Suggest the type of food eaten by organisms with the parts labeled A, B, C and F (4 mrks)
- With reasons, suggest the likely habitat of the organism from which the parts labeled D and E were obtained. (4 mrks)
-
- Suggest the type of evolution that is exemplified by the organisms labeled D, E and F. Give reason for your answer. The type of evolution (2mks)
- Suggest the significance of the above named type of evolution for the organism (2mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
Drawing – 1mk
Accuracy – 1mk
Labelling – 6/2 = 3mks
Magnification = 1mk
Total = 6mks - A berry / Hesperidium;
-
- Animal Dispersal
- – Succulent endocarp / juicy endocarp;
- Seeds resistant to digestions ;
- Scented ;
- Bright coloured exocarp;
-
- Animal
- -Fleshy/ juicy pericarp to attract the animal
- Brightly coloured epicarp to attract the animal
- Indigestible seed coats to avoid digestion by enzymes
-
Food substance Procedure Observation Conclusion Vit . C (Ascorbic Acid) - Put 2cm3 given vol. of DCPIP in test –tube.
- Add juice / test substance
DCPIP decolourised - Vit C present Reducing sugar - Put test substance in t.tube
- Add Benedict soln;
- Boil;
Colour changes to yellow / orange / red. Reducing sugar present Proteins To the juice add sodium Hydroxide Solution then copper (II) sulphate Solution Blue colour is retained Proteins absent
-
-
-
-
- epigeal
- - cotyledons are above the ground
-
- - positive hydrotropism in roots
- positive phototropism in shoot. - Positive phototropism
Light causes lateral migration of auxins away from the light side, towards the darker side; high auxin concentration stimulates growth in the shoot; thus the cells on darker side grew and elongated faster than the cells on the illuminated side; causing the curvature towards light; - Provides yield energy required by the cell for various functions;
Positive hydrotropism.
Water causes auxins to migrate towards the side with water / moisture, auxin, are positively hydrotropic; low auxin concentration stimulates growth in roots, auxin high concentration inhibit growth in roots; the cells on the side away from the water grow and elongated faster; leading to curvature towards water. - Phototropism enables plants (shoot) to obtain optimum light for photosynthesis.
Hydrotropism by roots enables plants to absorb water and mineral salts for metabolic processes.
- - positive hydrotropism in roots
-
-
- plate 6 - stamen plate 7 - pistil
-
- dioecium
- facilitates pollination leading to variation within the species and increase in hybrid vigour.
-
- wind pollination
- Small incospicuous bracts; that are dull coloured
-
- cross pollination.
- - male and female parts occur in different plants.
- the plant pollen grains are sterile to the stigma of the same plant
-
-
-
-
Specimen
Food
Reason
A
Aquatic matter and small invertebrates
Wide shovel shaped beak
B
Nectar
Long, thin beak
C
Nuts
Short, thick strong beak
F
Flesh
Strong sharp curved talons /claws
-
Part Habitat Reason D Aquatic Webbed feet for swimming/wadding E Tree branches Long feet/toes for grasping/perching
-
-
- Divergent evolution; (4mks)
Reason: Similar basic structure and embryonic origin but modified into different forms / appearance; - Enable the organisms / animals to utilize different ecological niches; to avoid competition for food; (2mks)
- Divergent evolution; (4mks)
-
CONFIDENTIAL
BIOLOGY REQUIREMENTS PRACTICALS
INSTRUCTIONS TO SCHOOLS
(Care must be taken to ensure that the information herein doesn’t reach the candidates)
Candidates require the following in the working Bench
- Ripe orange fruit- labeled E (Each candidate)
- Scalpel
- 1%Cuso4
- 10%NaoH
- Distilled water/tap water
- Test tube rack
- Test tube holder
- 0.01% Dichlorophenol Indophenol (DCPIP) Solution
- Three clean test tubes
- Means of labeling
- Source of heat
- Benedict’s solution
- Tripod stand
- Wire gauze
- 50ml glass beaker
- Water bath
Download Biology P3 Questions, Answers and Confidential - Mangu High School Trial Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

