INSTUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided
- This paper consists of three sections A,B and C.
- Answer all the questions in sections A and B and any other two in section C
- All answers must be written in the spaces provided in this booklet.
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
|
SECTION |
QUESTIONS |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATES SCORE |
|
A |
1-17 |
30 |
|
|
B |
18-21 |
20 |
|
|
C |
22-24 |
40 |
|
|
TOTAL SCORE |
90 |

QUESTIONS
SECTION A: 30 MARKS
- List four methods of farming. (2marks)
- Give four factors that would determine the stage at which a crop is harvested. (2marks)
- Give three reasons for early seedbed preparation. (1½marks)
- State four disadvantages of organic mulches. (2 marks)
- Outline four functions of magnesium in crops . (2 marks)
- State four objectives o f land tenure reform . (2marks)
- State two disadvantages of late defoliation in pasture management . (1mark)
- Define the following terms as used in economics .
- National income (1mark)
- Per capita income (1mark)
- Give four benefits of a good soil structure in crop production . (2marks)
- Name four farm records that should be kept by a poultry farmer. (2marks)
- Give three factors that should be considered when choosing the type of labour to use on the farm. (l1/2 marks)
- State four ways in which burning of vegetation may lead to lose of soil fertility (2 marks)
- State four symptoms of viral diseases in crops. (2marks)
- State three methods of classifying herbicides. (1½marks)
- Give four methods of applying fertilizers to crops. (2marks)
- State three advantages of drip irrigation (1½ marks)
- Outline two ways of controlling damping off diseases on vegetable seedlings in a nursery (1mark)
SECTION B(20 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- The diagram below shows a silo. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
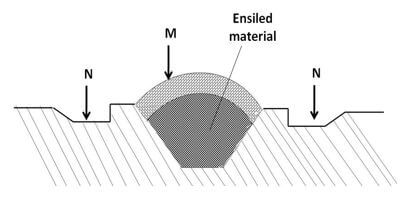
- Identify the type of silo shown on the diagram. (1mark)
............................................................................................................................................. - State the use of the part labeled M and N (2marks)
M ...................................................................................................................
N ................................................................................................................... - Give two ways of ensuring that anaerobic conditions are achieved during silage making process. (2marks)
- Identify the type of silo shown on the diagram. (1mark)
- Form two student put some soil sample in a measuring cylinder, added some water and sodium carbonate and then covered the cylinder with the hand and shook the cylinder for about two minutes. He left the cylinder on the bench for one hour. The result was as shown below.
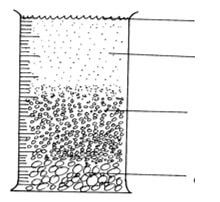
- Name the layers marked a,b,c, and d. (2marks)
- .............................................................................................................................................
- .............................................................................................................................................
- .............................................................................................................................................
- .............................................................................................................................................
- What was the function of sodium carbonate in this experiment? (1mark)
- What was the aim of this experiment ? (1mark)
- Name the layers marked a,b,c, and d. (2marks)
- Study the diagram below of crop propagation and answer the following questions
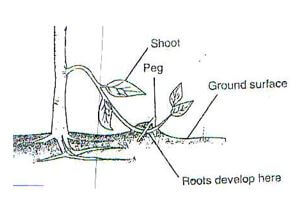
- Identify the propagation method (1mark)
- State two factors that encourage root formation in the above method of propagation (2marks)
- Name two crops that can be propagated using the above method (2marks)
-
- Describe the procedure which should be followed in spraying a crop in tomatoes using a fungicide in powder form, water and a knapsack sprayer. (3marks)
- Name one fungal disease of tomatoes that can be controlled using the above procedure. (1marks)
- State four safety measures that should be taken while spraying the crop with the fungicide. (4marks)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any TWO questions from this section in the spaces provided after question.
-
- Explain five factors that should be considered when siting a vegetable nursery. (5marks)
- Explain six factors that should be considered when selecting seeds for planting. (6marks)
- Explain the different ways in which each of the following environmental factors
Influence crop production:- Temperature; (4marks)
- Wind. (5marks)
-
- Explain the benefits of land consolidation. (6marks)
- Briefly explain six factors influencing mass wasting. (6marks)
- Explain four ways of improving labour productivity (8marks)
-
- Explain five factors that determine the spacing to be used in crops. (10marks)
- Describe seven nursery practices carried out while seedlings are still growing.(7marks)
- Outline three precautions taken in harvesting tea. (3marks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Methods of farming.
- Shifting cultivation
- Nomadic pastoralism
- Organic farming
- Mixed farming
- Agroforestry (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Factors determining stage of crop harvesting.
- Intended use of the crop
- Chemical concentration of the produce/stage of maturity/change in colour
- Prevailing weather conditions
- Market demand for the produce/market price (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- easons for early land preparation.
- Allows time for organic matter to decompose and form humus.
- Facilitates timely subsequent operations.
- Allows time for weeds to die /dehydrate
- Allows weathering of soil clods before subsequent operations
- Minimizes competition for labour
- Allow pests and diseases causing organisms to starve and die,
- Allows soil aeration /gaseous exchange to take place
- Allow s water infiltration (1½ marks)
- Disadvantages of organic mulches.
- Expensive to transport and apply/bulky
- Could be a fire risk.
- Provides breeding ground/hiding place for pests
- Intercepts light showers of rainfall.
- Can spread pests/weeds/diseases (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Necessary in chlorophyll formation .
- Promotes nitrogen fixation .
- Activates enzymes .
- Synthesis of oil in 0il crops . (2marks)
-
- Encourage conservation measures on land
- Improve productivity of land and labor
- Encourage commercial instead of subsistence production
- Encourage farmers to invest more through offering security
- Allow flexibility in production depending on the market
- Effect utilization of natural resources through irrigation (2 marks)
-
- Has low dry matter digestibility .
- _Has low leaf ; stem ratio / less leafy
- _Has low crude protein yield (1mark)
- National income is the monetary value of all goods and services produced in a country for a period of one year .
Per capita income is the average income per head in a country in a period of one year .[ 2 marks ] -
- Holds adequate moisture for crop growth
- Has better aeration
- Well drained
- Allows better root penetration / tuber expansion .[ 2 marks ]
- Farm records that should be kept by a poultry farmer.
- Egg production
- Labour records
- Feeding records
- Health records
- Marketing records
- Inventory records (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Factors on the choices of labour
- Availability of labour
- Size of the enterprise
- Financial ability of the farmer/cost of labour
- Type of the enterprise/type of the work
- Burning of vegetation.
- Destroys organic matter humus
- Destroys soil structure
- Kills useful soil micro-organisms
- Exposes soil to agent of erosion
- Causes nutrient imbalance/loss of volatile nutrients/accumulation of soils (2marks)
-
- Leaf curling ;
- Mosaic ;
- Malformation/distortion
- leaf chlorosis ;
- Rosetting/ short internodes . ( 1/2 x4)=2marks.
-
- Formulation ;
- Time of application ;
- Selectivity . ( 1/2 x3)=1.5marks.
-
- Broadcasting ;
- Placement method ;
- Side dressing/top dressing/band application/ring application ;
- Foliar spraying ;
- Drip application in drip lines ; (1/2 x4)=2marks.
-
- Economic /efficient use of water /requires a little amount of water
- Discourages the spread of diseases
- Less growth of weeds between rows
- Water under low pressure may be used
- Does not cause soil erosion (3x1/2 =1 ½ marks)
-
- Reduced /remove shade
- Thinning to reduce overcrowding
- Reducing amount and frequency of watering
- Spraying with copper fungicides /appropriate fungicides (2x1/2 =1mark)
-
- Trench silo 1x1=1mark
- M prevents entry of water into the silage 1x1=1mark
N drains away water 1x1=1mark - Fast filling of silo
Proper compaction
Sealing with polythene paper & soil 2x1=2marks
-
- Naming of layers.
A- Floating organic matter. (humus)
B-Water with fine clay materials and dissolved mineral salts.
C- Silt and clay. (4×½= 2marks)
D- Gravel. - Function of sodium carbonate.
Aid in dispensation of the particles. (1mark) - Aim of this experiment.
To show that soil is made up of different sized particles. (1mark)
- Naming of layers.
-
- Tip layering. 1 x ½ = ½ mark
- - Moist soil
- Rooting hormones
- Injury of the part 2 x 1 = 2marks - - Sweet potatoes
- Straw berry 2 x ½ = 1mark
-
-
- Read the label/ the manufactures instruction
- Measure the requirement amount of fungicide
- Place it into a container and mix thoroughly
- Powder has dissolved completed/ has formed slurry
- Pour the mixture into the knapsack sprayer though the sieve
- Spray the mixture onto the crop
- Blight (late or early) powdery mildew ( 1 mark)
- Spray following the direction of the wind
- Wear protective clothing
- Avoiding eating or smoking while handling fungicides
- Avoid spillage of the fungicide/ avoid containing the environment
- Do not suck/ blow a blocked nozzle 4 x 1/2 = ( 2 mks)
-
-
- Factors that should be considered when siting a vegetable nursery. (5 marks)
- Near a water source for easy watering
- In a well sheltered place to prevent strong winds which can uproot seedlings and cause excessive evaporation
- Security so as to protect them from theft and destruction by animals/ birds
- On a gentle slope to prevent erosion through run-off and to prevent flooding
- Type of soil, should be well drained and fertile
- Previous cropping/avoid an area where same crop family had been planted to avoid pest and diseases attack/build up
- Near the seedbed/main field to minimize damage to seedlings during transplanting
- Accessibility for ease of movement
- Away from shading effect to allow sunshine (5x1=5marks)
- Factors that should be considered when selecting seeds for planting.
- Adaptability – should be adapted to local ecological condition
- Physical deformities/damages – should be free from physical deformities/damages
- Health – should be free from pests/diseases
- Viability /germination percentage-should have high viability/germination percentage
- Parent plant – should be from high yielding/healthy parents/ high quality/early maturing
- Purity – should be clean/free from impurities
- Maturity – should be of correct maturity stage
- Age – storage period – seeds stored for long periods have low viability/germination percentage hence should not be selected
- Size of seeds – seeds should be of correct size (6x1=6marks)
- Environmental factors influence crop production:
- temperature; (4 marks)
- Affect quality of certain crops eg pineapples, pyrethrum.
- Influence the rate of physiological processes in a crop, hence faster growth rate
- Cause increase in incidences of diseases.
- Low temperatures cause frost injury
- High temperatures increase rate of evatranspiration hence wilting
- Influence distribution of crops
- wind. (5 marks)
- Strong winds increase the rate of evaporation/evapotranspiration/wilting
- Influences amount of rainfall in the given area
- Help in pollination of crops
- Strong winds have a cooling effect which influences rate of physiological processes.
- Strong winds may cause soil erosion
- Strong winds may cause lodging/destruction of certain crop structures
- Winds can spread diseases/pests/weeds.
- Winds help in seed dispersal
- Winds is fed in crop cleaning/winnowing of grains (5 marks)
- temperature; (4 marks)
- Factors that should be considered when siting a vegetable nursery. (5 marks)
-
- Explain the benefits of land consolidation.
- Proper supervision of land
- Economic use of time and saving of transportation costs.
- Easy provision of agricultural advice by extension officers.
- Ensures sound farm planning and adoption of crop rotation programmes.
- Facilitates soil conservation and land improvement.
- Promotes construction of permanent structures eg buildings and fences.
- Registered land gives the farmer legal ownership and the title deed which can be used to obtain loans.
- Weed, pest and disease control is enhanced.
- Facilitates mechanization especially because of large holdings. (6marks)
- Briefly explain six factors influencing mass wasting. (6marks)
- The slope of the land-Steep slopes leads to faster movement of materials.
- The nature of material-Mass wasting occurs easily where massive rocks overlie sedimentary rocks which have clay material underneath and also if the material contains a lot of water.
- Climate-Heavy rainy periods encourage wasting
- Vegetation cover-It is easy and faster in bare ground than where it iscovered with vegetation.
- Human activities-Eg deforestation, building, quarring etc interferes with the stability of surface layers.
- Forces within the earths crust eg earth tremors and some volcanic eruptions.
- Explain four ways of improving labour productivity (8marks)
- Training-This may be done formally or informally.Formally labour can be trained through schools and colleges.On the other hand labour can be improved through farmers training centres(FTCs), field days, agricultural shows, demonstration farms, workshops and visits to outstanding farms.
- Farm mechanization-It assists labour to perform work faster and more efficiently.
- Giving incentives and improving terms and conditions of service eg proper housing, transport, bonuses and medical services.
- Labour supervision-Brings efficiency and improves productivity.
- Explain the benefits of land consolidation.
-
- Factor that determine spacing in crops;
- The type of machinery to be used.
- Soil fertility.
- The size of the plant.
- Crop stand either pure or mixed.
- Number of seeds per hole.
- Moisture availability
- Use of the crop
- Pest and disease control. ( 5 x 2 = 10mks)
- Nursery practices carried to seedlings;
- watering
- Mulching
- Weed control
- Pricking out
- shading
- Pest and disease control
- Hardening off ( 1 x 6 = 6 marks)
- Precautions taken in harvesting tea;
- Plucked tea should be put in woven baskets and not polythene to allow free air movement.
- Pluck two leaves and a bud only because 3-4 leaves colder leaves) lower the quality due to low level of caffeine
- Leaves should not be compressed in the baskets as this can cause them to heat up and turn brown.
- Plucked tea should be kept cool and shaded while plucking continues and awaiting transportation to the factory.
- Plucked tea should be taken to the factory the same day it is harvested. (1 x3 = 3marks)
- Factor that determine spacing in crops;
Download Agriculture P1 Questions and Answers - Mangu High School Trial Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

