INSTUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided
- This paper consists of three sections A,B and C.
- Answer all the questions in sections A and B and any other two in section C
- All answers must be written in the spaces provided in this booklet.
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
|
SECTION |
QUESTIONS |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATES SCORE |
|
A |
1-19 |
30 |
|
|
B |
20-23 |
20 |
|
|
C |
24-26 |
40 |
|
|
TOTAL SCORE |
90 |

QUESTIONS
SECTION A ( 30 MARKS )
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED
- List two cattle diseases caused by viruses. (1mark)
- State one use for each of the following tools
- Spoke shave ………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………… - Plumb bob ………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Spoke shave ………………………………………………………………………………….
- List two distinguishing external characteristics of California breed of rabbit. (1mark)
- State four reasons for culling a breeding boar . (2marks)
- State any two disadvantages that may arise from inbreeding in livestock. (1mark)
- State two reasons for seasoning timber before use . (1mark)
-
- Differentiate between a roughage and a concentrate feed in animal nutrition. (1mark)
- State four desirable qualities of a livestock ration. (2marks)
- State three factors that may influence the amount of water intake by a farm animal .(1 ½ marks)
- State three advantages of keeping a herd of dairy cattle healthy. (1½ marks)
- Give three reasons for dehorning cattle. (1½ marks)
- Give two methods of extracting honey from honey combs (1mark)
-
- Give four reasons for candling eggs in poultry production. (2marks)
- Give four maintenance practices that should be carried out on the mould board plough.(2marks)
-
- List four harmful effects of internal parasites in livestock. (2marks)
-
- Give two reasons for washing the udder with warm water before milking . (1mark)
- Name three dairy goats kept in Kenya . (1½ marks)
- Name two diseases that affect female animals only (1mark)
- What is the function of a spillway in a fish pond (½ mark)
- Name three types of lubrication systems used in tractors . (1½ marks)
- Give the functions of the following parts of an ox-plough
- Land side …………………………………………………………………………… (½mark)
- Draft rod ……………………………………………………………………………( ½ mark)
- Give three structural requirements for a grain silo. (1½ marks)
- State three advantages of natural feeding in calf rearing. (11/2 marks)
SECTION B ( 20 MARKS )
Answer all the questions provided in this section in the spaces provided
- The diagram below shows the digestive system of cattle. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
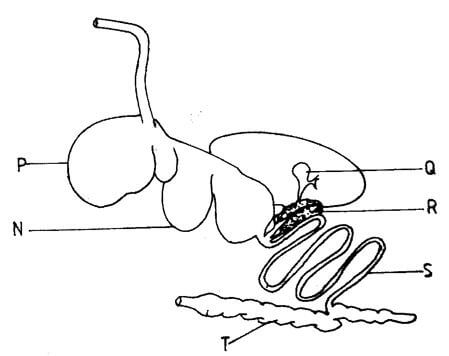
- Name the parts labelled N, P and Q.
N .......................................................................................................................... (1 mark)
P .......................................................................................................................... (1 mark) - State one function for each of the parts labelled S and T.
S....................................................................................................................... (1 mark)
T ......................................................................................................................... (1 mark) - Give one enzyme produced by each of the parts labelled R and S.
R .......................................................................................................................... (1/2 marks)
S ................................................................................................................ (1/2 marks)
- Name the parts labelled N, P and Q.
- The illustration below shows a cross section of a cattle dip.
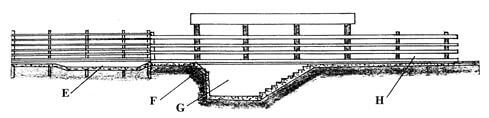
- Name the parts labelled E and G.
E…………………………………………………………………… (1mark)
G…………………………………………………………………… (1mark) - State one use for each of the parts labelled E, F and H. (3marks)
E………………………………………………………….
F………………………………………………………….
H………………………………………………………….
- Name the parts labelled E and G.
- The following diagrams show animals with deficiency symptoms of some minerals. Study the diagrams carefully and answer the questions that follow.

- State the nutrients lacking in the diet of each animal shown above.
Animal G …………………………………………………. (1mark)
Animal H……………………………………………………. (1mark) - Name the disease whose symptoms are shown by the animal labeled G above. (1 mark)
- Give two reasons why the disease named in (b) above should not be controlled by giving medicine through the mouth. (2marks)
- State the nutrients lacking in the diet of each animal shown above.
- The diagram below represents a foundation of a farm structure .Study it and answer questions that follow .
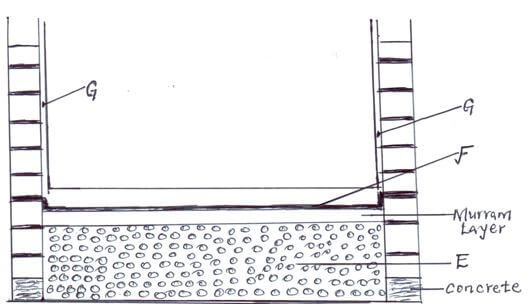
- Identify the parts labeled E and F .
E………………………………………………………………………………… (1mark)
F………………………………………………………………………………… (1mark) - State two uses of part labeled F in a foundation structure . (2marks)
- What ingredients are used to complete part G (1mark)
- Identify the parts labeled E and F .
SECTION C (40 MARKS )
Answer any two questions in this section in the spaces provided at the end of each question.
-
- Describe the uses of fences on the farm. (10 marks)
- Describe Newcastle disease under the following sub-headings
- causal organism; (1 mark)
- signs of infection; (7 mark)
- control measures. (2 marks)
-
- Describe the rearing of lambs from lambing up to weaning time (10 marks)
- Explain five causes of livestock diseases (5 marks)
- State five differences between Ruminants and non Ruminants (5 marks)
-
- State and explain five preventive measures of livestock diseases. (10 Marks)
- Describe long term service carried out during tractor servicing. (6 Marks)
- Outline four functions of the gearbox in a tractor. (4 Marks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Rinder pest
- Foot and Mouth disease
- Rabbies
- Mad cow disease (½ x 3 = 1½ marks)
-
- Spoke shave is used to finish or smoothen curved surfaces (½ mark)
- Plumb bob-used for checking the verticalness of a wall. (½ mark)
- White in colour ,with black ears , nose, paws or tail. (1mark)
-
- poor health
- Old age
- Physical deformities
- Hereditary defects
- Infertility/loss of libido (½ x4 = 2marks)
- Brings loss of hybrid vigour
- May lead to decline in fertility which lead to species extinction
- Brings about reduction in performance
- Leads to high rate of pre-natal mortality
- abortions (½ x2 = 1mark)
- Make it resistance to redant attack and weather elements
- Make it resistance to damage
- Prevent warping (½ x2 = 1mark)
-
- a roughage is a feed stuff with a high fibre and carbohydrates content and low in protein while a concentrate is a feed with high amount of protein or energy (carbohydrates) and crude fibre.
(award 1 mk and mark as a whole ) -
- it must be balanced /rich in nutrients required
- Must be enough for the animal to produce at an economical level.
- Must palatable
- digestible
- free from contaminants (4x ½ = 2mks)
- a roughage is a feed stuff with a high fibre and carbohydrates content and low in protein while a concentrate is a feed with high amount of protein or energy (carbohydrates) and crude fibre.
-
- Depend on
- species of the animal
- the breed animal
- age of animal
- physiological status of animal
- temperatures of the environment
- type of feed eaten
- weight of animal/body size ( 3x ½ = 1½ mks)
- To produce high quality milk
- To have a long lifespan and breed regularly
- To make it fetch high market values.
- To reduce managements cost/make it economical to keep/reduce veterinary bills
- Prevent spread of disease such as these which are zoonotic (½ x 3 = 1 ½ mks)
- To prevent fighting and inflicting injuries on each other
- To make the animal docile and easy to handle
- Make it easy during transportation and feeding because it reduce space the animal occupies .
- Prevent destruction of farm structure
(½ x3 = 1½ mks)
- Heat method
- Crushing and straining
- Use of centrifugal extractor
(½ x2 = 1mk)
-
-
- To check fertility of the egg
- To check egg abnormalities
- To determine condition of the embryo
- To check quality of the shell
- To determine the size of air space (2 x1 = 2mks)
- Clean plough after days work use
- tighten loose nuts and bolts
- lubricate moving parts
- replace broken or worn out parts
- repair broken parts
- sharpen the sharee when necessary
- paint the metallic points to avoid rust
- Apply old engine oil on the plough for long storage
(4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
-
- Retard growth of animals
- leads to malnutrition /emaciation
- lower production
- diarrhea/constipation
- damages to the organs/blindness
- blockage or organs/blindness
- irritation coughing
- cause anaemia
- lead to death
(4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
-
- to remove dirt /kill bacteria
- To stimulate milk let down =
( ½ x 2 = 1mk)
- Saanen
- toggenberg
- british alpine/ German Alphine
- Anglo –nubian
(3 x ½ = 1½ mk)
-
- Retard growth of animals
- Mastitis
- Milk fever (½ x 2 = 1mk)
- A channel used to allow excess water back to the river/ it prevents water from overflowing on the dykes. ½ mk
-
- splash feed type
- Force feed type
- Oil mist type
(½ x 3 = 1 ½ mks)
-
- land side-presses against the wall of the furrow hence prevent the plough from swaying sideways during/provide stability to the plough during ploughing. (½ mk)
- Draft rod
- used for adjusting the depth and width of ploughing. ( ½ mk)
- should have properly constructed roof to protect the grains crop from the sun and rain.
- Wall should be plastered with mortar or mud to make them smooth and air light.
- Should be completely sealed t avoid entry of rodents.
- An inlet and outlets be made of tight covers and should be easy to lock.
(½ x3 = ½ mks)
- Advantages of natural feeding in calf rearing.
- Calf takes milk at body temperature,
- Milk is free from contamination
- it prevents scouring in calves.
- Milk is provided ad libitum. (3 x ½ = 1 ½ marks)
-
-
- N - abomasum
- P - Rumen
- Q - Gall bladder (3 x ½ = 1 /2marks)
-
- S — Digestion/absorption of food
- T-— Absorption of water. (2 x 1 = 2 marks)
-
- R— Lipase/Trypsin/amyIase
- S — Peptidase/maltase/sacrase (invertase)/lactase. (2 x ½ = 1 mark)
-
-
-
- E- Foot bath
- G- Dip tank
- Functions of:
- E-Contain disinfectant to control foot rot
- F- Assist the animals jump into the dip tank
- H- Hold animals to enable excess acaricide in animals body to drain to tank
-
-
- State the nutrients lacking in the diet of each animal shown
- Animal G - Calcium 1x1 = (1mark)
- Animal H - Manganese 1x1=(1mark)
- Name the diseases whose symptoms are shown by the animal labeled G above. 1x1 = (1 mk)
- Milk fever
- Give two reasons why the disease named in (b) above should not be controlled by giving medicine through the month
- The animal is not able to swallow the medicine
- The medicine may get into the lungs ( 1 x2 = 2mks)
- State the nutrients lacking in the diet of each animal shown
-
- E…Hardcore (1mk) F….Damp proof material /PVC (polyvinyl chloride) (1mk)
-
- Prevents water rising beyond the floor or wall.
- Prevents insects beyond the floor or wall. (2mk)
- -sand; - cement (1mk)
-
- Use of fences in the farm:
- Mark boundaries.
- Help to avoid boundary disputes
- Keep off wild animals and intruders from outside the farm.
- Enable the fanner to practice mixed farming.
- Facilitates rotational grazing
- Controls movement of animals and people preventing formation of unnecessary paths in the farm.
- Control the spread of parasites and diseases by keeping off wild and stray animals the farm.
- Help the farmer to isolate or confine animals requiring special attention.
- Enable the farmer to control breeding by rearing different animals in different paddocks.
- Hedges act as windbreakers.
- Adds beauty to the farm,
- Add value
- For privacy. ( 10 x 1 = 10 marks)
- Newcastle disease.
-
- Casual organisms
- virus. (1 x 1 =1 mark)
- Signs of attack:
- Difficult in breathing.
- Beaks remain wide open and necks are strained
- Dullness.
- Birds stand with eyes closed all the time.
- Loss of appetite.
- Nasal discharge which force the birds to shake their heads to clear it.
- Birds walk in a staggering motion since the nervous system is affected.
- Often the bird have their heads and wings drooping,
- Birds produce watery greenish diarrhoea.
- Eggs laid have soft shells. ( 1 x 7 = 7 marks)
- Control Measures:
- Vaccination during the first six weeks and then two to three months later.
- Quarantine.
- Kill the infected birds and burn them.
- Obtain stock from reputable source. (1 x 2 = 2 marks)
-
- Use of fences in the farm:
-
- Rearing of lambs from lambing to weaning time
- Ensure lamb is breathing
- Ensure lamb is warm
- Ensure mother licks lamb to keep warm & remove mucus 10x1=10mks
- Ensure lamb suckles within 6 hours
- Deworming
- introduce lamb to soft pasture
- provide water
- foot trimming
- Dusting/dipping to control external parasites
- identification
- Docking
- Causes of livestock diseases
- Bacteria
- Protozoa
- Virus
- Nutritional diseases
- Amount of food eaten
-
5 x 1 = marksRuminants
Non-ruminants
-Chew cud
-Regurgitate food
-Polygastric
-Do not have salivary amylase
-Saliva is alkaline
-Water mainly absorbed in the omasum
-Able to digest cellulose in rumen
-Do not chew cud
-Do not regurgitate
- monogastric
--Have salivary amylase
-Saliva is neutral
-Water is absorbed in the large intestines
-Do not digest cellulose
- Rearing of lambs from lambing to weaning time
-
- Preventive measures of livestock diseases:
- Isolation of the sick. It’s a preventive measure taken when an animal is suspected to have contracted a disease.
- Imposition of quarantine. This is based on the principle of enclosure in which the affected animals are isolated and their movement restricted, to prevent spread of the disease.
- Use of prophylactic drugs. Include use of coccidiostats in water or food for poultry to control coccidiosis.
- Carrying out regular vaccinations. This is an artificial way of giving an animal immunity against a particular disease.
- Control of vectors. Vectors known to transmit diseases in livestock e.g. tsetse fly and ticks are controlled using appropriate methods.
- Treatment of sick animals. This is done to control spread of diseases.
- Slaughtering the affected animals. Incase of attack by highly infectious and contagious disease, it’s advisable to isolate and slaughter the infected animal.
- Use of antiseptic and dis-infectants. The farmer must ensure cleanliness in animal houses and surroundings. This can be achieved using dis-infectants.
(5 x 2 = 10 Marks)
- Long term tractor service and maintenance:
- Engine oil should be drained completely from the pump and new oil added.
- The steering gear box should be inspected and refiled if the level is low.
- The oil in the differential should be replaced as recommended.
- The linkage and pully attachment should be greased.
- Pully oil level should be checked and added if necessary.
- Oil filters and fuel filters should be replaced regularly.
(6 x 1 = 6 Marks)
- Functions of the gear box:
- Helps the driver to select any forward or reverse gear.
- Adjust the speed of the drive from the engine crank shaft to the drive shaft.
- Help to alter the speed ratio.
- Enable the driver to stop the tractor movement without stopping the engine.
- Enable the power from the engine to be more easily applied to the work done by the tractor.
(Any 4 x 1 = 4 Marks)
- Preventive measures of livestock diseases:
Download Agriculture P2 Questions and Answers - Mangu High School Trial Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

