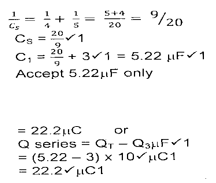INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided.
- This paper consists of two sections, A and B.
- Answer all the questions in section A and B in the spaces provided.
- All workings must be clearly shown.
- Mathematical table and silent non programmable electronic calculators may be used.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
For Examiner’s Use Only:-
|
SECTION |
QUESTION |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
A |
1 – 11 |
25 |
|
|
B |
12 |
11 |
|
|
13 |
10 |
||
|
14 |
13 |
||
|
15 |
11 |
||
|
16 |
10 |
||
|
TOTAL SCORE |
80 |
||

QUESTION
SECTION A (25 MKS):
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- Figure 1 shows a ray of light incident on a mirror at an angle of 450. Another mirror is placed at an angle of 450 to the first one as shown
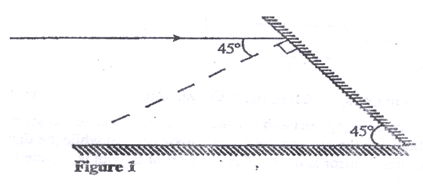
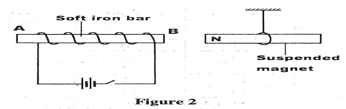
Sketch the path of the ray until it emerges (2 mks) - Figure 2 shows a soft iron bar AB placed in a coil near a freely suspended magnet.
Explain the observation made when the switch is closed. (2 mks) - Table 1 shows radiations and the irrespective frequencies.
Arrange the radiations in the order of increasing energy. (1 mk)Type of radiation
Yellow light
Gamma rays
Radio waves
Micro waves
Frequency (Hz)
1 x 1015
1 x 1022
1 x 106
1 x 1011
- State the reason why electrical power is transmitted over long distances at very high voltages. (1 mk)
- A boy standing in front of a cliff blows a whistle and hears the echo after 0.5s. He then moves 17 metres further away from the cliff and blows the whistle again. He now hears the echo after 0.6s. Determine the speed of the sound. (4mks)
- Figure 3 shows a human eye with a certain defect
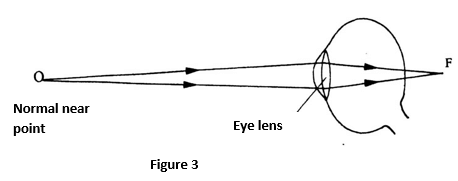
- Name the defect (1 mk)
- On the same diagram, sketch the appropriate Len and rays to show how the defect can be corrected. (2mks)
- Polarisation is a defect of a simple cell. State how it reduces the current produced and how this defect can be minimized (2mks)
- The figure below shows container loader which uses electromagnet to offload containers from a ship.
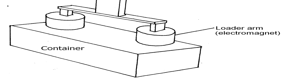
- Why should the container be made of iron or steel (1mk)
- State two ways in which the loader can be made to lift heavier container (2mks)
- Two 12V lead acid accumulators are rated 60Ah and 70Ah. State two physical differences between the accumulators (2mks)
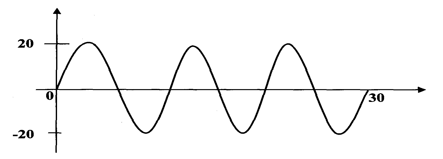
- The diagram below shows part of a wave form. The numbers on the diagram show scales in meters. If the speed of the wave is 20ms-1, determine the frequency and wavelength of the wave. (3mks)
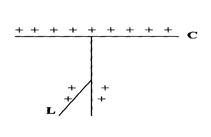
- A gold leaf electroscope is positively charged as shown in the diagram below where C is the cap and L is the gold leaf. State and explain what happens to L when a positively charged rod is brought near C without touching it. (2mks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
-
- State Ohm’s law (1mk)
- The figure below shows the voltage – current relating for a certain battery used in an electrical circuit.
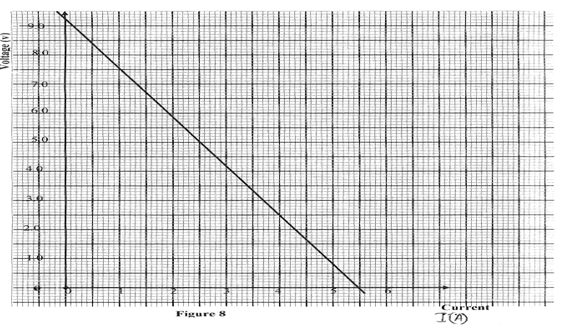
Given that the equation of the graph is V = E – Ir , from the graph , determine- The e.m.f of the battery. (1mk)
- The internal resistance of the battery used. (3mks)
- The figure below shows a circuit with a coil used to warm oil in a beaker.
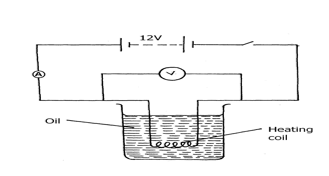
- Explain how heat is produced in the coil (2mks)
- Given that the reading of the ammeter is 2.4A determine the resistance of the coil. (3mks)
- How much heat is produced in the coil in a minute? (2mks)
- Give two changes that can be made in the set up in order to produce more heat per minute. (2mks)
-
- With an aid of a ray diagram show how a convex lens can be used as a magnifying glass (3mks)
- From the definition of magnification M and equation
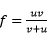 show that magnification
show that magnification 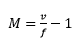 where the symbols have their usual meanings. (3mks)
where the symbols have their usual meanings. (3mks) - Two converging lenses whose focal lengths are f1=5cm and f2=10cm are arranged to have a common axis as shown in figure below.
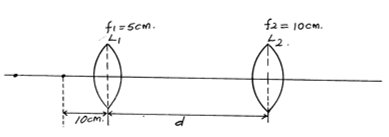
A point object is placed 10cm from L1. Given that the final image is formed 20cm to the left of L21 calculate the separation d of the lenses (4mks)
-
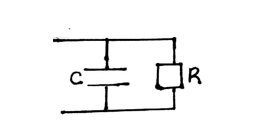
- Figure 8 shows a circuit that may be used to charge a capacitor.
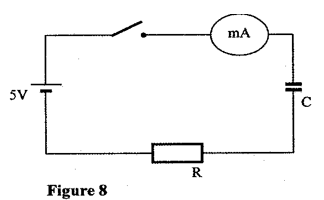
- State the observation on the milliameter when the circuit is switched on: (1mk)
- Explain the observation in (i) above. (2mks)
- The circuit in figure 8 is left on for some time. State the value of p.d. across:
- the resistor R; (1mk)
- the capacitor C; (1mk)
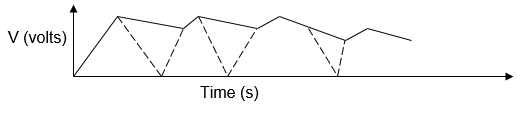
- Sketch the graph of potential difference (V) across R against time. (3mks)
- The Figure shows three capacitors connected to a 10V battery.
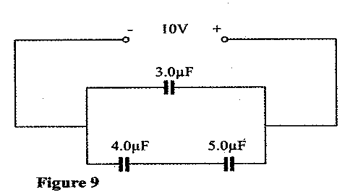
Calculate:- the combined capacitance of the three capacitors; (3mks)
- the charge on the 5.0 μF capacitor. (2mks)
- Figure 8 shows a circuit that may be used to charge a capacitor.
-
- Figure below shows two circuits close to each other
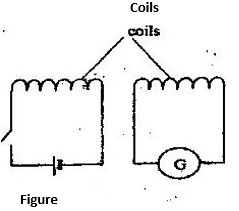
When the switch is closed, the galvanometer shows a reading and then returns to zero. When the switch is then opened, the galvanometer shows a reading in the opposite direction and then returns to zero. Explain these observations. (3mks) - An ideal transformer has 2000 turns in the primary circuit and 200 turns in the secondary circuit. When the primary circuit is connected to a 400V a.c. source the power delivered to a resistor in the secondary circuit is found to be 800W. Determine the current in:
- The secondary circuit (3mks)
- The primary circuit (3mks)
- Explain how energy losses in a transformer are reduced by having a soft- iron core (2mks)
- Figure below shows two circuits close to each other
-
-
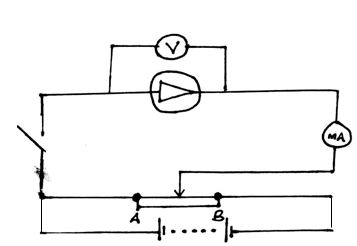
- State the meaning of the statement diode characteristic. (1mk)
- Sketch a circuit diagram that can be used to investigate p-n junction diode characteristics. (2mks)
- Define the term acceptor atom as applied in semiconductor. (1mk)
- Study figure 7 below and use it to answer questions that follow.
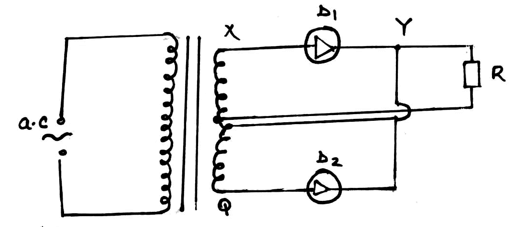
- Briefly explain how the circuit works to produce a rectified alternating current. (3mks)
- Draw on the diagram to show the position of the capacitor. (1mk)
- State the functions of the capacitor in the circuit. (1mk)
- Sketch the graph of the output as seen on a CRO screen. (1mk)
-

MARKING SCHEME
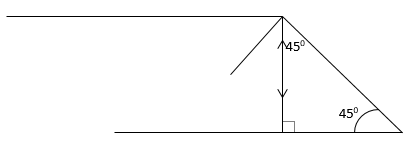
- 1 mk for showing all rays
- 1 mk for angles shown- The suspended bar magnet is repelled. The soft iron bar is magnetized and end B becomes the North pole hence like poles repel.
- Radio waves microwaves yellow light gamma rays
- High voltage leads to low current hence low power losses or energy loss
- 2d/05 = 2d/0.6 + 34 OR V = d/t
D = 17/0.2 = 85 m = 17 x 2
0.1
Speed = 2 x 86 = 340 m/s
0.5
= 340m/s -
- Long sightedness/ hypermetropia
- corrected using a convex/ converging lens; check rays converged at retina.
- Polarisation reduces current by production of hydrogen bubbles around the negative plate; can be reduced by adding a depolarizer e.g manganese (iv) oxide
-
- Magnetic material
- – using larger current
- Increasing the no of turns
- 70Ah 60Ah
- Plates with large surface – smaller surface area plates
- Many plates hence bigger – A few plates hence look smaller - λ = 30/3 = 10m
f = v/λ = 20/10 = 2m/s - - Leaf divergence increases
- Like charges repel -
- Current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its end provided the temperature and other physical conditions are kept constant
-
- emf of the battery equal to v intercept 9.2V
- internal resistance = gradient of the graph .
r = 2.5 Ω
-
- The work done in driving charges through the coil is high due to its resistance. This energy is converted into heat in the coil
- V = IR R = V = 12V
I 2.4
= 5.0Ω - H = VIt
H = 12 x 2.4 x 60
= 1728J - – Using a source with higher emf
- Reducing the length of the coil
= P = V2
R
-
-
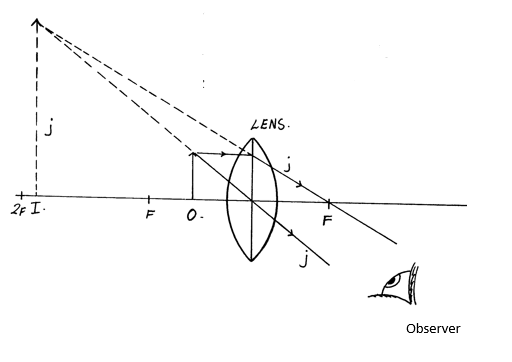
object placed between p and two lens
2 correctly drawn rays from object to image;
magnified, virtual, erect image; - We have
f = uv
v + u
But m = v/u ;
u = v/m
Substitution v/m for u we have ;
v
F = m + 1 ;
Re – arranging we have m = v/f – 1; - u1 = 10 cm, f1 = 5cm, v1 = ?
1/ v1 + 1/ u1 = 1/f1
1/ v1 + 1/ 10 = 1/5
v1 = 10 cm ;
u2 = ? f2 = 10 cm , v2 = 20 cm
1/v2 + 1/ u2 = 1/f2
1/20 + 1/U2 = 1/10
u2 = 20cm ;
d = v1 + u2 = 10cm + 20cm
therefore d = 30 cm ;
-
-
-
- Current falls off to zero / falling to zero / deflects to max. Then zero
Reducing gradually or after sometime. - Current flows when the capacitor is charging
When fully charged current stops (no current) and p.d is equal to charging voltage
- Current falls off to zero / falling to zero / deflects to max. Then zero
-
- VR = 0 V
- VC = 5V
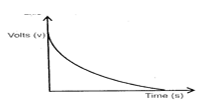
Touch both axis, award for no labeled axis-
-
-
- Flux growing/ linking
No flux change
Flux collapsing
Switch closed: Flux in the coil grows and links the other coil inducing an E.M.F
Current steady: No flux change hence induced E.M.F
Switch opened: Flux collapses in the R.H.S coil inducing current in opposite direction -
- VP = NP P = IsVs
Vs Ns Is = 800/40= 20A
400 = 200
Vs 20
Vs = 40 Volts - Pp Ps
800 = 400 Ip
Ip =800/400 = 2A
- VP = NP P = IsVs
- Reduces losses due to hysteresis (or magnetic losses)
Because the domain in soft- iron respond quickly to change in magnetic (or have low reluctance) i.e easily magnetized and demagnetized
- Flux growing/ linking
-
-
- A graph of current against voltage,
-
- The atoms that introduce holes in the pure semiconductors.
-
- - During the first half cycle D1 is forward biased while D2 is reverse biased.
- The path taken by current is D1, Y R Z.
- During the next half-cycle D2 is forward biased while D1 is reverse biased and the path of the current is Q D2 Y R Z.
- During both cycles, current flows through the resistor in the same direction. -
- Smoothen the output signal.
- - During the first half cycle D1 is forward biased while D2 is reverse biased.
-
Download Physics P2 Questions and Answers - Nambale Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students