INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
- Attempt ALL questions in sections A and B.
- All your answers must be written in the spaces provided in this question paper.
- All working must be clearly shown
- Non programmable silent electronic calculators and KNEC mathematics table may be used except where stated otherwise
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section
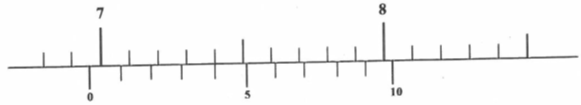
- Figure 1 below shows a scale of vernier calipers when measuring the width of a meter rule.
What is the actual width of the meter rule if the calipers has a zero error of + 0.6mm.? (2mks) - A clinical thermometer has a constriction in the bore just above the bulb. State the use of the constriction. (1mk)
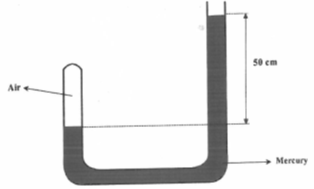
- Figure 2 below shows air trapped by a column of t6he mercury in a U-tube . The atmospheric pressure is 76 cm Hg.
At what pressure in mmHg is the enclosed air? (3mks) - A girl of mass 50 Kg runs up a flight of height 4m in 4 seconds . Calculate the power she developed in this time (2mks)
- Name the transducer in the following energy conversions.
- Kinetic to electrical (1mk)
- Solar to heat (1mk)
- Figure 3 below shows dots produced on a tape pulled through a ticker timer by a moving body.
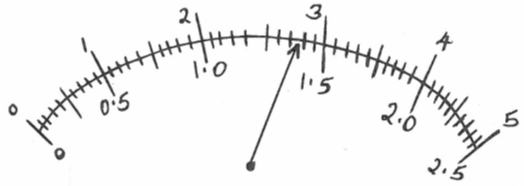
The frequency of the ticker –timer is 50 Hz. Calculate the acceleration of the body. (3mks) - Figure 4 below shows an ammeter used to measure current through the conductor .The student used the lower scale.
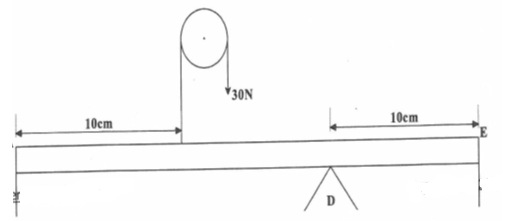
State the reading from the meter (1mk) - Figure 5 below shows a uniform rode AE which is 40 cm long. It has a mass of 2Kg and pivoted at D. If 2N is acting at point E , and 30N force is passed through a frictionless pulley.
Find the force X acting at end A. (3Mks) - Convert -200°C into Kelvins (1mk)
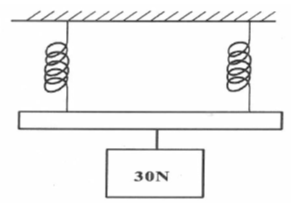
- Figure 6 below shows two identical springs constant 3N/cm supporting a load of 30N.
Determine the extension of each spring (3mks) - Explain why a bus should not carry standing passengers. (1mk)
- State TWO reasons mercury is preferred as a barometric liquid and not water . (2mks)
SECTION B (55MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section
-
- Define the term efficiency as used in machines . (1mk)
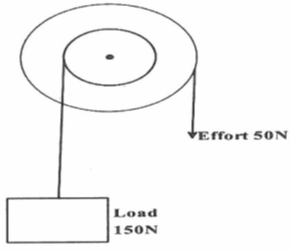
- Figure 7 below shows the cross –section of a wheel and axle of radius 6.5 cm and 1.5 cm respectively used to lift a load. Use it to answer the question that follow.
Determine the- Mechanical advantages (M.A) of the system (2mks)
- Velocity ratio (V.R) of the system (2mks)
- Efficiency of the machine (2mks)
- Give one reason why the above machine is not 100% efficient (1mk)
- State the law of conservation of energy (1mk)
-
- In inelastic collision , kinetic Energy is lost .Explain . (1mk)
- A Trailer of mass 30 tonnes travelling at a velocity of Km/ her rams onto a stationery bus of mass 10 tonnes . The two move together after impact. Determine the common velocity at which they move after impact. (3 Mks)
- A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 30 M/s
- Determine the maximum height reached. (2mks)
- Time taken to come back to the point of projection (2mks)
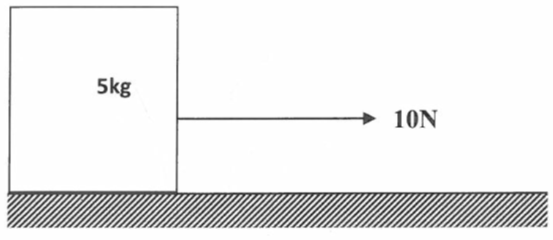
- The figure 6 below shows a body being pulled by a constant force of 10N for 4m over wooden surface . The co- efficient of friction is 0.03.
Find the acceleration of the body (3mks)
-
- State Hooke’s law (1mk)
- A graph of force (y-axis) against (x-axis) is provided. Use it to answer questions below.
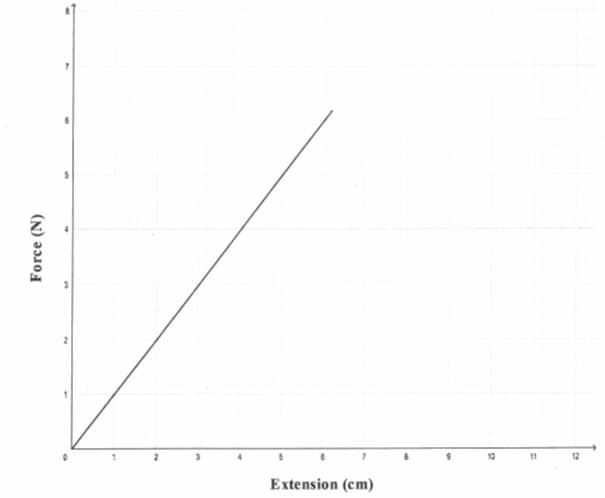
From the graph determine;- Work done in stretching the spring by 3cm. (3mks)
- Spring constant .Give your answer in SI Units. (3mks)
- State two factors that affect the spring constant. (2mks)
-
- Give reason why ink is likely to ooze a pen when one is up in an airplane. (1mk)
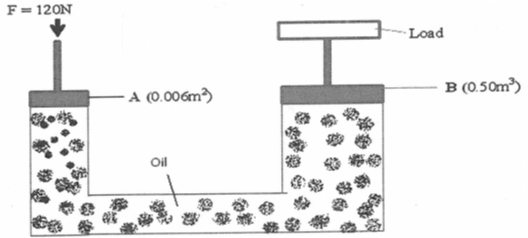
- The figure below is a simple hydraulic machine used to raise heavy loads.
Calculate;- The pressure exerted on the oil by the force applied at A (2mks)
- The load raised at B (2mks)
- Give two properties which make the oil suitable for use in this machine . (2mks)
- The barometer reading at the base of the mountain is 60cm/ Hg while at the top is 50 cm/Hg. If the densities of air and mercury are 1.25kgm-3 and 13,600kgm-3 respectively. Calculate the height of the mountain. (3mks)
-
- Distinguish between streamline and turbulent flow. (2mks)
- Figure below shows two light sheets of paper arranged as shown
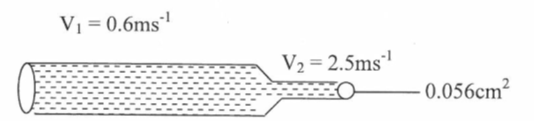
Explain the observation made when air is blown at the same time at point A and B. (2mks) - Figure 12 below shows an incompressible fluid moving through a tube of varied cross-section area. If the area of the small tube is 0.05m2, Calculate the area of large tube in cm2. (3mks)
- State the Bernoulli’s principle (1mks)
- State any TWO assumptions made when deriving the equation of continuity (2mks)
-
- State the principal of moments (1mk)
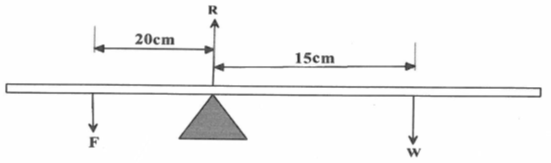
- A uniform metal strip is 3.0cm wide, 0.5 cm thick and 100 cm long. The density of the metal is 2.7 g/cm3. Determine
- The weight of the Metal strip. (2mks)
- The strip is placed on a pivot and kept in equilibrium by forces in the figure below.
- Determine the value of F . (3mks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
- MSR = 6.90cm
VSR = 0.04cm
= (6.90+ 0.04) cm
Actual width = 6.94cm-0.06
= 6.58cm 2 marks - It prevents the return of the mercury to the bulb when the thermometer is removed from the body to the surrounding
1mark - Pressure = Press. Due to atm. + press. due to liquid column
= (76+50) cmHg
= 126cmHg OR 1260mmHg 3 marks - Power = work done = mgh
Time Time
Power = 50 x 10 x 4
4
Power = 500W 2 marks -
- Dynamo 1 mark
- Solar panel 1 mark
- V = 5 = 250 cm/s
0.02
U = 2 = 100m/s
0.02
a= v−u
t
a = 250 −100
0.06
a = 2500cm/s² or 25cm/s² 3 marks - Reading =1.35 A 1mark
- 30 x 20 + 10 x 2 = 30 x +10W
600 + 20 =30X +200
620 = 30X +200
X = 14N 3MKS - −200 + 273=73K Working must not be shown 1 marks
- e = F
e = 30
2×3
e =5cm 3marks - Standing passengers raise the center of gravity making the bus unstable
-
- Mercury has a higher density than water
- Mercury does not stick on walls of the glass 2mks
SECTION B
-
- Efficiency is the ratio of work done on the load(work output) to the work done by the effort(work input) expressed as a percentage 1mk
-
- MA = L
E
MA= 150
50
= 3 2mks - VR = 2πR
2πr
VR = 2π x 6.5
2 π 1.5
= 4.333 2mks - efficiency = MA X100
VR
efficiency = 3 x 100
4.333
= 69.23% 2mks - the friction between the moving parts 1mk
- MA = L
- The sum of kinetic energy and potential energy of a system is constant
Or
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can only be changed from one form to another 1mk
9 marks
-
- The bodies undergo deformation
OR
Some of the energy is transformed to heat, sound or light 1mk - M1v1 + m2v2 = v(m1 + m2)
30000 x 20 + 10000 x 0 = v(30000 + 10000)
600000 = v(40000)
V = 15m/s 3mks -
- hmax = u²
g
hmax = 30²
10
= 90m 2mks - T = 2u
g
T = 2 x 30
10
= 6s 2mks
- hmax = u²
- Fr = µR
Fr = 0.03 x 5x 10
=1.5N
Resultant force = 10 − 1.5
= 8.5N
F = ma
8.5 = 5a
α = 1.7m/s² 3mks
11mks
- The bodies undergo deformation
-
- For a helical spring or any other elastic material, extension is directly proportional to the stretching force provided the elastic limit is not exceeded 1mk
-
- work done = area under the graph
Work done = ½ Fe
Work done = ½ x 6 x 0.06
= 0.18j 3mks - spring constant = gradient of the graph
= Δ force
Δ Extension
= 6 − 0
0.06 − 0
= 100N/m 3mks -
- Nature of the material of the spring
- Thickness of the wire of the spring
- The diameter of the spring
- The number of turns per unit length 2mks
- work done = area under the graph
-
- There is low atmospheric pressure hence the ink pressure in the pen is higher, forcing the ink out 1mk
-
- p = force
Area
p = 120
0.006
p = 20000 pa 2mks - 20000 = F
0.5
Load = 10000N 2mks -
- Oil is incompressible
- The oil does not corrode the parts the machine
- Have a high boiling point and a low freezing point 2mks
- p = force
- Pressure due to air column = Pressure difference
haęag = hmęmg
ha = hₘęₘ
ęa
ha = 0.1x13600
1.25
= 1088m 3mks
10mks
-
- Streamline flow is a flow in which all particles of the fluid at a point in a tube of flow are travelling at the same velocity and same direction while turbulent flow is a flow in which particles at a point move with different speeds and in different direction. 2 mks
- The papers move away from each other, the fast moving area reduces the pressure; the atmospheric pressure in between the papers pushes them apart 2 mks
- A1v1 = A2 V2
A1 = 0.056 X 2.5
0.6
= 0.233cm² 3mks - Provided the fluid is non - viscous, incompressible and flowing steadily, an increase in speed of the fluid produces a corresponding decrease in pressure. 1 mks
-
- the fluid in incompressible
- the fluid is non - viscous
- the flow is streamlined Any 2 x 1 = 2mks
10 marks
-
- For a system in equilibrium, the sum of clockwise moments must be equal to the sum of ant - clockwise moments at a point of support.
-
- w = 0.03 x 0.005 x 2700 x 10
W = 4.05N 2mk - Sum of clockwise moments - sum of the anticlockwise moments
20 x F = 15 x 4.05
F = 3.0375 N 3mks
06 marks
- w = 0.03 x 0.005 x 2700 x 10
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Bungoma Diocese Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students