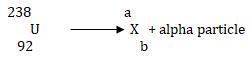PHYSICS
PAPER 2
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of two sections A and B.
- Answer all the questions in sections A and B in the spaces provided.
- Non programmable silent electronic calculators may be used.
- Candidates should check the questions to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and that no question is missing.
SECTION A 25MARKS.
Answer all questions in the space provided
- What is meant by virtual image? (1mk)
-
- Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in order of their increasing wavelength visible light, X-rays, Microwaves, infrared radiation. (1 mk).
- Name one device that can be used to detect infrared radiation. (1mk)
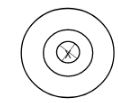
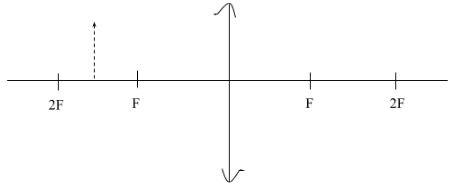
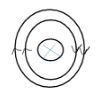
- Indicate the direction of the magnetic field in the conductor carrying current shown below. (1mk)
-
- Define the term ‘doping’. (1mk)
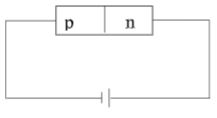
- The diagram below shows a p – n junction diode.
Complete the diagram above to show how the diode can be connected in reverse bias mode. (1mk)
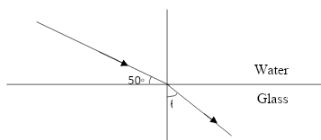
- Given that the refractive index of glass is 3/2 and that of water is 4/3. Determine the value of angle in the figure below. (3mks)
- State two factors that determine how far X- rays penetrate a given material. (2mks)
-
- Uranium238 92U emits an alpha particle to become another element X as shown in the equation below.
Determine the values of a and b. (2mks) - State two sources of background radiation. (2mks)
- Uranium238 92U emits an alpha particle to become another element X as shown in the equation below.
-
- Explain why Nichrome wire is used as a heating element rather than copper. (1mk)
- An electric bulb is rated 240V, 100W. Calculate the amount of current through its filament. (2mks)
- If ten such bulbs were used in a house for lighting, determine the most suitable fuse value. (1mk)
- State two conditions for the formation of a stationary wave. (2mks)
- A gun is fired and an echo heard at the same place 0.6s later. How far is the barrier which reflected the sound from the gun? (Speed of sound in air = 330m/s). (3mks)
- State how polarization is reduced in a dry cell. (1mk)
- A negatively charged rod is brought near the cap of lightly charged electroscope. The leaf divergence first reduces but as the rod comes nearer, it diverges more. State the charge of the electroscope. (1 mk)
SECTION B (55 MARKS).
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
-
- State one condition under which ohm’s law is obeyed in a metal conductor. (1mk)
- You are provided with three resistors R1, R2 and R3 connected in parallel. If the p.d across them is V, show that an expression for the effective resistance of the three resistors is given by. (3mks)
1 = 1 + 1 + 1
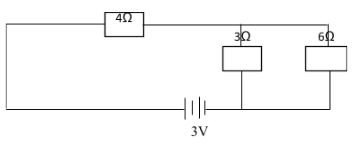
RT R1 R2 R3 - The diagram below shows the resistors connected in a circuit.
Calculate:- The total resistance in the circuit. (2mks)
- Total current flowing in the circuit. (2mks)
-
- State one way of increasing the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor. (1mk)
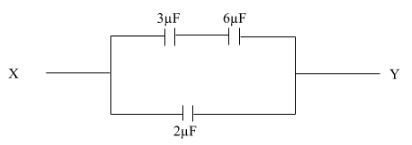
- The diagram below shows a simple network of capacitor.
If the potential difference between X and Y is 12V, calculate the total charge stored by the capacitors. (3mks)
-
- Define Principal focus of a biconcave lens
- The diagram below shows a virtual image of an object placed in front of a biconvex lens
Draw appropriate rays to locate the objects. (3mks) - A convex lens forms a real image five times the size of the object on a screen. If the distance between the object and screen is 120cm.
Determine:- Image distance (1mk)
- Focal length. (2mks)
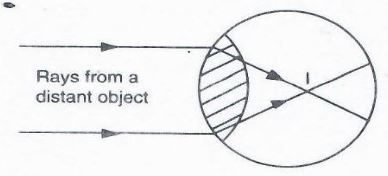
- The diagram below shows a defect in human eye.
- Name the defect. (1mk)
- State one cause of the defect. (1mk)
- How can the defect be corrected? (1mk)
-
- State Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction. (1mk)
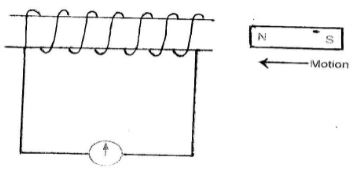
- The figure below shows a bar magnet being moved into a coil connected to a galvanometer in the direction indicated.
State the observation made on the galvanometer when:- The magnet is moved into the coil at a steady speed. (1mk)
- The magnet is held stationary inside the coil. (1mk)
- How is a transformer designed to minimize energy losses through flux leakage? (1mk)
- The primary coil of a transformer has 2000 turns and is connected to a 240V a.c supply. The secondary coil has 400 turns.
- State with a reason the type of the transformer. (1mk)
- Determine the voltage in the secondary coil. (2mks)
- If the current flowing in the primary coil is 0.5A and in the secondary coil is 2.0 A determine the efficiency of the transformer. (2mks)
- Electrical energy is transmitted at very high voltage and low current.
- State how the high voltages are attained. (1mk)
- State two reasons why aluminum wires are preferred to copper wires for transmission over long distances. (2mks)
-
- What is thermionic emission? (1mk)
- Explain why a cathode ray tube is evacuated. (1mk)
- Heated cathodes are coated with oxides of such metal as barium, Strontium or thorium. Explain. (1mk)
- State one property of cathode rays. (1mk)
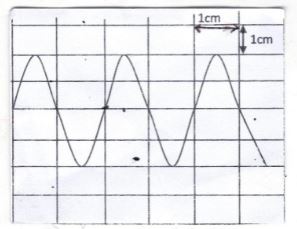
- The figure below shows the waveform displayed on C.R.O screen when an alternating voltage is applied on the Y – input. The time – base is at 1ms/cm and the Y- gain at 10v/cm.
Calculate :- The pick voltage of the input signal. (2mks)
- The frequency of the a.c signal. (2mks)
- In a certain X- ray tube, the electrons are accelerated by p.d of 12kv. Assuming that all the energy goes to produce X-rays, determine the frequency of the X rays produced.
(take planck’s constant h = 6.62 x10-34 Js, and the charge of an electron e = 1.6 x 10-19 C) (3mks)
-
- It is observed that when ultra – violet radiation is directed onto a clean Zinc plate connected to the cap of a negatively charged leaf electroscope, the leaf falls.
- Explain this observation. (1mk)
- Explain why the leaf of the electroscope does not fall when infrared radiation is directed onto the zinc plate. (1mk)
- State the effect on the electrons emitted by the photoelectric effect when the intensity of incident radiation is increased. (1mk)
- The maximum wavelength required to cause photoelectric emission on a metal surface is 8.0 x 10-7 m. The metal surface is irradiated with light of frequency 8.5 x 1014 Hz.
(Take lev = 1.6 x 10-19 J , c = 3.0 x 108 m/s , h= 6.63 x 10-34 Js)
Determine:- The threshold frequency. (2mks)
- The work function of the metals in electron volts. (2mks)
- The maximum Kinetic energy of the electrons. (3mks)
- It is observed that when ultra – violet radiation is directed onto a clean Zinc plate connected to the cap of a negatively charged leaf electroscope, the leaf falls.
MARKING SCHEME
- What is meant by virtual image? (1mk)
- Image which cannot be focused on a screen.
- Image which cannot be focused on a screen.
-
- Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in order of their increasing wavelength visible light, X-rays, Microwaves, infrared radiation. .
- X- rays → Visible light → Infrared → microwaves.
- X- rays → Visible light → Infrared → microwaves.
- Name one device that can be used to detect infrared radiation. (1mk)
- Skin, barometers, thermopile, thermometer with a blackened bulb. (Any one)
- Skin, barometers, thermopile, thermometer with a blackened bulb. (Any one)
- Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in order of their increasing wavelength visible light, X-rays, Microwaves, infrared radiation. .
- Indicate the direction of the magnetic field in the conductor carrying current shown below. (1mk)
-
- Define the term ‘doping’. (1mk)
- This is adding of impurities to an intrinsic semi conductor to enhance its conductivity.
- This is adding of impurities to an intrinsic semi conductor to enhance its conductivity.
- The diagram below shows a p – n junction diode.
Complete the diagram to show how the diode can be connected in reverse bias mode. (1mk)
- Define the term ‘doping’. (1mk)
- Given that the refractive index of glass is 3/2 and that of water is 4/3. Determine the value of angle in the figure below. (3mks)
- n = n x n
wg wa ag
= ¾ x 3/2 = 9/8 = 1.125
=1.125 = Sin 40 /SinǾ
Ǿ= 34.85º
OR - n1 Sin Ǿ = n2 Sin Ǿ2
4/3 Sin 40 = 3/2 Sin Ǿ2
Ǿ = 34.85º
- n = n x n
- State two factors that determine how far X- rays penetrate a given material. (2mks)
- Frequency of the X rays / wavelength / Energy.
- Density of the materials.
-
- Uranium 238 92 U emits an alpha particle to become another element X as shown in the equation below.
Determine the values of a and b. (2mks)- a + 4 = 238
a = 234 - b+2 = 92
b= 90
- a + 4 = 238
- State two sources of background radiation. (2mks)
- Cosmic rays of from outer space.
- Radiations from the sun.
- Some rocks which contain traces of radioactive materials e.g granite.
- Natural and artificial radio isotopes.
- Uranium 238 92 U emits an alpha particle to become another element X as shown in the equation below.
-
- Explain why Nichrome wire is used as a heating element rather than copper. (1mk)
- Nichrome wire has higher resistance than copper.
- Nichrome wire has higher resistance than copper.
- An electric bulb is rated 240V, 100W. Calculate the amount of current through its filament. (2mks)
- P = V1
I = P/V
100/240 = 0.4167A
- P = V1
- If ten such bulbs were used in a house for lighting, determine the most suitable fuse value. (1mk)
- Total I = 10 X 0.4167 = 4.167
5 A fuse is suitable
- Total I = 10 X 0.4167 = 4.167
- Explain why Nichrome wire is used as a heating element rather than copper. (1mk)
- State two conditions for the formation of a stationary wave. (2mks)
- Equal speed
- Same frequency.
- Same or nearly equal amplitude. Any 2
- A gun is fired and an echo heard at the same place 0.6s later. How far is the barrier which reflected the sound from the gun? (Speed of sound in air = 330m/s). (3mks)
- S = 2 d/t
2d = 330 x0.6
d = 330 x0.6
2
d = 99m
- S = 2 d/t
- State how polarization is reduced in a dry cell. (1mk)
- The presence of manganese (iv) oxide oxidizes the hydrogen to water. /Removing and brushing off copper electrodes
- The presence of manganese (iv) oxide oxidizes the hydrogen to water. /Removing and brushing off copper electrodes
- A negatively charged rod is brought near the cap of lightly charged electroscope. The leaf divergence first reduces but as the rod comes nearer, it diverges more. State the charge of the electroscope.
- Positive charge.
- Positive charge.
-
- State one condition under which ohm’s law is obeyed in a metal conductor. (1mk)
- Constant temperature/ thickness / length.
- Constant temperature/ thickness / length.
- You are provided with three resistors R1, R2 and R3 connected in parallel. If the p.d across them is V, show that an expression for the effective resistance of the three resistors is given by. (3mks)
1 = 1 + 1 + 1
RT R1 R2 R3- Since resistors are in parallel, total current I divides into I1 I2 and I 3
- Since resistors are parallel,total current IT divides into I1,I2 and I3
- IT=I1+I2+I3
But IT= VT
RT
1=VT , ,I2=VT , ,I3=VT
R1 R2
VT= VT+VT+ VT
RT R1 R2 R3
1= 1 + 1 + 1
RT R1 R2 R3
- The diagram below shows the resistors connected in a circuit.
Calculate:- The total resistance in the circuit. (2mks)
- RT = 4 + 3 x6/3+6 = 4+2 = 6
- RT = 4 + 3 x6/3+6 = 4+2 = 6
- Total current flowing in the circuit. (2mks)
- IT = V/RT = 3/6 = 0.5A.
- The total resistance in the circuit. (2mks)
-
- State one way of increasing the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor. (1mk)
- Increases the area of a plate overlap.
- Reduce distance between plates.
- Use a dielectric of greater permittivity. Any one .
- The diagram below shows a simple network of capacitor.
If the potential difference between X and Y is 12V. Calculate the total change stored by the capacitors. (3mks)- CT = 3 x 6/3 + 6 + 2 = 18/9 + 2 = 2+2 = 4 F
- C = Q/V , Q = CV , Q = 4 X 10-6 X 12
= 4.8 X 10-5 C
- CT = 3 x 6/3 + 6 + 2 = 18/9 + 2 = 2+2 = 4 F
- State one way of increasing the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor. (1mk)
- State one condition under which ohm’s law is obeyed in a metal conductor. (1mk)
-
- Define Principal focus of a biconcave lens.(1mk)
- It is a point on the principal axis from which rays parallel and close to the principal axis appear to diverge from after refraction by the biconcave lens.
- It is a point on the principal axis from which rays parallel and close to the principal axis appear to diverge from after refraction by the biconcave lens.
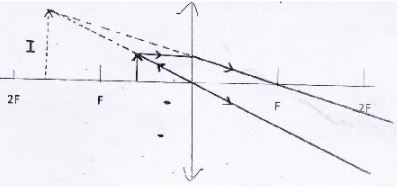
- The diagram below shows a virtual image of an object placed infront of a biconvex lens.
Draw appropriate rays to locate the objects. (3mks) - A convex lens forms a real image five times the size of the object on a screen. If the distance between the object and screen is 120cm.
Determine:- Image distance (1mk)
- u + v = 120cm u = 20cm
V = 5u v = 5(20)
6u = 120cm V = 100cm.
- u + v = 120cm u = 20cm
- Focal length. (2mks)
- 1/f = 1/u + 1/v
1/f = 6/100
= 1/20 + 1/100
f = 100/6 = 16.667cm
- 1/f = 1/u + 1/v
- Image distance (1mk)
- The diagram below shows a defect in human eye.
- Name the defect. (1mk)
- Myopia (Shortsightedness)
- Myopia (Shortsightedness)
- State one cause of the defect. (1mk)
- Longer eyeball./ too big eyeball
- Shorter focal length./too short focal length
- How can the defect be corrected? (1mk)
- Use diverging lens./Concave lens
- Name the defect. (1mk)
- Define Principal focus of a biconcave lens.(1mk)
-
- State Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction. (1mk)
- The direction of the induced emf is such that the induced current which it causes to flow produces a magnetic effect that opposes the change producing it.
- The direction of the induced emf is such that the induced current which it causes to flow produces a magnetic effect that opposes the change producing it.
- The figure below shows a bar magnet being moved into a coil connected to a galvanometer in the direction indicated.
- State the observation made on the galvanometer when:
- The magnet is moved into the coil at a steady speed. (1mk)
- The galvanometer deflects and goes back to zero.
- The galvanometer deflects and goes back to zero.
- The magnet is held stationary inside the coil. (1mk)
- No deflection is observed.
- No deflection is observed.
- The magnet is moved into the coil at a steady speed. (1mk)
- State the observation made on the galvanometer when:
- How is a transformer designed to minimize energy losses through flux leakage? (1mk)
- The secondary coil is wound over the primary coil or the primary coil is wound next to the secondary coil.
- The secondary coil is wound over the primary coil or the primary coil is wound next to the secondary coil.
- The primary coil of a transformer has 2000 turns and is connected to a 240V a.c supply. The secondary coil has 400 turns.
- State with a reason the type of the transformer. (1mk)
- Step down transformer the primary coil has a higher number of turns compared to the secondary coil.
- Step down transformer the primary coil has a higher number of turns compared to the secondary coil.
- Determine the voltage in the secondary coil. (2mks)
- Ns = Vs = 400 = Vs.
Np Vp 2000 240
Vs = 48 V.
- Ns = Vs = 400 = Vs.
- If the current flowing in the primary coil is 0.5A and in the secondary coils is 2.0 A determine the efficiency of the transformer. (2mks)
- = Vs x 1s X 100%
Vp 1p
48/240 x 2/0.5 x100 = 80%
- = Vs x 1s X 100%
- State with a reason the type of the transformer. (1mk)
- Electrical energy is transmitted at very high voltage and low current.
- State how the high voltages are attained. (1mk)
- By stepping up the low voltage input to high voltage output for transmission.
- By stepping up the low voltage input to high voltage output for transmission.
- State two reasons why aluminium wires are preferred to copper wires for transmission over long distances. (2mks)
- Light in weight.
- Cheaper than copper wire (readily available)
- State how the high voltages are attained. (1mk)
- State Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction. (1mk)
-
- What is thermionic emission. (1mk)
- This is emission of electrons from a heated cathode.
- This is emission of electrons from a heated cathode.
- Explain why a cathode ray tube is evacuated. (1mk)
- So that electrons do not lose some of their energy through collision with air molecules on their way to the screen.
- So that electrons do not lose some of their energy through collision with air molecules on their way to the screen.
- Heated cathodes are coated with oxides of such metal as barium, Strontium or thorium. Explain. (1mk)
- These oxides are preferred for they have low work function.
- These oxides are preferred for they have low work function.
- State one property of cathode rays.(1mk)
- Travel in straight lines
- Cause fluorescence.
- Possess kinetic energy.
- Have charge.
- The figure below shows the waveform displayed on C.R.O screen when an alternating voltage is applied on the Y – input. The time – base is at 1ms/cm and the Y- gain at 10v/cm.
Calculate :- The pick voltage of the input signal. (2mks)
- V= 2cm x 10v /cm = 20 v.
- V= 2cm x 10v /cm = 20 v.
- The frequency of the a.c signal. (2mks)
- T = 2cm x 1m/s /cm = 2ms
f = 1 = 1 = 500 HZ
T 0.002
- T = 2cm x 1m/s /cm = 2ms
- The pick voltage of the input signal. (2mks)
- In a certain X- ray tube, the electrons are accelerated by p.d of 12kv. Assuming that all the energy goes to produce X-rays, determine the frequency of the X rays produced (take constant h = 6.62 x10 -34 Js, and the charge of an electron e = 1.6 x 10 -19 C) (3mks)
- hf = eV
f = eV/h
f = 1.6 x 10‾¹⁹ x 12000
6.62 x 10-34.
f = 2.9003 x 1018 Hz.
- hf = eV
- What is thermionic emission. (1mk)
-
- It is observed that when ultra – violet radiation is directed onto a clean Zinc plate connected to the cap of a negatively charged leaf electroscope, the leaf falls.
- Explain this observation. (1mk)
- The negative electrons from the zinc plate are repelled away by the negative charge that are already on the electroscope hence the leaf falls due to electrons leakage.
- The negative electrons from the zinc plate are repelled away by the negative charge that are already on the electroscope hence the leaf falls due to electrons leakage.
- Explain why the leaf of the electroscope does not fall when infrared radiation is directed onto the zinc plate. (2mk)
- The photons of infrared have lower frequency than ultraviolet, hence the energy from infrared is not enough to eject electrons from Zinc.
- The photons of infrared have lower frequency than ultraviolet, hence the energy from infrared is not enough to eject electrons from Zinc.
- Explain this observation. (1mk)
- State the effect on the electrons emitted by the photoelectric effect when the intensity of incident radiation is increased. (1mk)
- The number of electrons emitted will increase.
- The number of electrons emitted will increase.
- The maximum wavelength required to cause photoelectric emission on a metal surface is 8.0 x 10-7 m. The metal surface is irradiated with light of frequency 8.5 x 1014 Hz.
Take lev = 1.6 x 10-19 J
c = 3.0 x 108 m/s
h= 6.63 x 10-34 Js
Determine:- The threshold frequency. (2mks)
- C = λOfo
fo = c / λO
3.0 x10⁸ = 3.75 x 1014 Hz.
8.0 x 10-7
- C = λOfo
- The work function of the metals in electron volts. (2mks)
- Wo = hfo = 6.63 x 10-34 x 3.75 x 1014
e = 2.49 x 10-19 Joules.
= 2.19 x 10‾¹⁹
1.6 x 10-19 = 1.55 eV.
- Wo = hfo = 6.63 x 10-34 x 3.75 x 1014
- The maximum Kinetic energy of the electrons. (3mks)
- K.E = hf – hfo
= h(f –fo)
= 6.63 x 10-34 (8.85 – 3.75 )1014.
= 6.63 x 10-34 x 4.75 x 1014.
= 3.14925 x 10-19 Joules.
- K.E = hf – hfo
- The threshold frequency. (2mks)
- It is observed that when ultra – violet radiation is directed onto a clean Zinc plate connected to the cap of a negatively charged leaf electroscope, the leaf falls.
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - MECS Cluster Joint Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students