PHYSICS
PAPER 3
PRACTICAL
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and admission number in the spaces provided.
- Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- You are supposed to spend the first 15 minutes of the allowed for this paper reading the whole paper carefully before commencing the work.
- Marks are given for a clear record of the observations actually made, their suitability, accuracy and the use made of them.
- Candidates are advised to record their observation as soon as they are made.
- Non programmable silent electronic calculators may be used.
- This paper consists of 8 printed pages.
- Candidates should check the questions to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and that no question are missing.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
QUESTION 1 (20 marks)
- You are provided with the following;
- A galvanometer
- A dry cell and a cell holder
- A switch
- A wire labelled Y mounted on a piece of wood.
- Eight connecting wires each with a crocodile clip at one end.
- A resistance wire labelled AB mounted on a millimeter scale.
- Six 10 Ohm carbon resistors
- A jockey or crocodile clip
- Micrometer screw gauge (to be shared)
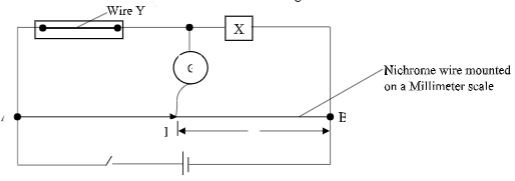
Proceed as follows:- Set up the circuit as shown in figure below, with X being one of the 10 ohms carbon resistors.
- Close the switch. Tap the jockey at various points on the wire AB and locate point P at which the galvanometer shows zero deflection, measure and record in table below the length, where = PB.
- Repeat the procedure in (b) using X as two 10Ω resistors, three resistors, four resistors, five resistors and six resistors. X is the effective resistance for the parallel combination i.e. x = 10/n where n is the number of resistors in parallel.
- Record your readings in table below. (6mks)
TABLE
Number of 10Ω
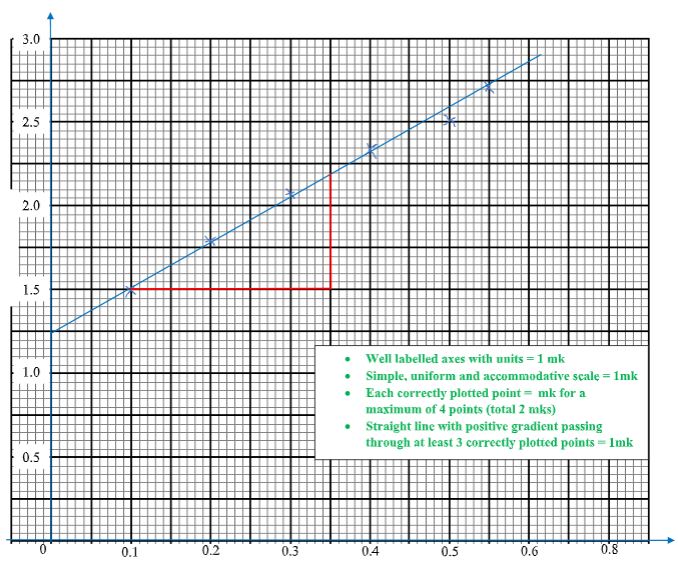
Carbon resistorOne Two Three Four Five Six X (Ω) L (cm) 1/x (Ω-1) 1/L(cm-1) - Plot a graph of 1/L (y-axis) against 1/x. (5mks)
- Determine the slope m of the graph. (2mks)
- Given that 1/L = R/KX + 1/K where K = 100cm. Use the graph to determine R. (2mks)
- Measure the diameter d and the length of wire Y. (2mks)
=…..……..…………………………..….m
d = ………….…………………………….. m - Determine its cross-sectional area A of the wire Y. (1mk)
A =………………………………………… m 2 - Determine the resistivity of the wire Y given that its Resistance, R= 1/A(2mks)
- Set up the circuit as shown in figure below, with X being one of the 10 ohms carbon resistors.
QUESTION 2 (20 marks)
PART A
You are provided with the following;
- Meter rule
- Retort stand, clamp and boss
- A spring and with a pointer
- Three masses (a 100 g and two 50g masses)
- Stop watch
Proceed as follows
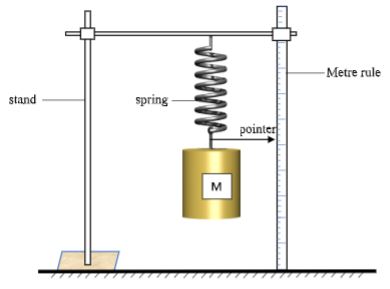
- Set the apparatus as shown below.
- Hang the unloaded spring and record the pointer readings
xo………………………………………………………….…………………………. m. (1mk) -
- Load a mass of 150 g and determine the extension of the spring, e1 .
e1……………………………………………………………………………. m. (1mk) - Displace the 150 g mass slightly downwards and release it to oscillate vertically. Time 20 oscillations and obtain time t1 t1 ………………………………………………….. (1mk)
- Find periodic time T 1
T1 …………………………………………………. (1mk) - Use the equation to find the value of P-1 . (2mks)
- Load a mass of 150 g and determine the extension of the spring, e1 .
-
- Load a mass of 200 g and determine the extension of the spring, e2 .
e2……………………………………………………………………………. m. (1mk) - Displace the 200 g mass slightly downwards and release it to oscillate vertically.
Time 20 oscillations and obtain time t2 .
t2 ………………………………………………….. (1mk) - Find periodic time T1
T1 …………………………………………………. (1mk) - Use the equation to find the value of P2 . (2mks)
- Load a mass of 200 g and determine the extension of the spring, e2 .
- Find the average of P (2mks)
Pav = P² + P¹
2
PART B
Apparatus- Lens and a lens holder
- A candleScreen
- A metre rule.
Procedure
- Focus a distant object and estimate the focal length, f of the lens
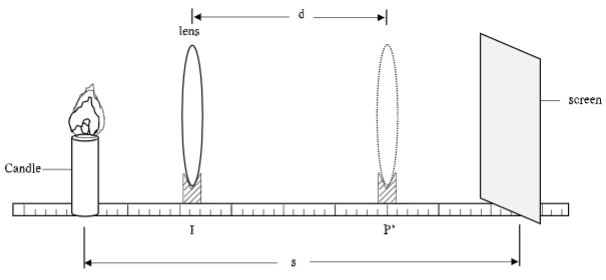
f …………………………………………. mm. (1mk) - Set up the apparatus as shown below.
- Set the distance s= 60 cm.
- Adjust the position of the lens to position p where a magnified sharp image is formed on the screen. Record position P.
P =………………………………………. cm. (1mk) - Maintaining distance s, adjust the lens to position P’ where a diminished sharp image is formed on the screen. Record position, P’.
P’ = ……………………………………… cm. (1mk) - Find distance d, between the original position and final position of lens
d = ………………………………………... cm (1mk)
- Adjust the position of the lens to position p where a magnified sharp image is formed on the screen. Record position P.
- Using the formula s2 - d2 = 4 Find the value of q. (2mks)
- What physical quantity do q represent (1mk)
CONFIDENTIAL
QUESTION 1
Each candidate will require
- Centre zero galvanometer
- One new size D dry cell & cell holder
- A switch
- Eight connecting wires each with crocodile clip at one end.
- A piece of nichrome wire swg 28 (diameter 0.32 mm) of length 30cm.
- Teacher to mount the piece of wire on piece of wood and label it Y see
- A resistance (nichrome wire gauge 30) wire labeled AB 100cm long mounted on a millimeter scale
- Six 10 Ohms carbon resistors.
- A jockey (a crocodile clip may be used)
- A micrometer screw gauge
QUESTION 2
Each candidate will require:
- A spiral spring of spring constant of approximately 10.0N/m.
- A complete stand
- A metre rule.
- Lens (focal length = 10cm) and a lens holder.
- A candle
- Screen
- Three masses (one 100g and two 50g masses)
- A stop watch
MARKING SCHEME
QUESTION 1 (20 marks)
- You are provided with the following;
- A galvanometer
- A dry cell and a cell holder
- A switch
- A wire labelled Y mounted on a piece of wood.
- Eight connecting wires each with a crocodile clip at one end.
- A resistance wire labelled AB mounted on a millimeter scale.
- Six 10 Ohm carbon resistors
- A jockey or crocodile clip
- Micrometer screw gauge (to be shared)
Proceed as follows:- Set up the circuit as shown in figure below, with X being one of the 10 ohms carbon resistors.
- Close the switch. Tap the jockey at various points on the wire AB and locate point P at which the galvanometer shows zero deflection, measure and record in table below the length, where = PB.
- Repeat the procedure in (b) using X as two 10Ω resistors, three resistors, four resistors, five resistors and six resistors. X is the effective resistance for the parallel combination i.e. x = 10/n where n is the number of resistors in parallel.
- Record your readings in table below. (6mks)
Number of 10Ω
Carbon resistorOne Two Three Four Five Six X (Ω) 10 5 3.333 2.5 2 1.667 (L cm) 66.5 53.3 48.2 43.5 40.2 37.4 1/x (Ω-1) 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 1/L(cm-1) 1.515 1.876 2.075 2.299 2.488 2.674
Plot a graph of 1/L (y-axis) against 1/x. (5mks) - Determine the slope m of the graph. (2mks)
- m = (2.2 - 2.5) 10‾² cm-1
(0.35 - 0.10) -1
(Correct substitution = 1mk)
(Correct evaluation with units = 1mk)
Wrong unit = 0mk, no unit = half mark
- m = (2.2 - 2.5) 10‾² cm-1
- Given that where 1/L = r/KX + 1/K where K = 100cm. Use the graph to determine R. (2mks)
- Slope = R/K
(Correct substitution = 1mk)
=28
(Correct evaluation = 1mk)
- Slope = R/K
- Measure the diameter d and the length of wire Y. (2mks)
- I = 30.0/100 = 0.300 m ±0.01 (Value within the range and 3dp a must = 1mk)
d = 0.32/100= 0.0032m ± 0.00002(Value within the range and 5dp a must = 1mk)
- I = 30.0/100 = 0.300 m ±0.01 (Value within the range and 3dp a must = 1mk)
- Determine its cross-sectional area A of the wire Y. (1mk)
- (Correct substitution = mk)
A m2 (Correct evaluation = mk)
- (Correct substitution = mk)
- Determine the resistivity of the wire Y given that its Resistance, (2mks)
- 7.508 x 10-7m
(Correct substitution = 1mk)
(Correct evaluation = mk, rule for units applies)
- 7.508 x 10-7m
QUESTION 2 (20 marks)
PART A
- You are provided with the following;
- Meter rule
- Retort stand, clamp and boss
- A spring and with a pointer
- Three masses (a 100 g and two 50g masses)
- Stop watch
Proceed as follows- Set the apparatus as shown below.
- Hang the unloaded spring and record the pointer readings
- xo = student value (3d.p a must) m (1mk)
-
- Load a mass of 150 g and determine the extension of the spring, e 1 .
- e1 = difference in student values = 0.148 ± 0.0 m (1mk)
(Correct subtraction = mk, correct evaluation =mk)
- e1 = difference in student values = 0.148 ± 0.0 m (1mk)
- Displace the 150 g mass slightly downwards and release it to oscillate vertically. Time 20 oscillations and obtain time t 1 .
- t 1 = 16.37 ± 0.5 (1mk)
(Value within the range and 2dp a must = 1mk, no unit deny a half mark)
- t 1 = 16.37 ± 0.5 (1mk)
- Find periodic time T 1
- T 1 = 16.37/20 = 0.8184s
(Correct division = mk, correct evaluation with unit=mk)
(1mk)
- T 1 = 16.37/20 = 0.8184s
- Use the equation to find the value of P 1 . (2mks)
- P = 0.148/0.01616 = 9.158 m/s2
(Correct substitution = 1mk)
(Correct evaluation to 4sf = 1mk)
- P = 0.148/0.01616 = 9.158 m/s2
- Load a mass of 150 g and determine the extension of the spring, e 1 .
-
- Load a mass of 200 g and determine the extension of the spring, e 2 .
- e2 = x2 - x0 = 0.196 ± 0.01 m. (Correct subtraction =
mk, correct evaluation=mk). (1mk)
- e2 = x2 - x0 = 0.196 ± 0.01 m. (Correct subtraction =
- Displace the 200 g mass slightly downwards and release it to oscillate vertically. Time 20 oscillations and obtain time t 2 .
- t 2 = 18.62 ± 0.5s (1mk)
(Value within the range and 2dp a must = 1mk, no unit deny a half mark)
- t 2 = 18.62 ± 0.5s (1mk)
- Find periodic time T 1
- T2 = 18.62/20 = 0.9310s
(1mk) (Value within the range and
2dp a must = 1mk, no unit deny a half mark)
- T2 = 18.62/20 = 0.9310s
- Use the equation to find the value of P2 . (2mks)
- (Correct substitution = 1mk)
(Correct evaluation to 4sf = 1mk)
- (Correct substitution = 1mk)
- Load a mass of 200 g and determine the extension of the spring, e 2 .
- Find the average of P
- (Averaging principle = 1mk). (2mks)
(Correct evaluation to 4sf = 1mk)
PART B
Apparatus - Lens and a lens holder.
- A candle
- Screen
- A metre rule.
Procedure
- (Averaging principle = 1mk). (2mks)
- Focus a distant object and estimate the focal length, f of the lens
- f mm ± 10 mm (1mk)
- f mm ± 10 mm (1mk)
- Set up the apparatus as shown below.
- Set the distance s= 60 cm.
- Adjust the position of the lens to position p where a magnified sharp image is formed on the screen. Record position P.
- P = Student’s value (1d.p a must) cm. (1mk)
- P = Student’s value (1d.p a must) cm. (1mk)
- Maintaining distance s, adjust the lens to position P’ where a diminished sharp image is formed on the screen. Record position, P’.
- P’ = Student’s value (1d.p a must) cm. (1mk)
- P’ = Student’s value (1d.p a must) cm. (1mk)
- Find distance d, between the original position and final position of lens
- d = cm (1mk)
(Correct subtraction = mk, correct evaluation =mk)
- d = cm (1mk)
- Adjust the position of the lens to position p where a magnified sharp image is formed on the screen. Record position P.
- Using the formula . Find the value of q. (2mks)
- (Correct substitution = 1mk)
- (Correct evaluation to 4sf = 1mk)
- What physical quantity do q represent (1mk)
- Focal length of the lens used.
Download Physics Paper 3 Questions and Answers with Confidentials - MECS Cluster Joint Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students