Instructions to candidate
- Answer all questions.
-
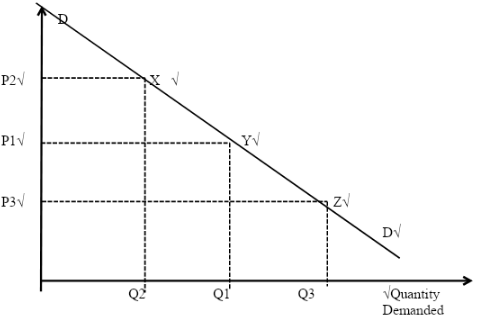
- Using a well labeled diagram, explain movement along a demand curve. (10 Marks)
- Discuss five functions of money. (10 Marks).
-
- Give four differences between a whole life policy and endowment policy. (8 Marks)
- Discuss five limitations of a trial balance. (10 Marks).
- Chemutai started business on 1st January 2005 with capital of sh 100,000 in cash. The following transactions took place during January 2005.
- Bought land for sh 50,000 cash.
- Bought building for sh 20,000, Paid 3,000 cash and the balance to be paid after two months
- Opened a bank account by depositing sh 10,000 from cash.
- Bought stock of goods worth sh 5,000 on credit from Mwenge Traders.
Required:- Prepare a balance sheet as at 31st January 2005 after all the transactions took place (10 Marks)
- Explain five functions of insurance companies (10 Marks)
-
- Discuss any five sources of public finance (10 Marks)
- Explain five mailing services that facilitate communication (10 Marks)
-
- Discuss five disadvantages of trade restrictions (10 Marks)
- Explain five features of successful entrepreneur (10 Marks)
-
- Explain four benefits of direct production (8 Marks)
- Rono started a hardware business on 1st January 2002. The following is a summary of his transactions during the month.
Invoices received
2002
January 2. Jirani Ltd shs 80,000
18. Chuma Ltd shs 140,000
26. Mwanaisha traders sh 160, 000
Invoices Issued
2002
January 10 Mungi traders shs 60,000
28 Jua Kali traders shs 4,000
Credit notes received
2002
January 12. Jirani ltd shs 3,000
24. Chuma ltd shs 8,000
30. Mwanaisha traders shs 12,000
Required
Prepare appropriate subsidiary books (12 Marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Movement along a demand curve
A normal demand curve slopes downwards from left to right from the above diagram i.e.- The initial price was P1 and the quality demanded was Q1. The price/quantity combination is at point Y.
- When price increased to P2, the quantity demanded reduced to Q2 leading to a movement along the demand curve from point Y to point X.
- When the price reduced to P3 the quantity demanded increased to Q3 resulting to a movement along the demand curve from point Y to point Z. 10x1= 10 marks
- Functions of money
- Medium of exchange
Money is generally acceptable by everybody in exchange for goods and services. It therefore enables trade to be carried out conveniently hence reducing the drawbacks of barter trade. - Measure of value
When commodities that are goods and services are valued in terms of money, the problem of fixing exchange rates is solved. - Unit of account
The value of different commodities is hence calculated and records kept in terms of money. - Store of value
Money is the most convenient means of storing wealth. This is because money is easily convertible into other forms of assets. Money can also be kept as savings for future transactions since it is durable and relatively stable in value. - Standard of deferred payment
A debt incurred today can be paid later using money. - Transfer of immovable assets
Money acts as a means of transferring immovable property such as land and buildings. E.g. one can sell a building in the rural area to buy a similar one in the urban area. 2x5= 10 marks
- Medium of exchange
- Movement along a demand curve
-
- Difference between a whole life policy and endowment policy.
Any 4x2= 8 marks (Don’t break the marks)Whole life Endowment (i) Compensation is paid after the death of the assured (i) Compensation is paid after the agreed period (ii) Premiums are paid throughout the life of the assured (ii)Premiums are paid only during an agreed period (ii)Benefits go to the dependants rather than the assured (ii)The assured benefits unless death precedes the expiry of the agreed period (iv) Aims at financial security of dependents (iv) Aims on financial security of the assured and dependents - Limitations of the trial balance. (10marks)
- Error of total omission.
This occurs when a transaction takes place and nothing about it is recorded in the books of accounts. - Error of original entry.
This error occurs when a transaction takes place and an amount other than the correct one is recorded in the affected accounts. - Error of commission
This error is said to occur when an entry is made in the wrong account of the same class with the correct amount. - Compensating errors
These are errors whose effects cancels out. - Complete reversal of entries
This error occurs when a transaction takes place and entries are made on the opposite sides of the accounts affected. - Error of principle
This is where a transaction is recorded in the wrong account of a different class from the correct one.
5x2= 10 marks
- Error of total omission.
- Difference between a whole life policy and endowment policy.
-
- Capital 100,000√
Cash 100,000 – 50,000√ -3,000√-1,000√ = 37,000√
Land 50,000 √
Buildings 20,000√
Creditors 17,000√
Bank 10,000√
CHEMUTAI
BALANCE SHEET√
AS AT 31ST JANUARY 2005
20x½ =10 marksASSETS
Land 50,000✓
Buildings 20,000✓
Current Assets
Bank 10,000 ✓
Cash 37,000✓ 47,000✓CAPITAL ✓✓100,000
Liabilities
Creditors ✓17,000117,000✓ 117,000✓ - Functions of insurance companies (10 marks)
- Enables policy holders to save through such schemes as endowment policies and education policies.
- Provide finance in form of loans to policy holders at law interest rates.
- Provide guarantee to policy holders wishing to obtain loans from other money lending institutions.
- Provide advisory services to policy holders on, for example, security measures to undertake to safeguard property.
- Provide finances to meet expenses and losses arising from the occurrence of the insured risks.
- Assume the role of underwriters to companies wanting to issue new shares to the public.
5x2= 10 marks
- Capital 100,000√
-
- Sources of public (10marks)
- Fines imposed by courts on offenders.
- Rent and rates paid for the use of government property.
- License fee paid by those who wants to operate business
- Dividends and profits earned from government direct investments.
- Interest earned on loans advanced by the government to firms.
- Proceeds from sale of government property.
- Taxes
- Government borrowing.
5x2= 10 marks
- Mailing services that facilitate communication (10marks)
- Speed post
This is a service offered by the post office to travellers who may wish to receive correspondence while away from their post office box. This address has to inform those who may wish to correspond with him/her of the nearest post office he/she is likely to use at a particular time. - Poste restante
This is a service offered by the post office to travellers who may wish to receive correspondence while away from their post office box. This address has to inform that post office he/she is likely to use at a particular time. - Express
The mail is delivered to the receiver’s nearest post office from where the post office will make arrangements to deliver to mail to the receiver within the shortest time possible. - Registered mail
This is a service offered by the offered by the post office and other service providers for sending articles of value for which security handling is required. - Business reply service
This is a service used by firms that intend to encourage their customers to reply to their letters promptly. 5x2= 10 marks
- Speed post
- Sources of public (10marks)
-
- Disadvantages of trade restrictions. (10 marks)
- Possible retaliation by other countries
When a country imposes restrictions on imports from another country, the other country can react by similarly imposing restriction on imports from the former country this would be detrimental to both countries. - Production of low quality commodities.
The protected local industries may end up producing low quality commodities due to lack of competition. The local consumer is therefore denied the chance of enjoying high quality goods which may have otherwise come from the other country. - High prices for locally produced commodities
The protected in fact local industries may not enjoy economies of large scale due to their small sizes. They therefore incur high production costs for their products the high production costs lead to high prices for the commodities. - Trade restrictions implies that there would be fewer goods and services that consumers can choose from this in turn leads to low standards of living for such consumers.
- Danger of the need for perpetual protection
- The protected infant industries have a tendency of remaining young. This means that these industries remain calling for continued protection with its inherent problems.
- Possible emergence of monopolies
- Protectionism may lead to emergence of monopolies. This may give rise to problems associated with monopolies.
Any 5x2= 10 marks
- Possible retaliation by other countries
- Features of a successful entrepreneur (10marks)
- Risk taker- he/she is not afraid of putting money into a new business whose profits are not assured.
- High level of tolerance – he/she is able to accommodate business unpredictable out comes without getting discouraged.
- Decision maker – take and implement decisions quickly or take right decisions at the right time/weighs different options to pick the success.
- Desire to achieve- has a strong urge to pursue his/her dream for success.
- Goal oriented – makes smart and monitor to see whether set goals are being achieved.
- Perseverance in the performance of a tast or does not give up easily.
- Open minded- he/she does not prejudge situations or respect other peoples’ opinions.
- Opportunity seekers – he/she keenly observes the surroundings to spot new opportunities.
- Self- confidence- he/she believes in his/her own abilities.
- Time conscious – every minute is well spent or waste no time in conduct of business. 5x2=10 marks
- Disadvantages of trade restrictions. (10 marks)
-
- Benefits of direct production (10marks)
- Cost is affordable as the capital required for one to produce goods for one’s own consumption is less compared to indirect production.
- No wastage as one produces what he/she can produce what he or she can consume alone hence no extras which can get spoilt.
- Variety of goods and services as one can produce different types of goods at the same times.
- Involves use of locally available simple tools hence one may not necessarily need advanced technology which could be expensive to acquire.
- Independence as production is self-sufficient and producers and produce enough for their own use.
- PURCHASES JOURNAL √
Date Particulars Invoices no. Ledger folio Amount 2002 Jan 2. Jirani ltd✓ 80,000 18. Chuma ltd✓ 140,000 26 Mwanaisha traders✓ 160,000 ✓380,000
SALES JOURNAL√Date Particulars Invoices no. Ledger folio Amount 2002 January 5 Mungi traders✓ 50,000 20 Moto traders✓ 150,000 25 Jua kali traders✓ 70,000 ✓270,000
SALES RETURNS JOURNAL√Date Particulars Invoices no. Ledger folio Amount 2002 January 10 Mutungi traders✓ 60,000 28 Jua kali traders✓ 4,000 ✓✓ 64,000
PURCHASES RETURNS JOURNAL√Date Particulars Invoices no. Ledger folio Amount 2002 January 12 Jirani ltd✓ 3,000 24 Chuma ltd✓ 8,000 30 Mwanaisha traders✓ 12,000 ✓✓ 23,000
- Benefits of direct production (10marks)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Business Studies Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Pavement Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students