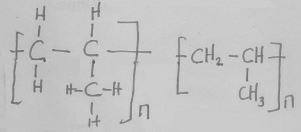CHEMISTRY
Paper 2
Instructions to candidates
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Scientific calculators may be used.

Questions
-
-
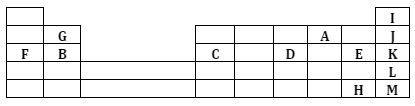
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study the information in it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
- Select an element that can form an ion with a charge of -2. Given a reason for your answer. (1 mark)
- What type of structure would the oxide of G have? (1 mark)
- How does the reactivity of H and E compare? Give a reason for your answer. (1 mark)
- 1.3g of B reacts completely when heated. 1.2 litres of chlorine gas at s.t.p (1 mole of any gas at s.t.p occupies 22.4 litres at s.t.p)
- Write an equation for the reaction between B and chlorine. (1 mark)
- Determine the relative atomic mass of B. (2 marks)
- Explain how you would expect the following to compare.
- Atomic radius of F and B (1 mark)
- The pH value of the aqueous solution of the oxide of B and D. (2 marks)
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study the information in it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
- Study the information below and answer the questions (the letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements).
Elements Electronic
ConfigurationLE(kj/mol) J 2.1 519 K 2.8.1 494 L 2.8.8.1 418 - What is ionization energy? (1 mark)
- Explain why element L has the lowest ionization energy. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction between K and water. (1 mark)
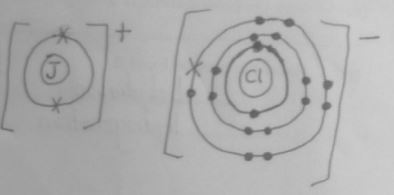
- Using dots (⚫) and crosses (×) show bonding in the compound between J and chlorine. (1 mark)
-
-
- Explain how one could distinguish between ethane and ethene gases using bromine water. (2 marks)
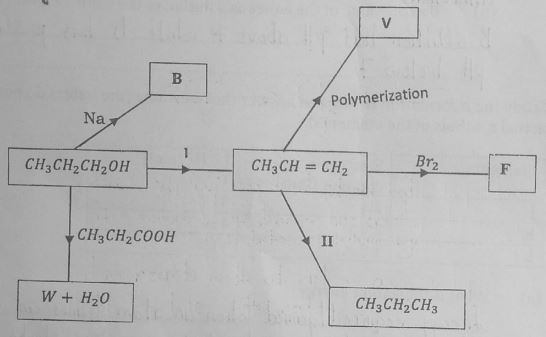
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify substances B and F by giving their names. (2 marks)
- Write an equation to show how substance W and water are formed. (1 mark)
- Give the general formula of the polymer V. (1 mark)
- Name the process I and II.(2 marks)
- Give the conditions required for the process named above to occur.(2 marks)
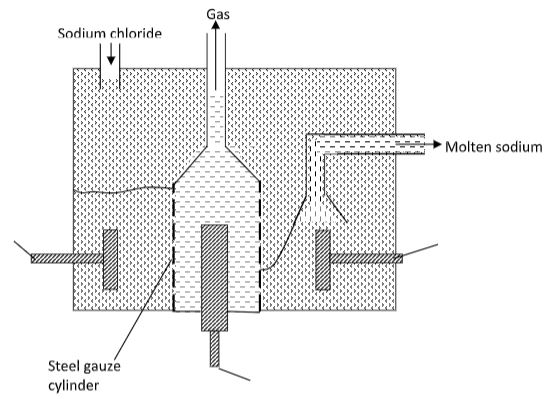
- The diagram below shows the extraction of sodium metal using the Down’s cell. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Explain why in this process sodium chloride is mixed with calcium chloride. (2 marks)
- Why is the anode made of graphite and not iron? (1 mark)
- State two properties of sodium metal that make it possible for it to be collected as shown in the diagram. (2 marks)
- What is the function of the steel gauze cylinder? (1 mark)
- Write ionic equations for the reactions which take place at;
- Cathode (1 mark)
- Anode (1 mark)
- Give one industrial use of sodium metal. (1 mark)
- Why is sodium metal stored under kerosene? (1 mark)
-
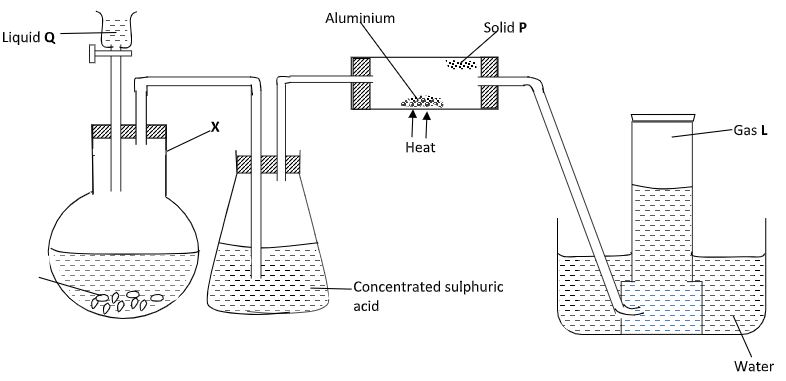
- In an experiment, hydrogen chloride gas was prepared and reacted with aluminium turnings to form a solid P and gas L as shown in the diagram.
- Name:
Solid P - (1 mark)
Gas L - (1 mark)
Liquid Q - (1 mark) - Give the name of another substance that could serve the same purpose as the concentrated sulphuric acid. (1 mark)
- Write a chemical equation that will occur in the reaction flask X.(1 mark)
- Name:
- Explain the following observations:-
- When blue litmus paper was dipped into the water in the beaker at the end of the experiment it turned red. (1 mark)
- Solid P collects away from the heated aluminium. (1 mark)
-
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place between ammonia gas and hydrogen chloride gas. (1 mark)
- Calculate the mass of the product that would be formed when 4000 cm3 of hydrogen chloride gas reacts completely with excess ammonia gas.
(H = 1, N = 14, Cl = 35.5, Molar gas volume at r.t.p = 24 litres) (3 marks)
- In an experiment, hydrogen chloride gas was prepared and reacted with aluminium turnings to form a solid P and gas L as shown in the diagram.
-
- Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic reaction.
Exothermic (1 mark)
Endothermic (1 mark) - Changes of state are either exothermic or endothermic. Name a change of state that is;
- exothermic (1 mark)
- endothermic (1 mark)
- When pure water is heated at 1 atmospheric pressure at sea level, the temperature of the water does not rise beyond 1000C even with continued heating. Explain this observation. (2 marks)
- Study the energy level diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- Give the names of the energy changes represented by ∆H1 ∆H4 ∆H5 ∆H6
∆H1 (1 mark)
∆H4 (1 mark)
∆H5 (1 mark)
∆H6 (1 mark) - When is ∆H5 endothermic? (1 mark)
- Show the relationship between ∆H1 ∆H2 ∆H3 ∆H4 ∆H5 and ∆H6. (1 mark)
- Give the names of the energy changes represented by ∆H1 ∆H4 ∆H5 ∆H6
- Distinguish between exothermic and endothermic reaction.
-
- What is the electronic arrangement of nitrogen in NO3- ? (1 mark)
- Study the standard electrode potentials below and answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
A+(aq) + e- → A(s) Eθ=-2.92V
B+(aq) + e- → B(s) Eθ+0.52V
C+(aq) + e- → ½C2(g) Eθ=0.00V
½D2(g) + e- → D-(aq) Eθ=+1.36V
E2+(aq) + 2e- → E(s) Eθ=-0.44V- With reasons, identify the;
- Strongest reducing agent. (1 mark)
- the reference electrode. (1 mark)
- Write the overall equation for the reaction that will be obtained when half cells of B and E are connected. (1 mark)
- Explain whether the reaction represented below can take place. (2 marks)
2A+(aq) + E(s) → 2A(s) + E2+(aq) - Draw the cell diagram obtained when the half cells in (ii) are combined. (2 marks)
- With reasons, identify the;
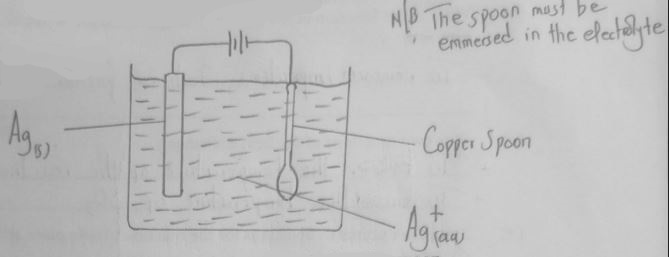
- In an experiment to electroplate a copper spoon with silver, a current of 0.5A was passed for 18 minutes.
- Sketch a diagram to show how the experiment was carried out. (2 marks)
- Calculate the amount of silver deposited on the spoon.
(IF = 96500C, Ag = 108) (2 marks)
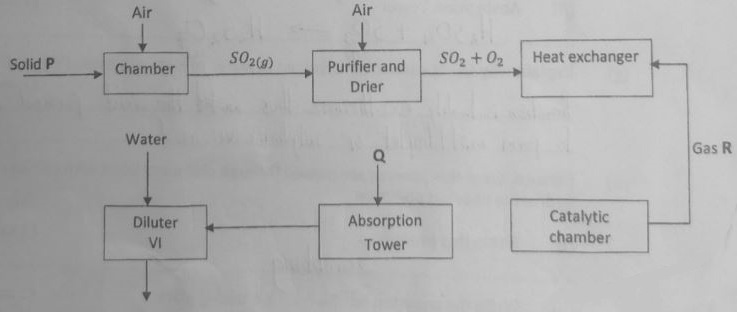
- The flow chart below shows the stages involved in manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid by the contact process. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Apart from Sulphur, identify other substance that can be used as solid P. (1 mark)
- What is the function of the purifier? (1 mark)
- Give two functions of the heat exchanger. (1 mark)
- State the optimum conditions for the reaction to take place at the catalytic chamber. (1 mark)
- Name;
- gas R. ……………………………………………………………………………… (1 mark)
- substance Q ………………………………………………………………………. (1 mark)
- Write equations for reactions taking place at the:-
- Catalytic chamber (1 mark)
- Absorption Tower (1 mark)
- Explain why Gas R cannot be dissolved in water to form sulphuric (VI) acid. (1 mark)
- Exhaust gases this process are passed through chimneys lined with calcium hydroxide to avoid pollution.
- Name this process (1 mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction taking place. (1 mark)
- State the observation made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is poured into a beaker containing sugar crystals. Name the property of conc. sulphuric acid. (1 mark)
Marking Scheme
-
-
-
- A- Reactsby gaining 2 electrons
- Giant ionic structure
- E is more reactive than H/H is less reactive than E. E can easily gain electron/ E has higher electron affinity than H/ E is more electronegative than H
- A- Reactsby gaining 2 electrons
-
- B(s) + Cl2(g) → BCl2(s) || Mg(s) + Cl2(g) → MgCl2(s)
- 22.4l → 1 mole
1.2L →
1.2 x 1 = 0.05357 moles
22.4
mole ratio 1:1
moles of B → 0.05357
1.3g → 0.05357
? → 1 mol
1.3 x 1 = 24.267
0.05357
ans → 24.2673
- B(s) + Cl2(g) → BCl2(s) || Mg(s) + Cl2(g) → MgCl2(s)
-
- E has larger atomic than B | B has a smaller atomic radius than F. B has more protons than F thus higher nuclear force of attractions.
- B solution has pH above 7 while D solution has pH below 7
-
-
- Energy required/ gained when an atom gains an election in the outermost energy level in gaseous state.
- Has the largest atomic radius
- 2K(g) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g) | 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
-
- Energy required/ gained when an atom gains an election in the outermost energy level in gaseous state.
-
-
- Bubble the two gases in two different test-tube containing bromine water. With ethene bromine water changes from yellow to colourless while ethane has no effect on bromine water.
-
- B Sodium propoxide | CH3CH2CH2ONa
F 1, 2-dibromopropane | CH3CHBrCH2Br - CH3CH2CH2OH + CH3CH2COOH → CH3CH2COOCH2CH2CH3 + H2O
-
-
- Dehydration
- Hydrogenation
-
- Conc. Sulphuric(VI) acid
- Nickel catalyst, temp 150 - 250º C
- B Sodium propoxide | CH3CH2CH2ONa
-
- To lower the m.p of NaCl from 800º C to 600º C in order to save on cost of production
- Graphite is inert this does not react with chlorine while iron is reactive and would react with chlorine.
- Has lower density than the electrolyte
Has m.p below 600º C - Prevent sodium and chlorine from recombining/ reacting
-
- Na+ + e- → Na(l)
- 2Cl-(l) → Cl2(g) + 2e-
-
- Sodium vapour used in street light to produce yellow glow
- Molten sodium is used in extraction of titanium
- Sodium is used in production of sodium cyanide usedd in extraction of gold
-
- Sodium reacts with atmospheric oxygen to farm oxides
- Highly reactive with water
- To lower the m.p of NaCl from 800º C to 600º C in order to save on cost of production
-
-
- Solid P - Aluminium chloride
Gas L - Hydrogen
Liquid Q - Conc. Sulphuric (VI) acid - Anhydrous Calcium Chloride
- NaCl(s) + H2SO4(l) → NaHSO4(aq) + HCl(g)
- Solid P - Aluminium chloride
-
- Unreacted HCl gas dissolves in the water to form HCl(aq) acid
- Aluminium Chloride sublimes on heating
- Unreacted HCl gas dissolves in the water to form HCl(aq) acid
-
- NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(g)
- 1 mole → 24,000cm3
? → 4,000cm3
4000 x 1 = 0.16667 moles
24,000
mole ratio
HCl: NH4Cl
1: 1
moles of NH4Cl → 0.16667
1 mole → 53.5 g
0.16667 moles → ?
53.5 x 0.16667
1
8.9168g
-
-
- Exothermic - a reaction that releases/ produces heat to surrounding/ environment
Endothermic - A treaction that absorbs heat from the environment - exothermic - freezing and condensation
endothermic - melting and boiling - The b.p of pure water at 1atm at sea level is 100ºC
-
- ∆H1 - Atomization of sodium
∆H4 - Electron affinity of chlorine
∆H5 - Lattice formation
∆H6 - Formation of NaCl - During dissociation of ionic compounds to gaseous ions
- ∆H6 = ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3 + ∆H4 + ∆H5
- ∆H1 - Atomization of sodium
- Exothermic - a reaction that releases/ produces heat to surrounding/ environment
-
- x + -2 x 3 = -1
x= +6-1
x=+5
Ans= 2 -
-
- Strongest reducing agent
A(s) can easily loose electrons/ most electropositive/ most negative - The reference electrode
C2. Has Eθ of 0.00V
- Strongest reducing agent
- E(s) + 2B+(aq) → 2B(s) + E2+(aq), Eθ = +0.96V
(must be balanced) - Reaction cannot take place. A is more reactive than E thus E cannot displace A from its solution
or
-2.96 + 0.44 = -2.52
Cannot take place. Has negative Eθ value - E(s)/ E2+(aq) // 2B+(aq)/2B(s) , Eθ = +0.96V
-
-
-
- Q= 0.5 x 18 x 60
540C
96500C → 100g
540C → ?
100 x 540
96500
=0.6044g
-
- x + -2 x 3 = -1
-
- Zinc blende/ZnS, Galena/PbS, Copper pyrite/CuFeS2
- To remove impurities which may poison the catalyst
- To raise the temperature of the reacting gases(SO2 + O2)
To lower the temperature of SO3 - Catalyst vanadium(v) oxide, pressure 2-3 atm temperature 450ºC
-
- Gas R- Sulphuric (VI) oxide
Substance Q - Conc Sulphuric(VI) acid
- Gas R- Sulphuric (VI) oxide
-
- 2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g)
- H2SO4(l) + SO3(g) → H2S2O7(l)
- Reaction is highly exothermic thus the acid formed boils to form multidroplet of Sulphuric (VI) acid
-
- Scrubbing
- Ca(OH)2(s) + SO2(g) → CaSO3(s) + H2O(l)
- Scrubbing
- Black solid is formed/ Sugar turns from brown to black
Dehydrating
- Zinc blende/ZnS, Galena/PbS, Copper pyrite/CuFeS2
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mokasa II Mock Examination 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students