AGRICULTURE
Paper 1
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions in section A and B.
- Answer any two questions in section C.
Questions
SECTION A: (30 marks)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- State four disciplines that confirm agriculture to be a science. (2 mks)
- Give four aspects of rainfall that determine the type of crop grown by the farmer. (2 mks)
- State two physical properties of soil that enable it to support plant life. (2 mks)
- Highlight four precautions one must take into account when using herbicides to prevent environmental pollution. (2 mks)
- Outline four factors that contribute to the competitive ability of weeds. (2 mks)
- Outline four characteristics of plants used as green manure. (2 mks)
- Name four types of pumps used to lift water from its source on the farm. (2 mks)
- Outline four information contained in an invoice. (2 mks)
- Outline two environmental factors that affect selectivity and effectiveness of herbicides. (1 mk)
- Highlight two deficiency symptoms of nitrogen in a maize crop. (1 mk)
- Name four methods of harvesting trees in agroforestry. (2 mks)
- State four factors considered when classifying crop pests. (2 mks)
- Agriculture promote the growth of industries in Kenya, give three reasons to qualify this statement. (1½ mk)
- Give three reasons why minimum tillage is practiced. (1½ mk)
- Distinguish economic injury level and integrated pest management as used in pest control (2 mks)
- State four methods of harvesting water on the farm. (2 mks)
- Outline two sites of agroforestry trees. (1 mk)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
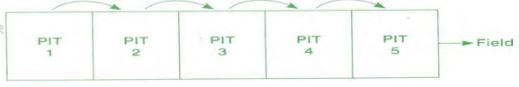
- The following diagram shows a certain method of preparing compost.
- Identify the method. (1 mk)
- Give two factors that, should be considered when siting a compost pit. (2 mks)
- State two factors that determine the time manure is ready for use on the field. (2 mks)
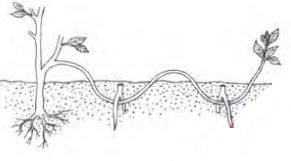
- The diagram below shows a method of crop propagation.
- Identify the method. (1 mk)
- State one advantage of the above method over the other methods of crop propagation. (1 mk)
- State three factors which influence the rooting of hardwood cutting of vegetation propagation. (3mks) ... .
- The figure below shows a disease affecting field crop.
- Name the disease. (1 mk)
- State two conditions that predispose tomato plant to the above disease. (2 mks) ..
- Suggest two possible ways of controlling the above disease. (2 mks)
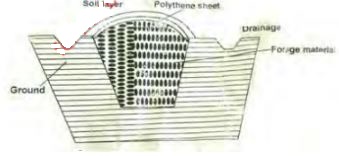
- The diagram below shows a method of forage preservation
- Identify the structure above (1 mk)
- State the form in which forage is preserved as illustrated above. (1 mk)
- Give the role played by each of the following in the structure above.
- Polythene sheet (1 mk)
- Drainage (1 mk)
- Name another method of forage conservation other than the one shown above. (1 mk) ..
SECTION C: (40 marks)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided after question 26.
-
- Explain four factors considered in designing a crop rotation programme (8 marks)
- Describe five benefits of intercropping food crops. (5marks)
- Outline seven post- harvest practices carried out in the production of maize (7marks)
-
-
- What is a partial budget (1 marks)
- Mr, Owino has 4 hectares of arable land, 1.5 hectare of which is under wheat, 0.5 hectare under maize, 0.3 hectare under fodder crops and the rest is under either improved grass ley or natural grass. He wishes to know whether replacing 0.3 ha of maize with potatoes the following season would be worthwhile. The fertilizer rate would have increased from 2 bags per hectare for maize to 2.5 bags per hectare for potatoes, an extra 40 days of casual labour per hectare would be necessary as a result of the change. Average yields of maize and potatoes are 56 and 90 bags per hectare respectively. The prices are Kshs 1200 per bag of maize and Kshs 300 per bag of potatoes, seed costs are Kshs 1350 per 10 kg of maize and Kshs 200 per 50 kg of potatoes. DAP fertilizer costs Kshs. 1400 per 50 kg bag. Labour is paid at Kshs 150 per man day. He would require 10 bags of potatoes seed and 1 bag of maize seed to cover 0 3 of a hectare. Draw up a partial budget and indicate the effect of the change (7 marks)
- What advice would you give this farmer (1 mark)
- State different ways through which farmers may adjust to risks and uncertainties (5 marks)
- Explain seven cultural measures used in control of soil erosion (7 marks)
-
-
- Describe under-sowing as a method of establishing grass pasture in maize plantation. (5 marks)
- Discuss five negative effects of wind to crops (5 marks)
- Describe the production of Dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) under the following sub headings
- Varieties (3 marks)
- Land preparation (3 marks)
- Harvesting (4 marks)
Marking Scheme
-
- Crop pathology
- Entomology
- Soil science
- Agricultural engineering
(½ x 4 = 2 marks)
-
- Rainfall intensify
- Rainfall Reliability
- Rainfall amount
(½ x 4 = 2 marks)
-
- Soil structure
- Soil texture
(1 x 2 = 2 marks)
-
- Do not wash the spraying equipment in water sources which are used by animals and human.
- The remaining chemical should be disposed off properly.
- Avoiding spilling during windy day.
(½ x 4 = 2 marks)
-
- Weeds are prolific seed products.
Weeds seeds have long dormancy periods. - Weeds are able to survive even when the nutrient supply in soil is limited.
- Most weeds have effective means of vegetative propagation.
- Their seeds are easily dispersed.
- Weeds grow very fast.
(½ x 4 = 2 marks)
- Weeds are prolific seed products.
-
- Invoice – A document issued to the buyer by the seller to show the goods taken on credit. (1 mark)
- Local purchase order – is a document issued to the seller by the buyer to request for the supply of goods on credits. (1 mark)
-
- (Centrifugal/rotardynamic pump
- Reciprocating/Piston/Displacement Pump.
- Rotary or semi-rotary pump.
- Hydroulic ram/hydram pump.
(½ x 4 = 2 marks)
-
- date of transaction
- people involved in the transaction
- type and quantity of goods delivered
- price per unit of goods
- total amount of money involved
- invoice serial number
- terms of payment (½ x 4 = 2 marks)
-
- Wind blow away spray
- Rain dilute/wash away chemicals
- Soil absorb /retain herbicides
- Light intensity increase absorption and translocation of herbicides
- Temperature increases translocation of herbicides
-
- Chlorosis yellowish.
- Stunted growth
- Stems turns brown sometime.
- Premature leaf fall
(½ x 2 = 1 mark)
-
- Pollarding
- Lopping
- Coppicing
- Thinning
- Prunning
(½ x 4 = 2 marks)
-
- The crop part attacked
- The mode of feeding of the pest.
- Scientific classification
- Where the pest attack crop field or store
(½ x 4 = 2 marks)
-
- Provide raw materials to the industries.
- Provide market for industrial goods.
- Provide capital used to establish industries.
(½ x 3 = 1½ marks)
-
- Reduce operational cost.
- Minimizes soil erosion
- Maintain soil structure due to minimal disturbance of soil.
- Minimizes damages to crop roots.
- Minimize volatilization.
(½ x 3 = 1½ marks)
- Economic injury level is a situation where pest population cause damage beyond tolerance while integrated pest control is a combination of both chemical and cultural pest control methods used.
-
- Use of ponds.
- Use of rock catchment.
- Use of rivers and dams
- Use of root catchment
(2 marks)
(½ x 4 = 2 marks)
-
- boundaries
- river abnks
- Terraces
- Slopes
- Homestead
Any first 2 (½ x 2 = 1 mark)
-
- Indore/Pit method. (1 mark)
-
- It should be sited in a well drained place.
- It should be sited on the leeward side in relation to homestead.
- The site should be accessible.
- Site should be well sheltered place.
- Site should be located near farm.
- The age of material used.
- The type of material used.
- The level management practices during preparation.
- Indore/Pit method. (1 mark)
-
- serpentive layering/compound layering. (1 mark)
- In can be used to produce many shouts from the branch while still attached to the mother plant. (1 mark)
-
- Optimum temperatures.
- High relative humidity which lowers transpiration rate.
- Optimum oxygen concentration.
- Growth hormones/Auxins.
- Adequate moisture supply.
- Low light intensify
- Absence of leaves.
(½ x 4 = 2 marks)
- serpentive layering/compound layering. (1 mark)
-
- Blossom and rot. (1 mark)
-
- Irregular, watering
- Excess application of nitrogen in the early stages.
- Deficiency of calcium in young fruits. Reject if identification is wrong
(½ x 3 = 3 marks)
-
- Regular watering
- Liming the soil/addition of calcium
- Mulching to avoid moisture stress
- Top dressing with enough nitrogen
- Blossom and rot. (1 mark)
-
- trench silo
- silage
-
- Make it airtight and protect water from getting into it.
- prevent runoff from getting into the silo
-
- hay
- standing forage
- trench silo
-
-
- Crop root depth. Deep-rooted crops should be alternated with shallow rooted crops.
- Soil structure. A grass ley should be included in the rotation programme because the soil becomes loose after continued use.
- Pests and disease control. Crops from the same family should not follow each other as the same pests and diseases attack them.
- Weed control. Crops that are associated with certain weeds should be alternated with those that are not. Crops that are not easily weeded should be alternated with those that are easy to weed.
- Crop nutrient requirement. Heavy or gross feeders (crops requiring high amounts of nutrients) should come first in a newly opened land, which is relatively fertile. Soil fertility. Leguminous crops should be included to improve soil fertility.
-
- Control of weeds
- Improve soil structure
- Control soil erosion
- Improve soil fertility
- Maximum utilization of soil nutrients
- High yield per unit area
- Economical in fertilizer use
-
- Threshing/shelling. This is the act of removing maize grains from the cobs, beans from the pods or sorghum from the heads. This is done to facilitate subsequent cleaning and storage. It is normally the first operation done after harvesting.
- Drying. Grains are dried up to a moisture content of 12-13%. This prevents rotting and fungal attack of the grains while in store.
- Cleaning. This is done by winnowing in cereals to remove the chaff from the grains. Sorting and grading. The produce is sorted and graded according to quality. In coffee the berries are sorted into grade I and II. Grade I has big and well ripened berries. Grade II berries are under-ripe, overripe, diseased or small. The first grade fetches the highest price.
- Dusting. This is application of chemical powders on seeds to prevent storage pest attack. Processing. It is the transformation of the raw material into a final product. Packaging. It is the placement of produce into containers for storage, sale or transportation. This reduces damage to the produce and also makes it possible for the farmer to quantify the produce and set prices.
-
-
-
- a budget drawn when minor changes are to be made in an enterprise or in a farm organization (14 mrk)
PARTIAL BUDGET FOR MR OWINO
Debit (-) ✓Vi Shs Cts Credit (-) ✓1/2 Shs cts Extra cost
i. fertilizer 2.5 x0.3xl400
i. Labour40x0.3x150
i. Seeds 200x10
Subtotal
1050
1800
2000
4850
0
0
0
0Extra revenue
potatoes 90x0.3x300
Subtotal
cost saved
maize
8100
8100
0
0Revenue forgone
Maize yield
50x0.3x120
Total13,440
18,2900
0i)seeds 1 xl350
Fertilizers
2x1400 x 0.3 Total1350
840
102900
0
0 - Extra Revenue + Cost saved ~ extra cost + revenue forgone 10,290 - 18,290 = - sh,8000
- Not to replace maize with potatoes because of a loss of - sh.8000loss of - sh.8000
Allocation of marks
Title ½ mk
Debit ½ mk mark
Credit ½ mk
Entries ½ mk each x 7 = 3 ½ mk
Totals ½ x 2 =1 mk
Calculation =1 mk
Total 7 mks
- a budget drawn when minor changes are to be made in an enterprise or in a farm organization (14 mrk)
- Ways of adjusting to risks and uncertainties
- Input rationing
- Flexibility in production
- Diversification
- Taking Insurance
- Contracting / contract farming
- Adopting modem farming methods
- Selection of more certain enterprises (1x5 mks)
- Cultural measures of controlling erosion
- Use of grass strips/filter strips
- Minimise speed of run-off water
- Trap soil contained in run off hence reducing erosive power.
- Cover crops-reduce impact of rain drops/ splash erosion reduce velocity of runoff
- Contour farming
- creates ridges of earth which hold water thus reducing run off and prevent rill erosion
- Grassed waterways
- Reduces speed of running water
- trap eroded soil
- Mulching - Reduces speed of run off
- Reduces impact of raindrops
- Afforestation or reafforestation
- Trees act as wind breakers
- Controls wind erosion
- Reduce impact of raindrops
- Strip cropping
- Reduces speed of run off
- Traps soil particles from run off( 7 x 1 = 7 mrks)
- Use of grass strips/filter strips
-
-
-
- land is ploughed and maize planted normally/
- weed the maize farm 2-3 weeks after the onset of rains
- bradcast the pasture seeds
- apply 100-200kg/hacter of SSP
- harvest maize early to expose pasture to sunlight.
- No father weeding is done
- Negative effects of wind to crops
- Increase rate of disease spread
- Contributes to lodging of crops/cereals
- can cause damage to farm structures
- Carries away rain bearing clouds
- Acts as an agent of soil erosion
- Production of dry beans
- Varieties
- Canadian wonder/GLP 24
- Mwitemania Wairimu/Red Haricot
- Rosecoco/GLP 2 Mexican 142
- Mwezi Moja/GLP 1004
- Land preparation
- Clear land
- Plough the land deeply to control perennial weeds / carry primary cultivation
- Harrow the land to a moderate/medium tilth
- Harvesting
- Uproot dry plants
- Uprooting the plants should be done in the
- Morning when the weather is cool to
- prevent shattering of pods
- Spread on mat/polythene to dry
- Thresh by beating with sticks
- Remove chaff through winnowing
- Dress the beans before packing in bags with suitable dust based pesticides
- Dry to the correct moisture content/12% MC
- Sort out to remove damaged bean seeds
(4 x 1 = 4 mrks)
- Varieties
-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Maranda Mocks 2021/2022 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students