QUESTIONS
You are provided with
- Magnesium powder
- 1M Hydrochloric acid solution R
- 0.2M sodium hydroxide solution S
You are required to determine the;
- Mass of Magnesium that reacted
- Molar enthalpy of reaction between magnesium and Hydrochloric acid
Procedure I
Using a measuring cylinder, transfer 100.0cm3 of the acid into a 200ml plastic beaker. Stir the acid with the thermometer. Take its initial temperature and record it in the table below at time =0 seconds. Add all the magnesium at once and start your stop watch immediately. Stir well and take the temperature after every thirty seconds up to the 5th minute.
Table 1
|
Time (seconds) |
0 |
30 |
60 |
90 |
120 |
150 |
180 |
210 |
240 |
270 |
300 |
|
temperature |
(4mk)
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of temperature (Y-axis) against time (3mk)
- On your graph show the highest temperature change ∆T (1mk)
- Calculate the heat change for the reaction (1mk)
Procedure 2
Transfer the content of the plastic beaker into a 250 ml volumetric flask. Rinse the beaker and place the rinsing water into the volumetric flask. Top up the solution to the 250ml mark using distilled water and label it solution D.
Fill the burette with sodium hydroxide solution S
Using a pipette, transfer 25.0cm3 of solution D into a conical flask. Add 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator and carry out titration .Record your results in the table 2 below. Repeat the procedure two more times and complete table 2 below.
Table 2
-
(4mks)titration
1
2
3
Final burette reading (cm3)
Initial burette reading (cm3)
Volume of solution S used (cm3)
- Determine
- average titre volume of sodium hydroxide solution S used (1mk)
- moles of NaOH in the average titre volume (1mk)
- moles of hydrochloric acid in solution D that reacted with NaOH (1mk)
- moles of HCl in 250cm3 of solution D (1mk)
- moles of HCl in 100cm3 of solution R (1mk)
- moles of HCl that reacted with Mg (1mk)
- moles of Mg that reacted (1mk)
- Molar enthalpy of reaction between Magnesium and HCl (2mk)
2. You are provided with solid Z. Carry out the tests below and record your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Place all solid Z in a boiling tube. Add 10cm3 of distilled water and shake. Filter the mixture. Divide the filtrate into two and preserve the residue.
observations
inferences
1mk
1mk
- To the first portion of filtrate add dilute sodium hydroxide and warm gently. Test the gas produced if any using moist blue and red litmus papers
observations
inferences
1mk
1mk
- To the second portion add 2 drops of lead (II) nitrate and warm
observations
inferences
1mk
1mk
- Place the residue in a test tube. Add dilute nitric (V) acid until reaction is complete and test the gas produced using a glass rod dipped in lime water. Divide the solution formed into two
- To the first portion add sodium hydroxide drop wise till in excess
observations
inferences
1mk
1mk
- To the second portion add ammonia solution drop wise till in excess
observations
inferences
1mk
1mk
3. You are provided with liquid L. Carry out the tests below and record your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Place 2 drops of liquid L on a watch glass and ignite using a wooden splint
observations
inferences
1mk
1mk
- To 2cm3 of liquid L in a test tube add 2 drops of acidified KMnO4
observations
inferences
1mk
1mk
- To 2cm3 of liquid L in a test tube add 2drops of acidified potassium dichromate (VI) and warm
observations
inferences
1mk
1mk
- Use the remaining liquid L to determine the pH of the liquid using universal indicator paper provided. Use the guide provided
procedure
observation
inferences
11/2mk
1/2mk
1mk
MARKING SCHEME
You are provided with
- Magnesium powder
- 2M Hydrochloric acid solution R
- 0.2M sodium hydroxide solution S
You are required to determine the
- Mass of Magnesium that reacted
- Molar enthalpy of reaction between magnesium and Hydrochloric acid
Procedure I
Using a measuring cylinder, transfer 100.0cm3 of the acid into a 200ml plastic beaker. Stir the acid with the thermometer. Take its initial temperature and record it in the table below at time =0 seconds. Add all the magnesium at once and start your stop watch immediately. Stir well and take the temperature after every thirty seconds up to the 5th minute.
Table 1
|
Time (seconds) |
0 |
30 |
60 |
90 |
120 |
150 |
180 |
210 |
240 |
270 |
300 |
|
temperature |
19 |
30 |
37 |
40 |
40 |
39 |
38 |
37 |
36 |
34 |
33 |
(4mk)
Complete table- 1mk
Decimal point consistency -mk1
Accuracy -1mk
Trend -1mk
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of temperature (Y-axis) against time (3mk)
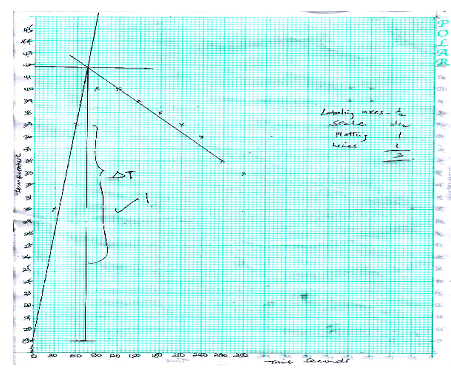
- On your graph show the highest temperature change ∆T (1mk)
(on the graph)
c) Calculate the heat change for the reaction (1mk)
100×4.2× correct Ans in (b) above
Procedure 2
Transfer the content of the plastic beaker into a 250 ml volumetric flask. Rinse the beaker and place the rinsing water into the volumetric flask. Top up the solution to the 250ml mark using distilled water and label it solution D.
Fill the burette with sodium hydroxide solution S
Using a pipette, transfer 25.0cm3 of solution D into a conical flask. Add 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator and carry out titration .Record your results in the table 2 below. Repeat the procedure two more times and complete table 2 below.
Table 2
|
titration |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Final burette reading (cm3) |
25.0 |
25.0 |
25.0 |
|
Initial burette reading (cm3) |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
|
Volume of solution S used (cm3) |
25.0 |
25.0 |
25.0 |
(4mks)
b) Determine
- average titre volume of solution S used (1mk)
25+25+25= 25
25 - moles of NaOH in the average titre volume (1mk)
(25×0.2)/1000=0.005 - moles of hydrochloric acid in solution D that reacted with NaOH (1mk)
Mole ratio HCl:NaOH
1:1
=0.005 - moles of HCl in 250cm3 of solution D (1mk)
Correct Ans in (III) above × 10 - moles of HCl in 100cm3 of solution R (1mk)
(100×1)/1000 =0.1 - moles of HCl that reacted with Mg (1mk)
Correct Ans in (v Above-Correct Ans in Iv above - moles of Mg that reacted (1mk)
Mole ratio HCl:Mg
2:1
=correct Ans in (VI) above×1/2 - Molar enthalpy of reaction between Magnesium and HCl (2mk)
Correct Ans in C → Ans in (VII)
? → 1mole
= -Correct Ans in Joules/mole
2. You are provided with solid Z. Carry out the tests below and record your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Place all solid Z in a boiling tube. Add 10cm3 of distilled water and shake. Filter the mixture. Divide the filtrate into two and preserve the residue.
observations
inferences
Colourless filtrate
White residue
Cu2+,Fe2+,Fe3+ absent
Z is partially soluble
- To the first portion of filtrate add dilute sodium hydroxide and warm gently. Test the gas produced if any using moist blue and red litmus papers
observations
inferences
Red litmus paper turns blue
Blue litmus paper remains blue
NH4+
- To the second portion add 2 drops of lead (II) nitrate and warm
observations
inferences
White ppt soluble on warming
Cl-
- Place the residue in a test tube. Add dilute nitric (V) acid until reaction is complete and test the gas produced using a glass rod dipped in lime water. Divide the solution formed into two
observations
inferences
Effervescence
White ppt/solid formed
1mk
CO32-
1mk
- To the first portion add sodium hydroxide drop wise till in excess
observations
inferences
White ppt soluble in excess
1mk
Zn2+,Al3+,Pb2+
2mk
- To the second portion add ammonia solution drop wise till in excess
observations
inferences
White ppt soluble in excess
Zn2+
3. You are provided with liquid L. Carry out the tests below and record your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Place 2 drops of liquid L on a watch glass and ignite using a wooden splint
observations
inferences
Burns with a blue flame
=C=C=, -C≡C- absent
- To 2cm3 of liquid L in a test tube add 2 drops of acidified KMnO4
observations
inferences
purple colour of acidified KMnO4 turns colourless
=C=C=,-C≡C- and R-OH absent
- To 2cm3 of liquid L in a test tube add 2drops of acidified potassium dichromate (VI) and warm
observations
inferences
Orange colour of acidified K2Cr2O7 turns green
R-OH
- Use the remaining liquid L to determine the pH of the liquid using universal indicator paper provided. Use the guide provided
procedure
observation
inferences
-Place a universal indicator paper into the liquid
-match the colour of the paper to ones in the chart
-read the pH
11/2mk
pH 7
1/2mk
Neutral
1mk
CONFIDENTIAL
- 120cm3 1M HCl solution R
- 100cm3 0.2 M NaOH sol S
- Exactly 0.6g Mg powder
- 100ml measuring cylinder
- 10ml measuring cylinder
- 200ml plastic beaker
- 250ml volumetric flask
- Stop watch
- Burette pipette
- Conical flask
- Glass rod
- Thermometer
- 2g solid Z
- 6 Test tubes in a rack
- 1 boiling tube
- Filter paper
- Filter funnel
- Red litmus paper
- Blue litmus paper
- 6cm3 liquid L
- Distilled water in a wash bottle
- 1 label
- Test tube holder
ACCESS TO
- Source of heat
- Phenolphthalein indicator with adropper
- 2 M NaOH with a dropper
- Lead (II) nitrate solution with a dropper
- Dilute HNO3 with adropper
- Lime water in a beaker
- Acidified KMnO4 with adropper
- Acidified potassium dichromate (VI) with a dropper
- Universal indicator paper
- pH chart
NB
Solid Z is a mixture of NH4Cl and ZnCO3 (1:2).each candidate requires about 2g
Liquid L is absolute ethanol. Each student requires about 6cm3 in a stoppered container
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions, Answers and Confidential - Kigumo Mocks 2021 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

