INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper contains sections A and B.
- Answer all questions in Section A.
- In section B, answer questions 6 and any other two.

QUESTIONS
SECTION A
Answer all questions in this section (25 marks)
- The diagram below represents structure of the earth.
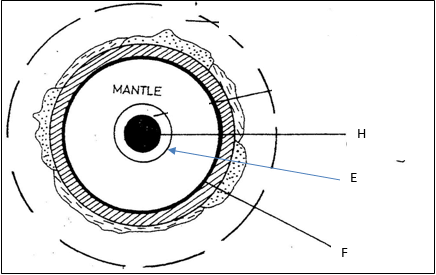
- Use it to answer questions that follow.
- Name the boundaries marked E and F. (2 marks)
E.......................................................F................................................. - Identify two minerals that make up the layer marked H. (2 marks)
- Name the boundaries marked E and F. (2 marks)
- Give two effects of the rotation of the earth on its axis. (2 marks)
- Use it to answer questions that follow.
-
- Define the term magmatic water (2 marks)
- List three surface features on Karst landscape (3 marks)
-
- Define the term vegetation (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the distribution of vegetation
- Relief (2 marks)
- Soils (2 marks)
- State four indicator of occurrence of sol creep in an area (4 marks)
-
- Name two types of submerged highland coasts (2 marks)
- Identify two resultant features of the emerged highland coasts (2 marks).
Section B. Answer question 6 and any other two. 75 marks
- Study the map of Kijabe provided to answer the questions that follow.
-
- Identify the tittle of the map provided. (1 mark).
- Give the latitudinal extent of the map given. (2marks)
- Identify any two methods used to represent relief in the map provided. (2 marks)
- Identify the feature in grid reference 402003. ( 1 mark)
-
- Determine the length of allweather road bound surface from grid reference 2589 to the junction at petrol station in kilometers. (2 marks)
- Identify three natural vegetation in the area covered by the map. (3marks)
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. ( 6 marks)
-
- Explain three social activities found in the area covered by the map. (6 marks)
- Give two proofs that suggests lumbering is taking place in the area covered by the map. ( 2 marks)
-
-
-
- Give three reasons why weather forecasting is important (3 marks)
- State three conditions that lead to fog formation. (3 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence climate.
- Aspect ( 2 marks)
- Altitude ( 2 marks)
- Distance from the sea. (2 marks)
- Using a well labeled diagram, describe the formation of orographic rainfall. (6 marks)
-
- State two advantages of studying weather through fieldwork. (2 marks).
Students from Turuturu Secondary conducted a field study on weather in a weather station. - Formulate a suitable hypothesis they could have used for the study. (2 marks)
- State three followup activities they would carry out after the study. (3 marks)
- State two advantages of studying weather through fieldwork. (2 marks).
-
-
- Identify three ways in which ice moves. (3marks)
- Describe plucking as a process in glacial erosion. (4marks)
-
- Using a well labeled diagram, describe the formation of a pyramidal peak. (6marks)
- Explain three factors that lead to glacial deposition. (6marks)
- You are required to carry out a field study on erosional features in glaciated lowland area
- Give three reasons why you would require a working schedule (3marks)
- Give three erosional features in the lowland areas they would have identified. (3marks
-
-
- A part from the Rift Valley name two other relief features that are formed as result of faulting. (2marks)
- With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe how a Rift Valley is formed by tensional forces. (8marks)
- Explain four effects of faulting (8marks)
- Students are planning to carry out a field study of an area affected by faulting
- State four reasons why it is important for the students to have a previsit of the area. (4marks)
- One of the ways they would use to collect data is through direct observation. Give three disadvantages of direct observation in the study of such an area. (3marks)
-
-
-
- Name three major deserts found in Africa (3 marks)
- Give two processes in which wind erodes the earth’s surface. (2 marks)
- Explain three ways in which wind transports its load. (6 marks).
- Using well labeled diagrams, explain how the following desert features are formed;
- Yardangs. (5 marks)
- Mushroom blocks. (6 marks)
- The diagram below represents features resulting from wind deposition in a desert
Use it to answer questions that follow.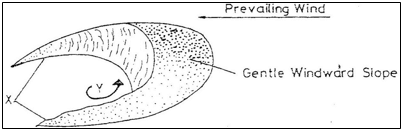
- Name the above feature (1 mark)
- Name parts marked X and Y
X .............................................
Y .............................................(2 marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
- The diagram below represents structure of the earth. Use it to answer questions that follow.
- Diagram on the boundaries marked E and F.
- E – Gutenberg discontinuity (1 mark)
F – Mohorovicin discontinuity (1 mark) - Identify minerals that make up the layer marked H (2 marks)
- Iron and Nickel
- E – Gutenberg discontinuity (1 mark)
- Give two effects of the rotation of the earth on its axis (2 mark)
- Causes day and night
- A difference of 1 hour between meridian 15 degrees apart.
- Causes deflection of winds and ocean currents
- Variation of speed of air masses
- Causes of rising and falling of ocean tides.
- Diagram on the boundaries marked E and F.
-
- Magnetic water – Plutonic water that gets trapped in the rocks underground
- Examples of surface features
- Grikes/grykes
- Clints
- Dolines
- Uvala
- Polge
- Swallow hole
-
- Define vegetation. (2 marks)
- It is the total mass of plant life that occupies a given area.
- Explain how the following factors influence the distribution of vegetation
- Relief (2 marks)
- high altitude areas have low temperature which encourages scanty/no vegetation / low altitude areas have moderate temperature which encourage dense vegetation.
- Gently sloping areas are well drained hence encouraging dense vegetation growth/steep slopes experience excessive drainage that discourages plant growth/ hence scanty vegetation. 1 x 2 = 2 marks
- Soils
- Fertile soils have a variety of nutrients which encourage the growth of dense vegetation / infertile soils have insufficient nutrients leading to scanty vegetation.
- Medium textured soils are well drained thus support a variety of plants / dense vegetation. Coarse / fine textured soils are poorly drained leading to scanty / no vegetation.
- Deep soils enable the penetration of long roots thereby supporting trees (forests) / thin soils support vegetation with shallow roots thereby supporting grass vegetation. (1 x 2 = 2 marks)
- Relief (2 marks)
- Define vegetation. (2 marks)
- State Four indicator of occurrence of soil creep in an area (4 marks)
- Telephone/fence poles that are inclined down a slope/bent tree trunk
- Accumulated soil at the foot of a slope/behind obstacles such as walls/ on roads/ railways.
- Existence of ribbed /stepped pattern across the slope
- Presence of dipped rock strata in the direction of the slope
- Presence of overhanging banks above roads/rivers. 4 x 1 = 4 marks
-
- Name two types of submerged highland coasts.
- Longitudinal/Dalmatian
- Ria
- Fiord/fjord
- Identify two resultant features of the emerged highlands coast
- Raised geo/blow hole
- Raised cliffs
- Raised wave-cut platforms
- Raised beaches
- Raised caves
- Raised notches
- Raised arch/Raised stack/stump
- Name two types of submerged highland coasts.
-
-
- Identify the tittle of the map provided. (1 mark).
- Kijabe
- Give the latitudinal extent of the map given. (2marks)
- 0053’ to 1000’ S
- Identify any three methods used to represent relief in the map provided. (2 marks)
- Contours
- Trigonometrical Stations
- Identify the feature in grid reference 402003. ( 1 mark)
- River confluence.
- Identify the tittle of the map provided. (1 mark).
-
- Determine the length of all-weather road bound surface from grid reference 2589 to the junction at petrol station in kilometers. (2 marks)
- 6.7 ± 0.1 Km
- Identify three natural vegetation in the area covered by the map. (3marks)
- Forest
- Scrub
- Scattered Trees
- Thicket
- Woodlands. 3 x 1 = 3 marks
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. ( 6 marks)
- The main drainage features are rivers.
- The main river is Ewaso Kendong.
- Most rivers in the area covered by the map are permanent as indicated by continuous blue lines.
- The main rivers are joined by many tributaries.
- There are many rivers in the area covered by the map.
- Most rivers are joined by their tributaries at an acute angle forming the dendritic patterns.
- Rivers flowing from Kijabe hill form radial drainage patten.
- Some rivers in the are covered by the map are disappearing eg at grid square 2796.
Mark the first 6 x 1 = 6 marks.
- Determine the length of all-weather road bound surface from grid reference 2589 to the junction at petrol station in kilometers. (2 marks)
-
- Explain three social activities found in the area covered by the map. (6 marks)
- Education: The presence of many school eg Kinare sch.
- Health Services. There are several dispensaries eg Kinale /Kijabe Hospital.
- Religious Services. Presence of several churches eg. Grid square 3890.
- Security services. Presence of police station at 3098.
- Recreation services. The presence of Rest House at Grid 3498.
- Administration. Evidenced by Location centers/Police post. 3 x 2 = 6 marks
- Give two proofs that suggests lumbering is taking place in the area covered by the map. ( 2 marks)
- Saw- Mill.at grid 4399.
- Dry weather road passing through the forest. 2 x 1 = 2 marks.
- Explain three social activities found in the area covered by the map. (6 marks)
-
-
-
- Give three reasons why weather forecasting is important.
- Help farmers plan their activities
- Help people to choose clothing for the day
- Influence designing of the houses and guide in landing of aircrafts.
- Help in planning military activities
- Guides fishing activities
Any 3 points 3 x 1 = 3 marks
- State three conditions that lead to fog formation. (3 marks)
- Air must have sufficient moisture
- Clear sky / absence of clouds to allow free terrestrial radiation
- Air must be cooled below dew point
- Wind must be light /calm conditions to help hold water droplets in suspension
Any 3 points 3 mks
- Give three reasons why weather forecasting is important.
- Explain how the following factors influence climate.
- Aspect
- In the Northern Hemisphere of temperate regions North facing sloper are cooler as they do not receive direct sunshine. Southern facing slopes are warmer because they receive direct sunlight.
- In the southern Hemisphere of the temperate region, North facing slopes are warmer while south facing slopes are cooler.
- Windward slopes receive higher rainfall as they trap moist prevailing winds which raise through orographic effect. leeward sides have little or no rainfall due to rain shadow effect. Any 2 points 2 x 1 =2 marks
- Altitude
- Temperature decrease with the increase in Height / Altitude as 1 at a loss of 6.5ºC for a rise of 1000 M ASL.
- Lower altitudes have a longer column of air that vetains a lot of heat .
- Higher altitudes have a shorter column of air leading to cooling which lower temp.
- Temperature is higher at lower altitudes than at high altitude since air is heated from below and not directly from the sun.
Any 2 points 2 x 1 = 2 marks
- Distance from the sea
- Relative humidity in places near the sea is higher than places far away in the continent.
- The amount of rainfall received in places near large water bodies is relatively higher than in places far away.
- Air pressure is relatively higher near large water bodies than in places far away.
- Near large water bodies temperatures are relatively warmer than in areas towards the continents.
- Aspect
- Using a well labeled diagram describe the formation of orographic reainfall. ( 6 marks)
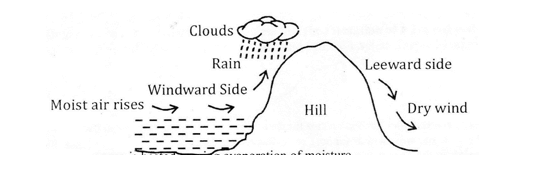
- Water in a lake /sea is heated causing evaporation of moisture formation.
- Most air is forced to move horizontally by wind.
- As the air rises, it expands, cools and condenses to form clouds.
- The clouds then form relief rainfall.
- The rainfall is mainly experienced on the wind wards.
- The cool air then crosses over the hill and descends on the leeward side as dry wind.
- There is little or no rainfall on the leeward side.
Mark- diagram 3 marks
Description 3 marks (Total 6 marks).
-
- State three advantages of studying weather through field work. (3 marks)
- Enable learners to collect firsthand information
- Help learners develop manipulative skills
- Enable students apply knowledge learnt in classroom in real life situation
- Makes learning interesting.
- Provides detailed or in depth or broadened learning.
- Enhances visual memory.
- Breaks classroom monotony and boredoms. 3 x 1 = 3 marks
- Students from Turuturu Secondary conducted a field study on weather in a weather station. Formulate a suitable hypothesis they could have used for the study. (2 marks)
- The area of study receives high rainfall.
- The area of study has cool temperatures.
- The area of study experiences convectional rainfall.
- The station has many weather recording instruments.
Mark any other relevant statement. 2 x1 = 2 marks
- State any three fall-up activities they would carry out after the study. ( 3 marks).
- Discussing the findings
- Analyzing data
- Writing a report
- Giving relevant advice to the state/residents
- Drawing sketches
- Displaying photographs / sketches Any 3 x 3= (3 marks)
- State three advantages of studying weather through field work. (3 marks)
-
-
- Identify three ways in which ice moves
- Plastic flowage
- Basal slip
- Extrusion flow
- Internal shearing
- Describe plucking as a process in glacial erosion (4marks)
- Pressure from the overlying mass of ice cause freeze and thaw action
- Melting water fills cracks / joints in the bed rock
- As the water freezes it exerts pressure on the cracks enlarging them
- The enlarged cracks led to disintegration of the rock
- the disintegrated rocks eventually get embedded within the mass of ice.4 x 1= 4 marks
-
- Using a well labeled diagram, describe the formation of a pyramidal peak. (6marks)
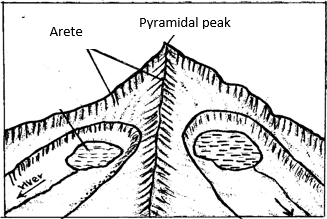
- Ice accumulates in several shallow pre-existing depressions on the mountain sides.
- As the ice moves it plucks the rocks steepening the sides of the hollows / depressions.
- Continued erosion by abrasion deepens and widens the hollows.
- Adjacent hollows continue to be eroded causing the cirques backwall to erode until they are separated by narrow steep ridges called aretes.
- Where aretes converge at the top of the mountain they form a sharp steep sided peak known as the pyramidal peak.
Mark Text 4 marks
Diagram 2
Total 6 marks.
- Explain three factors that lead to glacial deposition. ( 6 marks)
- rising temperature lead to melting of ice thereby causing the ice to deposit its loads.
- change of gradient to relatively flat surface will reduce the velocity of the glacial.
- movement which will subsequently lead to deposition of glacial materials.
- alternating warm and cold periods lead to seasonal melting of ice which allows materials embedded in the ice to be released and deposited.
- Stagnation/accumulation of glacier leads to pressure at the base of the glacier which in turn leads to melting of ice at the base.
- The melt water then carries and deposits materials underneath which loosens the heavy materials beneath the mass of ice and subsequently deposited.
Condition 1 mark
Explanation 1 mark (any 3 x 2 = 6 marks)
- Using a well labeled diagram, describe the formation of a pyramidal peak. (6marks)
- You are required to carry out a field study on erosional features in glaciated lowland area
- Give three reasons why you would require a working schedule (3marks)
- It enables the planned activities to be carried out systematically.
- It allows for proper use of available time.
- It enables the assessment of the progress of the fieldwork.
- It enables the estimation of total time required for the study.
- It confines the researcher to the scope of the topic.
- It ensures all areas are adequately covered.Any 2 x l = (2 marks)
- Give three erosional features in the lowland areas they would have identified. (3marks)
- Ice eroded plains.
- Depressions
- Roche Mountonee.
- Crag and tail
- Give three reasons why you would require a working schedule (3marks)
- Identify three ways in which ice moves
-
-
- A part from the Rift Valley name two other relief features that are formed as result of faulting. (2marks)
- Tilt block
- Escarpment/scrap slope
- Block mountain/ horsts Any 2x1=2marks
- With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe how a Rift Valley is formed by tensional forces. 8 marks
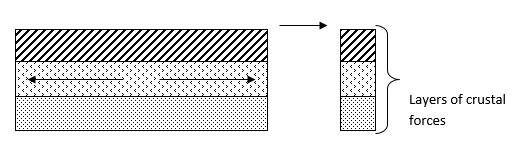
- Layers of rocks are subjected to tensional forces when there is some tensional forces when there is some instability within the earth’s crust.
- Parallel normal faults develop/lines of weakness develop.
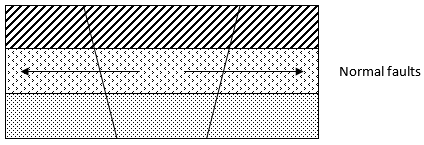
- The middle part gradually sinks/ subsides.
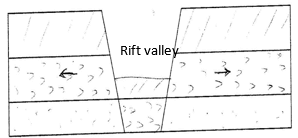
- The sunken middle part forms a depression known as the Rift Valley
- A part from the Rift Valley name two other relief features that are formed as result of faulting. (2marks)
- Explain four effects of faulting (8marks)
- Faulting / fault scraps make it difficult to construct roads/ railways.
- Depression in the Rift valley contain water that forms lakes
- Faulting exposes minerals such as diatomite.
- Step faulting makes rivers to have waterfalls, rapids and cataracts
- The scrap slopes / steep slopes tend to discourage settlement.
- Some rivers such as the Katonga in Uganda have had their directions of flow changed. (Any 4 x 2 = 8 marks)
- Students are planning to carry out a field study of an area affected by faulting
- State four reasons why it is important for the students to have a pre-visit of the area. (4marks)
- To enable them draw up study objectives / hypothesis
- To enable them draw a route map.
- To enable them prepare a work schedule / plan of activities
- To enable them identify / sort our relevant tools / equipment for the study
- To identify suitable methods of data collection.
- To seek permission from the occupants of their site of study.
- To enable them prepare financial (Any 4x1 = 4mks)
- One of the ways they would use to collect data is through direct observation. Give three disadvantages of direct observation in the study of such an area. (3marks)
- It is expensive
- It is time consuming
- It is tiresome
- It is limited only to direct sources / primary sources
- It is only suitable to the signed people (Any 3x1 =3 marks)
- State four reasons why it is important for the students to have a pre-visit of the area. (4marks)
-
-
-
- Name three major deserts found in Africa. ( 3 marks)
- sahara
- Kalahari
- Namib 3 x 1= 3 marks
- Give two processes in which wind erodes the earth’s surface. ( 2 marks).
- abrasion
- deflation
- attrition 2 x 1 = 2 marks.
- Explain three ways in which wind transports its load. ( 6marks)
- Saltation – This is where course granted sand particles are transported through a series of short jumps bouncing along the earth’s surface.
- Suspension - very fine materials are picked by wind raised high and blown for long distance.
- Surface creep - heavy materials are rolled pushed for short distances along the earth’s surface. 3 x 2 = 6 marks
- Name three major deserts found in Africa. ( 3 marks)
- Using well labeled diagram explain how the following desert feature are formed.
- yarding 5 marks
- Prevailing wind blow across the land where there are alternating vertical bands of resistant rocks.
- The rock layers lie parallel to direction of prevailing wind.
- Soft rocks are eroded by wind through abrasion to form depression, furrows while hard bands or rocks form ridges.
- The ridges form features called yardings.
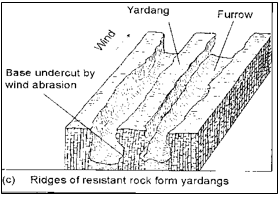
Diagram 2 Text 3 total 5 marks
- Mushroom Blocks 6 marks
- it is formed where there is a homogeneous rock outcrop along the direction of prevailing winds.
- The base of the rock is eroded more by wind abrasion
- The top part is polished and smoothened through abrasion to form a massive rock with a broad rounded top called a mushroom block.
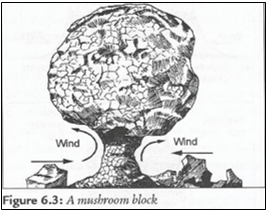
Diagram 3
Text 3 Total 6marks
- yarding 5 marks
- The diagram below represents features resulting from wind deposition in a desert.
Use it to answer the questions that follow.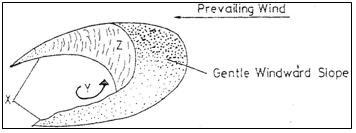
- Barchan 1 mark
- J – Horns
L- Steep slope 2 marks
-

CONFIDENTIAL
Provide the map of Kijabe.
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions,Answers and Confidential - Kigumo Mocks 2021 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

