Questions
INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer ALL the questions
- Use of Mathematical sets and silent calculators may be used.
- All working should be clearly shown.
-
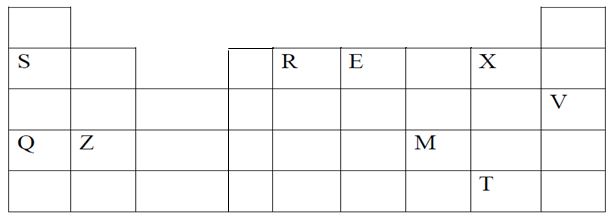
- The grid below represents part of a periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of elements.
- Identify the most reactive non-metal (1mark)
- Which of the metal is the most reactive? Explain. (1mark)
- What name is given to the family of elements to which X and T belong? (1mark)
- Give reasons for the following
- Ionic radius of Q is smaller than that of M 1mark
- Atomic radius of Q is greater than that of S (1mark)
- Give an element that does not form compounds under ideal conditions. Explain. (2marks)
- Give formula of compound formed between E and Z (1mark)
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Substance A B C D E F Melting point (°C) 801 113
119-39 5 -101 1356 Boiling point(°C) 1410 445 457 54 -36 2860 Electrical Conductivity (Solid) Poor Poor Good Poor Poor Poor Electrical Conductivity (Liquid) Good Poor Good Poor Poor Poor - Identify a substance with:
- Giant metallic structure (1mark)
- Has a molecular structure and exists in gaseous state at room temperature? and pressure (1mark)
- Suggest a reason why substance B has two melting points. (1mark)
- Substances A and C conduct electric current in the liquid state. State how the two substances differ as conductors of electric current. (2marks)
- Identify a substance with:
- The grid below represents part of a periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of elements.
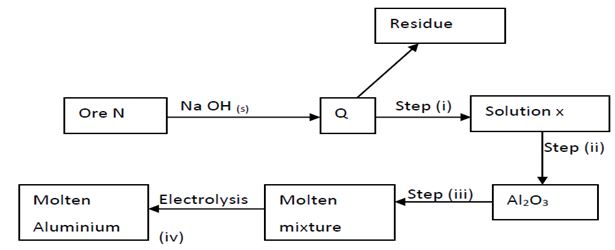
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name ore N (1mark)
- Explain why the ore is first dissolved in excess sodium hydroxide solution. (1mark)
- Name the major compound present in the residue. (1mark)
- Give the formula of the aluminium compound present in solution (1mark)
-
- Explain how to obtain aluminium hydroxide from solution X (1mark)
- Write equation for reaction that takes place in (e) above (1mark)
- What is the role of cryolite in the extraction of aluminium. (1mark)
- Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity. State two uses of aluminium based on this property. (2marks)
- If sodium carbonate is added to aluminium nitrate solution, effervescence occurs. Explain. (2marks)
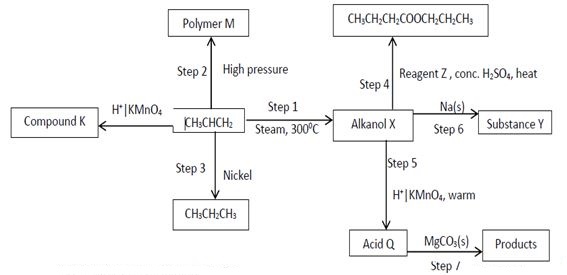
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Give the names of the following
- Compound K (1mark)
- Substance Y (1mark)
- Product obtained in step 4 (1mark)
- Identify the type of reaction that takes place in step 1 and give one other condition necessary for the reaction other than the temperature indicated.
Type of reaction……………………………………………………………………. (1mark)
Condition………………………………………………………………………………. (1mark) - Draw the structural formula of the following
- Polymer M (1mark)
- Acid Q (1mark)
- Give the industrial application for the reaction in step 3 (1mark)
- Write chemical equations for the reactions in step 6 and step 7 . (2marks)
Step 6 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
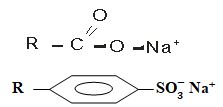
Step 7 - The following are structures of two cleansing agents.
In the table below, give one advantage and one disadvantage of each of them. (2marks)
Cleansing Agent Advantage Disadvantage R-COO-Na+ R-OSO3-Na+
- Give the names of the following
- The standard reduction potentials for five half cells are shown in the table below. Study it and answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbol of elements).
Elements Eθ(Volts) i
ii
iii
iv
vA2(aq) + 2e- → 2A-(aq)
Q2+(aq) + 2e- → Q(s)
R2+(aq) + 2e- → R(s)
Y2+(aq)+ 2e- → Y(s)
2S+(aq) + 2e- → S2(s)+1.09
-0.13
-2.37
+0.34
0.00-
- With a reason, identify the strongest reducing agent. (1mark)
- Which half-cell is likely to be hydrogen? (1mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction between two half cells in (ii) and (IV). (1mark)
- Calculate the e.m.f of the cell in (c) above. (2mark)
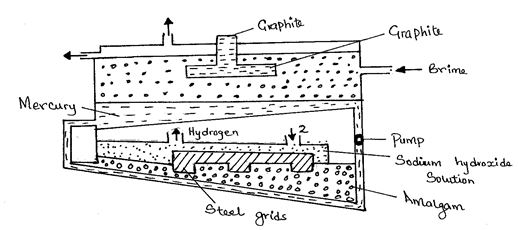
- The diagram below represents a mercury cell that can be used in the industrial manufacture of sodium hydroxide. Study it and answer the questions that follow:-
- Name:
- Raw material introduced at 2. (½ mark)
- Another substance that can be used in the cell instead of graphite. (½ mark)
- Identify the by-product that comes out at I. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction: -
- That occurred at the anode. (1 mark)
- In which sodium hydroxide was produced. (1 mark)
- Give two reasons why mercury is recycled. (2 marks)
- State one use of sodium hydroxide ( 1mark)
- Name:
-
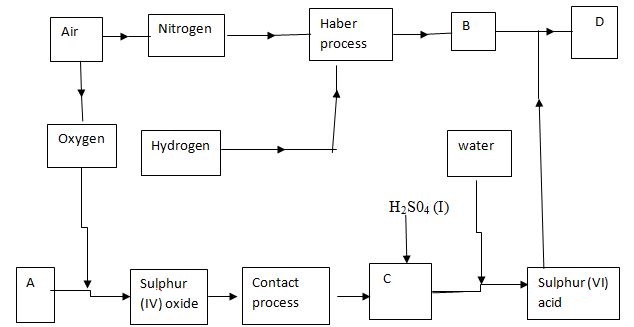
- The flow chart below illustrates two industrial processes. Harber process and the contact process.
- Name the process of obtaining nitrogen from atmospheric air. (1mark)
- List TWO sources of obtaining large volumes of hydrogen for industrial use.
- Write equation for Haber process. (1mark)
- Name the catalysts for: (1mark)
- Haber process ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Contact process …………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Identify substances: (1mark )
D……………………………………………………………………………………….
C ……………………………………………………………………………………. - Give ONE major use of compound D (1mark)
- Write an equation for dilution of C with water. (1mark)
- A farmer has three plots each measuring 0.25 acres. He applied nitrogenous fertilizers as follows.
- plot A 250 kg of ammonium phosphate
- plot B 250 kg of urea CO(NH2)2
- Plot C 250kg of ammonium nitrate
Which plot received the highest nitrogen content? (3marks)
H = 1, N = 14, 0 = 16. P = 31, C = 12.
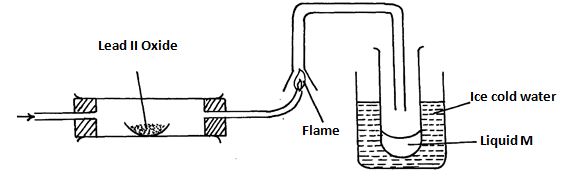
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions which follow.
- State two observations made when hydrogen gas pass over hot Lead (II) oxide. (2marks)
- Write the equation for the reaction which occurs in the combustion tube. (1mark)
- What property of hydrogen is shown in the experiment above. (1mark)
- Identify liquid M and describe the test for its purity (2marks)
- What would be observed if MgO was used instead of Lead II Oxide: Explain (2marks)
- What is the colour of the flame (1mark)
- Write a chemical equation of the reaction producing the flame. (1mark)
- Apart from hydrogen peroxide, state two other reagents that can be used to prepare oxygen gas. (1mark)
- Write an equation to show how hydrogen gas is formed from the reagents chosen in (vii) above. (1mark)
-
-
- Use the data below to calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction below
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H20 (l) (3marks)
Bond Energy (KJ)
C – H 314
O = O 296
C = O 149
H – O 283 - Given the following Standard Molar enthalpies of combustion. Calculate the standard heat of formation of butane (C4H8). (3marks)
ΔHθc Carbon (Graphite) = -393.5KJ/mol
ΔHθc Hydrogen = 285.8KJ/mol
ΔHθc butene = -2877KJ/mol - Use the following information to answer the questions that follow
ΔH lattice Mgcl2 = -2489 kJ/ mol-1
ΔH hydration Mg2+ = - 1891 kJ/ mol
ΔH hydrationCl - = -384 kJ/ mol
- Use the data below to calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction below
- Using energy level diagram calculate the molar heat of solution of magnesium chloride. (4marks)
-
Marking Scheme
-
- The grid below represents part of a periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of elements.
- Identify the most reactive non-metal 1mark
- X
- Which of the metal sis the most reactive? Explain. 1mark
- Q. has largest atomic radius, outermost electrons are loosely held hence lost easily.
- What name is given to the family of elements to which X and T belong? 1mark
- Halogens
- Give reasons for the following
- Ionic radius of Q is smaller than that of M 1mark
- Q forms ion by losing electron hence remaining electrons are pulled more close to nucleus, M forms ion by gaining electron, the gained electron is repelled by existing electrons hence repulsive effect increases ionic radius
- Atomic radius of Q is greater than that of S 1mark
- Q has many energy levels than S hence a greater atomic radius than S
- Ionic radius of Q is smaller than that of M 1mark
- Give an element that does not form compounds under ideal conditions.
Explain. 2marks- V, already is in the stable octet configuration hence does not lose or gain electron
- Give formula of compound formed between E and Z 1mark
- ZE2
- Identify the most reactive non-metal 1mark
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Substance A B C D E F Melting point (°C) 801 113
119-39 5 -101 1356 Boiling point(°C) 1410 445 457 54 -36 2860 Electrical Conductivity (Solid) Poor Poor Good Poor Poor Poor Electrical Conductivity (Liquid) Good Poor Good Poor Poor Poor - Identify a substance with:
- Giant metallic structure 1mark
- C
- Has a molecular structure and exists in gaseous state at room temperature and pressure 1mark
- E
- Giant metallic structure 1mark
- Suggest a reason why substance B has two melting points. 1mark
- Its allotropic // exhibit allotropy
- Substances A and C conduct electric current in the liquid state. State how the two substances differ as conductors of electric current. 2marks
- A is an ionic compound conduct in liquid state as ions are free .in solid they’re fixed. C is a metal, conduct in all states using free electrons.
- Identify a substance with:
- The grid below represents part of a periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of elements.
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name ore N 1mark
- bauxite
- Explain why the ore is first dissolved in excess sodium hydroxide solution. 1mark
- To remove impurities of silica and iron iii oxide.
- Name the major compound present in the residue. 1mark
- Iron (iii) oxide.
- Give the formula of the aluminium compound present in solution 1mark
- [Al(OH)4]2+
-
- Explain how to obtain aluminium hydroxide from solution X 1mark
- By seeding with pure aluminium hydroxide crystals // bubbling carbon (iv) oxide into it
- Write equation for reaction that takes place in (e) above 1mark
- 2[Al(OH)4]- + CO2(g) 2 Al(OH)3 + CO32-(aq) + H2O(l)
2[Al(OH)4] -(aq) Al(OH)3 Al(OH)3(s) + OH-(aq)
- 2[Al(OH)4]- + CO2(g) 2 Al(OH)3 + CO32-(aq) + H2O(l)
- What is the role of cryolite in the extraction of aluminium. 1mark
- added as impurity to lower melting point of aluminium oxide for electrolysis process
- Explain how to obtain aluminium hydroxide from solution X 1mark
- Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity. State two uses of aluminium based on this property. 2marks
- used make overhead cables
- If sodium carbonate is added to aluminium nitrate solution, effervescence occurs. Explain. 2marks
- Aluminium compounds easily hydrolyse releasing hydrogen ions that react with carbonate releasing carbon(iv) oxide causing effervescence.
- Name ore N 1mark
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Give the names of the following
- Compound K (1mark)
- ethan – 1,2 -diol
- Substance Y (1mark)
- sodium propoxide
- Product obtained in step 4 (1mark)
- propylbutanoate
- Compound K (1mark)
- Identify the type of reaction that takes place in step 1 and give one other condition necessary for the reaction other than the temperature indicated.
Type of reaction…hydration………………………. (1mark)- Condition……pressure of 60 – 70 atm and phosphoric (V) acid as catalyst…………………. (1mark)
- Draw the structural formula of the following
- Polymer M (1mark)
- Acid Q (1mark)
- Give the industrial application for the reaction in step 3 (1mark)
- Hardening of liquid oil into solids in manufacture of margarine
- Write chemical equations for the reactions in step 6 and step 7 . (2marks)
- Step 6 …… Na + C3H7OH C3H7ONa + H2
Step 7
……… C3H6O2 + MgCO3 (CH3CH2COO)2Mg + CO2 +H2O
- Step 6 …… Na + C3H7OH C3H7ONa + H2
- The following are structures of two cleansing agents.
In the table below, give one advantage and one disadvantage of each of them. (2marks)
Cleansing Agent Advantage Disadvantage R-COO-Na+ Biodegradable thus non – pollutant Wastes soap, since does not lather readily with hard water forms scum R-OSO3-Na+ Does not form scum, since readily lather with hard water Non - biodegradable thus pollutant
- Give the names of the following
- The flow chart below illustrates two industrial processes. Harber process and the contact process.
- Name the process of obtaining nitrogen from atmospheric air. ( 1 mark)
- Fractional distillation of liquid air
- List TWO sources of obtaining large volumes of hydrogen for industrial use.
- Electrolysis of acidified water ( ½ mk)
- Cracking of hydrocarbons ( ½ mk)
- Steam over carbon \hydrocarbon
- Write equation for Haber process. ( 1 mark )
- N2(g) +3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
Fe
- N2(g) +3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
- Name the catalysts for:
- Haber process Finely divided iron ( ½mk)
- Contact process Vanadium (IV) oxide\platinised astestos ( ½ mk)
- Identify substances:
- D Ammonium sulphate /( NH4)2SO4 ( ½ mk)
- C oleum, /H2S2O7 ( ½ mk)
- Give ONE major use of compound D ( 1 mark )
- Fertilizers
- Write an equation for dilution of C with water. (1 mark)
- H2S2O7(I)+H2O(I) 2H2SO4(I)
- A farmer has three plots each measuring 0.25 acres. He applied nitrogenous fertilizers as follows.
plot A 250 kg of ammonium phosphate
plot B 250 kg of urea CO(NH2)2
Plot C 250kg of ammonium nitrate
Which plot received the highest nitrogen content? (3 marks)
H = 1, N = 14, 0 = 16. P = 31, C = 12.- 42/149*100=28.19
CO(NH2)2
28/60*100=46.67
28/80*100=35
CO(NH2)2-has a highest % of Nitrogen
- 42/149*100=28.19
- Name the process of obtaining nitrogen from atmospheric air. ( 1 mark)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions which follow.
- State two observations made when dry hydrogen gas pass over hot Lead (II) oxide. (2marks)
- Lead (II) oxide changes colour from orange to grey.
- Droplets of a colourless liquid form on cool sides of the combustion tube.
- Write the equation for the reaction which occurs in the combustion tube. (1mark)
- PbO (s) + H2 (g) →Pb (s) + H2O (l)
- What property of hydrogen is shown in the experiment above (1mark)
- Reducing property.
- Identify liquid M and describe the test for its purity (2marks)
- Water, Heat liguid M to boiling while measuring the temperature. B.P of
1000C indicates that M is pure
- Water, Heat liguid M to boiling while measuring the temperature. B.P of
- What would be observed if MgO was used instead of Lead II Oxide: Explain (2marks)
- No change on MgO because H2 can not reduce MgO
- What is the colour of the flame (1mark)
- Blue
- Write a chemical equation of the reaction producing the flame. (1mark)
- H2(g) +O2(g) → H2O(l)
- Apart from hydrogen peroxide, state two other reagents that can be used to prepare oxygen gas. (1mark)
- Sodium peroxide and water.
- Write an equation to show how hydrogen gas is formed from the reagents chosen in (vii) above (1mark)
- 2Na2O2 (l) + 2H2O (l) →4NaOH (aq) + O2 (g)
- State two observations made when dry hydrogen gas pass over hot Lead (II) oxide. (2marks)
-
-
- Use the data below to calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction below
- CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H20 (l) (3marks)
Bond Energy (KJ)
C – H 314
O = O 296
C = O 149
H – O 283 - Ans = -418kJ/mol
- CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H20 (l) (3marks)
- Given the following Standard Molar enthalpies of combustion. Calculate the standard heat of formation of butane (C4H8). (3marks)
- Ans = +159.8kJ/mol
- Use the following information to answer the questions that follow
ΔH lattice Mgcl2 = -2489 kJ/ mol-1
ΔH hydration Mg2+ = - 1891 kJ/ mol
ΔH hydrationCl - = -384 kJ/ mol
- Use the data below to calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction below
- Using energy level diagram calculate the molar heat of solution of magnesium chloride. (4marks)(well drawn energy level diagram - 3marks)
- Ans = - 175kJ/mol
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - KCSE 2021 Westlands Mock Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students