QUESTIONS
- The diagram below shows an experiment set by a form one student to investigate properties of a non-luminous flame.
During the experiment a white card paper was placed horizontally over the flame at each of the regions I and II as shown in the diagram.
- Draw the appearance of the white card board at the end of experiment. (2 marks)
- Explain the appearance of each card board. (1 mark)
- Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. Explain briefly how you can get a sample of copper metal from powdered brass. (3 marks)
- In an experiment, soap solution was added to three samples of water. The results below shows the volume of soap solution required to lather with 500cm3 of each water sample before and after boiling.
Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Volume of soap used before water boiled 26.0 14.0 4.0 Volume of soap after water boiled 26.0 4.0 4.0 - Which water samples are likely to be soft. (1mark)
- Explain the change in volume of soap solution used in sample 2 (1mark)
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Describe how a pure sample of each of the solids can be obtained from a mixture of the three. (3 marks)SOLID COLD WATER HOT WATER A SOLUBLE SOLUBLE B INSOLUBLE INSOLUBLE C INSOLUBLE SOLUBLE - A test tube contains lemon juice. Some sugar is added to sweeten it. What would be the PH of the mixture if universal indicator is added to it? Explain (2 marks)
- Draw a well labeled diagram of the set-up that can be used to prepare and collect oxygen gas using sodium peroxide and water. (3 marks)
- The diagram below shows the apparatus for the preparation of gas A and investigates its properties. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
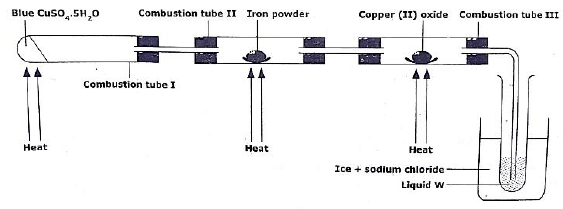
- Identify
- gas A ______________________________________________ (1 mark)
- liquid W ___________________________________________ (1 mark)
- Suggest the property of gas A under investigation. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for reaction that took place in combustion tube II. (1 mark)
- Identify
- You are provided with Lead (II) oxide powder, dilute nitric (V) acid, solid potassium carbonate and distilled water. Explain how a solid sample of Lead (II) carbonate can be prepared. (3 marks)
- Use the information below to calculate the enthalpy of formation of calcium hydroxide. (3 marks)
- H2(g) + ½ O2(g) H2O(l) Δ H = -286.78kJ/mol
- CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(s) Δ H = -64.26kJ/mol
- Ca(s) + ½ O2(g) CaO(s) Δ H = -637.56kJ/mol
- The information below represents a certain group of metals in the periodic Table.
Element Melting point ºC A 39 B 180 C 98 D 64 - Which element is most reactive? Explain. (2 marks)
- Comment on the electrical conductivity of the elements. Explain. (1 mark)
- A bottle containing nitric (V) acid has a label with the following information.
Density = 1.42g/cm3
Percentage purity = 68%
Calculate the concentration of the acid in moles per litre.
(H=1, N=14, O=16) (3 marks) - Name the processes taking place in I, II and III below.
- NaOH(s) → NaOH(aq)
- Na2CO3.10H2O(s) → Na2CO3.H2O(s)+ 9H2O(l)
- CuSO4(s) + 5 H2O(l) → CuSO4.5H2O(s)
- In a titration experiments, 25.0cm3 of sodium hydroxide containing 8g per litre was required for complete neutralization of 0.245g of adibasic acid. Calculate the relative molecular mass of the acid. (3 marks)
(Na=23, O=16, H=1) - The molecular formula of a hydrocarbon is C8H18. The hydrocarbon can be converted into 2 other hydrocarbons as shown in the equation below.
C8 H18 → C3 H8 + M- Name and draw the possible structural formula of M. (2 marks)
- A few drops of bromine water were added to a sample of state and explain the observations made. (2 marks)
- 0.12g of a metal X reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid to form X2+ ions with liberation of 240cm3 of hydrogen at r.t.p. Determine the RAM of X. (3 marks)
( Molar gas volume at r.t.p = 24dm3) - The gases exists in a dynamic equilibrium as shown below at 20ºC.
2 XO2(g) ⇌ X2 O4(g)
Brown⇌ Pale yellow ΔH = -32KJ/mol- What is a dynamic equilibrium? (1 mark)
- The syringe containing the mixture is heated to 40ºC. State and explain the observation made. (2 marks)
- You are given the following half equation;
I2(s) +2e- ⇌ 2I- (aq) Eθ=+0.54V
Br2(l) +2e- ⇌ 2Br - (aq) Eθ=+1.09V- Name the oxidizing agent. (1 mark)
- Calculate the Eθ value for the cell. (1 mark)
- In preparation of nitric (V) acid, ammonia is converted into nitric (II) oxide as shown in the equation below.
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(l)
Calculate the volume of air needed to produce 200cm3 of nitrogen (II) oxide given that air contains 20% oxygen. (Molar gas volume = 22.4dm3) (3mks) - A certain polymer has the following structure.
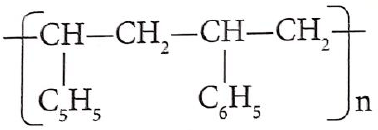
- Draw the structure of the monomer. (1 mark)
- If the molecular mass of the polymer is 20800, what is the value of n? (2 marks)
- The table below shows the ions of element W, X, Y, Z and their electronic configurations.
Ion Electronic Configuration
W- 2, 8, 8
X2+ 2, 8, 8
Y3+ 2, 8
Z2- 2, 8- Which two elements belong to the same period? (1 mark)
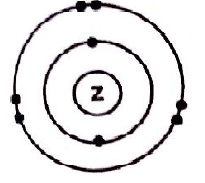
- Draw the atomic structure of element Z. (2 marks)
- Use the information in the table below to answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbol of the element).
Oxide J2O TO X2O3 WO2 Y2O5 ZO2 PH of oxide in water 13 9 X X 1 4 Melting point (ºC) 1193 3075 2045 1728 563 -91 - Identify the oxide with
- Giant ionic structure. ( ½ mark)
- Giant atomic structure. ( ½ mark)
- Simple molecular structure. ( ½ mark)
- Write the formula of the chloride of W. ( ½ mark)
- State one way in which conductivity of sodium chloride differs from graphite. (1 mark)
- Identify the oxide with
- The set up below was used to electrolyze sodium chloride.
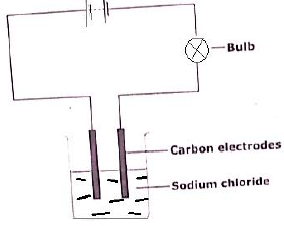
- What was missing in the set-up? (1 mark)
- State the observations made at the anode during the experiment. (1 mark)
- Write the equations that occurred at the cathode. (1 mark)
- The flow diagram below represents the extraction of Trona from Lake Magadi in Kenya’s Rift valley. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
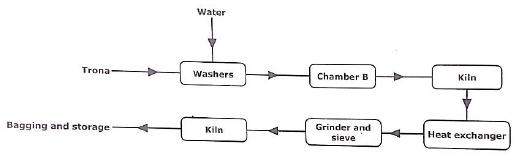
- Write the formula of Trona. (1 mark)
- Name chamber B. (1 mark)
- State functions of the washers. (1 mark)
- In an experiment 4 drops of bromine water were put in a gas jar. An empty gas jar was then inverted over the gas jar with bromine liquid. State and explain the observations. (2 marks)
- Air was passed through reagent as shown below.
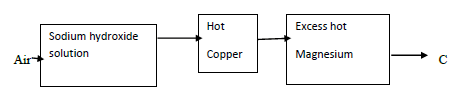
- State the role of sodium hydroxide solution. (1 mark)
- Name one component in C. Explain. (2 mark)
- When hydrogen sulphide gas was bubbled into an aqueous solution of iron (III) chloride, a yellow precipitate was deposited.
- State another observation that would be made (1mk)
- Write an equation of the reaction that took place. (1mk)
- Chlorine can be prepared in the laboratory by using the following reagents and chemicals. Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid, water, manganese (IV) oxide, concentrated hydrochloric acid.
- State the role of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid. (1 mark)
- Write the equation for formation of chlorine. (1 mark)
- What is the role of manganese (IV) oxide? (1 mark)
- The flow chart below shows steps used in the extraction of lead from one of its ores.
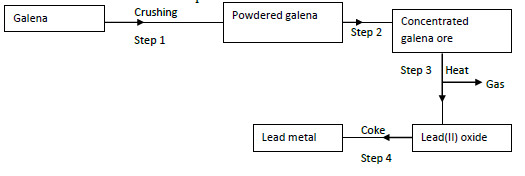
- Name the process that is used in step 2 to concentrate the ore. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in step 3. (1 mk)
- State one use of lead. (1mk)
- A mass of X grammes of radioactive isotope decay to 5 grams in 100 days. If the half-life is 25 days, calculate the initial mass. (2 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
QUESTIONS
-
-

-
- the uncharred area was placed in region of unburnt gas// no burning ½ mk
- charred areas was in contact with region of burnt gas// complete burning ½ mk
-
- Add dilute hydrochloric// sulphuric(VI) acid(1) rej.use of nitric(V) acid and conc.H2SO4
Filter (1) to obtain copper as residue(1) -
- sample 3 1mk
- Boiling precipitates calcium or magnesium ions hence removing hardness 1mk
- Add cold water (1/2)to dissolve A. Filter to obtain filtrate of A and residue of B and C.
Evaporate to obtain A(1/2)
To the residue add hot water(1/2) to dissolve solid C. Filter to obtain filtrate of solid C and residue B(1)
Evaporate filtrate C to obtain C(1/2) - PH 4-6(1) sugar is neutral and thus will not have an effect on the PH of the lemon juice which is a weak acid.(1)
-
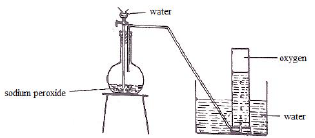
Accept if collected using syringe- Apparatus 1mk
- Labelling 1mk
- Workability 1mk
-
-
- hydrogen
- water
- reducing
- 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
-
- Add excess lead(II)oxide to dilute nitric(V) acid(1/2mk)
Filter (1/2)
Add solid potassium carbonate to water to obtain solution(1/2)
Add the potassium carbonate solution to the filtrate(1/2)
Filter(1/2mk)
Wash residue with distilled water
Dry between filter papers(1/2) - H + 64.26= -637.56 – 286.78 (1)
H = -637.56-286.78 – 64.26(1)
= -988.6kJ/mol (1) -
- A(1)
Has a bigger atomic radius hence a weaker metallic bond (1)//atoms are not closely packed hence easily
looses an electron - They have similar electrical conductivity(1/2) because of equal number of delocalized electrons(1/2)
- A(1)
- mass of 1cm3 of acid = 1.42g
Actual mass of acid= 68/100 x1.42 = 0.9656g ½ mk
RFM of HNO3= 1+ 14+ 48 = 63(1/2)
Moles of acid = 0.9656/63 = 0.01533 ½ mk
Molarity = 1000 x 0.01533 1mk
1
= 15.33M ½ mk -
- deliquescence
- efflorescence
- hygroscopy
- molarity of NaOH = 8/40 = 0.2M(1/2)
Moles of NaOH = 0.2 x 25=0.005(1/2)
1000
MR 2:1//equation(1/2)
Molesofacid =1/2 x 0.005 = 0.0025(1/2)
RFM = 0.245/0.0025(1/2) = 98 (1/2) -
- any isomer of pentene, C5H10
Structure 1mk name 1mk - yellow brominewater is decolourised(1) because M is unsaturated// contains a double bond(1)
- any isomer of pentene, C5H10
- X(s) + 2HCI(aq) XCI2(aq) + H2(g)// MR 1:1(1/2)
Moles of H2 = 240/24000 = 0.01(1/2)
Moles of X = 0.01moles(1/2)
RAM OF X = 0.12/0.01(1)
= 12(1/2) -
- State where the rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction
- Brown colour intensifies (1mk) . equilibrium shift to the left to absorb heat//lower temperature(1mk)// backward reaction is favoured because it is endothermic
-
- Br2
- E.M.F=EѲ(reduction)-EѲ(oxidation)
=1.09-0.54
=0.45V
- moles of NO = 200/22400 =0.0089mols(1mk)
Moles of O2 = 5/4 x 0.0089 = 0.01116moles(1/2)
Volume of O2 = 0.01116 x 22400 = 250cm3(1/2)
Volume of air = 100/20 x 250= 1250cm3(1) -
- CH = CH2
Ι
C6H5 - RFM of monomer = 12x8+ 8x1 = 104(1)
n=20800/104= 200(1)
- CH = CH2
-
- W and Y
- Diagram, atomic structure of Z
-
-
- X2O3// J2O//TO
- WO2
- ZO2// Y2O5
- WCl4
- Sodium chloride conducts in molten//aqueous states while graphite conducts in solid//
Sodium chloride conducts using mobile ions whereas graphite by use of delocalized electrons
-
-
- heat
- green yellow gas//fumes
- Na+(l) +e → Na(s)
-
- Na2CO3.NaHCO3 .2H2O
- Centrifuge// centrifugation chamber
- Removal of impurities and small rocks
- the two gas jars were filled with brown coloured fumes 1mk
The particles in bromine water vapourised and diffused in the air inside the gas jars 1mk -
- absorb carbon(IV) oxide(1)
- argon// noble gas (1) is unreactive(1)
-
- The solution turned from yellow to pale green // Red brown to pale green/ brown to pale green(1)
- 2FeCl3 (aq) + H2S (g) → 2FeCl2 (aq)+S(s) +2HCl(aq)
-
- To dry chlorine
- MnO2(s) + 4HCl(aq) → MnCl(aq) + Cl2(g) + 2H2O(l)
- Oxidizes HCl to chlorine
- To dry chlorine
-
- froth flotation
- 2PbS(s) + 3O2( g) → 2 PbO(s) +2 SO2(g)
- in lead acid accumulators
making of water pipes
- R.M = O.M (½) 100/25
5 = O.A ×(½)4
Initial mass = 5 ×16
= 80g
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Butere Mock Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

