INSTRUCTION TO CANDIDATE.
- This paper has two sections A and B.
- Answer All questions in section A.
- In section B, Answer question six and any other two questions.
For examiners use only
|
SECTION |
QUESTION |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CADINDATE SCORE |
|
A |
1-5 |
25 |
|
|
B |
6 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
TOTAL SCORE |
|
||

QUESTIONS
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section.
-
- What is a Land Breeze (2mks)
- Give three ways in which sea breeze influence the adjacent land. (3mks)
- State 5 characteristics of the mantle (5mks)
-
- Differentiate between magnitude and intensity of an earthquake. (2mks)
- State three precautions which can be taken against earthquake destruction? (3mks)
-
- Give two causes of Ocean currents (2mks)
- List three reasons why Oceans tend to heat more slowly than land masses. (3mks)
-
- What is humus (2mks)
- State three ways through which humus improve the quality of a soil. (3mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section.
- You are provided with a map of Kijabe East Africa 1: 50,000(KENYA) sheet 134/3, use it to answer the following questions.
-
- Give the six figure grid reference of the trigonometrical station (2610m) (2mks)
- What is the general flow of River Gatamaiyu (2mka)
-
- measure the length of Nairobi-naivasha railway to the west of easting 27and east of easting 24 give your answer in kilometers .( 2mks)
- Citing evidence from the map, identify three social services offered in the area covered by the map (6mks)
-
- Explain three physical factors favouring cattle rearing in the area covered by the map. (6mks)
- Identify three physical features found at grid square 2695 (3mks)
-
- On the graph paper provided draw a rectangle measuring 12cm by 8cm to represent the area bordered by Easting 26 and 29 and northing 94 and 96 (2mk)
- On it mark and label
- All weather road loose surface ( 1 mk)
- Power line ( 1 mk)
-
-
-
- State two processes of wind erosion in the desert areas (2mks)
- Give three reasons why wind action is effective in the hot deserts. (3mks)
- With aid of well labelled diagrams describe the formation of Yardangs. (7mks)
-
- State two factors that influence the transportation of materials in the desert by wind (2mks)
- Give three processes through which wind transport materials in desert (3mks)
- Name two features that are formed due to action of water in deserts. (2mks)
- Explain three positive effects of desert landforms to human activities (6mks)
-
-
-
- List two effects of horizontal earth movements (2mks)
- Give three causes of earth movements (3mks)
-
- Name and describe three types of plate tectonic boundaries (6mks)
- Name three types of folds (3mks)
- With aid of well labelled diagrams, describe the formation of fold mountains (7mks)
- State four significance of folding to the human and physical environment. (4mks)
-
-
- Define the following term;
- water table – (2mks)
- aquifer – (2 mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the occurrence of underground water.
- Nature of the rock (2mks)
- Gradient of the land (2mks)
- State four conditions that are necessary for the formation of an artesian well (4mk)
-
- Explain three conditions that are necessary for development of Karst Scenery (6mks)
- Give two reasons why there are few settlements in karst region (2mks)
- Students carried out a field study in a karst landscape.
- State two methods they would have used to record data (2mks)
- State three importance of studying a karst landscape through field work. (3mks)
- Define the following term;
-
-
- What is ice sheet (2mks)
- Explain the reason why there are no ice -sheets in Kenya (2mks)
- Describe the formation of a pyramidal peak. (5mks)
-
- Name three types of moraine (3mks)
- Explain four effects of glaciated features in upland areas. (8mks)
- Students from a school near Mt. Kenya were planning to carry out a field study on the glaciated features on the mountain
- Give three reasons why it would be difficult to undertake the field study on glaciated features on the mountain (3mks)
- Highlight two methods of collecting data they would have used (2mks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- What is a Land Breeze (2mks)
- Refers to a mass of cool air blowing from the land to the sea during the night 1x2 = 2mks
- Give three ways in which sea breeze influence the adjacent land. (3mks)
- It lowers the temperature of the adjacent land.
- It may increase rainfall
- It may increase relative humidity
- It moderates diurnal range of temperature
- It may lead to convectional rainfall. Any 3x1 = 3 marks
- What is a Land Breeze (2mks)
- State 5 characteristics of the mantle.
- It is composed of upper mantle and lower mantle.
- It has an average thickness of 2900 km
- It has a density of 3.0 – 3.3g/cm3
- The dominant mineral is olivine (ferrous magnesium silicate)
- It has a high temperature of about 40000c
- The rocks are in semi-molten state. Any 5x1= 5 marks
-
- Differentiate between magnitude and intensity of an earthquake. (2mks)
- Magnitude refers to the amount of energy given off by an earthquake while intensity refers to how hard or strong an earthquake shakes the ground.1x2=2marks
- State three precautions which can be taken against earthquake destruction?
- Avoiding settling in earthquake prone regions.
- Discouraging construction of high building and constructing earthquake resistant structures eg. Bridges
- Timely warning of the occurrences of an earthquake.
- Constructing dykes along the coast to prevent Tsunamis. Any 2x1 = 2mks
- Differentiate between magnitude and intensity of an earthquake. (2mks)
-
- Give two causes of Ocean currents (2mks)
- Winds
- Rotation of the earth
- Shape of the landmasses
- Temperature and water density
Any 2x1 = 2mks
- List three reasons why Oceans tend to heat more slowly than land masses. (3mks)
- Water surfaces reflect much light
- Water is mobile with circulating currents
- Large volume of water has to be heated deep / through penetration any 3x1= 3marks
- Give two causes of Ocean currents (2mks)
-
- What is humus (2mks)
- This is the black/dark brown thin layer on the top soil made of decomposed dead plants or animal materials /remains. 1X2 = 2mks
- State three ways through which humus improve the quality of a soil.
- It helps to improve soil texture, tilth and structure.
- It provides essential soil minerals from the decomposed plant matter.
- It enables the soil to retain moisture and prevents leaching of soil minerals salts.
- It facilitate aeration of the soil
- It is a source of food for micro- organisms in the soil. Any 3x1 =3mks
- What is humus (2mks)
-
-
- Give the six figure grid reference of the trigonometrical station (2610m) (2mks)
- 377939 or 378939 1x2 =2marks
- What is the general flow of River Gatamaiyu
- South Eastwards / North West to South East 1X2= (2mks)
- Give the six figure grid reference of the trigonometrical station (2610m) (2mks)
-
- Measure the length of Nairobi-Naivasha railway to the west of easting 27 and east of easting 24. Give your answer in kilometers. ( 2mks)
- 4.7km ± 0.1 km
- Citing evidence from the map, identify three social services offered in the area covered by the map (6mks)
- education services evidenced by many schools
- health /medical services evidenced by hospital and dispensary.
- Religious services evidenced by churches for example at grid square 3890.
- Water supply services evidenced by pump house at grid square 3198
- Security services evidenced by police station at grid square 3097.
- Services -any 3x1= 3mks
- Evidence -any 3x1= 3mks
N.B service can score alone but evidence cannot score alone.
- Measure the length of Nairobi-Naivasha railway to the west of easting 27 and east of easting 24. Give your answer in kilometers. ( 2mks)
-
- Explain three physical factors favouring cattle rearing in the area covered by the map. (6mks)
- Gentle slopes in the South Western side which offers suitable sites for the growth of pasture which forms food for cattle/ Gentle slopes also facilitate easy movement of cattle from one place to another.
- High rainfall evidenced by many permanent rivers which provide adequate drinking water for cattle.
- Cool temperatures evidenced by high altitude and forest. This provides ideal condition for dairy farming.
Any 3x2 = (6mks)
- Identify three physical features found at grid square 2695 (3mks)
- Scrub
- River
- River valley
- Gentle slope any 3x1 = (3 mks)
- Explain three physical factors favouring cattle rearing in the area covered by the map. (6mks)
-
- On the graph paper provided draw a rectangle measuring 12cm by 8cm to represent the area bordered by Easting 26 and Easting 29 and northing 94 and 96 (2mk)
- On it mark and label
- All weather road loose surface (1mk)
- Power line (1mk)
- On the graph paper provided draw a rectangle measuring 12cm by 8cm to represent the area bordered by Easting 26 and Easting 29 and northing 94 and 96 (2mk)
-
-
-
- State two processes of wind erosion in the desert areas ( 2mks)
- Abrasion
- Deflation
- Attrition Any 2x1= (2mks)
- Give three reasons why wind action is effective in the hot deserts. (3mks)
- The presence of loose unconsolidated dry masses of sand and gravel which are easily acted upon by wind.
- The occurrence of strong tropical storms within most hot deserts which move violently.
- Absence of vegetation cover since most hot deserts are bare. ( any 3x1= 3mks)
- With aid of well labelled diagrams describe the formation of Yardangs. (7mks)
- Vertical and alternating layers of resistant and less resistant rock outcrop lying parallel to the direction of the prevailing wind.
- Wind abrasion and deflation erode the soft rocks creating large furrows between the hard layers.
- Continued wind abrasion and deflation deepens the furrows leaving the hard layers standing out as ridges
- The ridges are called yardangs.
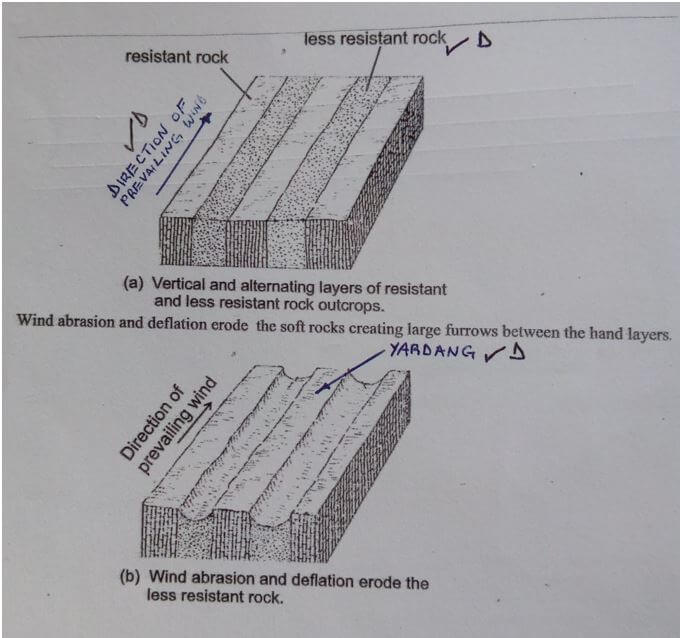
text - 4mks
diagrams - 3mks
(on wind, resistant and less resistant rock and yardangs. )
- State two processes of wind erosion in the desert areas ( 2mks)
-
- State two factors that influence the transportation of materials in the desert by wind (2mks)
- The speed and force of the wind
- Nature of the load
- Presence of obstacles reduce the speed of wind and force the wind to deposit some of the load
- Absence of vegetation cover. Any 2x1 = (2mks)
- Give three processes through which wind transport materials in desert (3mks)
- Saltation
- Suspension
- Surface creep 3x1 =3mks
- Name two features that are formed due to action of water in deserts. (2mks)
- Wadis
- Alluvial fans / bajadas
- Mesas and buttes
- Canyons
- Pediments
- Pediplanes
- Inselbergs Any 2x1 = (2mks)
- State two factors that influence the transportation of materials in the desert by wind (2mks)
- Explain three positive effects of desert landforms to human activities (6mks)
- Desert features like Zeugen, Yardangs and rock pedestals forms beautiful scenery that attract tourists earning a country foreign exchange.
- When loess is deposited in wet areas it forms fertile soils for agriculture.
- Extensive bare desert surfaces are used as testing, grounds for military weapons car and jet engines.
- Oasis found in some deflation hollows forms sources of water for irrigation, livestock or domestic use.
- Players and Salinas are economically used for salt production.
Any 3x2= (6mks)
-
-
-
- List two effects of horizontal earth movements
- Stretching the rocks of the earth crust
- Shortening of the rocks of the earth crust
- Shearing of the rocks of the crust Any 2x1= (2mks)
- Give three causes of earth movements
- Movement of magma within the crust
- Gravitative pressure
- Convectional current in the mantle
- Isostatic adjustment Any 3x1= (3mks)
- List two effects of horizontal earth movements
-
- Name and describe three types of plate tectonic boundaries (6mks)
- Constructive / extensional /divergent boundary – The plates move away from each other creating a new crust known as extension boundary.
- Destructive / compressional/ convergent boundary- The plates move towards each other due to convectional current and as they move they may collide with each other forming compressional boundary.
- Transform / conservative boundary -The plates moves past each other due to convectional current such that no new materials are added or lost.
Naming 3x1= (3mks)
Describing 3x1= (3mks)
N.B: name can score alone without description, but description cannot score alone
- Name three types of folds (3mks)
- Simple symmetrical fold
- Asymmetrical folds
- Isoclinal folds
- Overthrust folds
- Over fold
- Recumbent
- Synclinorium anticlinorium complex Any 3x1 = (3mks)
- Name and describe three types of plate tectonic boundaries (6mks)
- With aid of well labelled diagrams, describe the formation of fold mountains (7mks)
- A wide shallow depression called geosyncline is formed on the earth surface due to earth movement
- The geosyncline gets filled up with water forming a sea.
- Weathering and erosion occurs in the surrounding highlands.
- The sediments are deposited on the seabed forming thick layers.
- The weight of the sediments causes subsidence/ sinking of the geosyncline and accumulation of more sediments which triggers compressional forces.
- he layers of sediments are subjected to compressional forces which causes them to fold,these folds forms thefold mountains.
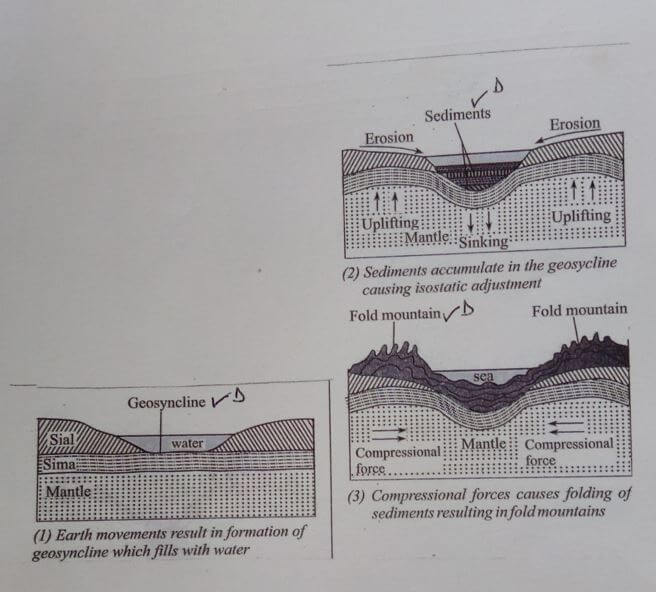
Text 4mks
Diagram 3mks
- State four significance of folding to the human and physical environment. (4mks)
- Fold mountains landscape provides a unique scenery that attract tourist.
- Fold mountains forms barriers to transport and communication.
- Folding process brings minerals to the surface facilitating easy extraction.
- Warmer slopes of fold mountains encourage settlement and agriculture.
- Heavy rainfall received on windward slopes of fold mountains support agriculture.
- Cold descending winds on fold mountains cause harm to crops Any 1x4= (4mks)
-
-
- Define the following term;
- water table – It is the upper level of the zone of saturation of water in permeable rocks which keep on fluctuating (2mks)
- aquifer – It is a permanently saturated rock which can hold water in its mass that is found between layers of impermeable rocks (2mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the occurrence of underground water.
- Nature of the rock (2mks)
rock with pores/cracks allow more infiltration to occur. ( 1x2=2 marks) - Gradient of the land (2mks)
Flat areas like plains give water time to infiltrate as water remain stagnant for a long time.
Steep slopes will allow a lot of surface run off hence less infiltration (Any 1x2 ( 2mks)
- Nature of the rock (2mks)
- State four conditions that are necessary for the formation of an artesian well (4mk)
- An aquifer must be sandwiched between two layers of impermeable rocks so as to retain water
- One or both ends of the aquifer must be exposed in a region which has high rainfall.
- The aquifer must be syncline to ensure that the water has sufficient pressure to flow out naturally.
- The aquifer must be of the same permeable material.
- The mouth of the well must be lower than the water intake area for water to flow out naturally by hydraulic pressure.
- The artesian well must be sunk to reach below the water table in the permeable rock for it to have water permanently. Any 4x1 = (4mks)
-
- Explain three conditions that are necessary for the development of Karst Scenery
- Presence of thick limestone or dolomite or chalk which consist of calcium carbonate to react with rainwater for carbonation and solution process to take place.
- The rocks should be hard and well jointed to allow water to percolate along the joints for carbonation process to take place.
- Presence of a hot humid climate with moderate rainfall to facilitate chemical weathering.
- The water table should be deep far below limestone rock surface to allow the formation of Karst features. Any 3x2 = (6mks)
- Give two reasons why there are few settlements in the Karst region (2mks)
- Limestone region are covered with thin soils which limit agriculture.
- The areas are rocky hence unsuitable for human activities.
- The areas have rugged surfaces which are unsuitable for human settlement.
- Karst regions have poor vegetation cover.
- There is inadequate water supply since most of the water sinks underground.
Any 2x1 = (2mks)
- Explain three conditions that are necessary for the development of Karst Scenery
- Students carried out a field study in a karst landscape.
- State two methods they would have used to record data (2mks)
- Photographing / film /video taking
- Writing notes /taking notes.
- Drawing sketches /diagrams ( any 2x1= 2mks)
- State three importance of studying a karst landscape through field work. (3mks)
- It gives first hand information.
- It makes learning real and interesting
- It enhances visual memory
- It helps the students to apply the knowledge learnt in classroom.
- It helps students to develop manipulative skills of observation and recording data.
Any 3x1= (3mks)
- State two methods they would have used to record data (2mks)
- Define the following term;
-
-
- What is an ice sheet (2mks)
- An ice sheet is a large continuous mass of ice which covers extensive areas of lowland.
1x2 = (2mks)
- An ice sheet is a large continuous mass of ice which covers extensive areas of lowland.
- Explain the reason why there are no ice -sheets in Kenya (2mks)
- Kenya is located within the tropics where the temperatures are high discouraging formation of ice sheets. 1x2= (2mks)
- What is an ice sheet (2mks)
- Describe the formation of a pyramidal peak. (5mks)
- Ice accumulates in several pre-existing shallow depression on a mountain side.
- Nivation and abrasion make the depression deeper.
- The sides of the two depressions are eroded through plucking making them wider.
- The back walls are eroded through plucking which makes them retreat.
- The processes form several adjacent cirques around the mountain sides.
- Back walls of adjacent cirques continue to be eroded eventually resulting in the cirques being separated by narrow steep ridges called aretes.
- * Where Several aretes converge at the top of the mountain, a steep sided peak is formed.
- This peak is called pyramidal peak.
Any 5x1 = (5mks)
NB. The point on * must be mentioned to score maximum marks. (5mks)
-
- Name three types of moraine (3mks)
- Terminal moraine
- Lateral moraine
- Medial moraine
- Ground/subglacial moraine
- Recessional moraine
- Englacial moraine Any 3x1 = (3mks)
- Explain four effects of glaciated features in upland areas. (8mks)
- Glacial upland areas form beautiful features such as pyramidal peaks which attract tourists
- Glaciated mountains encourage the growth of forests which encourage lumbering supporting the building industry
- Water falls formed in glaciated uplands provide suitable sites for hydroelectric power production which is used in industries and domestic use.
- Corrie lakes / tarns offer suitable areas for fishing
- U-shaped glacial valley, form natural route ways where roads and railways are well- sheltered natural harbours as well as rich fishing grounds promoting fishing industries
- Melt water on glaciated mountain form sources of rivers that provide water for industrial, domestic and agricultural use. Any 4x2= (8mks)
- Name three types of moraine (3mks)
- Students from a school near Mt. Kenya were planning to carry out a field study on the glaciated features on the mountain
- Give three reasons why it would be difficult to undertake the field study on glaciated features on the mountain
- Inaccessibility of some features due to the rugged terrain
- Heavy rainfall and extreme low temperature would hinder their activities.
- Thick vegetation in the lower slopes may hinder their movement.
- Attacks from wild animals may make it difficult to access the area. Any 3x1 = (3mks)
- Highlight three methods of collecting data they would have used (3mks)
- Taking photographs/video/films
- Observation
- Counting
- Measuring
Any 3 x1 = (3mks)
- Give three reasons why it would be difficult to undertake the field study on glaciated features on the mountain
-

CONIFIDENTIAL
PROVIDE A MAP OF KIJABE EAST AFRICA 1:50,000 SHEET 134/3
PROVIDE A GRAPH PAPER.
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions, Answers and Confidential - Mathioya Mock 2021 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

