QUESTIONS
-
- The table below shows the ions of elements W, X, Y, Z, and their electron arrangement.
The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the element.
Ion Electron configuration W- 2.8.8 X2+ 2.8.8 Y3+ 2.8 Z2- 2.8 - Which two elements belong to the same period? Give a reason. (2 marks)
- In which group of the periodic table does Y belong? (1 mark)
- Write the formula of the compound formed between W and X (1 mark)
- What type of bond is formed between W and X. Explain. (2 marks)
-
- What is a coordinate bond? (1 mark)
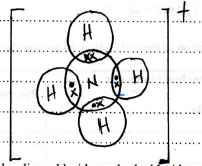
- Draw a dot (•) cross (×) diagram to show bonding in the Ammonium ion (NH4+)
(N = 7, H = 1) (2 marks)
- Aluminum chloride and sodium chloride are both chlorides of period 3 elements.
Use this information to explain the following observations.- A solution of A1CI3 in water turns blue litmus paper red while that of sodium chloride does not (1 mark)
- The melting point of sodium chloride (801°C) is higher than that of AlC13 (180°C). (1 mark)
- The table below shows the ions of elements W, X, Y, Z, and their electron arrangement.
-
- Give the names of the following compounds:
- CH3COOCH2CH3 (1 mark)
- CH3CHCHCH2CH3 (1 mark)
- Study the information in the table below ad answer the questions that follow.
No. of carbon atoms per molecule Relative molecular mass of hydrogen 2 28 3 42 4 56 - Write the general formula of the hydrocarbons in the table. (1 mark)
- Predict the relative molecular mass of the hydrocarbon with 5 carbon atoms. (1 mark)
- Determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon in ii) above and draw its structural formula. (2 marks)
- Study the scheme given below and answer questions that follow.
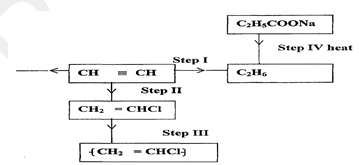
- Name the reagent used in
Step I (1 mark)
Step II (1 mark)
Step III (1 mark) - Write an equation for complete combustion of CH CH (1 mark)
- Explain one disadvantage of the continued use of items in step III. (1 mark)
- Name the reagent used in
- Give the names of the following compounds:
-
- The solubilities of potassium nitrate and potassium bromide at different temperatures was determined. The following data was obtained.
Temperature ºC 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Solubility
g/100g H2OKNO3 5 15 26 43 61 83 105 135 165 KBr 50 55 60 65 70 77 85 90 95 - Plot a graph of solubility against temperature for both salts on the same axis (3 marks)
- What was the solubility of each salt at 65ºC (1 mark)
- 100g of a saturated solution of potassium nitrate at 70ºC was cooled to 20ºC. What mass of the salt will be crystallized? (2 marks)
- Plot a graph of solubility against temperature for both salts on the same axis (3 marks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
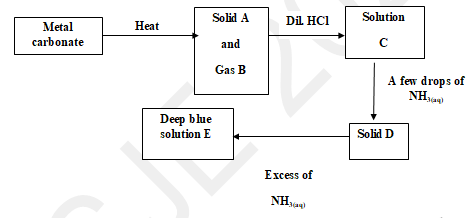
- Write an equation for the formation of solid A and gas B. (1 mark)
- Name:
Solution C …………………………………………………………...…… (1 mark)
Solid D ………………………………………………………….………… (1 mark)
- Write the formula of the complex ion in solution E. (1 mark)
- The solubilities of potassium nitrate and potassium bromide at different temperatures was determined. The following data was obtained.
-
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
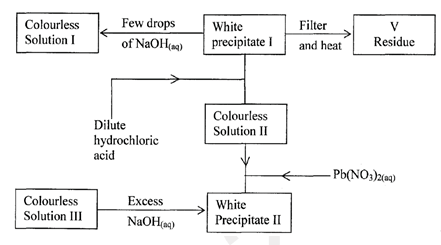 Residue V was yellow when hot and white when cold. Identify:
Residue V was yellow when hot and white when cold. Identify:- White precipitate I. (1 mark)
- Solution II. (1 mark)
- Residue V. (1 mark)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction of solution II with Pb(NO3)2 (aq) (1 mark)
- Write observations that would be made when ammonia solution is added drop-wise till in excess to the colourless solution II (l mark)
- The diagram below represents a set-up for large scale manufacture hydrochloric acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
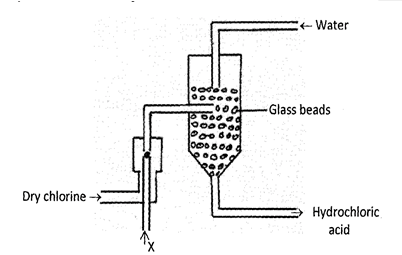
- Name substance X. (1 mark)
- What is the purpose of glass beads? (1 mark)
- Give one source of substance X used in the above process. (1 mark)
- Give two uses of hydrochloric acid. (2 marks)
- The table below shows the ammeter readings obtained when two different electrolytes the same concentration was tested.
Why does Ethanoic acid give a lower ammeter reading? Explain your answer (2 marks)Electrolyte Ammeter reading (Amps) Hydrochloric acid 4.0 Ethanoic acid 1.2
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- The figure below shows parts of Le’Clanche cell (dry cell).
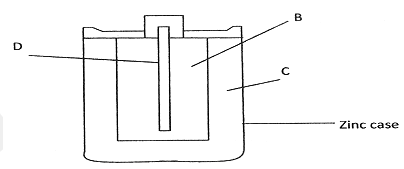
- Name:
- Substance D (1 mark)
- Mixture B (1 mark)
- Electrolyte C (1 mark)
- In the cell, the electrolyte is a paste. Explain. (1 mark)
- The following reaction occurs when the cell is in use.
Zn(s) + 2NH4+(aq) →MnO2 → Zn2+(aq) + 2NH3(aq)+ H2O(l)
Given that:
Zn2+(aq) + 2e- → Zn(s) EФ = -0.76V
2NH+(aq) + 2e- →MnO2→ 2NH3(g) + H2O(l) EФ = +0.74V
Calculate the e.m.f. of the cell. (2 marks) - Use the standard reduction electrode potentials given below to answer the questions that follow.
Zn2+(aq) + 2e- → Zn(s) EФ = -0.76V
Pb2+(aq) + 2e- → Pb(s) EФ = -0.13V
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) EФ = +0.34V
Ag2+(aq) + 2e- → Ag(s) EФEФ = +0.80V
The metal copper, zinc, silver and lead were placed in different solutions as shown:
Metal Metal ion Reaction / No reaction Cu Ag2+(aq) Zn Cu2+(aq) Ag Pb2+(aq) Pb Zn2+(aq) - Indicate in the table with a tick (√) where a reaction occurs and a cross (×) where no reaction occurs. (2 marks)
- Identify the strongest reducing agent. (1 mark)
-
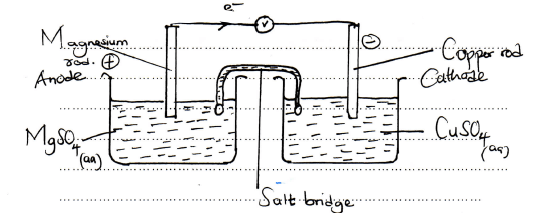
- Draw a well labeled diagram of the electrochemical cell when copper and magnesium half cells are connected. (3 marks)
- On the diagram you have drawn in e i) above, label the anode and the cathode and show the direction of flow of electrons. (2 marks)
- Name:
-
- The set up below is used to prepare nitric acid
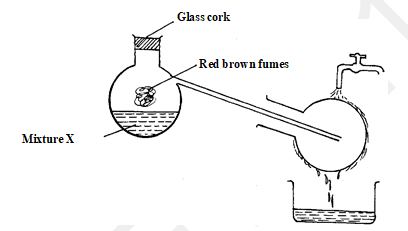
- Name the reagents in mixture X (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in the glass retort (1 mark)
- Explain the reason why the apparatus used is all glass and why heating should be gentle as possible. (2 marks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
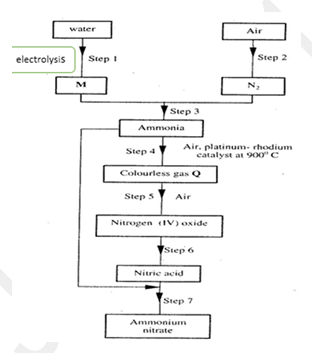
- Name element M. (l mark)
- Why is it necessary to use excess air in step 4? (1 mark)
- Identify gas Q (l mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction in step 7 (l mark)
- Give one use of ammonium nitrate. (l mark)
- Ammonia can be formed by the reaction shown below
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) ; ∆H = - 92kJ/mol
State and explain what happens if:- The volume of the system is increased (1 mark)
- Cold water is poured over the system (1 mark)
- The set up below is used to prepare nitric acid
- In an experiment to determine the heat of combustion of compound X, a pupil used heat from the burning compound of X to heat 100cm3 of water in a beaker. He obtained the following results:
Volume of water in the beaker = 100cm3
Initial temperature of water = 17ºC
Final temperature of water = 42ºC
Initial mass of burner + compound X = 10.5g
Final mass of burner + compound X = 10.2g.- Determine the mass of the compound burnt? (1 mark)
- Calculate the rise in temperature? (1 mark)
- Determine the amount of heat produced by the compound (2 marks)
(specific heat capacity 4200Jg-1K-1, density of H2O = 1g/cm3) - Calculate the molar heat of combustions of compound X (2 marks)
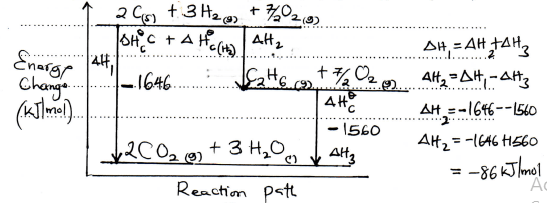
(R.M.M. of X = 256) - Use the following thermochemical equations below to answer the questions that follow.
C2H6(g) + 7/2O2(g) → 2CO2(g)+ 3H2O (s) ∆H1, = -1560kJmol-1
C (graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ∆H2 = - 394 kJ mol-1
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) ∆H3 = - 286 kJ mol-1- Calculate the molar enthalpy of combustion of C2H6. (2 marks)
- Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction represented by the first equation above (3 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- W and Y
Have three energy levels; - Group III
- XW2
- Ionic bond;
There is complete transfer of 2 electrons from X to W
- W and Y
-
- Type of bond in which the shared pair of electrons forming the bond is contibuted by only one of the atoms forming the bond
-
-
- AlCl3 is hydrolised in water to form HCl and Al(OH)3, while NaCl is not hydrated; HCl is acidic
- NaCl has a giant ionic structure with stronger ionic bonds while AlCl3 has simple udecular structure with weaker intermolecular forces
-
-
-
- Ethylethanoate
- Pent-2-ene
-
- CnH2n
- 70
- CH3CH2CH2CHCH2
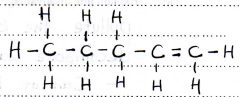
-
- Hydrogen
Hydrogen Chloride
Chloroethene - 2C2H2(g) + 5O2(g) 4CO2(g) + 2H2O(I)
- Pollute the environment as they do not decompose easily (They are non-biodegradable) - cannot be digested by microorganisms
- Hydrogen
-
-
-
-
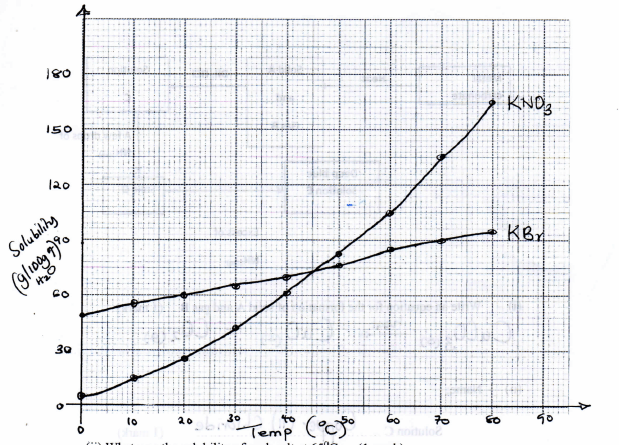
- KBr - 87g/100g of H2O
KNO3 - 120g/100g of H2O - 70ºC → 135g (135-26)g
20ºC → 26g = 109g
-
-
- CuCO3(s) → CuO(s) + CO2(g)
- Copper(II) Chloride
Copper(II) hydroxide
-
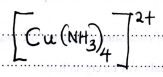
-
-
-
-
- Zinc hydroxide, Zn(OH)2
- ZnCl2
- ZnO
- Pb2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → PbCl2(s)
- White precipitate that dissolves in excess NH3(aq) to form a colourless solution
-
-
- Dry Hydrogen gas
- Increase surface area over which HCl gas dissolves in water
- Cracking of long chain hydrocarbons;
Reacting uethane gas with steam; - Sewage treatment;
Treatment of water
Removing rust from metal;
Making dyes, drugs & photographic materials
- Ethanoic acid is a weak acid;
It dissociates partially to yield few ions hence low ammeter reading
-
-
-
- Carbon(graphite) rod
- Powdered carbon and maganese(iv) oxide
- Ammonium chloride and zinc chloride paste
- Solid NH4Cl is a poor electrolyte (no free ions)
- Eθcell = ERed - Eoxi
= {(0.76) - (-0.76)}
0.74 + 0.76
= +1.5V -
-
Metal Metal ion Reaction / No reaction Cu Ag2+(aq) √ Zn Cu2+(aq) √ Ag Pb2+(aq) X Pb Zn2+(aq) X - Zn
-
-
-
-
-
- Potassium nitrate
Conc sulphuric(vi) acid - KNO3(s) + H2SO4(I) → KHSO4(aq) + HNO3(aq)
- HNO3 attacks rubber and cork connections;
Heating should be gentle to minimize thermal decomposition of HNO3
- Potassium nitrate
-
- Hydrogen
- To ensure all ammonia is converted to nitrogen(II) oxide
- NO, nitrogen(II) oxide
- HNO3(aq) + NH3(aq) → NH4NO3(aq)
- As a nitrogenous fertilizer
-
- Pressure decreases and less ammonia yield i.e equilibrium shifts to the left hand side
- More yield of Ammonia which is favored by decrease in temperature
-
-
-
- 10.5 - 10.2 = 0.3g
- (42 - 17)ºC
= 25ºC - ΔH = MCT
= 100 x 4200 x 25
= 1.05 x 107J - Moles = Mass/RMM
= 0.3/256 = 0.001171moles
0.001171 - 1.05 x 107J
1.07 x 107 = -8.96 x 109Jmol
0.001171
-
- 2C(s) + 3H2(g) C2H6(g)
2CO2(g) + 3H2O
Hf = 2(-394) + 3(-286) - (-1560)
= -1646 + 1560
= -86kJ/mol -
- 2C(s) + 3H2(g) C2H6(g)
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Bondo Mocks 2021 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students