Questions
Instructions
- This paper consists of two sections, section I and II. Answer all the questions in both sections.
- Mathematical tables and silent non – programmable calculators may be used.
Section I (25 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section
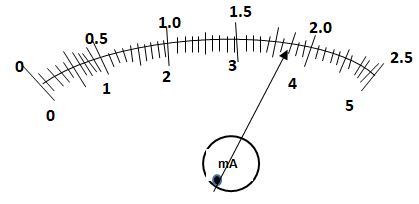
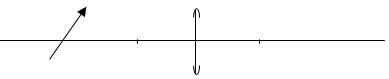
- What is the reading shown by the pointer in the figure below, if the full scale range is;
- 0 - 2.5 (1 mark)
- 0 – 5 (1 mark)
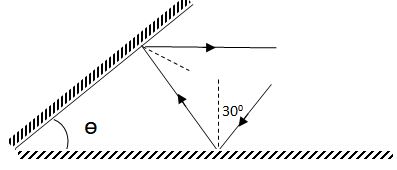
- The following diagram shows two mirrors inclined at an angle to each other. A ray of light is incident on one of the mirrors and finally reflected from the second mirror parallel to the first mirror find the angle between the mirrors. (2 marks)
- It is not possible to charge an electroscope by contact method using a metal rod. Explain (2 marks)
- A car battery is rated 40 Ah and it is expected to supply a constant current for 120 minutes.
- What is the strength of the current delivered? (2 marks)
- Explain why eight dry cells in series cannot be used to start a car engine even though they have the same e.m.f. (1 mark)
- A coil of insulated wire is wound around a u – shaped soft iron core X Y and connected to a battery as shown below.
State the polarities of the ends X and Y. (2 marks)
X ……………………………………
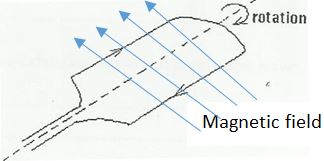
Y…………………………………… - The figure below shows a coil carrying a current flowing in the direction shown in a magnetic field.
On the same diagram draw the magnetic field lines across the coil. (1 mark) - An object of height 5 cm is placed 25 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. determine the image distance and hence state the nature of the image formed. (3 marks)
- Loudspeaker placed between two wall A and B is sending out constant wave pulses. Determine how far the loudspeaker is from wall B if it is 100m from wall A, and the time between the two echoes received is o.2 seconds (speed of sound is 340m/s) (3 marks)
- The following table shows part of the electromagnetic wave spectrum.
Ultraviolet rays Microwaves X-rays Visible light - On the right column of the table, arrange the waves in the order of decreasing energy. (1 marks)
- Give an application of each of the following electromagnetic waves. (2 marks)
- Ultraviolet rays:
- Microwaves:
- A 4 resistor is connected in series to a battery of e.m.f 6V and negligible internal resistance. Determine the power dissipated by the resistor. (2 marks)
- State any two laboratory safety rules that deal with electrical safety in the lab. (2 marks)
Section II (55 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section.
-
- Define term focal length as used in thin lenses (1 mark)
- Give the functions of the following parts of a lens camera. (3 marks)
- Shutter: …………………………………………………………………………………...
- Film: ………………………………………………………………………………………
- Diaphragm: …………………………………………………………………………………
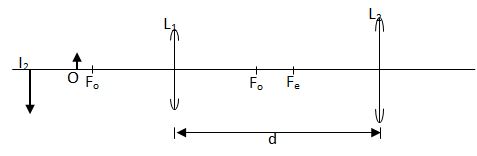
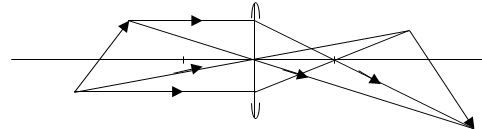
- A compound microscope with objective lens L1 of focal length 0.8cm and an eyepiece lens L2 of focal length 2.5cm is shown in figure below. An object O is placed in front of the objective lens at a distance u1 of 1.2cm. The system forms a final image I2 at a distance of 10cm from L2. Determine the distance of separation of lenses L1 and L2. (4 marks)
- The figure below (figure 9) shows an object placed in front of a convex lens. Complete the ray diagram to show the position of the image. (3 marks)
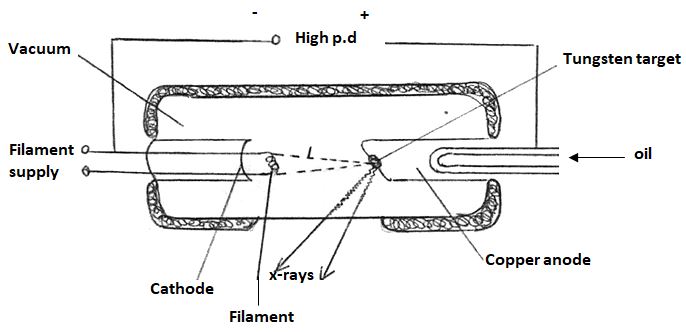
- The figure below shows the features of an X-ray tube
-
- What is the purpose of the oil going in and out of the anode (1mk)
- State the property of tungsten that makes it suitable as a target (1mk)
- An X-ray tube operates with a potential difference of 100kv and filament current is 20mA. Calculate;
- The power transferred to the target of X-ray tube (2mks)
- The number of electrons hitting the target per second (2mks)
- The maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons (Take charge of an electron=1.6x10-19C, mass of an electron =9.1x10-31kg) (2mks)
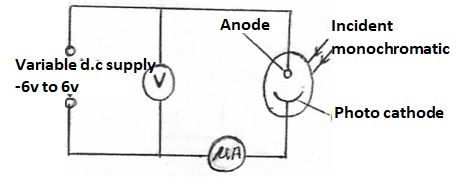
- The diagram shows monochromatic radiation falling on a photocell connected to a circuit
The incident radiation has a wavelength of 2.15x10-7m. The metal surface of the photocell has a work function of 2.26 eV.- Calculate the energy in eV of a photon of the incident radiation (Take c=3.0x108m/s, h=6.63x10-34Js and e=1.6x10-19C) (3mks)
- What is the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons (2mks)
- Write down the value of the stopping potential (1mk)
-
-
- State Snell’s law (1 mark)
- A student prepares to swim to the bottom of a pool to pick a coin on the bed. It is only while under the water that she realizes the presence of a sharp object beside the coin that she had not seen. Explain a possible reason why it was not visible in clear swimming pool water. (1 mark)
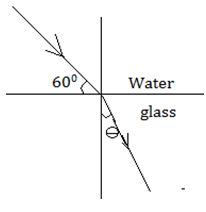
- The figure below shows a ray of light travelling
- Calculate the refractive index of water with respect to glass given the refractive index of glass and water are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. (2 marks)
- Calculate the angle Ɵ (2 marks)
- Using a well-labeled diagram, describe how optic fibers are used for communication. (3 marks)
-
- Define the term capacitance. (1 mark)
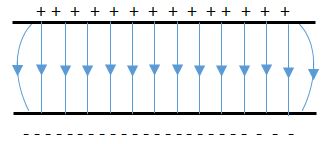
- The figure below shows two charged plates close to each other
- Complete the diagram to show the electric field patterns between the plates (1 mark)
- Without changing the area of overlap, suggest any two ways of increasing the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor. (2 marks)
- You have been provided with THREE identical capacitors each of capacitance 12 F. State and show how you would combine them to get the following effective capacitance
- 36µF (2marks)
- 4µF (2marks)
- 8µF (2marks)
-
-
- The following nuclear reaction is part of a radioactive series
- Name the radiation represented by r and s (1mk)
- Determine the number represented by x and y (1mk)
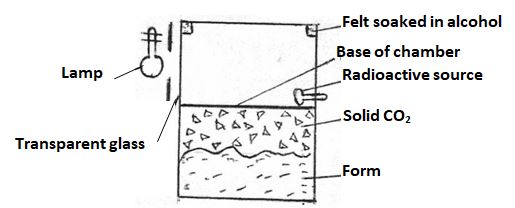
- The figure below shows the features of diffusion cloud chamber used for detecting radiations from radioactive sources
- State the property of alcohol that makes it suitable for use in the chamber (1mk)
- What is the purpose of the solid CO2? (1mk)
- Explain how the radiation from the radioactive source is detected in the chamber. (2mks)
- State one advantage of the cold chamber over a charged gold leaf electroscope when used as detectors of radiation (1mk)
- The following nuclear reaction is part of a radioactive series
- The graph below shows how the activity of a sample of the radioisotope technetium which is used extensively in medicine, varies with time
- Use the graph to determine the half-life. T ½ of technetium (1mk)
- Hence calculate the decay constant for technetium given that T½ = 0.6931/λ where λ is the decay constant. (1mk)
- Determine the number of technetium atoms remaining in the sample after 24 hours (1mk)
-
Marking Scheme
Section I
-
- 1.85 mA
- 3.7 mA
-
- metal is a good conductor of charges
- causes earthing of the electroscope
-
- Q = It
40 = I x 120/60
I = 20 A - Increased internal resistance by combining cells in series, leads to insufficient current to start the car engine
- Q = It
- X – North
Y – South -
- 1/f = 1/u + 1/v
-1/15 = 1/25 + 1/v
v= -9.375
image is virtual - t2 - t1 = 0.25
t1 = 2d/v = 2 x 100/340
= 0.588 S
2d /v =0.588+0.2
2d/340 =0.788 s
d=133.96 -
-
Ultraviolet rays X- rays Microwaves UV - rays X-rays Visible light Visible light microwaves -
- Ultraviolet rays: detect forgeries, mineral analysis, vitamin D etc
- Microwaves: cooking, communication
-
- P = V2/R
62/4 = 9 W -
- do no insert foreign objects in sockets
- Do not handle electrical apparatus with wet hands
- Ensure all electrical switches are turned off when not in use.
-
- is the plane perpendicular to principal axis that passes through the principal focus
-
- Shutter: controls the exposure of the film to light
- Film: captures and records the image
- Diaphragm: controls the amount of light entering the camera
- For the first image 1/v=1/f-1/u =1/0.8-1/1.2 therefore v=2.4cm
1/(d-2.4)=1/2.5-1/10 d-2.4=3.33 d=5.733 -
-
-
- It is used to cool the anode by conducting heat away
- Has a high melting point
-
- P = I X V
= 20X 10-3 X 100,000
= 2000W - I= nxe
n= I/e
= 20x103/1.6x10-19
= 1,25 x1017 - eV = KE
=1.6 x 10-19 x 100000
= 1.6 x 10-14 J
- P = I X V
- Energy = hc/λ
6.63 x 10³⁴ x 3.0 x 108
2.15 x 10-7
= 9.251 x 10-19
=5.782eV
-
-
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for given pair of media
- Due to total internal reflection
-
- 1n3 = 1n2 x 2n3
3/2=4/3×2n3
2n3 = 3/2×3/4= 9/8=1.125 - n=sini/sinr
1.125=sin40/sinr
sin r= sin40°/1.125
∴r=26.39
- 1n3 = 1n2 x 2n3
- Through successive total internal reflection
-
- Charge stored per unit volt.
-
-
-
- Decreasing the distance between the two plates
- Using a dielectric material of higher dielectric constant
-
-
- capacitors arranged in parallel
Ceff=C1 + C2 + C3
=12μF+12μF+12μF
=36μF - Capacitors in series and parallel
1/Ceff =1/C1 +1/C2 +1/C3
= 1/12 + 1/12 + 1/12
= 1/4
∴Ceff=4μF - Combining series and parallel
Parallel
C = 12 + 12 = 24µF
Series
1/C=1/24+1/12
=1/8
∴C=8μ F
- capacitors arranged in parallel
-
-
-
- r- beta
s- alpha - x…83……….
y…82……
- r- beta
-
- volatile
- Lowers the temperature in the chamber until is super saturated
- Radiation ionizes air inside the chamber alcohol droplets form on the air ions produced by the radiation forming white tracks
- the type of radiation can be detected , i.e can identify the nature of radiation
-
-
- 6 hours
- 0.1155m
- 4 x 106
-
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Asumbi Girls High School KCSE Mock 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students