Questions
Instructions to candidates
- This paper consists of TWO Sections: A and B.
- Answer ALL the questions in section A and B in the spaces provided.
- All working MUST be clearly shown.
- KNEC mathematical tables and silent non-programmable electronic calculators may be used.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English
Section A (25 marks)
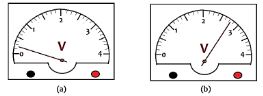
- The fig. 1 below shows a voltmeter before and after use to take the emf of a cell.
Record the value of emf of the cell. (2 marks) - The chart below shows an arrangement of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Radiowave A B Visible light C D Gamma rays - Name the radiation represented by C. (1 mark)
- Name a device that can be used to detect radiation A. (1 mark)
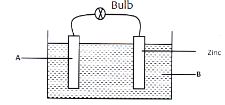
- Figure 2 below shows a set-up of a simple cell.
- Name the material used in part A (1 marks)
- Name the electrolyte B. (1 mark)
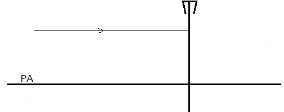
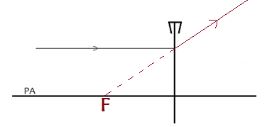
- The fig. 3 below shows a ray incident to a concave lens.
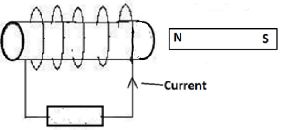
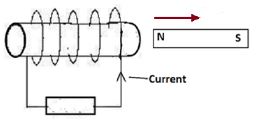
Draw on the diagram to show the resulting ray. (1mark) - The figure 4 below shows a magnet and a solenoid in relative motion.
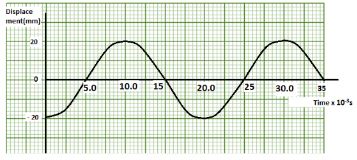
If the current shown was induced current indicate the motion of the magnet. (1mark) - Figure 5 represents a displacement – time graph for a wave.
Determined the frequency of the wave. (2marks) - State the reasons for the following in the filament bulb:
- Inside is filled with inert gas at low pressure. (1 mark)
- The filament is coiled. (1 mark)
- A girl standing at a distance claps her hands and hears an echo from a tall building 2 seconds later. If the speed of sound in air is 340m/s, determine how far the building is. (3marks)
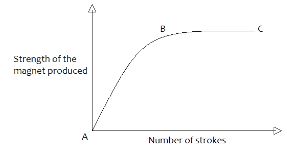
- In an experiment to magnetize an iron bar by single stroke method, the graph below was plotted.
Explain what is happening between points AB and BC. (2marks) - State two ways of confirming that an accumulator is fully charged. (2marks)
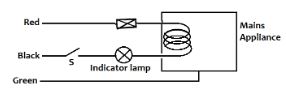
- The fig. 6 below shows an electrical appliance with leads labelled Red, Black and Green.
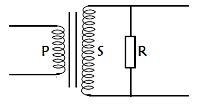
Identify one mistake in the connection. (1 mark) - Figure 7 below shows a perfectly efficient transformer. The number of turns in the secondary coil S is six times that of the primary coil P.
If a supply voltage of 4V d.c is connected across P, state with reason what happens to the voltage across R (2 marks). - Explain what is meant by radioactive decay. ( 1 mark)
- A part from the field, state two ways of increasing the magnitude of current generated. (2 marks)
- State one structural difference between a.c and d.c generators. (1 mark)
Section B (55 marks)
-
- State one application of each of the following. (2marks)
- Convex mirror
- Parabolic mirror
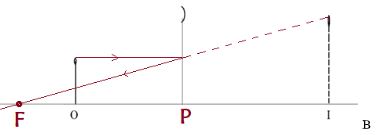
- Fig. 9, which is drawn to a scale of 1:5, represents an object O and its image ‘I’ formed by a concave mirror.
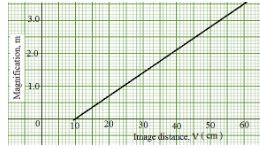
By drawing suitable rays, locate and mark on the figure the position of the principal focus ‘F’ of the mirror. Determine the focal length f. (3 marks) - The graph in Fig. 10 shows the variation of magnification, M with image distance, V for a concave mirror.
Determine:- The object position when the image position is 45cm. (3marks)
- The focal length of the mirror. (1mark)
- state two reasons why a concave mirror is used as a doctor’s dental mirror. (2 marks)
- State one application of each of the following. (2marks)
-
- State two factors that determine the capacitance of a parallel place capacitor. (2marks)
- A 5μF capacitor is charged to a potential difference of 200V and isolated. It is then connected to a 10μf capacitor.
Find ;- The resultant potential difference across the combination (3marks)
- Energy stored before connection (3marks)
- Total energy in the capacitors after connection. (2marks)
- Give two applications of capacitors (2 marks)
-
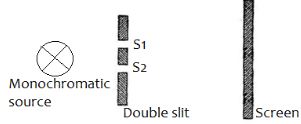
- In an experiment to observe interference of light waves a double slit is placed close to the source. See figure 12
- What is a monochromatic source of light. (1 mark)
- State the function of the double slit ( 1 mark)
- Describe what is observed on the screen ( 1marks)
- State what is observed on the screen when
- The slit separation S1S2 is reduced ( 1 mark)
- White light source is used in place of monochromatic source ( 1 mark)
- During physics lesson, the teacher noticed that Joe had to sit behind in order to see the writings on the board clearly.
- Name the eye defect experienced by Joe. (1 mark)
- State one possible cause of the defect. (1 mark)
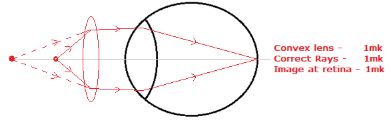
- On the diagram in fig 11 below, draw to show how the defect can be corrected by use of a lens. (3 marks)
- In an experiment to observe interference of light waves a double slit is placed close to the source. See figure 12
-
- Distinguish between an ohmic and non-ohmic conductors. (1 mark)
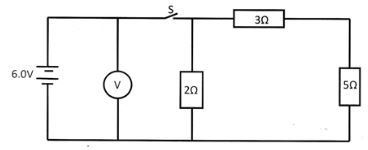
- Figure 16 shows a circuit with resistors and voltmeter connected to a battery
- If each cell has an internal resistance of 0.7Ω, determine the total resistance in the circuit. (3 marks)
- Calculate the value of current flowing through the 3Ω resistor when the switch is closed? (2 marks)
- What is the reading of the voltmeter when the switch S is
- Open (1 mark)
- Closed (3 mark)
- Account for the difference between the answers in (I) and (II) above (1 mark)
-
- The figure below shows a waveform on a CRO screen: Given that the Y-gain control is set at 20 V/cm and the time-base set to 10 ms/ cm,
Calculate the:- Periodic time of the wave. ( 2 marks)
- Frequency of the wave. ( 2 marks )
- Peak voltage (2 marks)
- Calculate the frequency of X-rays produced by an X-ray tube operating at 20 kV, assuming that no energy is dissipated as heat. (Planck’s constant h = 6.63 x10-34 Js, and the electronic charge is 1.6 x10-19 C) (3 marks)
- Calculate the energy of photons associated with radiation of frequency 4.8 × 1014 Hz, stating your answer in eV (3 marks)
- The figure below shows a waveform on a CRO screen: Given that the Y-gain control is set at 20 V/cm and the time-base set to 10 ms/ cm,
Marking Scheme
- The fig. 1 below shows a voltmeter before and after use to take the emf of a cell.
Record the value of emf of the cell. (2 marks)- Accuracy = 1.0V/8 = 0.125V
Error = +0.125 x 2 = 0.25V
Reading = 2.75V
emf = 2.75 - 0.25 = 2.50V
- Accuracy = 1.0V/8 = 0.125V
- The chart below shows an arrangement of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Name the radiation represented by C. (1 mark)
- Ultraviolet √
- Name a device that can be used to detect radiation A. (1 mark)
- Thermistor / Bolometer √
- Name the radiation represented by C. (1 mark)
- Figure 2 below shows a set-up of a simple cell.
- Name the material used in part A (1 marks)
- Copper √
- Name the electrolyte B. (1 mark)
- Dilute √ sulphuric acid
- Name the material used in part A (1 marks)
- The fig. 3 below shows a ray incident to a concave lens.
Draw on the diagram to show the resulting ray. (1mark) -
- The figure 4 below shows a magnet and a solenoid in relative motion.
If the current shown was induced current indicate the motion of the magnet. (1mark)
-
- Figure 5 represents a displacement – time graph for a wave.
Determined the frequency of the wave. (2marks)- T= (25.0 - 5.0)-3 = 0.02S
f = 1/T = 1/0.02 = 50Hz
- T= (25.0 - 5.0)-3 = 0.02S
- State the reasons for the following in the filament bulb:
- Inside is filled with inert gas at low pressure. (1 mark)
- To minimize oxidation of the filament √
- The filament is coiled. (1 mark)
- To increase the length in a small space which increases resistatnce √
- Inside is filled with inert gas at low pressure. (1 mark)
- A girl standing at a distance claps her hands and hears an echo from a tall building 2 seconds later. If the speed of sound in air is 340m/s, determine how far the building is. (3marks)
- t= 2.0S/2 = 1.0S
d= Vt
= 340ms-1 x 1.0s
= 340m
- t= 2.0S/2 = 1.0S
- In an experiment to magnetize an iron bar by single stroke method, the graph below was plotted.
Explain what is happening between points AB and BC. (2marks)- AB
- – More dipoles are being aligned √
- BC
- All dipoles are already aligned √
- AB
- State two ways of confirming that an accumulator is fully charged. (2marks)
- Measure voltage √
- Relative density √
- The fig. 6 below shows an electrical appliance with leads labelled Red, Black and Green.
Identify one mistake in the connection. (1 mark)- Switch and bulb are on neutral wire √
- Figure 7 below shows a perfectly efficient transformer. The number of turns in the secondary coil S is six times that of the primary coil P.
If a supply voltage of 4V d.c is connected across P, state with reason what happens to the voltage across R (2 marks).- No voltage across R √
- No changing magnetic field to cut the secondary coil √
- Explain what is meant by radioactive decay. ( 1 mark) (1 mark)
- Radioactive decay is the spontaneous disintegration of a nucleus, resulting in increase of particles and energy from that nucleus. √
- A part from the field, state two ways of increasing the magnitude of current generated. (2 marks)
- Increasing current √
- Increasing number of coils/turns √
- Increasing speed/frequency of rotation
- State one structural difference between a.c and d.c generators. (1 mark)
- A.c generators have two complete rings / slip / commutators attached while d.c have a split ring √
-
- State one application of each of the following. (2marks)
- Convex mirror
- Driving mirror / Super markets √
- Parabolic mirror
- Headlamps / torches √
- Convex mirror
- Fig. 9, which is drawn to a scale of 1:5, represents an object O and its image ‘I’ formed by a concave mirror.
By drawing suitable rays, locate and mark on the figure the position of the principal focus ‘F’ of the mirror. Determine the focal length f. (3 marks)|
- PF = 8cm √
- F = 8 x 5 = 40cm √
- The graph in Fig. 10 shows the variation of magnification, M with image distance, V for a concave mirror.
Determine:- The object position when the image position is 45cm. (3marks)
- V=45cm
m = 2.5 = V/U
2.5 = 4.5/U
U=18cm
- V=45cm
- The focal length of the mirror. (1mark)
- V/f = m +1
at x intercept , 10/f = 1
f= 10cm
- V/f = m +1
- The object position when the image position is 45cm. (3marks)
- state two reasons why a concave mirror is used as a doctor’s dental mirror. (2 marks)
- When placed between F and P √, produces erect / upright / magnified image √
- State one application of each of the following. (2marks)
-
- State two factors that determine the capacitance of a parallel place capacitor. (2marks)
- Area of the overlap of plates √
- Separation distance of the plates √
- A 5μF capacitor is charged to a potential difference of 200V and isolated. It is then connected to a 10μf capacitor.
Find ;- The resultant potential difference across the combination (3marks)
- Q=CV
= 5 x 10‾⁶ x 200
= 1000 x 10‾⁶C
C = 5μF + 10μF = 15μF
V=Q/C
= 1000 x 10‾⁶
15 x 10‾⁶
=66.67V
- Q=CV
- Energy stored before connection (3marks)
- Total energy in the capacitors after connection. (2marks)
- E= CV2
2
= 15 x 10-6 x (1000 x 10‾⁶/15 x 10‾⁶)2
2
333.35 x 10-4
= 0.0333J
- E= CV2
- The resultant potential difference across the combination (3marks)
- Give two applications of capacitors (2 marks)
- Tuning knob of radio
- Reduce sparking in ignition coil
- Wave rectification smoothening
- Store charges
- State two factors that determine the capacitance of a parallel place capacitor. (2marks)
-
- In an experiment to observe interference of light waves a double slit is placed close to the source. See figure 12
- What is a monochromatic source of light. (1 mark)
- Light of single frequency or wavelength / Source that produces one colour of light √
- State the function of the double slit ( 1 mark)
- To produce coherent waves √
- Describe what is observed on the screen ( 1marks)
- Alternating bright and dark fringes √
- State what is observed on the screen when
- The slit separation S1S2 is reduced ( 1 mark)
- Fringe separation reduces √
- White light source is used in place of monochromatic source ( 1 mark)
- Coloured fringes √
- The slit separation S1S2 is reduced ( 1 mark)
- What is a monochromatic source of light. (1 mark)
- During physics lesson, the teacher noticed that Joe had to sit behind in order to see the writings on the board clearly.
- Name the eye defect experienced by Joe. (1 mark)
- Long sightedness / Hypermetropia √
- State one possible cause of the defect. (1 mark)
- Short eye ball / lens with longer focal length √
- On the diagram in fig 11 below, draw to show how the defect can be corrected by use of a lens. (3 marks)
-
- Name the eye defect experienced by Joe. (1 mark)
- In an experiment to observe interference of light waves a double slit is placed close to the source. See figure 12
-
- Distinguish between an ohmic and non-ohmic conductors. (1 mark)
- Ohmics; the variation of p.d with current through them obey ohms law while non ohmics do not √
- Figure 16 shows a circuit with resistors and voltmeter connected to a battery
- If each cell has an internal resistance of 0.7Ω, determine the total resistance in the circuit. (3 marks)
- Rs = 3 + 5 = 8Ω
RT = 2 x 8 = 1.6Ω
2 + 8
R = 1.6 + 0.7 = 2.3Ω
- Rs = 3 + 5 = 8Ω
- Calculate the value of current flowing through the 3Ω resistor when the switch is closed? (2 marks)
- l = V/R
= 6/2.3 = 2.609
= 2/10 x 2.609
= 0.5218A
- l = V/R
- What is the reading of the voltmeter when the switch S is
- Open (1 mark)
= 6.0V √ - Closed (3 mark)
- Open (1 mark)
- Account for the difference between the answers in (I) and (II) above (1 mark)
- The difference is due to voltage drop / lost voltage from internal resistance √
- If each cell has an internal resistance of 0.7Ω, determine the total resistance in the circuit. (3 marks)
- Distinguish between an ohmic and non-ohmic conductors. (1 mark)
-
-
- Periodic time = 4 × 10= 40 ms (4.0 × 10-2 s) √
- Time base setting = 10ms/cm
Number of cycles shown = 2
Number of divisions covered by 1 cycle = 4ms
- Time base setting = 10ms/cm
- Frequency of the wave. ( 2 marks )
- Frequency=1T
=140 ×10-3√
=25Hz√
- Frequency=1T
- Peak voltage (2 marks)
-
- Y-gain = 20 V/cm
Deflection = 2 div from zero level
Peak voltage = 2 × 20√
= 40 V√
- Y-gain = 20 V/cm
-
- Periodic time = 4 × 10= 40 ms (4.0 × 10-2 s) √
- Calculate the frequency of X-rays produced by an X-ray tube operating at 20 kV, assuming that no energy is dissipated as heat. (Planck’s constant h = 6.63 x10-34 Js, and the electronic charge is 1.6 x10-19 C) (3 marks)
- E=hf√
eV=hf
1.6×10-19×(20,000)=(6.63×10-34)×f√
f=4.8265×1918Hz√
- E=hf√
- Calculate the energy of photons associated with radiation of frequency 4.8 × 1014 Hz, stating your answer in eV (3 marks)
- E=hf√
E=6.63×10-344.8×1014=3.18×10-19J√
E=3.18×10-191.6×10-19=1.9875eV√
- E=hf√
-
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - KCSE 2022 Mock Exams Set 2.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students