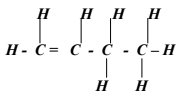INSTRUCTIONS.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- Explain why luminous flame of a Bunsen burner appears yellow. (2mks)
- The empirical formula of a compound is CH2 and it has a molecular mass of 42.
- What is the molecular formula ofhis compound? (1mk)
- Write the general formula of the homologous series to which the compound belongs. (1mk)
- Draw the structural formula of the third member of this series and give its IUPAC name. (1mk)
- Magnesium was burnt in air forming a white residue T. when put in a boiling tube with water effervescence was noticed and a colourless gas D with a characteristic pungent smell was evolved.
Identify:- Residue T. (1mk)
- Gas D (1mk)
- Write an equation for the liberation of gas D. (1mk)
- Study the enthalpes of sodium chloride given below and answer the questions that follow.
Na+(g) + Cl-(g)NaCl(s) ΔH1= -781KJmol-1
H2O
NaCl(s)Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) ΔH2 = +7KJmol-1
- What is the name of ΔH1? (1mk)
- Calculate the heat change for the process represented by the equation: (2mks)
Na+(g) + Cl-(g)H2O(l) Na+(aq) +Cl-(aq)
- Both methane (CH4) and diamond have covalent bonds. Explain why methane is a gas whereas diamond is a solid at room temperature. (2mks)
- Study the table below of certain properties of substance A, B, C and D.
Which of the substances;Melting point (°C) Solubility in water Electrical conductivity A -119°C Soluble Solution does not conduct B 1020 Soluble Solution conducts C 1740 Insoluble Does not conduct D 1600 Insoluble Conduct at room temp - Is a metal? ( ½ mk)
- Has a simple molecular structure? ( ½ mk)
- Has a giant ionic structure? ( ½ mk)
- Has a giant covalent structure? ( ½ mk)
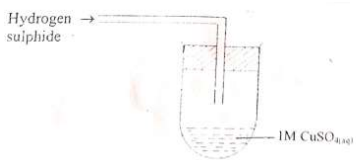
- In an experiment hydrogen sulphide was passed through 1.0M CuSO4 solution in a boiling tube as shown in the diagram.
- State the observation made in the boiling tube. (1mk)
- Write the ionic equation for the above reaction. (1mk)
- What precaution should be taken in carrying out this experiment? Explain. (1mk)
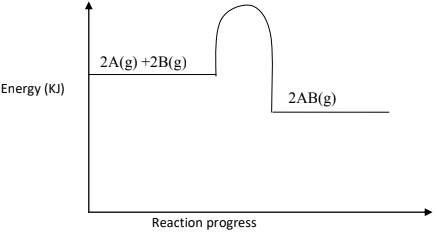
- The figure below is an energy level diagram for the reaction.
2A(g) + 2B(g)2AB(g)
- Explain how the following conditions would affect the yield of AB.
- Increase in pressure. (1 ½ mks)
- Decrease in temperature. (1 ½ mks)
- Explain why the rate of reaction is found to increase with temperature. (2mks)
- Explain how the following conditions would affect the yield of AB.
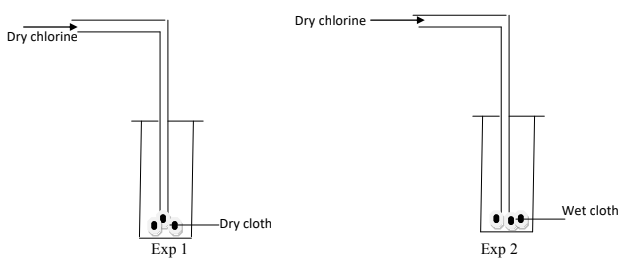
- Dry chlorine gas was passed through two pieces of coloured cotton cloth as shown.
- State what is observed in each experiment. (2mks)
- Explain your observation using equations. (1mk)
- During the extraction of copper and zinc from their ores, some of the processes include;
- Crushing
- Mixing of the crushed ore with oil and water and bubbling air through it.
- Name the process (ii) above. (1mk)
- What is the purpose of (ii) above? (1mk)
- Bronze is an alloy of copper and another metal. Identify the other metal. (1mk)
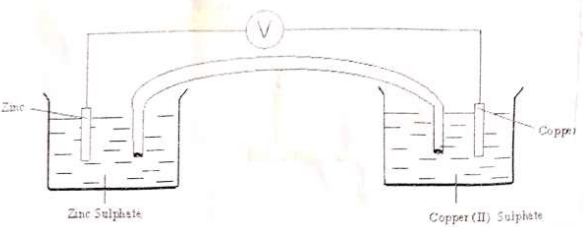
- The diagram below represents an electrochemical cell.
- On the diagram:
- Label the salt bridge. (1mk) i
- Show the direction of flow of electrons. (1mk)
- Write the overall ionic equation. (1mk)
- What is the oxidation number of chlorine in ClO4-(1mk)
- On the diagram:
- A gas at 27°C and 750mmHg was found to occupy 36cm3. Calculate the temperature at which the same mass of gas will occupy twice the volume at a pressure of 100mmHg pressure. (2mks)
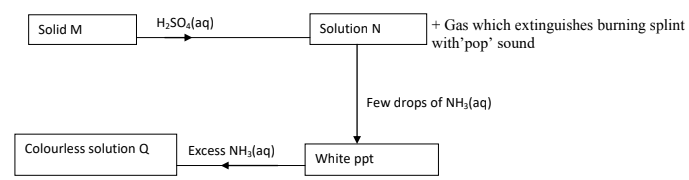
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name solid M. (1mk)
- Write an equation for formation of a complex ion present in solution Q. (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation of the reaction between barium nitrate and solution N. (1mk)
- When a current of 2.5 amperes was passed through a cell containing N2+ ions of a metal for 25 minutes, the mass of the cathode increased by 0.36g. determine the relative atomic mass of element N. (IF= 96500 coulombs) (3mks)
- An oxide of potassium has a relative formula mass of 110, if 2.75g of the oxide contains 1.95g of potassium; determine the formula of the oxide. (K=39.0, O=16.0) (3mks)
- The arrangement below was used to compare the penetrating power of emissions in a radio-active decay.
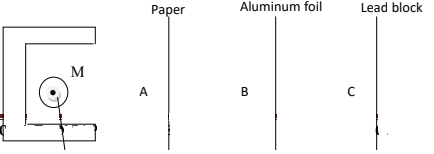
- Name the radio-active that can be detected at A, B and C. (2 ½ mks
- The half life of
is 4500 years. The isotope decays by alpha emission.
Write a nuclear equation for its decay to form Thorium (Th) (1mk)
- Study the following changes that took place when the following substances are exposed in air.
- I
NaOH(s)NaOH(aq)
- II
Na2CO3.10H2O(s)Na2CO3(s) + 10H2O(l)
- III
CuSO4(s) + 5H2O(l)CUSO4.5H2O(s)
Name the process I,II and III. (3mks)
- I
-
- Complete the table below to show the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to the substances shown. (2mks)
Substance Observation Iron fillings Crystals of white sugar - Give reason for the observations made using;
- Iron fillings (1mk)
- Crystal’s of white sugar. (1mk)
- Complete the table below to show the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to the substances shown. (2mks)
- A saturated solution of a salt at 30°C weighs 60g. when evaporated to dryness, it leaves a dry mass of 10g
- What is the solubility of the salt at 30oC? (2mks)
- A compound whose general formula is Y(OH)3 reacts as shown by the equation below.
Y(OH)3(s) + OH-(aq)[Y (OH)4] (aq)
Y(OH)3(s) + 3H+(aq)Y3+(aq) + 3H2O(l)
- What name is given to compounds which behave like Y(OH)3 in the two reactions. (1mk)
- Name an element whose hydroxide behave like that of Y. (1mk)
-
- Define a flame. (1mk)
- Name the type of a flame produced by the Bunsen burner when the air hole is closed. (1mk)
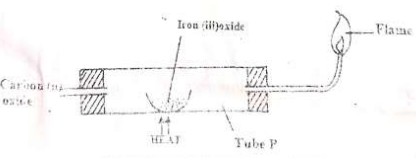
- Carbon (II) Oxide gas was passed over heated iron (III) oxide as shown below.
- Give one observation made in tube P. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in tube P. (1mk)
- The flame at the end of combustion tube P is blue in colour. Explain how the flame is obtained. (1mk)
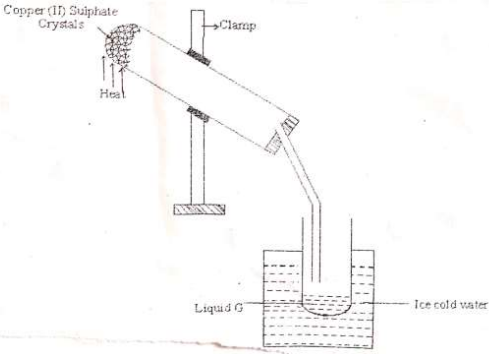
- The diagram below is a set up to investigate the effect of heat on hydrated Copper (II) Sulphate. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Why is the boiling tube slanted as shown? (1mk)
- What is observed in the boiling tube? (1mk)
- Identify liquid G. (1mk)
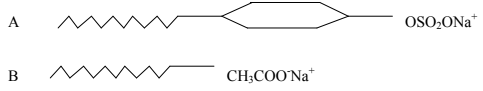
- The following diagrams represent two types of detergents. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the two types of detergents. A and B. (2mks)
- What is the problem of continued use of substance A? (1mk)
- The table below is part of the periodic table. The letters are not the actual symbols of the element. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Select an element which is stored in paraffin in the laboratory. (1mk)
- Element H and I react to form a compound. Write the equation that takes place. (1mk)
- How do the ionic radii of E and I compare? Explain. (2mks)
- Describe an experiment to show that group one elements react with cold water to form alkaline solutions. (3mks)
- A solution was made by dissolving 8.2g of calcium nitrate to give 2 litres of solution. (Ca=40.0, N=14.0, O=16.0)
- Identify the method used to obtain oil from nut seeds. (1mk)

MARKING SCHEME
- Explain why luminous flame of a Bunsen burner appears yellow. (2mks)
- Due to incomplete combustion of the gas resulting to production of carbon particles which glow in presence of heat to yellow.
- The empirical formula of a compound is CH2 and it has a molecular mass of 42.
- What is the molecular formula of this compound? (1mk)
- (CH2)n = 42
(12+2)n=42
14n=42
n=3
M.F = 3(CH2)
C3H6
- (CH2)n = 42
- Write the general formula of the homologous series to which the compound belongs. (1mk)
- CnH2n
- Draw the structural formula of the third member of this series and give its IUPAC name. (1mk)
- What is the molecular formula of this compound? (1mk)
- Magnesium was burnt in air forming a white residue T. when put in a boiling tube with water effervescence was noticed and a colourless gas D with a characteristic pungent smell was evolved.
- Identify:
- Residue T. (1mk)
- Magnesium nitride (Mg3N2)
- Gas D (1mk)
- Ammonia / NH3
- Write an equation for the liberation of gas D. (1mk)
- Mg3N2(s) + 6H2O(l) → 3Mg(OH)2(aq) + 2NH3(g)
- Residue T. (1mk)
- Identify:
- Study the entheupies of sodium chloride given below and answer the questions that follow.
Na+(g) + Cl-(g)NaCl(s) ΔH1= -781KJmol-1
H2O
NaCl(s)Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) ΔH2 = +7KJmol-1
- What is the name of ΔH1? (1mk)
- Latrice energy
- Calculate the heat change for the process represented by the equation: (2mks)
Na+(g) + Cl-(g) → H2O(l) Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
- ΔH3 = ΔH(latt) + ΔH(soln)
= - 781 + 7
= -774KJmol-1
- ΔH3 = ΔH(latt) + ΔH(soln)
- What is the name of ΔH1? (1mk)
- Both methane (CH4) and diamond have covalent bonds. Explain why methane is a gas whereas diamond is a solid at room temperature. (2mks)
- Methane has simple molecular structure with weak van der waals forces while diamond has giant atomic/covalent structures with strong covalent bond.
- Study the table below of certain properties of substance A, B, C and D.
Which of the substances;- Is a metal? ( ½ mk)
- D
- Has a simple molecular structure? ( ½ mk)
- A
- Has a giant ionic structure? ( ½ mk)
- B
- Has a giant covalent structure? ( ½ mk)
- C
- Is a metal? ( ½ mk)
- In an experiment hydrogen sulphide was passed through 1.0M CuSO4 solution in a boiling tube as shown in the diagram.
- State the observation made in the boiling tube. (1mk)
- A black solid is formed.
- Write the ionic equation for the above reaction. (1mk)
- Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) → CuS(s)
- What precaution should be taken in carrying out this experiment? Explain. (1mk)
- Experiment should be done in a fume chamber since H2S gas is poisonous.
- State the observation made in the boiling tube. (1mk)
- The figure below is an energy level diagram for the reaction.
2A(g) + 2B(g)2AB(g)
- Explain how the following conditions would affect the yield of AB.
- Increase in pressure. (1 ½ mks)
- The yield of AB is increased. The forward reaction is accompanied by a decrease in volume. Equilibrium shifts to the right following the forward reaction.
- Decrease in temperature. (1 ½ mks)
- The yield AB is increased. The forward reaction is exothermic; decrease in temperature favours the forward reaction hence equilibrium shifts to the right.
- Increase in pressure. (1 ½ mks)
- Explain why the rate of reaction is found to increase with temperature. (2mks)
- Increase in temperature results in increase in the kinetic energy of the particles. This makes particles move faster and collide frequently leading to faster rate of reaction.
- Explain how the following conditions would affect the yield of AB.
- Dry chlorine gas was passed through two pieces of coloured cotton cloth as shown.
- State what is observed in each experiment. (2mks)
- In experiment I; No change on the dry cloth because of the absence of hypochlorous acid responsible for bleaching.
- In experiment II; the wet cloth turned white due to bleaching as chlorine dissolves in water in the wet cloth to form hypochlorous acid.
- Explain your observation using an equation. (1mk)
- Cl2(g) + H2O(l) → HCl(aq) + HOCl(aq)
- Dye + HOCl(aq) → (Dye +O) + Hcl(aq)
- State what is observed in each experiment. (2mks)
- During the extraction of copper and zinc from their ores, some of the processes include;
- Crushing
- Mixing of the crushed ore with oil and water and bubbling air through it.
- Name the process (ii) above. (1mk)
- Froth floatation
- What is the purpose of (ii) above? (1mk)
- To concentrate the mineral ore by making impurities to sink at the bottom.
- Bronze is an alloy of copper and another metal. Identify the other metal. (1mk)
- tin (Sn)
- Name the process (ii) above. (1mk)
- The diagram below represents an electrochemical cell.
- On the diagram:
- Label the salt bridge. (1mk) i
- Show the direction of flow of electrons. (1mk)
- Write the overall ionic equation. (1mk)
- Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq)+ Cu(s)
- What is the oxidation number of chlorine in C10-4. (1mk)
- Cl + ( −2 x 4) = −1
Cl − 8 = −1
Cl = −1+8
Cl = +7
- Cl + ( −2 x 4) = −1
- On the diagram:
- A gas at 27°C and 750mmHg was found to occupy 36cm3. Calculate the temperature at which the same mass of gas will occupy twice the volume at a pressure of 100mmHg pressure. (2mks)
- P1 = 750mmhg
V1 = 36cm3
T1 = (27+273)=300k
P2 =100mmHg
V2 = 72cm3
T2 = ?
T2 = P2V2T1
P1V1
= 100x72x300
750x36
= 80k or 193°C
- P1 = 750mmhg
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name solid M. (1mk)
- Zinc metal/zinc
- Write an equation for formation of a complex ion present in solution Q. (1mk)
- Zn(OH)2(s) + 4 NH3(aq) → [Zn(NH3)4]2+(aq) + 2OH- (aq)
- Write an ionic equation of the reaction between barium nitriate and solution N. (1mk)
Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → BaSO4(s)
- Name solid M. (1mk)
- When a current of 2.5 amperes was passed through a cell containing a cell containing N2+ ions of a metal for 25 minutes, the mass of the cathode increased by 0.36g. determine the relative atomic mass of element N. (IF= 96500 coulombs) (3mks)
Q = 1t
Q=2.5 x 25 x 60 = 3750C
N2+ − 2 faradays
1F= 96500
2F = 193,000C
3750C= 0.36g
193000C=?
193000 x 0.36
3750
=18.528
=18.5 - An oxide of potassium has a relative formula mass of 110, if 2.75g of the oxide contains 1.95g of potassium; determine the formula of the oxide. (K=39.0, O=16.0) (3mks)
Mass of Oxygen = 2.75 – 1.95 =0.9
Element K O
Mass 1.95 0.8
RAM 39 16
Moles 0.05 0.05
M.R 0.05 0.05
1 : 1
EFKO
(KO)n =110
(39+16)n = 110
55n=1
n=2
formula K2O2 -
- The arrangement below was used to compare the penetrating power of emissions in a radio
- Name the radio-active that can be detected at A, B and C. (2 ½ mks)
- A - Alpha, Beta, Gamma
- B - Beta, Gamma
- C - Gamma
- The half life of
is 4500 years. The isotope decays by alpha emission. Write a nuclear equation for its decay to form Thorium (Th) (1mk)
- Study the following changes that took place when the following substances are exposed in air.
Name the process I,II and III. (3mks)- I - Deliquescence
- II - Efflorescence
- III - Hygroscopy
-
- Complete the table below to show the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to the substances shown. (2mks)
Substance Observation Iron fillings Effervescence occurs
Bubbles of colourless gas with a pungent smell
A brown solution is formedCrystals of white sugar Black spongy solid - Give reason for the observations made using;
- Iron fillings (1mk)
- Sulphuric (VI) acid oxidizes iron to iron (III) sulphate while it is reduced to SO2 and water.
- Crystal’s of white sugar. (1mk)
- Formation of carbon by dehydration of sugar.
- Iron fillings (1mk)
- Complete the table below to show the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to the substances shown. (2mks)
- A saturated solution of a salt at 30°C weighs 60g. when evaporated to dryness, it leaves a dry mass of 10g.
- What is the solubility of the salt at 30°C? (2mks)
Mass of solvent = 60 − 10 =50g
50g of solvent contains 10g of salt
100g of solvent = ?
= 100 x 10
50
= 20g/100g of water - A compound whose general formula is Y(OH)3 reacts as shown by the equation below.
Y(OH)3(s) + OH-(aq) → [Y (OH)4] (aq)
Y(OH)3(s) + 3H+(aq) → Y3+(aq) + 3H2O(l)- What name is given to compounds which behave like Y(OH)3 in the two reactions. (1mk)
- Amphoteric hydroxides.
- Name an element whose hydroxide behave like that of Y. (1mk)
- Zinc/lead/zluminium
- What name is given to compounds which behave like Y(OH)3 in the two reactions. (1mk)
- What is the solubility of the salt at 30°C? (2mks)
-
- Define a flame. (1mk)
- a flame is a mass of burning gases
- Name the type of a flame produced by the Bunsen burner when the air hole is closed. (1mk)
- Luminous flame
- Define a flame. (1mk)
- Carbon (II) Oxide gas was passed over heated iron (III) oxide as shown below.
- Give one observation made in tube P. (1mk)
- The brown solid turns to grey solid.
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in tube P. (1mk)
- Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(s) 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
- The flame at the end of combustion tube P is blue in colour. Explain how the flame is obtained. (1mk)
- The flame is obtained by burning excess carbon (II) oxide gas.
- Give one observation made in tube P. (1mk)
- The diagram below is a set up to investigate the effect of heat on hydrated Copper (II) Sulphate. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Why is the boiling tube slanted as shown? (1mk)
- Prevent water formed from running back to the hot part of the apparatus which could crack.
- What is observed in the boiling tube? (1mk)
- Blue solid (CuSO4) turns white/crystals turn to powder/ colourless liquid condenses on the cooler parts of combustion tube.
- Identify liquid G. (1mk)
- G is water
- Why is the boiling tube slanted as shown? (1mk)
- The following diagrams represent two types of detergents. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the two types of detergents. A and B. (2mks)
- A – Soapless detergent
- B – Soapy detergent
- What is the problem of continued use of substance B? (1mk)
- It is non-biodegradable hence a pollutant.
- Identify the two types of detergents. A and B. (2mks)
- The table below is part of the periodic table. The letters are not the actual symbols of the element. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Select an element which is stored in paraffin in the laboratory. (1mk)
- G
- Element H and I react to form a compound. Write the equation that takes place. (1mk)
- H(s) + I2(g) → HI2(s)
- How do the ionic radii of E and I compare? Explain. (2mks)
- The ionic radius of I is bigger than that of E since I has more energy levels than E.
- Select an element which is stored in paraffin in the laboratory. (1mk)
- Describe an experiment to show that group one elements react with cold water to form alkaline solutions. (3mks)
- Put water in a water trough/ beaker. Cut a small piece of sodium metal and put it in water.
- After the reaction is over, put a red litmus in the resultant solution. The red litmus paper turns blue indicating that the solution is alkaline.
- A solution was made by dissolving 8.2g of calcium nitrate to give 2 litres of solution. (Ca=40.0, N=14.0, O=16.0)
Determine the concentration of nitrate ions in moles per litre. (3mks)- RFM of Ca(NO3)2= 40+28+96=164
Thus 164g – 1mol
8.2g = 8.2 x 1
164
= 0.05mols
2 litres = 0.05 moles
1 litres = ?
= 1 x 0.05
2
= 0.025 moles
Ca(NO3)2 Ca2+ + 2NO3 -(aq)
1 : 2
Conc. Of NO3- ions = 0.025 x 2
= 0.05m
- RFM of Ca(NO3)2= 40+28+96=164
- Identify the method used to distain oil from nut seeds. (1mk)
- Solvent extraction
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Lanjet Joint Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students