QUESTIONS
SECTION A: ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION. (25MKS)
-
- Define the term Geography. (2mks)
- What is the relationship between Geography and Chemistry. (2mks)
-
- State three characteristics of intrusive igneous rocks. (3mks)
- Give two earthquake zones of the world (2mks)
-
- What is folding. (2mks)
- Give four of features formed as a result of folding. (4mks)
-
- State three stages of the hydrological cycle. (3mks)
- State two factors that influence the amount of surface run-off. (2mks)
-
- The diagram below shows a river capture. Name the parts marked K and L (2mks)
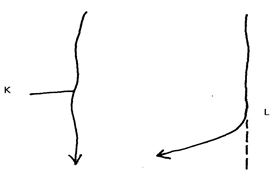
- Outline three ways through which a gorge is formed (3mks)
- The diagram below shows a river capture. Name the parts marked K and L (2mks)
SECTION B: ANSWER QUESTION SIX AND ANY OTHER TWO QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION. (75MKS)
- Study the map of NYERI 1:50,000 provided and use it to answer the following questions.
-
- Determine the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map.(2mks)
- From which hemisphere of the globe was the map taken? (1mk)
- Give three physical features found in grid square 5065. (3mks)
-
- What is the bearing of the Air Photo Principal Point (104 KE 024) at grid square 6048 from trigonometrical station primary SKP 211 at grid square 6654? (2mks)
- Give the sheet to the North West and South of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
- Citing evidence from the area covered by the map, give two social functions of Mweiga town to the north of the area. (4mks)
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. (5mks)
- Explain three factors that have influenced distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map(6mks)
-
-
- What is a rock (2mks)
-
- Name two examples of extrusive igneous rocks (2mks)
- Give three sources of sedimentary rocks. (3mks)
- State three reasons why sedimentary rocks are widespread in the coastal plains of Kenya. (3mks
- State four factors that influence the change of original rocks to metamorphic rocks (4mks)
- You are planning to carry out a field study on the rocks within your school environment.
- Give three secondary sources of information you would use to prepare for the field study (3mks)
- State three advantages of dividing the students into groups during the field study (3mks)
- Identify three problems you are likely to face during the study (3mks)
- Give two advantages of studying the rocks through fieldwork. (2mks)
-
-
- Name three types of faults. (3marks)
- Apart from compressional forces, explain two other processes that may cause faulting.(4 marks)
-
- With the aid of well labelled diagrams, describe how compressional forces may have led to the formation of the Great Rift Valley. (8marks)
- Apart from the Rift valley, name two other resultant features of faulting (2mks )
- Explain four effects of faulting on human activities. (8 marks)
-
-
-
- What is the process through which wave transport the eroded materials along the coast. (1mks)
- State three factors that influence wave deposition. (3mks)
-
- Name two types of submerged coasts. (2mks)
- State three characteristics of emerged highland coast. (3mks)
- With the aid of well labelled diagrams, describe the formation of a spit. (7mks)
- Students from Moi secondary school were planning to conduct a field study on wave erosional features to areas along the coast.
- Give three ways in which the students will prepare for the field study (3mks)
- Name three erosional features they are likely to identify. (3mks)
- Identify three methods of data collection that they will use during the field study. (3mks)
-
-
-
- What is soil catena? (2 marks)
- Draw a well labelled diagram showing the structure of a well-developed soil profile. (5 marks)
- Differentiate between mineralization and humification in soil formation. (2 marks)
- State three factors that determine the colour of soil. (3 marks)
-
- State four factors that influence soil formation. (4 marks)
- Explain how the following farming practices can cause soil degradation:
- Burning. (2 marks)
- Continuous application of fertilizer on farm land. (2 marks)
- Monoculture. (2 marks)
- State three uses of soil. (3 marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- It is the scientific study of the earth as the home of mankind OR
- It is the study of distribution and interrelationship of the natural and human phenomena on the earth’s surface.
-
- Geography uses chemistry to study the chemical composition of rocks, minerals and in soil formation
- Chemistry uses geography to show distribution of rocks and minerals of the and in soil formation
-
-
-
- Are hard and highly resistant to erosion
- Coarse textured /have large grains
- Have large crystals
-
- Circum-pacific belt
- Mediterranean -east indies belt
- Mid-Atlantic ocean belt
- The great rift valley belt
-
-
- Folding is the bending or distortion of crustal rocks due to compressional forces
-
- Simple symmetrical fold
- Asymmetrical fold
- Overfold
- Isoclinal folds
- Recumbent
Any other
-
-
- Evaporation and transpiration /evapotranspiration
- Cooling and condensation
- Precipitation which includes rainfall and snowfall
- Run-off or overland
- Infiltration or percolation
-
- Amount of rainfall
- Gradient of the land
- Nature of the surface rocks /soil
- Level of soil saturation /water table
- Absence of vegetation
-
-
- K-The pirate river
L-Elbow of capture -
- Where a river flows along a line of weakness
- Where a waterfall retreats upstream
- Where a river flows over less resistant rocks
- K-The pirate river
-
-
- 36045IE to 37000IE
- Southern hemisphere
-
- River
- River valley
- Steep slopes
- Scrub vegetation
-
- 225º
- North west-Ndaragwa 120/1
South -Kangema 134/2
-
- Education services evidenced by the school
- Administration services evidenced by the district officer, police post
- Residential services evidenced by the built-up areas
-
- The main drainage feature is rivers
- Most of the rivers are permanent rivers e.g r.Chanya
- The main rivers are Chanya, Kagumo, Mboni
- Most of the rivers are flowing from the west to the east e.g r.Chanya
- Most of the rivers have several meanders e.g r.Chanya
- The main drainage pattern in most rivers is dendritic
-
- Areas covered by forests have few settlement because they have been set aside as reserves by the government e.g. Aberdare forest, nyeri forest
- The steep slopes areas have few settlements since the land is rugged hence difficult to construct settlements e.g the west of easting 52
- Presence of roads have resulted to linear settlement pattern along the roads e.g along Wanderi road
-
-
- Rocks are naturally occurring agglomeration of mineral particles that make up the earth crust
-
-
- Andesite
- Basalt
- Pumice
- Scoria
- Obsidian
- Phonolite
-
- Sediments obtained from weathered rocks
- Dissolved minerals in water
- Dead plants and animals
-
- Coastal plain is a lowland which facilitates deposition
- Shallow continental shelf-suitable for formation of coral rocks
- Much of the coastal plain emerged from the sea where sediments had been deposited
-
-
- Rock resistant /hardness
- Rock texture and structure
- Rock porosity
- Solubility of rock minerals
- Chemical properties of rock minerals
-
-
- Textbooks /geography notes
- Magazines /journals
- Atlases
- Geological maps
- Internet browsing /electronic media
-
- Helps to study the entire area at once
- Helps to save on time
- Enables the study to be carried out in an orderly manner
- Prevents congestion in specific areas
- Encourages participation of all students
-
- Attack by wild animals e.g., snakes, insect bites
- Adverse weather condition
- Tiredness or fatigue due to walking for long distances
-
- It helps to breakdown the classroom monotony
- Enables students to study the processes through which various types of rocks were formed
-
-
-
-
- Normal faults
- Reversed faults
- Shear/tear fault
- Thrust /overthrust faults
- Anticlinal faults
-
- Faulting may be caused by force acting horizontally away from each other which cause tension in the crystal rocks. Due to tensional forces the rocks stretch and fracture causing faults.
- Faulting may occur where horizontal forces act parallel to each other in the opposite/same direction resulting in shearing.
- Faulting may occur due to vertical movements which may exert a strain in the rocks making them to fracture.
-
-
-
- Layers of rocks are subjected to compression forces
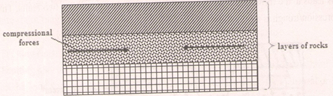
- Two parallel lines of weaknesses develop/reverse faults
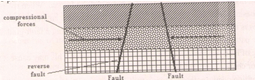
- Compression forces may take the outer blocks towards each other. The outer blocks ride over the middle block and the middle block sinks or subsides or may remain stable. The sunken middle part forms a depression called a rift valley.
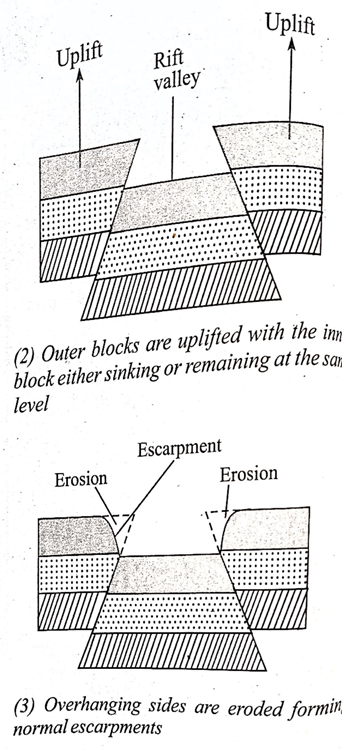
- Compression forces may push the outer blocks towards each other (the outer blocks ride over the middle block) the middle block sinks/subside/may remain stable.
- The overhanging edges undergo denudation/are eroded.
- This widens the depression.
- The sunken middle part forms a depression called a rift valley.
- Diagrams (3 mks) (forces, reverse faults, Rift valley)
Description (5 mks)
- Layers of rocks are subjected to compression forces
-
- Fault scarp
- Fault step
- Fault blocks
- Tilt block
-
-
- Fault blocks form beautiful scenery which attracts tourists, hence foreign exchange.
- Fault block causes displacement of rocks which exposes valuable minerals.
- Block mountains formed through faulting experience rainfall on the windward side give rise to rivers which provide water for industrial/domestic/agricultural use/Industrial use for production of H.E.P.
- Block mountains formed through faulting lead to formation of relief rainfall on the windward side which favours agriculture/and settlement/forestry.
- Rivers flowing over faults blocks from waterfalls which are sites for H.E.P production.
- Faulting creates deep faults which are passages of steam jets which may be utilized for geothermal power production.
- Rivers flowing over fault scarps may form waterfalls which can be harnessed to produce H.E.P for industries.
- Springs occurring at the foot of fault scarps attract settlements.
-
-
-
- Longshore drift
-
- Presence of gentle gradient of the shore
- Presence of shallow waters
- Presence of constructive waves
- Irregular coastline
- Waves that break at low frequency
-
- Highland submerged coasts
Lowland submerged coasts -
- Raised beaches
- Raised wave cut platforms
- Abandoned or raised cliffs
- Abandoned or raised caves caves and notches
- Raised archs, stacks and stumps
- Raised geo and blowhole
- Highland submerged coasts
-
- Forms on a shallow shore where the coastline bends towards the land e.g a bay or entrance of a bay
- Longshore drift deposits materials in the material in the water at this point after its movement is halted by the protruding land
- The deposits accumulate at the end of the headland and extend towards the sea forming an elongated ridge
- The result is a low-lying ridge of sand and shingle with one side projecting into sea and the other attached to the coast, this ridge is called a spit
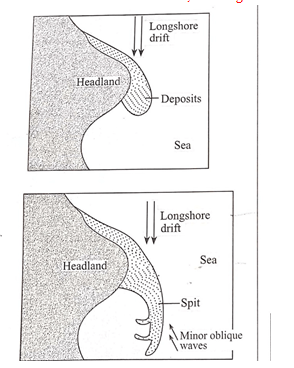
Diagram -3mks
Text -4mks
-
-
- Seeking permission from the relevant authorities
- Carry out a pre-visit
- Decide on the methods of data collection and data recording
- Draw a working schedule
- Divide the students into groups
-
- Draw a route map
- Cliff
- Headland and bays
- Wave-cut platforms
- Caves and caverns
- Blowhole
- Geo
- Arch
- Stack
- stump
-
- direct observation
- oral interviews
- taking photographs
- taking measurement of the cliff
- administering questionnaire
-
-
-
-
- It is the arrangement of soil along a slope from top to bottom.
-
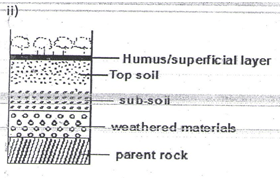
- Mineralization is the biological and chemical breakdown of dead plant tissues by soil micro-organisms to produce simple organic substances while Humification is the process through which organic matter is changed into humus
-
- Humus content/ content of organic matter present in the soil: black/dark brown colour indicates a soil rich in humus
- Drainage of the area in which the soil is found: grey colour denotes a poorly drained and water-logged soil
- Acidity/salinity/soil PH/ chemical composition of the soil: White colour denotes a soil with high salts concentration
- Type of parent material from which a soil has developed.
-
-
- Nature of the parent rock material
- Climate
- Influence of living organisms
- Topography/Relief
- Time factor
-
- Kills soil micro-organisms and robs the soil of organic matter/humus
Kills nitrogen fixing bacteria resulting to lack of nitrogen in the soil - Leads to increase acidity in the soil which interferes with soil formation micro-organisms like bacteria and fungi thus lowering the level of humus content.
- Results in the crops using all the minerals that it requires, which increases a deficiency of the mineral in the soil
- Kills soil micro-organisms and robs the soil of organic matter/humus
-
- Give physical support for the rooting system of plants and protects root system from damage.
- Habitat for borrowing animals and bacteria necessary for breakdown of organic matter into humus.
- Medium through which nutrients and air are made available to plants.
- Provides mineral elements to plants e.g. nitrogen, calcium, phosphates, etc.
- Is used in building and construction e.g. clay for making bricks and tiles.
- Clay soils are used for decorative purpose e.g. ache used among Maasai.
- Sources of minerals especially to expectant mothers.
- Soil contains valuable minerals such as alluvial gold.
- Soils supports plant life which is source of food for people and animals especially herbivores.
- Soils are used for medicinal purposes e.g. clay is mixed with some herbs for medical purpose in some communities.
-
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - MECS Cluster Joint Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
