Questions
SECTION A: (30 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- What is the meaning of seed dressing? (1mk)
- Give four advantages of row planting. (2mks)
- List four factors to be considered when choosing site for tomato nursery. (2mks)
- State three reasons of treating water in the farm. (1 ½ mks)
- Give three ways through which HIV/AIDS affect agriculture. (1 ½ mks)
- State four advantages of overhead irrigation. (2mks)
- State three ways of conveying water in the firm. (2mks)
- A farmer in Premier was advised to apply 150kg C.A.N/ha while top dressing the maize crop. CAN, contains 21% N. Calculate the amount of nitrogen applied per ha. (2mks)
- Give two reasons why opportunity cost is zero. ( lmk )
- Give three importance of tissue culture in crop production. (2mks)
- State four principles which govern agricultural economics. (2mks)
- Highlight four problems facing the marketing of cabbages. (2mks)
- State four variable costs in maize production. (2mks)
- State four constituents of soil. (2mks)
- Give four types of product -product relationships. (2mks)
- Differentiate between topping and top-dressing as used in pastures. (lmk)
- State five factors which influence the spacing of crops. (2mks)
SECTION B (20 MKS)
Answer ALL Questions in this section
- Below are illustrations of common weeds. Study them and answer the questions that follow
- Identify the weeds (2mks)
A…
B… - State the harmful effects of the weed B above (1mk)
- Give four advantages of leasehold tenure systems (2mks)
- Identify the weeds (2mks)
- Describe the procedure which should be followed when spraying a crop of onions using a fungicide in powder form, water and a knapsack sprayer (5mks)
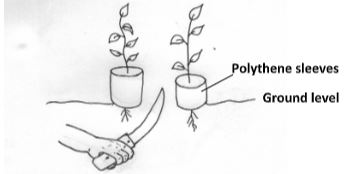
- The diagram below illustrates a nursery practice carried out on tree seedlings before transplanting. Study it carefully and then answer the questions below
- Identify the practice being carried out on the diagram (1mk)
- Give three reasons why the practice is encouraged when raising tree seedlings (3mks)
- Give two reasons why the polythene sleeves are used in the nursery bed as shown in the diagram (2mks)
-
- Calculate the elasticity of demand when 20 bags of potatoes are demanded at a price of Kshs.1000 while 22 bags were demanded at Kshs.800. (4mks)
- Identify the type of elasticity of demand resulting from the situation above (1mk)
SECTION C (40MKS)
Answer any two Questions in this section
-
- Describe harvesting of pyrethrum under the following sub-headings
- Procedure (4mks)
- Precautions (6mks)
- Describe the safety measures observed when handling farm herbicides (10mks)
- Describe harvesting of pyrethrum under the following sub-headings
- Describe the production of Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana) under the following sub-headings
- Land preparation (5mks)
- Pasture establishment (8mks)
- Maintenance (7mks)
-
- State four major questions a farm manager needs to ask and answer while preparing a partial budget (4mks)
- Under what conditions is partial budget an appropriate tool for planning (4mks)
- Mzee mkulima has 5 hectare of arable land which is under maize. He wishes to know whether replacing 0.3 ha of maize with beans the following season would be worthwhile. The fertilizer rate would have to be increased from 2 bags per hectare for maize to 2.5 bags per hectare, for beans and an extra 40 man days of casual labour per hectare would be necessary as a result of the change. Average yield of maize and beans are 56 and 90 bags per hectare respectively. The prices are ksh 1200 per bag of maize and ksh 300 per bag of beans. Seed costs are ksh 1350 per 10 kg of maize ksh 200 per 50 kg beans DAP fertilizer costs ksh 1400 per 50 kg bag. Labour is paid at ksh 150 per man day . he would require ten bag of beans seed and 1 bag of maize seed to caver 0.3 of ha.
Draw up a partial budget and indicate the effects of the change (12mks)
Marking Scheme
- Seed dressing is the process of coating of seeds with insecticides or fungicides chemical to prevent the seed from soil borne diseases. (lx1= 1 mk)
- advantages of row planting
- Machines can be used easily between the rows
- Easy to establish crop population.
- Low seed rate is used.
- Easy to carry out other operations like weeding, spraying and harvesting. (4x ½ = 2mks)
- Factors considered when choosing site for tomato nursery.
- type of soil
- nearness to water source
- topography
- security
- previous cropping
- well sheltered place (4x ½ =2mks)
- Reasons for treating water.
- To kill disease causing micro-organism
- To remove chemical impurities
- To remove dour / bad smell
- To remove foreign particles. (3x ½ = 1½ mks)
- Effect of HIV/AIDS to agriculture.
- Loss of skilled labour through death of skilled personnel.
- Wastage of time in caring of patients.
- A lot of money is spent on treating people with HIV/AIDS.
- Government and NGOs’ spend a lot of money to control HIV in expense of development ofagriculture. (3x ½ = 1½ mks)
- Advantages of overhead irrigation.
- Eradicate pests e.g. Aphids.
- Minimizes wastage of water.
- Can be used in sloppy areas.
- Water is evenly distributed.
- Can irrigate a large area by changing the location of pipes.
- Foliar fertilizers can be applied using this method (4x ½ =2mks)
- Ways of conveying water in the farm.
- piping
- canals
- containers (3x ½ = 1½ mks)
- A farmer in PREMIER was advised to apply 150kg CAN/ha, while top Dressing the maize crop.CAN contain 21% N. Calculate the amount of nitrogen applied/ha.
If 100kg of C.A.N→21kg N
150kg of C.A.N→ ?
150kg C.A.N x 21kgN
100kg C.A.N
=31.5kg N/ha (2 ½ mks) - Opportunity cost is zero.
- When the item is free.
- When the item is plenty
- When the item has no alternative
- Importance of tissue culture
- mass production of prop gules
- Establish pathogen free plants
- Establish fast.
- Requires less space. (3x ½ = 1½ mks)
- Principles of agriculture.
- Law of opportunity cost
- Law of diminishing returns
- Law of profit - maximization.
- Principle of equal-marginal returns.
- Principle of substitution (4 x ½ =2mks)
- Problems facing marketing of cabbages.
- Perish ability of cabbages.
- Poor transport
- Lack of marketing information.
- Change of market prices.
- Change of government policy. (4x ½ =2mks)
- Variable costs
- cost for fertilizers.
- Cost of chemicals.
- Wages.
- Cost of fuel.
- Cost of planting seeds. (4x ½ =2mks)
- Constituents of soil
- soil air
- soil water
- soil micro-organisms
- soil particles
- Soil organic matter/humus. (4x ½ =2mks)
- Product-product relationship
- joint products
- competitive products
- complementary product
- Supplementary products. (4x ½ =2mks)
- Topping — is removal of fibrous materials from the pasture after harvesting or grazing pasture while top-dressing is the application of fertilizers at the base of the pastures. (2mks)
(mark as whole) - factors which influence spacing of crops
- type of soil
- growth habit
- soil fertility
- soil moisture
- number of seeds per hole
- use of the crop
- Occurrence of pests and diseases. (5x ½ =2 ½ mks)
-
-
- - Devil’s horse whip(Achyranthes apora) ( 1mk)
- - Datura stramomium (Thorn apple) (1mk)
-
- Poisonous to livestock
- Competes with crops for nutrients / light / water or space
- Increase cost of production
- Lower yields / quality 1x1 = 1mk
-
- Enables land owners / landlord to earn income from land
- Enable people who have no land to have acres to farmers land
- Idle land put into productive use
- Enable tenants to increase / decrease acreage of land leased depending on profitability
½ x 4 = ( 2mks)
-
-
- Read the label / manufacture instructions and follow them
- Measure the required amount of fungicide
- Place the fungicide into a container and mix thoroughly with a little water / pre-mix (pre-cream) until it forms a uniform slurry
- Pour the mixture into the knapsack sprayer through the sieve
- Top up / add up to the required level on the knaprack sprayer
- Spray the mixture onto the cap as required 1 x5 = 5 marks
Observe the procedure
-
- Root prunning / trimming
-
- Build up of strong rooting system / compact system .
- Encourage formation of lateral roots
- Make lifting easy
- Prevent root damage
- Increase survival rate during transplanting
1 x3 = 3 mks
-
- To prevent soil erosion / water run off
- Prevent roots from being exposed
- Protect seedlings from damage
1 x2 = 2 mks
-
- Elasticity of Demand = % change in Quality Demand
% change in price
ie ED = % ∆ in QD
% ∆ in P√
% change in QD = ((22-20)/20) x 100 = 2/20 x 100 = 10 %√
% change in price = (800 - 100/1000) x 100 = 10/-20= -20% ( mark as a whole)
ED = 10/20√= -0.2 ( Mark as awhole) - Inelastic demand ( i.e. since ED is less than 1)
- Elasticity of Demand = % change in Quality Demand
-
-
- Pick flowers selectively
- Pick flower with horizontal petals / three to two roses of disk florets
- Use fore finger and thumb
- Pick by twisting the lead so that no stem is left attached
- Put the pricked flowers in woven baskets 1x 4 = ( 4mks)
-
- Picking starts 3 -4 months after planting
- Picked flowers are put in woven baskets to allow ventilation and avoid fermentation
- Wet flowers should not be picked since they heat up and ferment
- Should not be comp[acted to avoid heating up and fermentation
- Suitable picking intervals 14 – 21 days to avoid overgrown or young flowers
- Break flower stalks to maintain quality 1 x6 = 6 mks
-
-
- Land preparation
- Clear the land to remove all stumps
- Dig, plough the land to remove perennial weeds / roots
- Harrow the land ; to a fine filth
- Prepare the land during the dry season / before the rains 1 x5 = 5 mks
- Pasture establishment
- Select a desirable variety of grass for the ecological condition / select the correct
- variety for the same zone
- Plant or the onset of rains / plant early
- Use certified seeds
- Drill / broad cast the seeds evenly
- Apply phosphatic fertilizers or appropriate rate
- Use ssp rate of 200- 300 kg/ ha
- Use recommended seed rate for the variety
- Use 1.5-2 kg /ha PGS / 5-10 /ha for any available seed
- Drag a twig / gunny bag to cover the seeds lightly
- Cover seeds 3-5 times the diameter of seeds / depth 1x8 = 8 mks)
- Maintenance
- Control weeds by uprooting /use herbicides
- Top dress with nitrogenous fertilizers
- Top dress with nitrogenous fertilizers
- Top dress in split application
- Cut / graze in the initial stage when 4- 6 months
- Control pests and diseases when they appear
- Avoid grazing when too young / Early defoliation
- Topping posture using appropriate method when to stemmy
- Carry out controlled grazingIrrigate when desirable
Re – seeding when need be 1x7 = 7mk
- Land preparation
-
-
- What extra coats will be involved in the change
- What costs will be saved
- What extra revenue from the change
- What revenue will be fore gone
- Is the change worthwhile
(1 x4) = 4 mk
-
- When replacing one enterprise with another
- When expanding are enterprise to the expense of another / reduce another
- When introducing an enterprise which is subsiding to the existing one
- When replacing one technique of production with another
(1x4) = 4 mks
-
(EXTRA REVENUE +COST SAVE) – (EXTRA COSTS +REVENUE FORGONE)Debit (-) ksh Cts Credit (+) ksh Cts EXTRA COSTS BEANS
Fertiliser
2 ½ x 0.3 x 1400
Labour
40 x 0.3 x 150
Seed
200 x 10.
1050
.
1800
.
2000
..
00
.
00
.
00
.EXRA REVENUE BEANS
Yield 90 x 0.3 x 300
8100 00 SUB-TOTAL SUB TOTAL 8100 00 REVENUE FOREGONE MAIZE YIELD MAIZE
56 X 0.3 X 1200COSTS SAVE
SEED
1X1350
FERTILISER
2X0.3X1400.
1350
.
840
..
00
.
00
.TOTAL 25010 00 TOTAL 10290 00
(4850+20160) – (8100+2190)
-14750
If mzee mkulima replace maize for beans he will experience a lose of 14750 so he should not replace maize with beans.
-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Moi Tea Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students